Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2678-2684.doi: 10.12307/2022.534
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of a severe heatstroke pig model under high-temperature and high-humidity environment
Yang Yanwen, Zhang Jing, Mao Yuling, Ni Jun, Mao Libin, Yao Lu, Wang Huiying, Liu Qiuming, Ma Zhenzhen
- The 83rd Army Hospital of Chinese PLA, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-12-22Revised:2021-01-27Accepted:2021-09-13Online:2022-06-18Published:2021-12-24 -
Contact:Ni Jun, Master, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, The 83rd Army Hospital of Chinese PLA, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Yang Yanwen, Attending physician, The 83rd Army Hospital of Chinese PLA, Xinxiang 453000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:PLA Logistics Scientific Research Project, No. CLJ20J026 (to NJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yanwen, Zhang Jing, Mao Yuling, Ni Jun, Mao Libin, Yao Lu, Wang Huiying, Liu Qiuming, Ma Zhenzhen. Establishment of a severe heatstroke pig model under high-temperature and high-humidity environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2678-2684.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
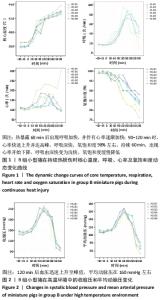
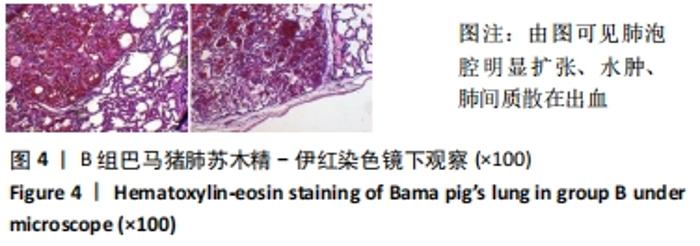
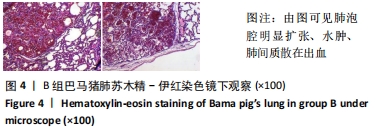
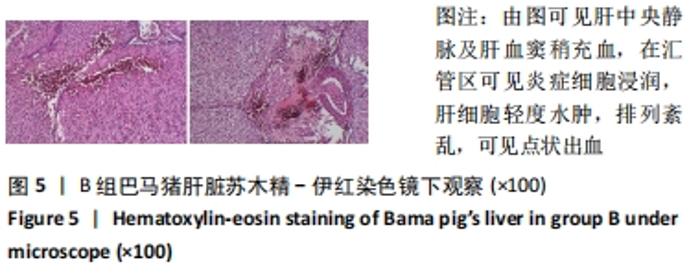
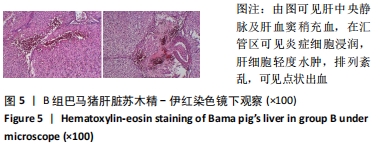
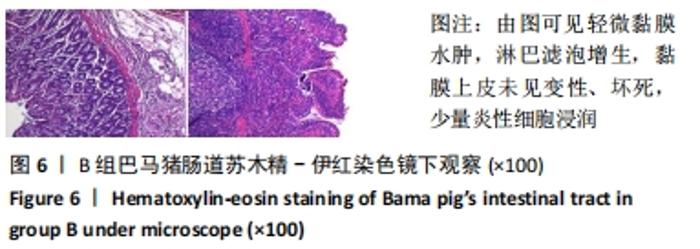
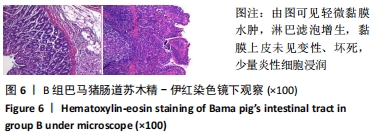
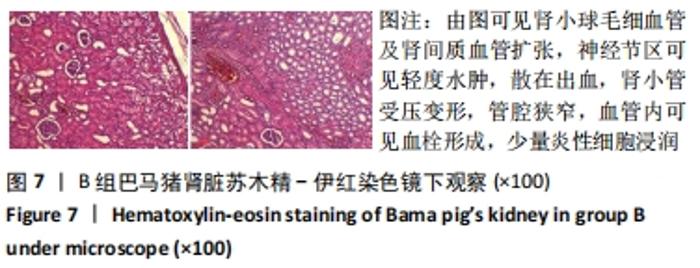
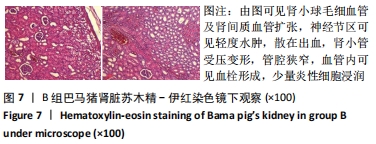
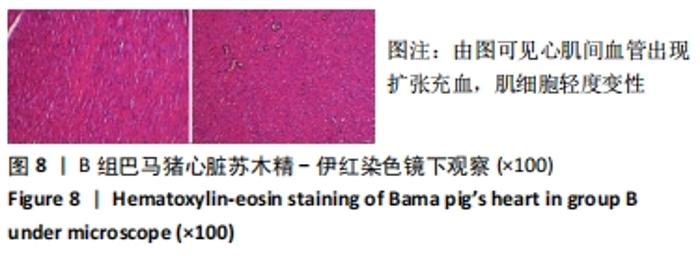
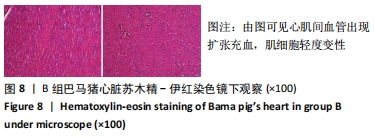
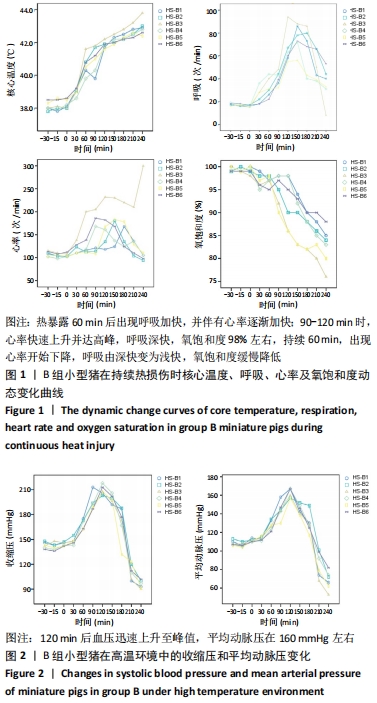
2.3 两组小型猪在持续热应激时生命体征的动态变化 两组小型猪在进入热舱后,在热暴露期间A组各实验动物核心温度无明显升高,维持在40 ℃左右的水平。在120 min时,出现呼吸频率32次/min,心率128次/min,直至实验结束,各实验猪呼吸及心率较前无明显变化,考虑各实验动物逐渐适应高温高湿环境。 B组在热暴露期间各实验小型猪表现出相似的体温调节反应,前90 min上升速率较快,核心温度从基础体温迅速上升到41 ℃,此后30 min内,核心温度上升速率有所下降,随后平稳上升;180 min时上升至42 ℃以上。热暴露60 min后出现呼吸加快,约40次/min,并伴有心率逐渐加快约112次/min;随后的90-120 min时,心率快速上升并达高峰180次/min左右,呼吸深快,氧饱和度98%左右,持续60 min,出现心率开始下降,呼吸由深快变为浅快,氧饱和度缓慢降低,见图1;120 min后血压迅速上升至峰值,平均动脉压在160 mmHg左右,见图2。随着热应激的延长,血压、心率、氧饱和度开始缓慢下降,当平均动脉压下降25 mmHg后,呼吸、心率、氧饱和度迅速降低。"
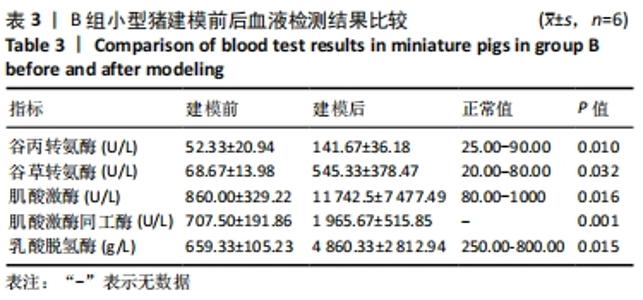
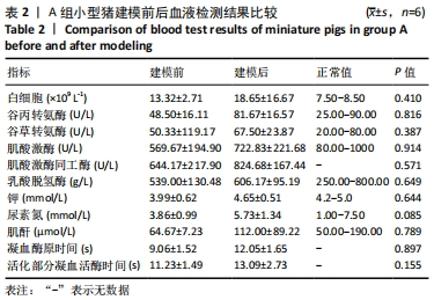
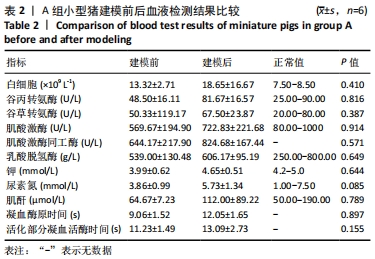
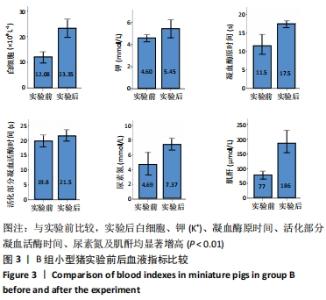
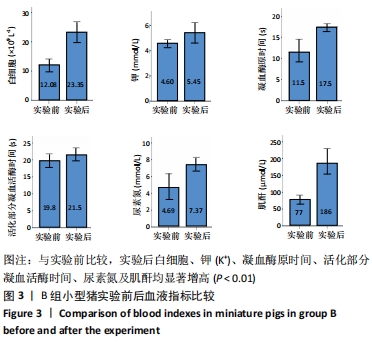
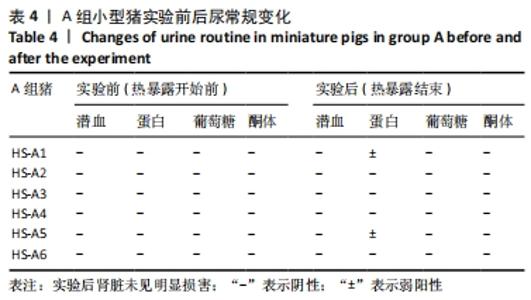
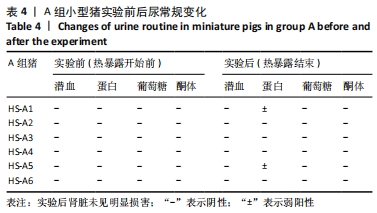
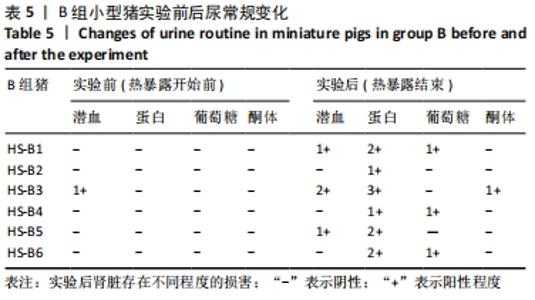
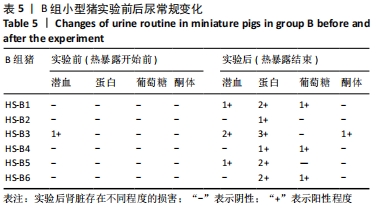
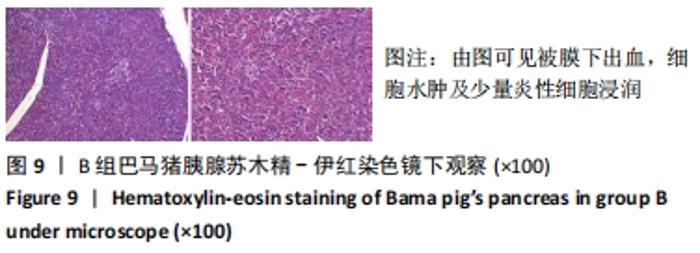
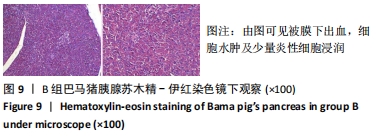
2.4.2 热应激状态下对凝血的影响 与实验前比较,A组小型猪实验后凝血指标活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间无明显异常(P > 0.05);B组实验后凝血指标活化部分凝血活酶时间、凝血酶原时间明显异常(P < 0.05),见表2,图3。 2.4.3 热应激状态下对电解质的影响 随着热应激时间的延长,A组小型猪实验后血K+水平与实验前比较无明显异常 (P > 0.05);B组实验后血K+水平明显异常(P < 0.05),见表2,图3。 2.4.4 肾功能的影响 与实验前比较,A组小型猪实验后小型猪肾功能指标未见明显异常(P > 0.05);B组小型猪实验后肾功能相关指标肌酐及尿素氮均出现明显异常(P < 0.05),见表2,图3。 2.4.5 热应激状态下对酶学指标的影响 随着热应激时间的延长,A组小型猪实验后转氨酶及肌酸激酶水平与实验前比较,未见明显异常(P > 0.05),见表2;B组实验后转氨酶及肌酸激酶水平出现明显异常(P < 0.05),见表3。"

| [1] 全军热射病防治专家组,全军重症医学专业委员会.中国热射病诊断与治疗专家共识[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(3):181-196. [2] LEON LR, BOUCHAMA A. Heat stroke.Compr Physiol. 2015;5(2):611-647. [3] HIFUMI T, KONDO Y, SHIMAZAKI J, et al. Prognostic significance of disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with heat stroke in anationwide registry. J Crit Care. 2018;44:306-311. [4] 杜力文,石永伟,许兆军,等.热射病动物模型综述[J].现代实用医学,2019, 31(4):563-565. [5] 陈华主.小型猪医学研究模型的建立与应用[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2015. [6] 桑剑锋,马虎成,施晓雷,等.巴马小型猪 85%肝切除术后急性肝功能衰竭模型的建立[J].中国实验动物学报,2017,25(2):174-180. [7] RAMOS L, OBREGON-HENAO A, HENAO-TAMAYO M, et al. The minipig as an animal model to study Mycobacteriumtuberculosis infection and natural transmission. Tuberculosis(Edinb). 2017;106:91-98. [8] BADIN J K, KOLE A, STIVERS B, et al. Alloxan-induceddiabetes exacerbates coronary atherosclerosis and calcification in Ossabaw miniature swine with metabolic syndrome. Transl Med. 2018;16(1):58. [9] 赵铭,张承刚,张 薇,等.99 Tcm-DMSA 肾显像诊断肾盂肾炎和肾脏瘢痕的动物模型实验研究[J].中华核医学杂志,2000,20(5):202-204. [10] KÄSER T, RENOIS F, WILSON HL, et al. Contribution of the swine model in the study of human sexually transmitted infections. Infect Genet Evol. 2018;66:346-360. [11] 冯媛媛,白雪源,贺津,等. 中国实验用小型猪血液指标正常参考值分析[J].中国畜牧兽医,2013,40(6):139-142. [12] 汪洁英,孙佳琪,宁博.小型猪模型在医学研究领域中的应用[J].中兽医医药杂志,2019(5):91-95. [13] 秦川.实验动物学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2010. [14] LIN MT, LIU HH, YANG YL. Involvement of interleukin-1 re-ceptor mechanisms in development of arterial hypotension inrat heatstroke.Am J Physiol. 1997;273(4):H2072-2027. [15] 周京江,宋青,赵佳佳,等.大鼠热射病发病早期免疫状态的观察[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(10):817-822. [16] 王楠.高温季节猪中暑的原因、临床症状、治疗和预防措施[J].现代畜牧科技,2020(5):132-133. [17] BOUCHAMA A, ROBERTS G, AL MOHANNA F, et al. Inflammatory, hemostatic, and clinical changes in a baboon experimental model for heatstroke. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98(2):697. [18] GANESAN S, VOLODINA O, PEARCE SC, et al. Acute heat stress activated inflammatory signaling in porcine oxidative skeletal muscle. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(16):e13397. [19] 张婷,宋青,周飞虎,等.经典型与劳力型热射病动物模型之比较[J].解放军医学院学报,2013,34(12):1209-1212. [20] 高俊涛,万鹏,王春艳,等.急性高温暴露对清醒非束缚大鼠血液动力学的影响[J].环境与健康杂志,2018,35(3):198-201. [21] 耿瑶,朱玲勤,刘法东,等.高温、高湿环境对自发性高血压大鼠胸主动脉细胞凋亡的影响[J].环境与健康杂志,2017,34(10):847-850. [22] 田锐,谢云,杜江,等.热射病早起肠道屏障功能损害与炎症反应因子的相关性研究[J/OL].中华重症医学电子杂志,2018,3(4):333-337. [23] RAMANATHAN M, PEDERSEN MM, RAMSEY R, et al. Dagnostic value of coagulation factor and intracranial pressure monitoring in acute liver failure from heat stroke:casereport and review of the literature.Transplant Proc. 2015;47(3):817-819. [24] BOUCHAMA A, AL-SEDAIRY S, SIDDIQUI S, et al. Elevated pyrogenic cytokines in heatstroke. Chest. 1993;104(5):1498-1502. [25] Hammami MM, Bouchama A, Al-Sedairy S, et al. Concentrations of soluble tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 receptors in heatstroke and heatstress. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:1314-1319. [26] TAYLOR FB JR, WADA H, KINASEWITZ G. Description of compensated and uncompensated disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) responses (non-overt and overt DIC) in baboon models of intravenous and intraperitoneal Escherichia coli sepsis and in the human model of endotoxemia: toward a better definition of DIC.Crit Care Med. 2000; 28(9 Suppl):S12-S19. [27] 张泽丹.热气候环境下运动对肝肾功能的影响及其相关机制研究[D].福建:福建医科大学,2017. [28] ROBERTS GT, GHEBE HH, CHISHTI MA, et al. MicrovascularInjury, Thrombosis, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Heatstroke A Study in Baboon Modell. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(6):1130-1136. [29] 黄泼泼,刘江伟,张波,等.沙漠干热环境下中暑大鼠的心肌酶及心肌组织形态学改变[J].中国比较医学杂志,201,24(2):11-15,后插1页 [30] Mclaren C, Null J, Quinn J. Heat stress from enclosed vehicles: moderate ambient temperatures cause significant temperature rise in enclosed vehicles. Pediatrics. 2005;116(1):e109-112. [31] Bouchama A. The 2003 European heat wave. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30(1):1-3. [32] 岳慧,宋青,季筠,等.肌酸激酶浓度在劳力型热射病早起判别预后的研究[J].军医进修学院报,2008,29(6):4572459. [33] 汪晓.高温高湿条件下运动致大鼠多脏器损伤及其机制研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2013. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [4] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [5] | Lü Yiyan, Li Hanbing, Ma Xiaoqing, Zhang Han, Zhang Yuhang, Li Genlin. Establishment and characteristic analysis of interior heat and diabetes mouse model using compound factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1187-1193. |
| [6] | Chen Shijian, Li Ge, Zhang Yu, Guan Yalun, Li Xuejiao, Liu Shuhua, Li Yongchao, Li Yunfeng, Gao Jinfeng, Wei Xiaoyue, Zhao Yuhong. Comparison and evaluation of MPTP-induced subacute and chronic models of Parkinson’s disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1247-1252. |
| [7] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [9] | Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie. Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [10] | Feng Jianbo, Li Chencheng, Liu Jinyue, Wang Xiaomin, Peng Jiachen. Implantation of Kirschner wire with Staphylococcus aureus biofilm establishes a traumatic osteomyelitis model in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 700-705. |
| [11] | Wang Shihui, Cheng Yang, Zhu Yunjie, Cheng Shaodan, Mao Jianying. Effect of arc edge needle-scalpel therapy on inflammatory factors and histomorphology of the frozen shoulder in rabbit models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 706-711. |
| [12] | Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723. |
| [13] | Deng Zhaoyang, Yang Zhaohui. Three-dimensional model analysis of tibial plateau fracture lines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 334-339. |
| [14] | Li Yanting, Chen Jian, Liu Menglan, Ren Manman, Zhong Weihong, Chen Changxing. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of Daogaijinbei manipulation on lumbar intervertebral disc biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 340-343. |
| [15] | Li Shulun, Hao Peng, Hao Fei, Duan Hongmei, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Chaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Pathological changes in rats with ischemic stroke induced by improved photochemical embolization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 218-224. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||