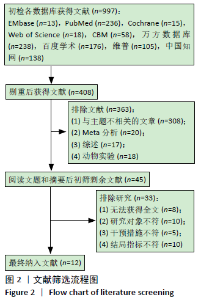
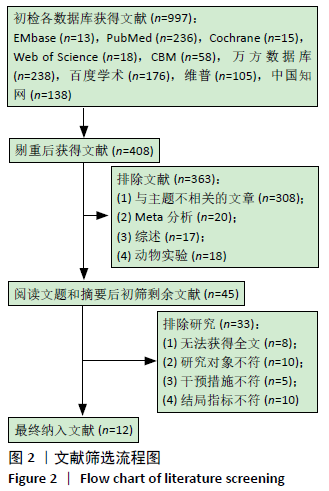
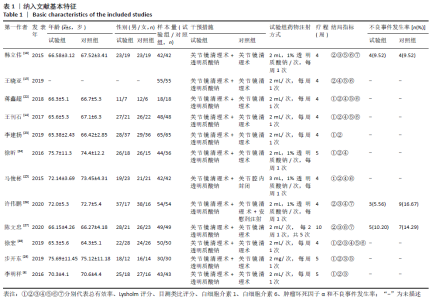
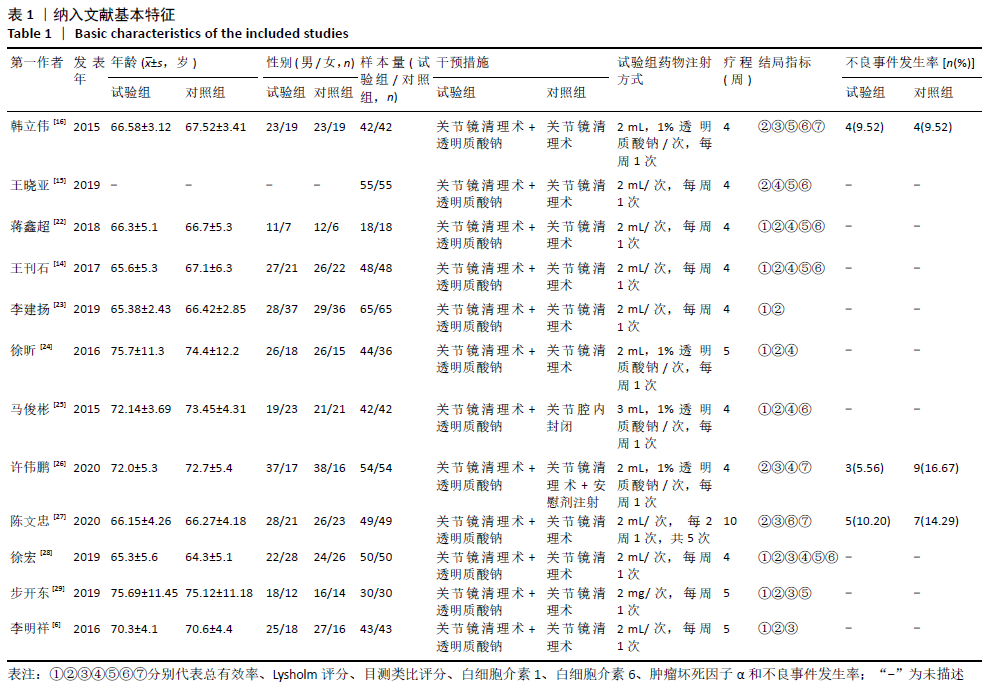
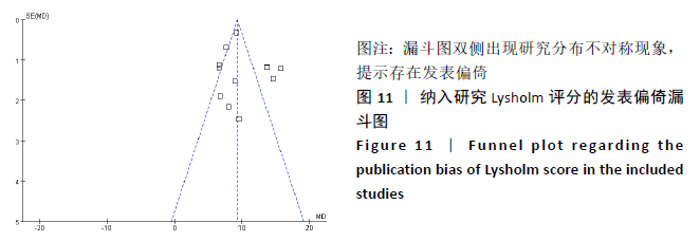
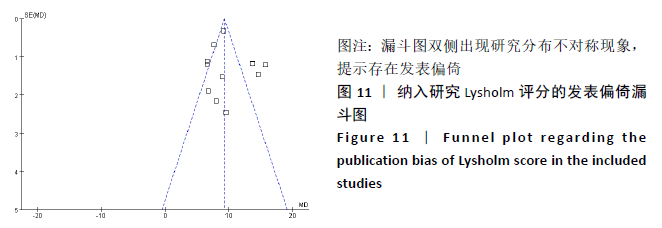
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (26): 4249-4256.doi: 10.12307/2021.129
Previous Articles Next Articles
Arthroscopic debridement combined with sodium hyaluronate injection for the treatment of senile knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis of changes in pain, inflammatory factor, and joint function
Huang Linfeng1,2, Gu Yingxuan3, Quan Xiaoming4, He Wei2, Chen Leilei2
- 1The Third Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 4The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-15Revised:2020-10-22Accepted:2020-11-21Online:2021-09-18Published:2021-05-14 -
Contact:Chen Leilei, Doctoral supervisor, Associate chief physician, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Linfeng, Master candidate, The Third Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81673999 (to CLL); Guangdong Provincial Outstanding Youth Science Fund, No. 2015A030306037 (to CLL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Linfeng, Gu Yingxuan, Quan Xiaoming, He Wei, Chen Leilei. Arthroscopic debridement combined with sodium hyaluronate injection for the treatment of senile knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis of changes in pain, inflammatory factor, and joint function[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4249-4256.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
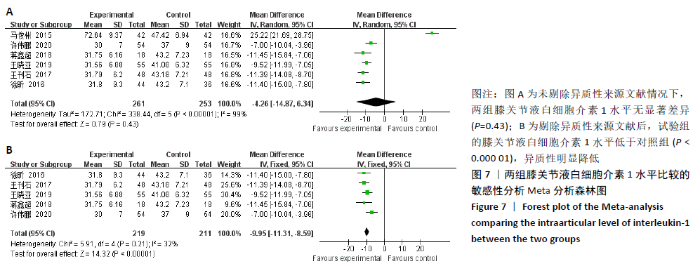
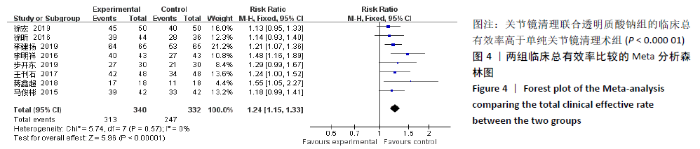
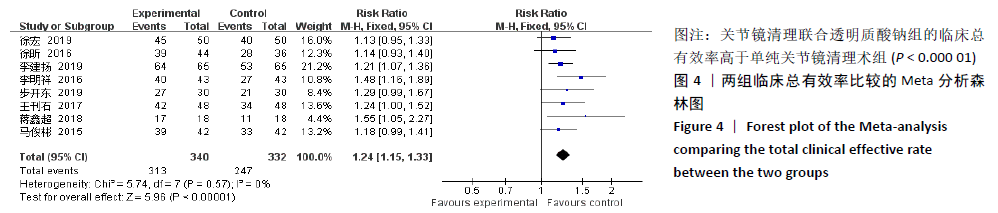
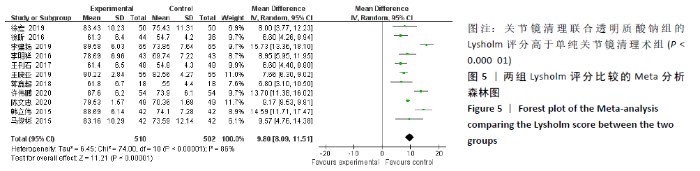
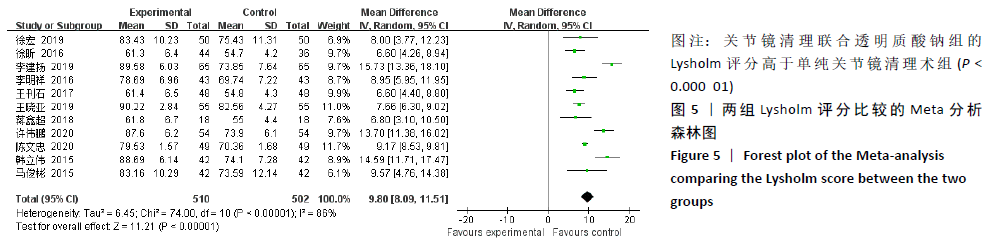
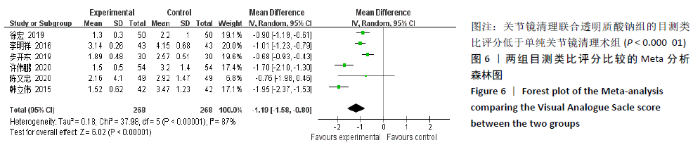
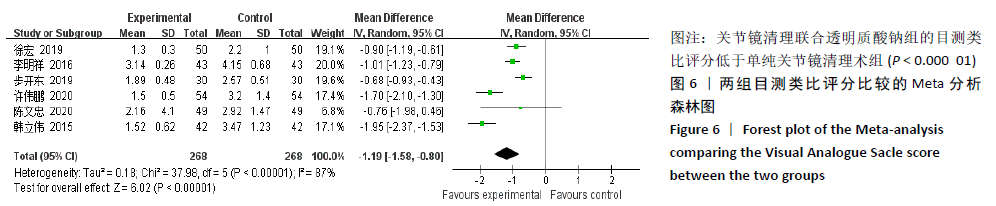
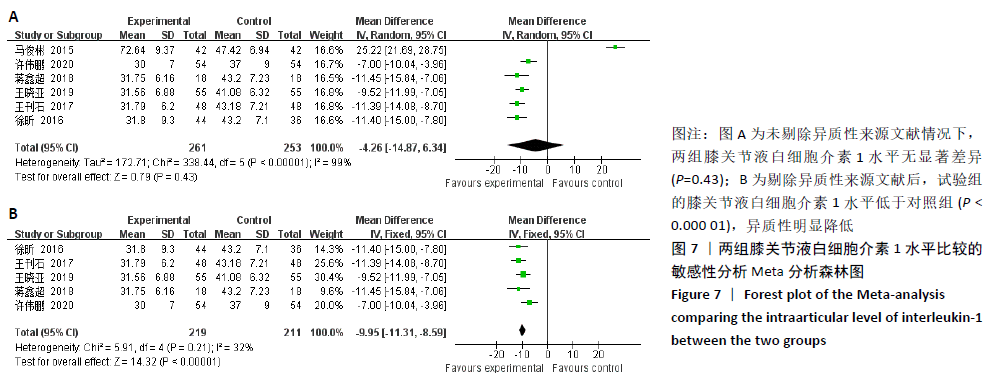
2.3.4 各组膝关节液白细胞介素1水平差异 有6项研究的结局指标包括白细胞介素1表达水平[14-15,22,24-26]。各项研究间的异质性较大(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),采用随机效应模型,分析结果提示试验组与对照组的合并效应大小无显著性差异(MD=-4.26,95%CI: -14.87-6.34,P=0.43),见图7A。敏感性分析发现异质性来源于文献[25],剔除该文献后各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.21,I2=32%),采用固定效应模型重新Meta分析,结果提示两组白细胞介素1水平差别有显著性(MD= -9.95,95%CI:-11.31至-8.59,P < 0.000 01),可认为关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠治疗组的膝关节液白细胞介素1水平低于单纯关节镜清理术治疗组,见图7B。"
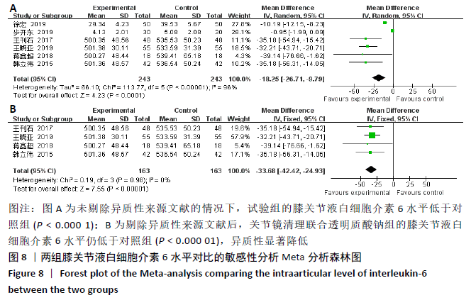
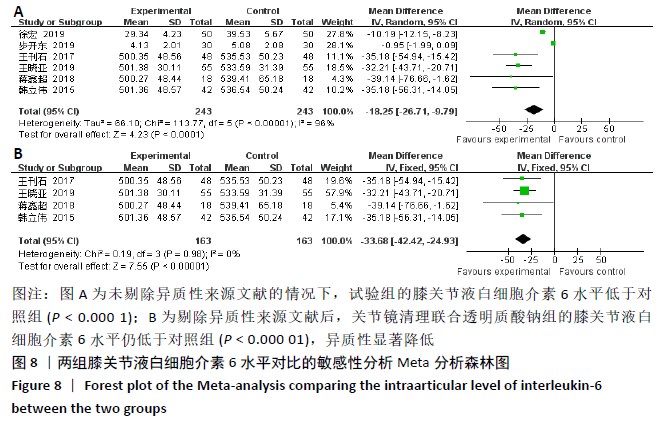
2.3.5 各组膝关节液白细胞介素6水平差异 对结局指标包括白细胞介素6表达水平的6项研究进行Meta分 析[14-16,22,28-29]。各项研究间存在明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果提示试验组与对照组的合并效应大小存在显著性差异(MD=-18.25,95%CI: -26.71至-9.79,P < 0.0001),见图8A。敏感性分析发现异质性来源于文献[28-29],剔除后各研究间的异质性明显降低(P=0.98,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型分析,结果表明两组白细胞介素6水平对比仍具有显著性差异(MD=-33.68,95%CI:-42.42至-24.93,P < 0.000 01),见图8B。故认为关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠组的白细胞介素6水平低于单纯关节镜清理术组。"
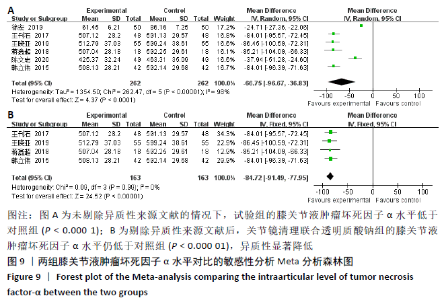
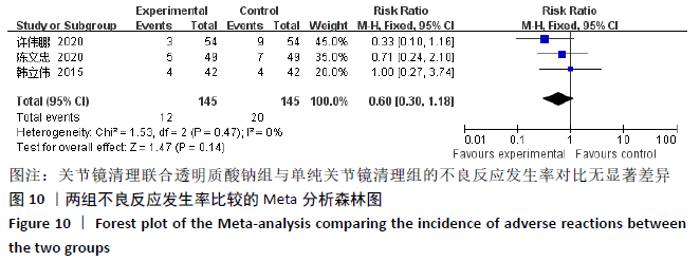
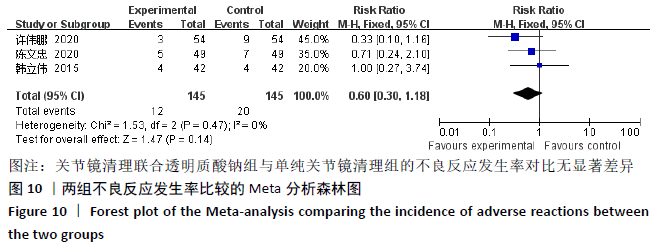
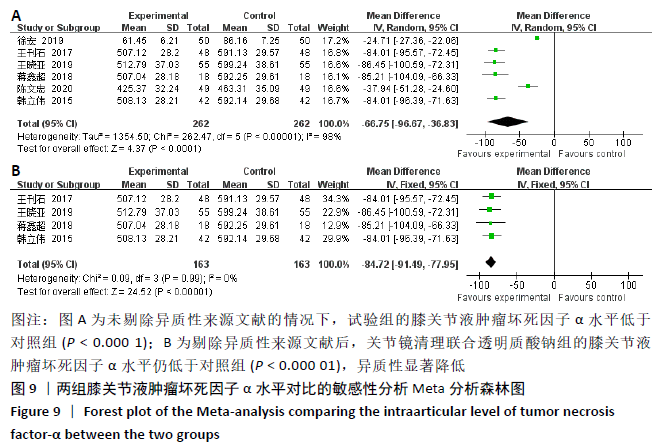
2.3.6 各组膝关节液肿瘤坏死因子α水平差异 对结局指标包括肿瘤坏死因子α表达水平的6项研究进行Meta分析发现[14-16,22,27-28],各项研究间具有明显异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),选用随机效应模型,分析结果显示试验组与对照组的合并效应大小有显著性差异(MD=-66.75,95%CI:-96.67至-36.83,P < 0.000 1),见图9A。敏感性分析发现异质性来源于文献[27-28],剔除后各研究间异质性显著降低(P=0.99,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型重新进行Meta分析结果提示,两组肿瘤坏死因子α水平比较差别仍然有显著性意义(MD=-84.72, 95%CI:-91.49至-77.95,P < 0.000 01), 见图9B。表明关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠组的肿瘤坏死因子α水平低于单纯关节镜清理术组。"
| [1] PEREIRA D, RAMOS E, BRANCO J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015;28(1): 99-106. [2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [3] URBAN H, LITTLE CB. The role of fat and inflammation in the pathogenesis and management of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4): iv10-iv21. [4] GEYER M, SCHÖNFELD C. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):98-107. [5] 国家统计局.中华人民共和国2019年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[1][N].人民日报,2020-02-29(005). [6] 李明祥,俞维英.老年膝骨性关节炎术后应用玻璃酸钠治疗对减轻其疼痛的作用分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2016,21(4): 722-723. [7] CHEN P, HUANG L, MA Y, et al. Intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injection for knee osteoarthritis: a summary of meta-analyses. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):385. [8] BANNURU RR, OSANI MC, VAYSBROT EE, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1578-1589. [9] 白朝奇,封鹏,张雪艳,等.关节镜清理联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛程度、炎症介质及膝关节功能的影响[J].海南医学,2020, 31(17):2203-2206. [10] ROSETI L, DESANDO G, CAVALLO C, et al. Articular cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. Cells. 2019;8(11):1305. [11] YANG X, LIN JH, SUN TS, et al. The efficacy and safety of sodium hyaluronate injection (Adant®) in treating degenerative osteoarthritis: a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, positive-drug parallel-controlled and non-inferiority clinical study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(3):271-278. [12] 刘爱峰,裴开源,王平,等.玻璃酸钠注射液与生理盐水对照对于膝骨性关节炎临床疗效的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(17):1581-1586. [13] SHIMIZU M, HIGUCHI H, TAKAGISHI K, et al. Clinical and biochemical characteristics after intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: prospective randomized study of sodium hyaluronate and corticosteroid. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(1):51-56. [14] 王刊石,周超,赵磊.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠对老年膝骨关节炎患者的临床疗效及对关节液内IL-6、IL-1、TNF-α水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017, 37(13):3290-3291. [15] 王晓亚,任猛,王浩,等.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠在老年膝骨关节炎治疗的效果及炎性因子的影响[J].河北医药, 2019,41(8):1235-1237. [16] 韩立伟.关节镜下清理术联合透明质酸钠对老年膝骨关节炎疼痛及IL-6、TNF-α的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2015,32(5): 778-780. [17] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨关节炎诊治指南(2007年版)[J].中国临床医生,2008, 36(1):28-30. [18] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [19] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;10(18):343:d5928. [20] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10:ED000142. [21] HIGGINS JP, GREEN S. Cochrane Handbook For Systematic Reviews Of Interventions Version 5.0.0. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie. 2008;5(2):S38. [22] 蒋鑫超.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠在老年膝骨关节炎治疗的效果及炎性因子的影响评价[J]. 国际感染杂志(电子版), 2018,7(3):76-77. [23] 李建扬,杨先腾,罗锐,等.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠治疗老年膝骨关节炎的疗效观察[J].双足与保健,2019,28(19):156-157. [24] 徐昕,董耘,徐华,等.关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠腔内注射治疗80例高龄膝关节骨性关节炎患者临床分析[J].中华全科医学,2016,14(9):1463-1465. [25] 马俊彬,朱传银,鲁兵.透明质酸钠联合膝关节镜治疗老年膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(15): 184-185. [26] 许伟鹏,徐志强,吴峰,等.关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠治疗膝骨关节炎的短期疗效[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2020,14(3):370-374. [27] 陈文忠,侯颖周,李科伟,等.关节镜清理联合玻璃酸钠注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国老年保健医学, 2020,18(2):47-49. [28] 徐宏.关节镜与玻璃酸钠联合治疗膝骨关节炎的效果[J].中国合理用药探索,2019, 16(2):73-76. [29] 步开东,范顺武,翁科迪.关节镜微创手术联合玻璃酸钠治疗对老年膝关节骨性关节炎患者生活质量及血清IL-6、IL-10的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(7): 1637-1639. [30] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [31] NEES TA, ROSSHIRT N, REINER T, et al. Inflammation and osteoarthritis-related pain. Schmerz. 2019;33(1):4-12. [32] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obeaqsity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38-50. [33] WOJDASIEWICZ P, PONIATOWSKI A, SZUKIEWICZ D, et al. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:561459. [34] ALTMAN RD, MANJOO A, FIERLINGER A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:321 [35] 廖瑛,张兴,周君,等.透明质酸对膝关节骨性关节炎相关细胞因子及生物标志物的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2019, 29(4):33-38. [36] 王波,余楠生.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):124-130. [37] HENROTIN Y, RAMAN R, RICHETTE P, et al. Consensus statement on viscosupplementation with hyaluronic acid for the management of osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015;45(2):140-149. [38] BRONSTONE A, NEARY JT, LAMBERT TH, et al. Supartz (sodium hyaluronate) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a review of efficacy and safety. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;12:1179544119835221. [39] LI ZM, LI M. Improvement in orthopedic outcome score and reduction in IL-1β, CXCL13, and TNF-α in synovial fluid of osteoarthritis patients following arthroscopic knee surgery. Genet Mol Res. 2017. doi: 10.4238/gmr16039487. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [6] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [7] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [8] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [9] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||