Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 5041-5050.doi: 10.12307/2025.065
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of acute liver injury
Yang Na, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin
- Basic Laboratory of Integrative Medicine, Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-15Accepted:2024-04-30Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Hao Huiqin, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Basic Laboratory of Integrative Medicine, Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Liu Yang, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Basic Laboratory of Integrative Medicine, Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Yang Na, MD, Lecturer, Basic Laboratory of Integrative Medicine, Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, No. 202203021222272 (to YN); Key Scientific Research Innovation Team Project of Shanxi Province, No. 202204051002033 (to HHQ); Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2023BK32 (to YN); Scientific Research Innovation Team Project of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022TD2003; Basic Research of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Rheumatic immune Diseases of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2023XKJS-03 (to HHQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Na, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Molecular mechanism of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of acute liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5041-5050.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
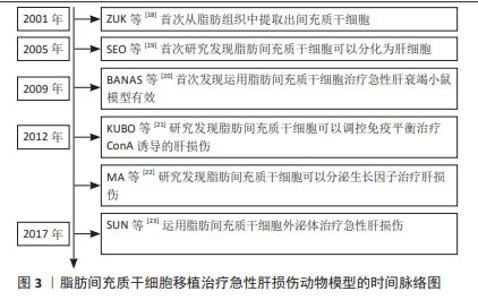
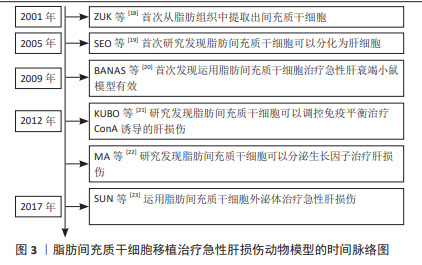
2.1 脂肪间充质干细胞用于治疗肝脏相关疾病的生物学优势 脂肪间充质干细胞是来源于脂肪组织的间充质干细胞。尽管以往认为脂肪组织是储脂器官,但随着科学研究的逐步深入,脂肪组织被认为是机体重要的内分泌器官和代谢器官,参与维持机体的生理平衡。有研究学者对脂肪组织的细胞成分进行分析,结果显示脂肪组织中仅有20%的细胞为储脂的脂肪细胞,约80%为成纤维细胞、血管细胞、脂肪间充质干细胞以及免疫细胞等[2]。单细胞测序分析结果显示非储脂细胞中有70%表达血小板衍生生长因子受体α、整联蛋白β1及糖蛋白CD34等脂肪间充质干细胞的标志蛋白[3]。形态学研究结果显示,白色脂肪组织中的血小板衍生生长因子受体α阳性的脂肪间充质干细胞均匀分布于间质和血管周围空间,并伸出树突状伪足接触组织微环境中包括脂肪细胞在内的多种细胞[4]。当白色脂肪组织受损时会招募表达M2型标记物的巨噬细胞清除坏死的白色脂肪组织,这些巨噬细胞可以表达高水平的骨桥素蛋白,使得血小板衍生生长因子受体α阳性的脂肪间充质干细胞在趋化作用下迁移到白色脂肪组织坏死区域,增殖分化为脂肪细胞进而参与脂肪组织损伤修复[5]。 MCINTOSH等[6]分析了来自骨髓、脐血和脂肪组织的3种间充质干细胞特性,结果显示脂肪和骨髓组织分离间充质干细胞的成功率较脐血来源更高。SCHAFFLER等[7]认为与骨髓来源的间充质干细胞相比,脂肪间充质干细胞同样具有分化成中胚层或非中胚层细胞的潜力。但有相关研究表明,从脂肪组织中分离得到间充质干细胞数量是从等量骨髓组织中获得的间充质干细胞数量的500倍[8]。RUSSELL等[9]对犬脂肪组织和骨髓来源的间充质干细胞进行了系统研究,结果显示脂肪间充质干细胞增殖速度是骨髓间充质干细胞的2倍以上。同源盒转录因子Nanog是维持干细胞未分化状态和自我更新所必需的关键因子,有文献报道,脂肪间充质干细胞的Nanog表达量相较来源于骨髓的间充质干细胞高出2.5倍,且体外扩增的脂肪间充质干细胞的增殖能力明显较骨髓来源的间充质干细胞更高[10];对两类干细胞的分化能力进行评估,结果显示两者在脂肪生成和成骨分化能力方面无明显差异[9]。以上研究提示脂肪间充质干细胞可以维持未分化状态,并且其自我更新能力比骨髓的间充质干细胞更强。有研究发现脂肪间充质干细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞相比,两类干细胞表面均表达组织相容性复合体(major histocompatibility complex,MHC)MHC Ⅰ、整联蛋白β1、归巢细胞黏附分子CD44和细胞黏附分子免疫球蛋白CD90,几乎不表达MHC Ⅱ和白细胞共同抗原CD45,提示与其他类型间充质干细胞相似,脂肪间充质干细胞的免疫原性较低[11]。由此可知,脂肪间充质干细胞具有与其他间充质干细胞类似的低免疫原性,且自我更新能力和体外增殖能力优于骨髓来源的间充质干细胞,具有较强的生物学优势。 此外,由于医美行业的迅速发展,脂肪组织的获取较骨髓、脐带组织更为便捷,并且脂肪组织抽取手术几乎不会导致手术并发症或美观缺陷等副作用,医学伦理问题少,因此从脂肪组织中获取脂肪间充质干细胞具有来源丰富、获取便捷的优势[12]。因此,脂肪间充质干细胞被认为是组织工程的理想来源,具有重要的应用和研究价值。脂肪间充质干细胞具有向软骨和骨方向分化的能力,可以用于遗传性和肿瘤或创伤性骨缺损的骨骼再生[13]。脂肪间充质干细胞可以分泌多种生长因子,可以用于促进新血管生成和治疗缺血性疾病[14]。由于脂肪间充质干细胞具有向神经元方向分化的能力,研究人员正在研究脂肪间充质干细胞治疗脑损伤、脑卒中以及周围神经损伤等,初步发现脂肪间充质干细胞可以显著改善神经损伤[15-16]。值得注意的是,尽管肝脏具有再生能力,脂肪间充质干细胞移植也可以分化为肝细胞,促进肝再生[17]。近期的研究表明脂肪间充质干细胞可以归巢到肝脏受损部位,并分泌多种细胞因子和生长因子,发挥多种生物学效应。综上所述,脂肪间充质干细胞较其他间充质干细胞治疗肝损伤具有显著的生物学优势,有可能成为延缓肝损伤,挽救急性肝衰竭的种子细胞。 2.2 脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤的分子机制 近年来,研究学者围绕脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤进行了大量的研究工作。研究报道脂肪来源的间充质干细胞治疗多种急性肝损伤动物模型均有良好疗效,其作用机制研究也取得了一定进展。现对脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤的分子机制做归纳总结。 自2001年ZUK等[18]首次从脂肪组织中提取出间充质干细胞后,研究学者逐渐对脂肪间充质干细胞的生物学功能和作用展开了研究。2005年有研究学者发现细胞生长因子和抑瘤素-M处理可以将脂肪间充质干细胞诱导分化为肝细胞样细胞,并在分化过程中高表达白蛋白和甲胎蛋白等标志物,该项研究首次提供了脂肪间充质干细胞向肝细胞方向分化的体外证据[19]。之后研究学者对于脂肪间充质干细胞在肝脏相关疾病中的作用进行了研究。在2008年,有学者将脂肪来源的间充质干细胞注射到肝移植大鼠体内并发现可以显著缓解肝移植的急性排斥反应,这一现象可能与其对T淋巴细胞的抑制作用有关。在2009年BANAS等[20]首次将脂肪间充质干细胞直接应用于急性肝衰竭小鼠模型,其研究结果显示脂肪间充质干细胞对体外肝细胞分化和肝再生具有特殊的亲和力,可能是治疗肝脏损伤的优越的细胞工具。随后研究学者们对脂肪间充质干细胞如何治疗急性肝损伤的具体分子机制进行了探索研究,逐步发现脂肪间充质干细胞可能通过分化为肝细胞、调节免疫平衡、分泌生长因子和外泌体等对急性肝损伤起到损伤修复作用[21-23],具体时间脉络见图3。"
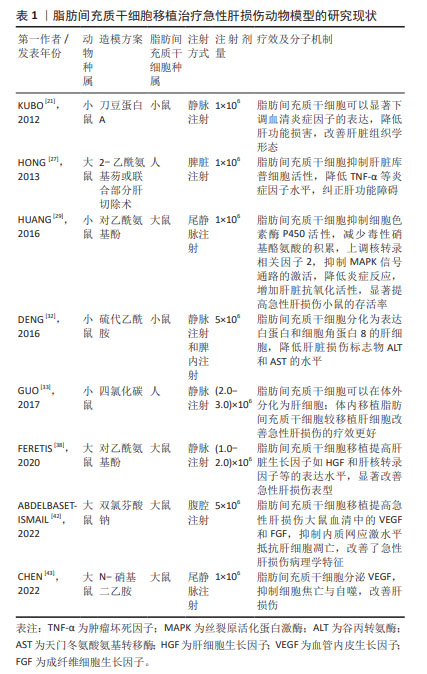
2.2.1 脂肪间充质干细胞调节免疫平衡抑制炎症反应 脂肪间充质干细胞作为一种间充质干细胞具有免疫抑制作用[24-25]。研究表明间充质干细胞可以抑制T细胞、B细胞和自然杀伤细胞等发挥免疫调节作用参与组织修复[26]。有研究利用佛波酯、离子霉素以及刀豆蛋白A(concanavalin A,ConA)等刺激淋巴单核细胞构建异常免疫反应细胞模型并评估脂肪间充质干细胞对免疫稳态的调控作用,结果显示当脂肪间充质干细胞与淋巴单核细胞共培养时,以剂量依赖性的方式抑制淋巴单核细胞的过度增殖。运用脂肪间充质干细胞移植治疗ConA诱发的免疫性肝炎小鼠,结果显示脂肪间充质干细胞可以显著下调血清炎症因子的表达,降低肝功能损害,改善肝脏组织学形态,提示脂肪间充质干细胞具有强大的免疫调节能力[21]。有研究发现脂肪间充质干细胞移植可以促进2-乙酰氨基芴(AAF)或AAF联合部分肝切除术诱导的急性肝损伤大鼠肝脏再生,分析肝脏的免疫细胞类型结果显示脂肪间充质干细胞移植对肝脏T细胞和B细胞的数量无明显影响,但会使肝脏库普细胞增多;而当脂肪间充质干细胞成功移植到肝脏后则会抑制库普细胞活性,降低肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子水平[27]。相关研究报道肿瘤坏死因子α水平降低是由于脂肪间充质干细胞可以使血清中可溶性肿瘤坏死因子受体1的表达升高,增加的可溶性肿瘤坏死因子受体会削弱肿瘤坏死因子α的生物学效应从而改善急性肝损伤[28]。另有文献报道,大鼠大网膜脂肪组织来源的间充质干细胞移植后通过抑制细胞色素酶P450活性,减少毒性硝基酪氨酸的积累,上调核转录相关因子2,抑制丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路的激活,降低炎症反应,增加肝脏抗氧化活性,显著提高急性肝损伤小鼠的存活率[29]。综上所述,脂肪间充质干细胞可以通过抑制免疫细胞过度增殖或降低炎症反应发挥肝脏保护作用。 2.2.2 脂肪间充质干细胞分化为肝细胞发挥肝保护作用 脂肪间充质干细胞作为一种间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能。研究表明未分化的脂肪间充质干细胞表达肝脏特异性标记物,如甲胎蛋白、细胞角蛋白(CK)-18、CK-19和肝细胞核转录因子4等[30]。成纤维细胞生长因子4是调控肝脏早期发育的重要因子,当成纤维细胞生长因子4连续干预脂肪间充质干细胞至第9天时,脂肪间充质干细胞高表达白蛋白等肝细胞标记物;干预至第13天时脂肪间充质干细胞具备了肝细胞摄取低密度脂蛋白和储存糖原的能力[20]。以上研究提示脂肪间充质干细胞具有向肝细胞方向分化的能力。为了研究脂肪间充质干细胞在急性肝损伤动物模型的分布情况,有研究人员在脂肪间充质干细胞移植后建立肝损伤模型,发现脂肪间充质干细胞可以直接植入肝组织中并表达人类肝细胞特异性蛋白[31]。DENG等[32]使用绿色荧光蛋白标记脂肪间充质干细胞并将其腹腔注射到硫代乙酰胺导致的急性肝损伤小鼠体内,结果显示第7天起急性肝损伤小鼠肝脏表达增强绿色荧光蛋白阳性细胞,第4周时增强绿色荧光蛋白阳性细胞呈现出肝细胞样形态并表达细胞角蛋白18和白蛋白等肝细胞标记物。同样地,运用增强绿色荧光蛋白-脂肪间充质干细胞治疗硫代乙酰胺导致的急性肝损伤,结果显示脂肪间充质干细胞可在受损肝脏分化为肝细胞从而发挥肝保护作用,而且这一作用与脂肪间充质干细胞的注射途径无关。GUO等[33]分别向CCl4肝损伤小鼠体内静脉注射了脂肪间充质干细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的肝细胞样细胞,但是移植脂肪间充质干细胞的治疗效果更优。这一现象可能是由于损伤的肝脏中局部高表达基质细胞衍生因子1,而干细胞表面高表达趋化因子受体4,因此,在趋化作用下脂肪间充质干细胞逆浓度梯度差招募到损伤部位[34]。此外,脂肪间充质干细胞还可以释放其他生长因子,其抗炎、抗凋亡和再生作用较肝样细胞更为显著。综上可知,脂肪间充质干细胞注射到急性肝损伤动物模型体内可以分化为肝细胞,但是脂肪间充质干细胞分化为肝细胞如何发挥肝保护作用的分子机制研究较少,仍需更多的研究工作证实。 2.2.3 脂肪间充质干细胞分泌生长因子促进肝损伤修复 脂肪间充质干细胞作为间充质干细胞具有分泌生长因子的功能。研究认为脂肪间充质干细胞也可以分泌肝细胞生长因子改善肝纤维化[35-36]。LIU等[37]运用脂肪间充质干细胞移植显著抑制了肝大部切除术后24 h的血清谷草转氨酶、谷丙转氨酶和总胆红素水平,增加细胞生长因子的表达水平,改善了肝大部切除术模型大鼠的肝脏再生。FERETIS等[38]的研究表明脂肪间充质干细胞移植后,肝脏生长因子如细胞生长因子和肝核转录因子等明显升高,脂肪间充质干细胞的形态也从纤维细胞样转变为肝细胞样细胞,显著改善了对乙酰氨基酚诱导的急性肝损伤。血管内皮生长因子在内皮细胞新生成血管以及血管的损伤修复过程中发挥重要作用[39]。有文献报道急性肝损伤后的肝再生过程需要血管内皮生长因子的参与,而脂肪间充质干细胞可以分泌血管内皮生长因子等生长因子[40-41]。 ABDELBASET-ISMAIL等[42]研究发现,脂肪间充质干细胞可以有效降低急性肝损伤小鼠血清的丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase,AST)、胆红素水平以及其他促炎、促凋亡因子,增加血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和B细胞淋巴瘤/白血病-2基因的表达,促进肝细胞再生。相似地,CHEN等[43]运用尾静脉注射N-亚硝基二乙胺使小鼠肝脏Beclin1、LC3Ⅱ等自噬相关蛋白表达上调并出现急性肝损伤表型。运用脂肪间充质干细胞移植治疗则可显著提高血管生长因子血管内皮生长因子的表达,抑制细胞焦亡和自噬从而改善肝损伤。有研究人员利用缺血再灌注诱导肝移植术后急性肝损伤大鼠模型,通过RNA干扰技术抑制脂肪间充质干细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子,结果显示缺失血管内皮生长因子的脂肪间充质干细胞移植后不能改善肝脏微循环障碍、门静脉炎性细胞浸润和肝细胞坏死,而血管内皮生长因子正常表达的脂肪间充质干细胞植入后则可以显著纠正肝损伤表型,促进肝窦内皮细胞和肝细胞再生[22]。脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的生长因子较多,目前在治疗急性肝损伤方面的研究主要集中于血管内皮生长因子和细胞生长因子两种生长因子方面,脂肪间充质干细胞是否通过分泌其他生长因子发挥肝脏保护作用仍需研究工作证实。 通过对以上脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤的分子机制进行归纳,可知脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤的分子机制较为复杂,不存在单一作用机制和主要作用机制之分。脂肪间充质干细胞作为一种具有多向分化潜能和低免疫原性的间充质干细胞,在进入机体之后可能通过分化为损伤部位的主要细胞类型替代其功能发挥修复作用,也可能通过抑制炎症因子调节免疫平衡,或分泌生长因子对肝脏起保护作用。但是目前的研究进展中仍然存在具体分子机制尚不明确的问题,见表1,仍有大量研究工作尚需进行。"
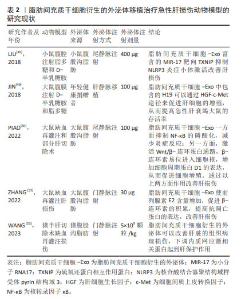
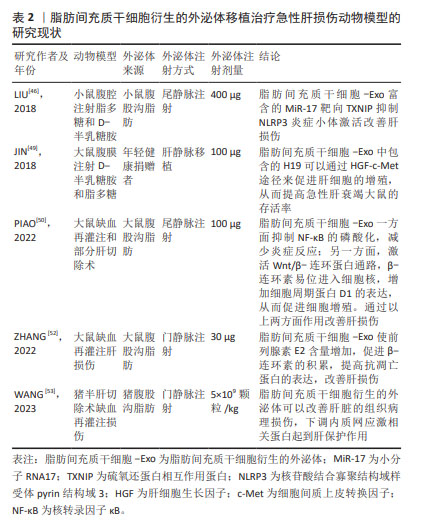
2.2.4 脂肪间充质干细胞分泌外泌体促进肝损伤修复 脂肪间充质干细胞作为间充质干细胞具有分泌外泌体的功能。外泌体是机体内所有细胞均可分泌的直径范围为50-160 nm的纳米颗粒,携带核酸、蛋白质、脂质和代谢物等多种生物信号分子,并通过包括胞吞、质膜融合等在内的多种机制进入受体细胞实现细胞间的通讯过程[44]。由于不同细胞分泌的外泌体携带的核酸、蛋白、脂质以及代谢物等具有异质性,因此,不同类型细胞分泌的外泌体具有独特的特征。研究表明,脂肪间充质干细胞衍生外泌体参与组织修复与再生、血管生成、炎症反应调节、成骨和脂肪生成,皮肤愈合、抑制细胞凋亡以及调节免疫反应等生物学过程[45]。多篇文献报道了脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体对急性肝损伤的治疗作用。 SUN等[23]分离了小型猪的脂肪间充质干细胞并收集培养基中的外泌体,体外作用于脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞,结果显示,猪来源的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体可以显著抑制巨噬细胞分泌的白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子表达,减少基质金属蛋白酶9和环氧化酶2的表达水平,降低细胞凋亡相关蛋白3表达水平,提示异种外泌体具有抑制炎症、细胞凋亡和氧化应激的内在能力。随后,研究人员利用静脉注射外泌体治疗急性肝缺血再灌注导致的急性肝损伤大鼠,结果显示外泌体可以通过显著减少急性肝损伤肝实质中的CD3阳性T细胞的数量,降低炎症细胞浸润比例,下调NADPH氧化酶1和2的水平,增加抗凋亡蛋白和抗氧化应激蛋白的表达,进而保护DNA和线粒体免受损伤,对纠正肝损伤具有一定的保护作用[23]。另有研究表明,脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体内富含的MiR-17可以减少炎症小体激活进而修复肝损伤[46]。核苷酸结合和寡聚化结构域样受体3(nucleotide binding oligomerization domain like receptors 3,NLRP3)炎性小体在肝脏中高表达,参与多种肝脏疾病的发病机制[47]。研究人员利用脂多糖和D-半乳糖胺腹腔注射诱发小鼠出现急性暴发性肝炎并立即尾静脉注射脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体,结果显示注射外泌体后急性肝损伤小鼠的肝功能指标谷草转氨酶和谷丙转氨酶显著降低,血清炎症因子表达显著下降。同时研究人员利用体内体外实验研究均发现脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体含有高水平的miR-17,可以显著抑制与NLRP3相互作用的硫氧还蛋白互作蛋白,进而抑制NLRP3炎症小体的激活,降低炎症因子的分泌从而改善暴发性肝炎诱导的急性肝损伤[46]。H19是一个长度为2.3 kb的非编码RNA,在肝脏中表达活跃但是在个体出生后迅速减少。研究表明在多个肝切除再生模型中,发现H19在肝细胞增殖活跃的组织中的表达显著增加,提示H19在肝组织再生和增殖中起着不可或缺的作用[48]。JIN等[49]运用基因沉默和过表达技术证实脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体中包含的H19可以通过细胞生长因子-c-Met途径促进肝细胞的增殖,从而提高急性肝衰竭大鼠的存活率。另有研究表明,移植脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体较直接移植脂肪间充质干细胞可能更有优势。PIAO等[50]研究发现移植脂肪间充质干细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体均可以通过激活Wnt/β-catenin途径促进肝脏再生,抑制核转录因子κB信号通路减少细胞焦亡,挽救肝损伤;但是与移植脂肪间充质干细胞衍生外泌体不同,移植脂肪间充质干细胞反而增加了GSDMD-N的释放。GSDMD-N是活性胱天蛋白酶-1裂解成孔蛋白(gasdermin D,GSDMD)在细胞焦亡途径中被活化的胱天蛋白酶剪切后的N端片段,可以促使细胞膜穿孔、细胞死亡[51]。GSDMD-N的释放可能是由于损伤部位的巨噬细胞大量释放IFN-β诱发募集到损伤部位的脂肪间充质干细胞产生细胞焦亡[50]。同样的,ZHANG等[52]运用脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体治疗肝缺血再灌注模型,结果显示脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体使前列腺素E2含量增加,通过次级信使cAMP激活ERK信号通路,失活GSK-3β,促进β-连环素的积累,提高抗凋亡蛋白的表达,改善肝损伤。WANG等[53]构建了猪半肝切除缺血再灌注损伤模型并运用脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体进行治疗,结果显示单剂量注射脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体可以改善肝脏的组织病理损伤,显著提高了碱性磷酸酶、总蛋白和过氧化氢酶的表达水平,下调内质网应激相关蛋白起到肝保护作用。 以上相关研究成果表明脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体主要通过降低炎症反应、促进肝细胞增殖和减少肝细胞凋亡等方面改善肝损伤。外泌体内容物成分较为复杂,目前研究仅报道了脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体中小分子RNA、非编码RNA和蛋白质在治疗肝损伤中的作用,其携带的脂质和代谢物是否在治疗肝损伤中发挥作用,尚需研究工作进一步证实。文章最后总结了脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体移植治疗急性肝损伤动物模型的研究现状,见表2。"

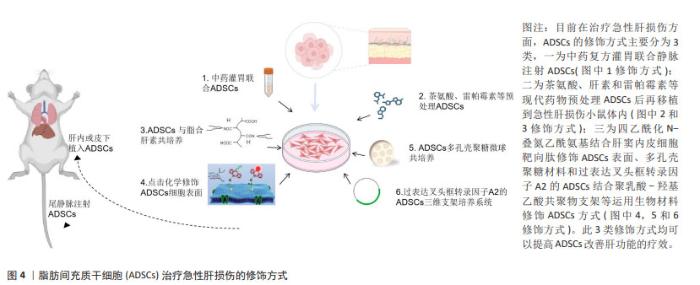
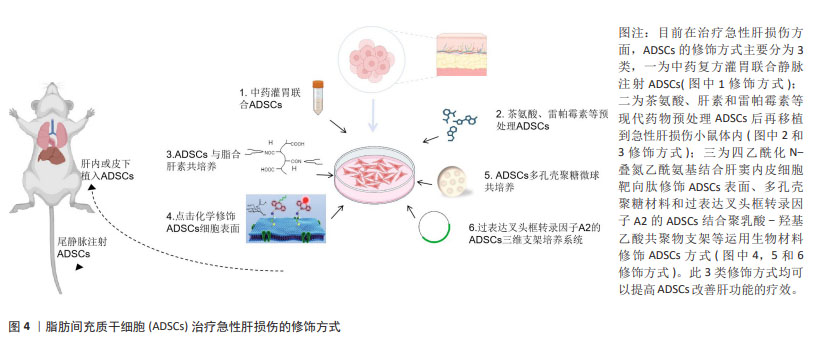
2.3 修饰脂肪间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤的研究现状 虽然脂肪间充质干细胞移植治疗急性肝损伤的优势备受临床工作者的重视,但目前还存在许多问题制约干细胞移植技术在临床中的应用。细胞疗法成功的关键是维持干细胞的活力,使细胞可以整合入病变部位并保障充足的血液、氧气和营养素供应。由于病变部位多为氧化应激、缺血缺氧等环境,不利于移植的干细胞长期存活,增强移植干细胞的活性,提高存活能力使其有效发挥生物学作用从而更好地治疗疾病是干细胞移植领域亟待解决的问题。为了提高干细胞对急性肝损伤的疗效,突破干细胞分化效率低、寿命短、大规模生产成本高等限制,研究人员运用不同技术进行了多种研究[54-61],见表3,图4。"

| [1] GARCIA-CORTES M, ORTEGA-ALONSO A, ANDRADE RJ, et al. Safety of treating acute liver injury and failure. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022;21(2): 191-203. [2] TANG L, LI T, XIE J, et al. Diversity and heterogeneity in human breast cancer adipose tissue revealed at single-nucleus resolution. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1158027. [3] RONDINI EA, GRANNEMAN JG. Single cell approaches to address adipose tissue stromal cell heterogeneity. Biochem J. 2020;477(3):583-600. [4] LIU P, AN Y, ZHU T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: emerging concepts and recent advances in their roles in organismal homeostasis and therapy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1131218. [5] LEE YH, PETKOVA AP, GRANNEMAN JG. Identification of an adipogenic niche for adipose tissue remodeling and restoration. Cell Metab. 2013; 18(3):355-367. [6] MCINTOSH K, ZVONIC S, GARRETT S, et al. The immunogenicity of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in vitro. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5): 1246-1253. [7] SCHAFFLER A, BUCHLER C. Concise review: adipose tissue-derived stromal cells--basic and clinical implications for novel cell-based therapies. Stem Cells. 2007;25(4):818-827. [8] KAVALA AA, TURKYILMAZ S. Autogenously derived regenerative cell therapy for venous leg ulcers. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2018;3:e156-e163. [9] RUSSELL KA, CHOW NH, DUKOFF D, et al. Characterization and immunomodulatory effects of canine adipose tissue- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167442. [10] TAKEMITSU H, ZHAO D, YAMAMOTO I, et al. Comparison of bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived canine mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Vet Res. 2012;8:150. [11] BUNNELL BA. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cells. 2021;10(12):3433. [12] ZHANG Q, PIAO C, MA H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver ischaemia reperfusion injury subsequent to hepatectomy in rats by regulating mitochondrial dynamics and biogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(21):10152-10163. [13] XUE N, DING X, HUANG R, et al. Bone tissue engineering in the treatment of bone defects. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15(7):879. [14] HAO Z, QI W, SUN J, et al. Review: Research progress of adipose-derived stem cells in the treatment of chronic wounds. Front Chem. 2023;11: 1094693. [15] ZHANG Z, ZHANG M, SUN Y, et al. Effects of adipose derived stem cells pretreated with resveratrol on sciatic nerve regeneration in rats. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):5812. [16] PELEGRI NG, MILTHORPE BK, GORRIE CA, et al. Neurogenic marker expression in differentiating human adipose derived adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Investig. 2023;10:7. [17] ALI S, HAQUE N, AZHAR Z, et al. Regenerative medicine of liver: promises, advances and challenges. Biomimetics. 2021;6(4):62. [18] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZYNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [19] SEO MJ, SUH SY, BAE YC, et al. Differentiation of human adipose stromal cells into hepatic lineage in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(1):258-264. [20] BANAS A, TERATANI T, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. Rapid hepatic fate specification of adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential for liver failure. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(1):70-77. [21] KUBO N, NARUMI S, KIJIMA H, et al. Efficacy of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for fulminant hepatitis in mice induced by concanavalin A. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(1):165-172. [22] MA T, LIU H, CHEN W, et al. Implanted adipose-derived stem cells attenuate small-for-size liver graft injury by secretion of VEGF in rats. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(3):620-629. [23] SUN CK, CHEN CH, CHANG CL, et al. Melatonin treatment enhances therapeutic effects of exosomes against acute liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(4):1543-1560. [24] ZHOU JH, LU X, YAN CL, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-dependent immunoregulation in chemically-induced acute liver failure. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(3):208-220. [25] LI TT, WANG ZR, YAO WQ, et al. Stem cell therapies for chronic liver diseases: progress and challenges. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11(9):900-911. [26] YI T, SONG SU. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(2):213-221. [27] HONG IH, HAN SY, KI MR, et al. Inhibition of kupffer cell activity improves transplantation of human adipose-derived stem cells and liver functions. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(3):447-459. [28] SUN J, DING X, LIU S, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate acute lung injury and improve the gut microbiota in septic rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):384. [29] HUANG YJ, CHEN P, LEE CY, et al. Protection against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure by omentum adipose tissue derived stem cells through the mediation of Nrf2 and cytochrome P450 expression. J Biomed Sci. 2016;23(1):12. [30] ZEMEL R, BACHMETOV L, AD-EL D, et al. Expression of liver-specific markers in naive adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Liver Int. 2009;29(9):1326-1337. [31] RUIZ JC, LUDLOW JW, SHERWOOD S, et al. Differentiated human adipose-derived stem cells exhibit hepatogenic capability in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2010;225(2):429-436. [32] DENG L, KONG X, LIU G, et al. Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells efficiently rescues thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(6):2208-2215. [33] GUO DL, WANG ZG, XIONG LK, et al. Hepatogenic differentiation from human adipose-derived stem cells and application for mouse acute liver injury. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017;45(2):224-232. [34] SAITO Y, SHIMADA M, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Homing effect of adipose-derived stem cells to the injured liver: the shift of stromal cell-derived factor 1 expressions. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(12):873-880. [35] QIN L, LIU N, BAO CLM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in fibrotic diseases—the two sides of the same coin. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2022;44(2):268-287. [36] GHARBIA S, NAZARIE SR, DINESCU S, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) supplemented with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) attenuate hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-beta/smad signaling pathway in chemical-induced liver fibrosis associated with diabetes. Cells. 2022;11(21):3338. [37] LIU T, MU H, SHEN Z, et al. Autologous adipose tissue‑derived mesenchymal stem cells are involved in rat liver regeneration following repeat partial hepatectomy. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):2053-2059. [38] FERETIS T, KATSELIS C, PAPANIKOLAOU IG, et al. ATSC transplantation contributes to liver regeneration following paracetamol-induced acute liver injury through differentiation into hepatic-like cells. Am J Stem Cells. 2020;9(3):36-56. [39] SHINEH G, PATEL K, MOBARAKI M, et al. Functional approaches in promoting vascularization and angiogenesis in bone critical-sized defects via delivery of cells, growth factors, drugs, and particles. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(2):99. [40] ITO Y, HOSONO K, AMANO H. Responses of hepatic sinusoidal cells to liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1171317. [41] AI G, MENG M, GUO J, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells promote the repair of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure by inhibiting granulosa cells apoptosis and senescence. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):75. [42] ABDELBASET-ISMAIL A, THARWAT A, AHMED AE, et al. Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates acute hepatic injury caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac sodium in female rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;155:113805. [43] CHEN TS, LAI YA, LAI YJ, et al. Adipose stem cells preincubated with theanine exert liver regeneration through increase of stem cell paracrine VEGF and suppression of ROS, pyroptosis as well as autophagy markers in liver damage induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine. Life Sciences. 2022; 308:120969. [44] CLOSA D. Pancreatic cancer, stroma, and exosomes. J Physiol Biochem. 2022;79(1):205-211. [45] WEILIANG Z, LILI G. Research advances in the application of adipose-derived stem cells derived exosomes in cutaneous wound healing. Ann Dermatol. 2021;33(4):309-317. [46] LIU Y, LOU G, LI A, et al. AMSC-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by miR-17-mediated reduction of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. EBioMedicine. 2018;36:140-150. [47] CHEN F, LI B, LI W, et al. Polysaccharide of atractylodes macrocephala Koidz alleviate lipopolysaccharide-stimulated liver inflammation injury of goslings through miR-223/NLRP3 axis. Poult Sci. 2023; 102(1):102285. [48] YAMAMOTO Y, NISHIKAWA Y, TOKAIRIN T, et al. Increased expression of H19 non-coding mRNA follows hepatocyte proliferation in the rat and mouse. J Hepatol. 2004;40(5):808-814. [49] JIN Y, WANG J, LI H, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs) improve survival rate of rats with acute liver failure by releasing lncRNA H19. EBioMedicine. 2018;34: 231-242. [50] PIAO C, SANG J, KOU Z, et al. Effects of exosomes derived from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on pyroptosis and regeneration of injured liver. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12065. [51] WEI S, FENG M, ZHANG S. Molecular characteristics of cell pyroptosis and its inhibitors: a review of activation, regulation, and inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):16115. [52] ZHANG Y, LI Y, WANG Q, et al. Attenuation of hepatic ischemia‑reperfusion injury by adipose stem cell‑derived exosome treatment via ERK1/2 and GSK‑3β signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(2):13. [53] WANG Y, LIU T, JIAO G, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells can attenuate liver injury caused by minimally invasive hemihepatectomy combined with ischemia-reperfusion in minipigs by modulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Life Sci. 2023;321:121618. [54] 黄坤.3D多孔壳聚糖微球复合脂肪干细胞修复SD大鼠急性肝损伤研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2019. [55] CHAE YJ, JUN DW, LEE JS, et al. The use of foxa2-overexpressing adipose tissue-derived stem cells in a scaffold system attenuates acute liver injury. Gut and Liver. 2019;13(4):450-460. [56] LIAO N, ZHANG D, WU M, et al. Enhancing therapeutic effects and in vivo tracking of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for liver injury using bioorthogonal click chemistry. Nanoscale. 2021;13(3):1813-1822. [57] 钟庭燕,王绒,刘鹏,等.茵陈四苓颗粒联合脂肪间充质干细胞移植治疗对急性肝衰竭大鼠TNF-α及HGF、VEGF的影响研究[J].智慧健康,2020,6(32):37-41. [58] KIM JC, TAE G. The modulation of biodistribution of stem cells by anchoring lipid-conjugated heparin on the cell surface. J Control Release. 2015;217:128-137. [59] HWANG Y, KIM JC, TAE G. Significantly enhanced recovery of acute liver failure by liver targeted delivery of stem cells via heparin functionalization. Biomaterials. 2019;209:67-78. [60] EL NASHAR EM, ALGHAMDI MA, ALASMARI WA, et al. Autophagy promotes the survival of adipose mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and enhances their therapeutic effects in cisplatin-induced liver injury via modulating TGF-beta1/smad and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Cells. 2021;10(9):2475. [61] LAI YJ, SUNG YT, LAI YA, et al. L-theanine-treated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate the cytotoxicity induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine in liver. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(6): 1207-1221. [62] LIU Y, PU X, QIN X, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps regulate HMGB1 translocation and kupffer cell M1 polarization during acute liver transplantation rejection. Front Immunol. 2022;13:823511. |
| [1] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [2] | Zhang Min, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Li Zhuangzhuang, Wang Xue, Wang Huike. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosomes repair radiation-induced submandibular gland damage in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7804-7815. |
| [3] | Han Mengjun, Xu Fang. Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization: advantages and disadvantages of different plans and improvements in predictive models and technologies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7863-7871. |
| [4] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [5] | Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277. |
| [6] | Wu Ziwei, Luo Yicai, Wei Yinge, Liao Hongbing. Application of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7393-7404. |
| [7] | Zhang Pulian, Liu Baoru, Yang Min . Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of aplastic anemia: inhibiting or activating relevant targets in its pathological evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6800-6810. |
| [8] | Dai Yueyou, Guo Dandan, Wang Qianqian, Wang Baiyan, Feng Shuying. Anti-tumor effects of engineered exosomes for targeted drug delivery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6753-6764. |
| [9] | Wang Jiaqian, , Jiang Changjun, Peng Yi, Ma Mi, Li Junhan. Study on the role of aerobic exercise in regulating the CNPY2-mediated AKT/GSK3β pathway for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6441-6448. |
| [10] | Liu Yang, Yang Jilei, Wang Wenli, Cui Yingying, Sun Qihao, Li Yourui. Application characteristics of thermosensitive hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6094-6100. |
| [11] | Chen Senlin, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing. Application of Janus micro/nanoparticles in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6101-6109. |
| [12] | Zhang Tong, Wang Yan, Yang Chunjia, Yue Qingkun, Wu Qingtian. Role of functional hydrogels in tissue repair after traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6110-6117. |
| [13] | Chen Zhenkun, Zhu Shiwei, Xiao Jingnan, Tang Weiping. Mechanism of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes regulating autophagy of hepatic stellate cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5296-5303. |
| [14] | Yang Feng, Xu Jinfan, Long Huan, Yang Fengchun, Zhang Guixin, Jiang Tao, Chen Qingzhen, Shao Min. Estrogen receptor alpha-activated adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling pathway promotes proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5061-5070. |
| [15] | Feng Qiang, Pi Yihua, Huang Huasheng, Huang Delun, Zhang Yan. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for myocardial infarction in rats: effects of acute and chronic exercises [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4868-4877. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||