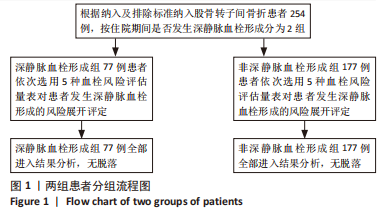
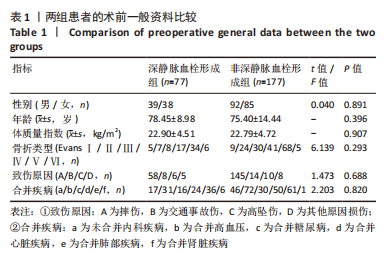
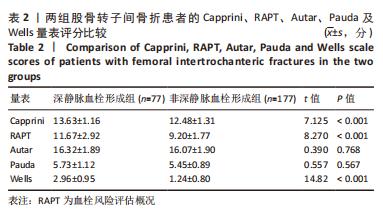
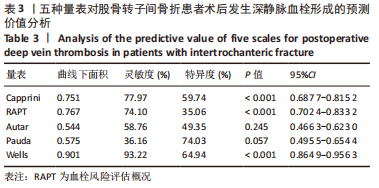
[1] 张璐,祁志强.PFNA治疗股骨粗隆骨折的临床效果及并发症分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,17(96):63-68.
[2] 唐咸敏,李强.股骨粗隆间骨折临床治疗进展[J].华夏医学,2021, 34(2):181-185.
[3] VIRCHOW R. Gesammalte abhandlungen zur wissenschaftlichen medtzin. Frankfurt, Medinger Sohn & Company. 1856:219-732.
[4] 王华颖.老年髋部骨折深静脉血栓形成的原因分析和护理对策[J].中国现代药物应用,2015,9(8):187-188.
[5] 周亚婷,史颜梅,白琳,等.两种血栓风险评估模型在住院患者深静脉血栓形成中的预测价值研究[J].解放军护理杂志,2018,35(4): 27-31+47.
[6] 付亚辉,尚昆,王宝辉,等.不同血栓风险评估量表对骨盆髋臼骨折患者深静脉血栓形成的预测价值分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2020,22(6):489-494.
[7] 费晨,王鹏飞,张斌飞,等.股骨转子间骨折患者围术期下肢深静脉血栓形成危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2020,36(3):251-258.
[8] GELBER RP, SETO TB. Patient ethnicity and use of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. Int J Qual Health Care. 2006;18(1):23-29.
[9] GEERTS WH, BERGQVIST D, PINEO GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl): 381S-453S.
[10] 郑紫磊,杨延江,李海英.老年髋部骨折患者术前深静脉血栓发生率的回顾性研究[J].承德医学院学报,2021,38(5):392-395.
[11] FEI C, WANG PF, QU SW, et al. Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Retrospective Study. Indian J Orthop. 2020;54(1):101-108.
[12] NIU S, LI J, ZHAO Y, et al. Preoperative deep venous thrombosis (DVT) after femoral neck fracture in the elderly, the incidence, timing, location and related risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):264.
[13] ZHAO X, ALI SJ, SANG X. Clinical Study on the Screening of Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis by D-Dimer Combined with RAPT Score Among Orthopedic Trauma Patients. Indian J Orthop. 2020; 54(2):316-321.
[14] CRONIN M, DENGLER N, KRAUSS ES, et al. Completion of the Updated Caprini Risk Assessment Model (2013 Version). Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019;25:1076029619838052.
[15] 杨淼,谢晶,马亮英,等.3种血栓风险评估表对老年下肢骨折病人术后并发深静脉血栓的预测价值[J].实用老年医学,2021,35(9): 914-917.
[16] WANG MM, QIN XJ, HE XX, et al. Comparison and screening of different risk assessment models for deep vein thrombosis in patients with solid tumors. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019;48(2):292-298.
[17] 周玥杉,黄小红.Padua评分在国内静脉血栓栓塞症风险评估中的研究进展[J].全科护理,2021,19(26):3640-3643.
[18] CHEUNG CL, ANG SB, CHADHA M, et al. An updated hip fracture projection in Asia: The Asian Federation of Osteoporosis Societies study. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2018;4(1):16-21.
[19] ARIZA-VEGA P, KRISTENSEN MT, MARTÍN-MARTÍN L, et al. Predictors of long-term mortality in older people with hip fracture. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96(7):1215-1221.
[20] 周锋,舒爱华,姜丽.合并心血管疾病老年患者髋部骨折手术围术期麻醉管理[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2021,37(12):1325-1329.
[21] 张英泽. 临床创伤骨科流行病学[M]. 北京:北京人民卫生出版社, 2009:150-170.
[22] 高嘉锴,王陶然,牛志霞,等.可膨胀髓内钉治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折的疗效[J].实用骨科杂志,2021,27(2):103-107.
[23] 刘泽民,吕欣,刘晋元,等.髋部骨折2342例流行病学分布特点的单中心分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(32):5085-5091.
[24] LIM TK, KOH KH, LEE SH, et al. Inferior anchor cortical perforation with arthroscopic Bankart repair: a cadaveric study. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29(1):31-36.
[25] 陈光,李靖年.准确理解和掌握《中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南》[J].医学与哲学(B),2016,37(8):1-3.
[26] SPENCER FA, EMERY C, LESSARD D, et al. The Worcester Venous Thromboembolism study: a population-based study of the clinical epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. J Gen Intern Med. 2006; 21(7):722-727.
[27] HONG J, LEE JH, YHIM HY, et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in Korea from 2009 to 2013. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0191897.
[28] NG HJ, LEE LH. Trends in prevalence of deep venous thrombosis among hospitalised patients in an Asian institution. Thromb Haemost. 2009;101(6):1095-1099.
[29] ANGCHAISUKSIRI P. Venous thromboembolism in Asia--an unrecognised and under-treated problem? Thromb Haemost. 2011;106(4):585-590.
[30] 胡家骏,王辰.骨科手术与肺栓塞[J].中国医刊,2008(1):12-13.
[31] DI NISIO M, VAN ES N, BÜLLER HR. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 2016;388(10063):3060-3073.
[32] 吕波,薛锋,唐果,等.下肢骨折后深静脉血栓形成的影响因素分析[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(6):373-377.
[33] SHIN WC, WOO SH, LEE SJ, et al. Preoperative Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with a Hip Fracture: An Indirect Multidetector CT Venography Study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(24):2089-2095.
[34] 王龙刚.低分子肝素钙对股骨粗隆间骨折患者术后下肢深静脉血栓风险的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2020,20(24):4119-4121.
[35] 魏俊强,刘利蕊,王新宇,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉修复老年骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折:发生下肢深静脉血栓的特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(35):5224-5230.
[36] 覃芹丹,王春秀,李芬,等.3种风险评估量表预测肿瘤住院患者静脉血栓栓塞症发生的应用研究[J].西北国防医学杂志,2019,40(11): 712-717.
[37] 周武,曹发奇,曾睿寅,等.创伤骨科患者围术期下肢静脉血栓形成诊断及防治专家共识(2022年)[J].中华创伤杂志,2022,38(1):23-31.
[38] DOZIO E, VETTORETTI S, CALDIROLI L, et al. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGE) and Soluble Forms of AGE Receptor: Emerging Role as Mortality Risk Factors in CKD. Biomedicines. 2020;8(12):638.
[39] KHAN F, TRITSCHLER T, KAHN SR, et al. Venous thromboembolism. Lancet. 2021;398(10294):64-77.
[40] 王宝辉,王鹏飞,付亚辉,等.下肢骨折患者RAPT评分结合D-二聚体监测预防DVT的意义[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(8): 846-848.
[41] LINDSEY P, ECHEVERRIA A, POI MJ, et al. Thromboembolic Risk of Endovascular Intervention for Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis. Ann Vasc Surg. 2018;49:247-254.
[42] GIBSON CJ, ALQUNAIBIT D, SMITH KE, et al. Probative Value of the D-Dimer Assay for Diagnosis of Deep Venous Thrombosis in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(12): e1322-e1326.
[43] 谢渊,牟绍玉,张川林,等.3种血栓风险评估表对骨科大手术患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的应用价值研究[J].检验医学与临床,2017, 14(9):1243-1245.
|