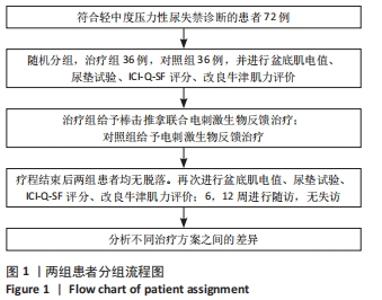
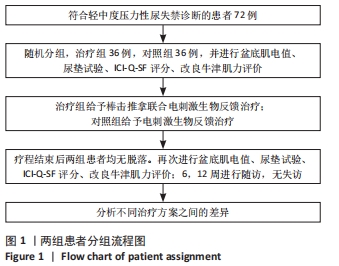
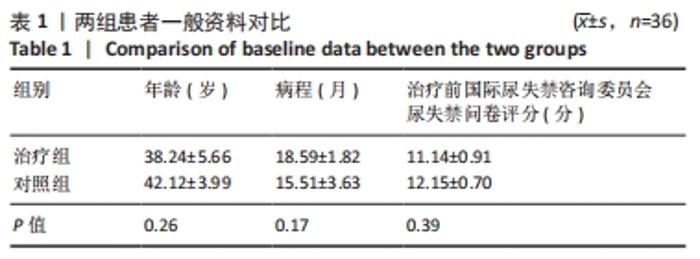
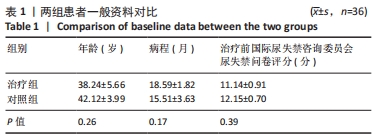
[1] 张田雨,马铁明.压力性尿失禁发病因素及机制探讨[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2021,19(10):196-199.
[2] 周慧清,尚华,李晓冬,等.女性盆底肌解剖与功能[J].解剖学杂志, 2020,43(5):434-436.
[3] Parkkinen A,Karjalaninen E,Vartiainen M,et al.Physiotherapy for female stress urinary incontinence: individual therapy at the outpatient clinic versus home-based pelvic floor training:a 5-year follow-up study. Neurourlo Urodyn. 2004;23(7):643-648.
[4] 王孟琦,王峰.近20年来针灸治疗压力性尿失禁的临床研究进展[J].中医药学报,2019,47(6):73-78.
[5] 冯春雨,孟珊.穴位针灸疗法联合盆底康复治疗仪对高龄产后压力性尿失禁患者盆底功能及预后的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2020,29(20):2230-2033.
[6] 李小娟,刘莉莎.针刺联合生物反馈训练治疗产后压力性尿失禁50例临床观察[J].甘肃中医药大学学报,2020,37(4):76-79.
[7] 刘水清清,叶平.补中益气颗粒联合生物反馈盆底肌训练治疗产后压力性尿失禁的疗效及对尿动力学指标水平影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(10):202-205.
[8] 赵鑫,刘莉君.加味补中益气汤配合盆底肌训练治疗中老年女性压力性尿失禁疗效及对阴道压力和尿动力学参数的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2018,27(23):2559-2562.
[9] 徐丹丹,辜锐鑫,周晶,等.盆底康复训练结合太极推拿治疗产后压力性尿失禁的临床观察[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(6):1412-1414.
[10] 年自强,安惠琴,李依洁.中医整脊联合盆底筋膜手法、电刺激疗法治疗女性压力性尿失禁的临床观察[J].中国民间疗法,2021, 29(13):66-69.
[11] 中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科盆底学组.女性压力性尿失禁诊断和治疗指南(2017)[J].中华妇产科杂志,2017,52(5):289-293.
[12] 张晨,息金波,骆睿翔,等.腹针、艾灸联合盆底肌训练治疗女性压力性尿失禁60例临床观察[J].江苏中医药,2021,53(7):44-47.
[13] 密琳,包洁,董娴蔚,等.推拿传统桑枝棒的制作及其应用价值[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2010,34(4):577.
[14] 肖文贵,梅犁.棒击法在推拿临床上的应用[J].山东中医杂志,1983, 2(3):4-5.
[15] 韩露轩,吴云川.内功推拿流派学术特色和传承[J].吉林中医药, 2016,36(1):84-87.
[16] 董桦,李正飞.电针、透灸结合津沽脏腑推拿对产后并发压力性尿失禁患者治疗效果的影响及其影响因素分析[J].中国妇幼保健, 2021,36(22):5133-5136.
[17] Skardoon GR,Khera AJ,Emmanuel AV,et al. Review article:dyssynergic defaecation and biofeedback therapy in the pathophysiology and management of functional constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46(4):410-423.
[18] 缪雪钦,王红日,高美云,等.金匮肾气丸联合盆底生物反馈治疗肾阳虚型产后压力性尿失禁临床研究[J].康复学报,2021,31(3):222-227.
[19] 胡静,袁钰宁,程思.Kegel训练联合生物反馈电刺激治疗产后压力性尿失禁的疗效观察[J].徐州医科大学学报,2021,41(6):464-468.
[20] 胡爱萍,赵玉红.盆底生物反馈电刺激在治疗压力性尿失禁中的应用分析[J].安徽卫生职业技术学院学报,2021,20(3):134-135+137.
[21] 蔡文智,张焱,陈玲,等.电刺激联合生物反馈治疗初产妇和经产妇压力性尿失禁的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(2):141-145+150.
[22] 翁佳丽,王慧丽,李小红,等.生物反馈电刺激对围绝经期女性压力性尿失禁患者的有效性及并发症发生的影响[J].中国妇幼保健, 2021,36(2):429-431.
[23] 杨秀英.女性压力性尿失禁的诊断与治疗[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2008,17(7):1051-1052.
[24] 范炳华.推拿治疗学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2017:40-42.
[25] 王喜凤,刘丹,谭增德,等.以足运感区针刺为主结合盆底肌训练治疗女性轻中度压力性尿失禁的临床研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2021,30(20):2198-2202.
[26] 王陶然,李晓燕,蒋丽君,等.微点阵激光治疗老年女性压力性尿失禁的效果[J].中国临床保健杂志,2021,24(5):687-691.
[27] ROZA TD, MASCARENHAS T, DE ARAUJO MP, et al.Oxford grading scale VS manometer for assessment of pelvic floor strength in nulliparous sports students. Physiotherapy. 2013;99:207-211.
[28] 杨秋晔,孙玉坤,林壮腾.艾灸对产妇产后尿动力学及盆底功能的影响[J].中国针灸,2021,41(8):883-886.
[29] 朱兆领,王睿丽,黄蓉,等.智能盆底超声对二次自然分娩女性盆底结构的观察[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2021,29(7):738-741+743.
[30] EL SAYED RF, ALT CD, MACCIONI F, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of pelvic floor dysfunction-joint recommendations of the ESUR and ESGAR Pelvic Floor Working Group. Eur Radiol. 2016;330(16):4471-4477.
[31] MORRISSEY D,GINZBURG N,WHITMORE K. Current advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic pelvic pain. Curr Opin Urol. 2014;24(4):336-344.
[32] 柯先莎,雷正权,孙子昕.近5年中医药治疗压力性尿失禁临床研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(10):211-216.
[33] 王元毅,曾凯,郝雨,等.南疆地区女性压力性尿失禁的预测模型构建[J].现代泌尿外科杂志,2021,26(9):735-739.
[34] 王钲,易锦,郑庆山.推拿与温针灸治疗压力性尿失禁对照研究[J].中国中医急症,2013,22(4):555-556+567.
[35] 热娜·亚力买买提.电刺激生物反馈疗法联合推拿治疗I、II及女性雅安例行尿失禁的随机对照临床研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2020.
[36] 黄先寿,黄飞,邓赛男.电针、推拿综合治疗尿失禁[J].中国中医急症,2009,18(9):1505.
[37] 赵天慈.推拿结合康复疗法治疗脑卒中后小便失禁的临床研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2015.
[38] 李翠英,李金香.湘西刘氏小儿推拿“推经治脏”论治小儿遗尿[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2017,24(2):106-108.
[39] 宋石龙,薛明新,陈莹,等.薛明新教授辩证推拿治疗小儿遗尿症经验[J].世界中医药,2019,14(9):2460-2463.
[40] 范宏岩.针灸配合推拿治疗遗尿60例临床分析[J].中国卫生产业, 2012(26):173.
[41] 齐兆双.推拿结合针灸治疗成人遗尿2例[J].中国民族民间医药, 2012,21(7):77.
[42] 魏慧强.按摩手法的命名与分类初探[J],现代诊断与治疗,1999,1(1):84-91.
[43] 王士安,姚斐,赵毅.对内功推拿几个重要问题的探讨[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2016,23(4):5-7.
[44] 韩露轩,吴云川.内功推拿流派学术特色和传承[J].吉林中医药, 2016,36(1):84-87.
[45] 陈香仙.棒击法治疗网球肘的实践研究[J].河南大学学报(医学版), 2015,24(4):73-75.
[46] ZHANG H, XU J, YAN JT. Effect of Static Exercise on Nervous Function and Emotion.Shanghai:Theses Collection of the 2011 Annual Meeting of Tuina Association of Shanghai Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2005:1-4.
[47] 张晓红,梁莉明,苗娅莉,等.盆底重建手术前后患者生活质量及盆底肌肌电变化初步探讨[J].中国妇产科临床杂志,2010,11(1):12-14.
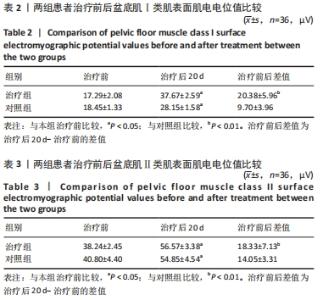
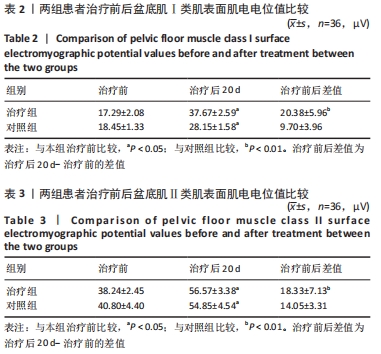
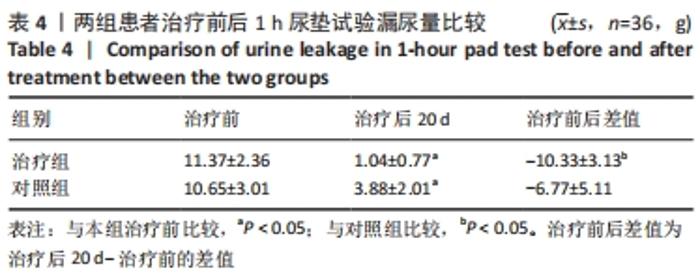
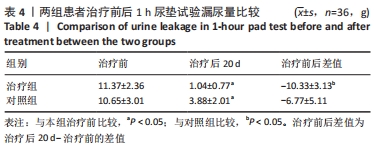
[48] 陈娟,任远,朱兰.改良牛津肌力分级和盆底表面肌电评估女性压力性尿失禁患者盆底肌功能的相关性[J].中华医学杂志,2020, 100(37):2908-2912.
[49] 王之虹.推拿手法学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2015:58-59.
|