Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (26): 4223-4229.doi: 10.12307/2021.125
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism of osteoarthritis by multi-chip combination analysis
Rong Weiming1, Yuan Changshen2, Duan Kan2, Lu Zhixian1, Mei Qijie2, Guo Jinrong2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-07-07Revised:2020-07-13Accepted:2020-08-19Online:2021-09-18Published:2021-05-13 -
Contact:Yuan Changshen, Master, Associate chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Rong Weiming, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the First-class Discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region ([2018]12), No. 2019XK030 (to YCS); the Natural Science Research Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019QN022 (to YCS); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060875 (to YCS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Rong Weiming, Yuan Changshen, Duan Kan, Lu Zhixian, Mei Qijie, Guo Jinrong. Molecular mechanism of osteoarthritis by multi-chip combination analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4223-4229.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
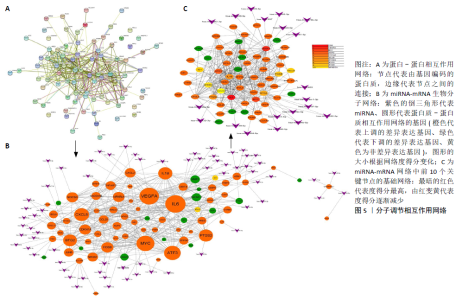
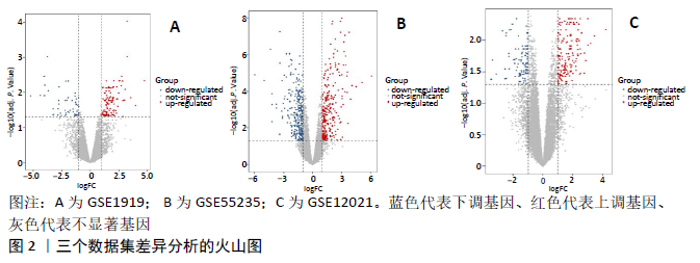
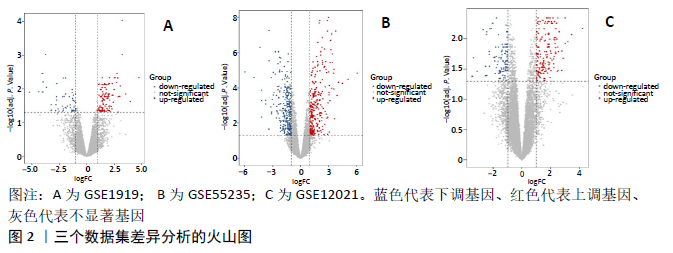
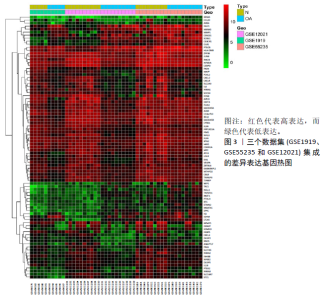
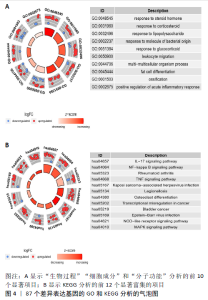
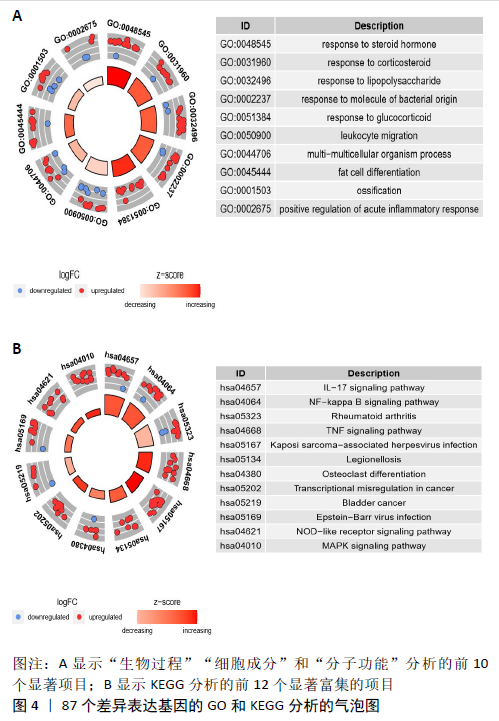
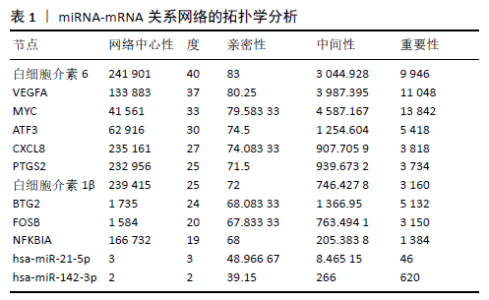
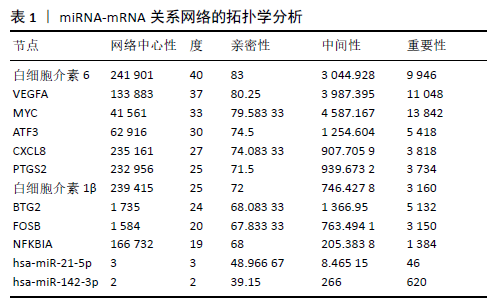
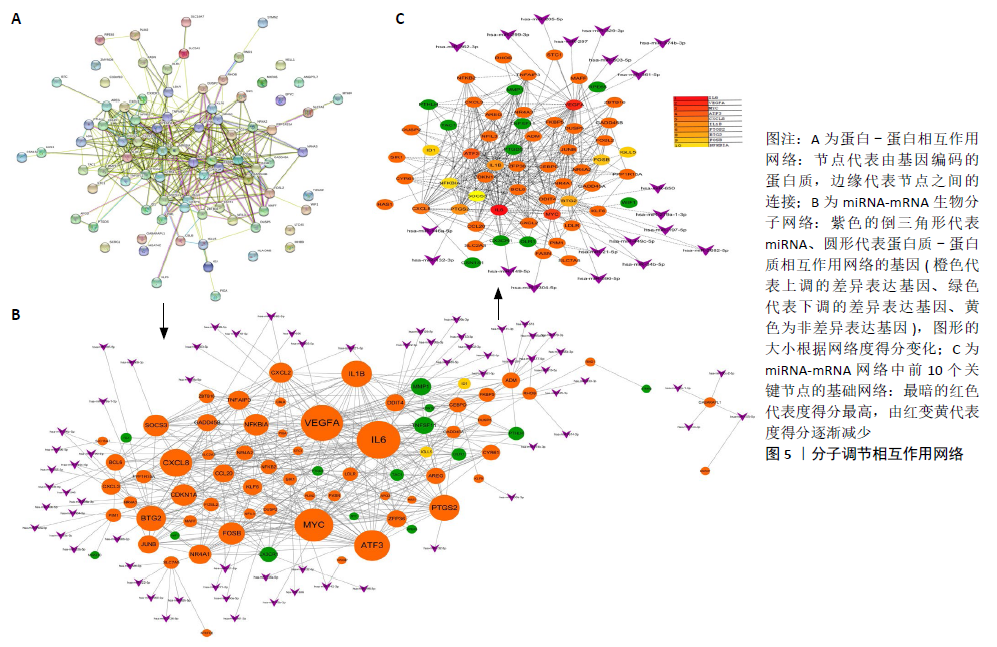
2.3 miRNA-mRNA调控网络 采用STRING数据库构建差异表达基因蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络,包含84个节点和338个边,边线的粗细代表两种蛋白间关系的强弱,见图5A。通过miRDB数据库预测差异表达基因上游miRNA,同时满足靶标得分> 60和结合位点< 800的miRNA共265个;miRNet数据库预测到1 501个miRNA;将2个数据库的网络交集得到1个含有67个miRNA和30个差异表达基因的网络;再利用Cytoscape将合并后的网络构建成1个包括142个节点和415条边的miRNA-mRNA调控网络,见图5C;最后利用“CytoHubba”插件筛选出前10位关键基因(白细胞介素6、VEGFA、MYC、ATF3、CXCL8、白细胞介素1β、PTGS2、BTG2、FOSB和NFKBIA)及2个重要的miRNA(hsa-miR-21-5p、hsa-miR-142-3p),见图5B,表1。"
| [1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015; 386(9991):376-387. [2] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. CurrOpinRheumatol. 2018;30(2):160-167. [3] LI MH, XIAO R, LI JB, et al. Regenerative approaches for cartilage repair in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(10):1577-1587. [4] 何超鹏,陈铖,蒋欣宸,等.失配性因素在骨关节炎发病机制中的作用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2019,40(6):353-356. [5] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21. [6] FURMAN BD, KIMMERLING KA, ZURA RD, et al. Articular ankle fracture results in increased synovitis, synovial macrophage infiltration, and synovial fluid concentrations of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(5):1234-1239. [7] ZENG C, LI YS, LEI GH. Synovitis in knee osteoarthritis: a precursor or a concomitant feature? Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(10):e58. [8] SOKOLOVE J, LEPUS CM. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: latest findings and interpretations. TherAdvMusculoskelet Dis. 2013;5(2):77-94. [9] 王学宗,丁道芳,薛艳,等.TLR4/NF-κB通路参与大鼠膝骨关节炎滑膜早期病变的研究[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(1):68-71. [10] UNGETHUEM U, HAEUPL T, WITT H, et al. Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics. 2010;42A(4):267-282. [11] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84. [12] HUBER R, HUMMERT C, GAUSMANN U, et al. Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R98. [13] LU TX, ROTHENBERG ME. MicroRNA.J Allergy ClinImmunol. 2018;141(4): 1202-1207. [14] HERMANN W, LAMBOVA S, MULLER-LADNER U. Current Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis. CurrRheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):108-116. [15] FERNANDES JC, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, PELLETIER JP. The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology.Biorheology. 2002;39(1-2):237-246. [16] HUNTER CA, JONES SA. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol. 2015;16(5):448-457. [17] KLOCKE R, LEVASSEUR K, KITAS GD, et al. Cartilage turnover and intra-articular corticosteroid injections in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(3):455-459. [18] HUANG Z, KRAUS VB. Does lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation have a role in OA? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(2):123-129. [19] SCANZELLO CR. Chemokines and inflammation in osteoarthritis: Insights from patients and animal models. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(4):735-739. [20] JIANG Y, TIAN M, LIN W, et al. Protein Kinase Serine/Threonine Kinase 24 Positively Regulates Interleukin 17-Induced Inflammation by Promoting IKK Complex Activation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:921. [21] AMATYA N, GARG AV, GAFFEN SL. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017;38(5):310-322. [22] LIU Y, PENG H, MENG Z, et al. Correlation of IL-17 Level in Synovia and Severity of Knee Osteoarthritis. Med SciMonit. 2015;21:1732-1736. [23] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275. [24] RIGOGLOU S, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. The NF-κBsignalling pathway in osteoarthritis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(11):2580-2584. [25] PEGORETTI V, BARON W, LAMAN JD, et al. Selective Modulation of TNF-TNFRs Signaling: Insights for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment. Front Immunol. 2018;9:925. [26] HOSSEINZADEH A, KAMRAVA SK, JOGHATAEI MT, et al. Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and possible protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(4):411-425. [27] LUAN Y, KONG L, HOWELL DR, et al. Inhibition of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 degradation of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein by alpha-2-macroglobulin. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(11):1413-1420. [28] ZHAO Y, LI Y, QU R, et al. Cortistatin binds to TNF-α receptors and protects against osteoarthritis. EBioMedicine. 2019;41:556-570. [29] SUN J, NAN G. The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling Pathway as a Discovery Target in Stroke. J MolNeurosci. 2016;59(1):90-98. [30] SUN Y, LIU WZ, LIUT, et al. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35(6):600-604. [31] CHEN Y, SHOU K, GONG C, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Osteoarthritis by Suppressing the Activation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8384576. [32] LAAVOLA M, LEPPÄNEN T, HÄMÄLÄINEN M, et al. IL-6 in Osteoarthritis: Effects of Pine Stilbenoids. Molecules. 2018;24(1):109. [33] VICENTI G, BIZZOCA D, CARROZZO M, et al. Multi-omics analysis of synovial fluid: a promising approach in the study of osteoarthritis. J BiolRegulHomeost Agents. 2018;32(6 Suppl. 1):9-13. [34] IEZAKI T, OZAKI K, FUKASAWA K, et al. ATF3 deficiency in chondrocytes alleviates osteoarthritis development. J Pathol. 2016;239(4):426-437. [35] ZHAI G, PELLETIER JP, LIU M, et al. Activation of The Phosphatidylcholine to Lysophosphatidylcholine Pathway Is Associated with Osteoarthritis Knee Cartilage Volume Loss Over Time. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):9648. [36] LARSSON S, ENGLUND M, STRUGLICS A, et al. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial fluid are associated with progression of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in subjects with previous meniscectomy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1906-1914. [37] QIAO Z, TANG J, WU W, et al. Acteoside inhibits inflammatory response via JAK/STAT signaling pathway in osteoarthritic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):264. [38] XIONG H, LI W, LI J, et al. Elevated leptin levels in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis promote proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 expression in synovial fibroblasts. J Oral Pathol Med. 2019;48(3):251-259. [39] LU L, HUANG XW, XIE Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of intra-articular parecoxib injection for the treatment of early knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(5):418-422. [40] LI H, PENG Y, WANG X, et al. Astragaloside inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. ImmunopharmacolImmunotoxicol. 2019;41(4):497-503. [41] MACDONALD IJ, LIU SC, SU CM, et al. Implications of Angiogenesis Involvement in Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):2012. [42] 梁治权,顾文飞,廖军.清热解毒通络汤联合塞来昔布对骨关节炎患者血清相关炎性因子水平的影响[J].中国医药,2018,13(3):433-436. [43] 郭静,张娜,秦丽娟,等.膝骨关节炎患者中IL-18、VEGF和NF-κB的表达及意义[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(18):3024-3026. [44] NEES TA, ROSSHIRT N, ZHANG JA, et al. Synovial Cytokines Significantly Correlate with Osteoarthritis-Related Knee Pain and Disability: Inflammatory Mediators of Potential Clinical Relevance. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):1343. [45] SCHICK M, HABRINGER S, NILSSON JA, et al. Pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting of aberrant MYC expression in haematological cancers. Br J Haematol. 2017;179(5):724-738. [46] YATSUGI N, TSUKAZAKI T, OSAKI M, et al. Apoptosis of articular chondrocytes in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: correlation of apoptosis with degree of cartilage destruction and expression of apoptosis-related proteins of p53 and c-myc. J Orthop Sci. 2000;5(2):150-156. [47] WU YH, LIU W, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of microRNA-24 targeting C-myc on apoptosis, proliferation, and cytokine expressions in chondrocytes of rats with osteoarthritis via MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10):7944-7958. [48] 杨鹏.骨关节炎患者细胞因子/趋化因子表达谱分析以及CXCL8和CXCL11对软骨细胞的调节作用[D].西安:第四军医大学,2017. [49] JIN Z, REN J, QI S. Human bone mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes overexpressing microRNA-26a-5p alleviate osteoarthritis via down-regulation of PTGS2. IntImmunopharmacol. 2020;78:105946. [50] MANIAR KH, JONES IA, GOPALAKRISHNA R, et al. Lowering side effects of NSAID usage in osteoarthritis: recent attempts at minimizing dosage. Expert OpinPharmacother. 2018;19(2):93-102. [51] YUNIATI L, SCHEIJEN B, VAN DER MEER LT, et al. Tumor suppressors BTG1 and BTG2: Beyond growth control. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5379-5389. [52] BARRETT CS, MILLENA AC, KHAN SA. TGF-β Effects on Prostate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Require FosB. Prostate. 2017;77(1):72-81. [53] LIU Y, MI B, LV H, et al. Shared KEGG pathways of icariin-targeted genes and osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem.2018 Dec 3.doi: 10.1002/jcb.28048. [54] WANG XB, ZHAO FC, YI LH, et al. MicroRNA-21-5p as a novel therapeutic target for osteoarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019:kez102. [55] WANG X, GUO Y, WANG C, et al. MicroRNA-142-3p Inhibits Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Inflammation in Osteoarthritis by Targeting HMGB1. Inflammation. 2016;39(5):1718-1728. [56] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of inflammation and the immune system in the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [57] TATEIWA D, YOSHIKAWA H, KAITO T. Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategy: A Literature Review. Cells. 2019;8(8):818. [58] ZHOU Y, MING J, DENG M, et al. Berberine-mediated up-regulation of surfactant protein D facilitates cartilage repair by modulating immune responses via the inhibition of TLR4/NF-ĸB signaling. Pharmacol Res. 2020; 155:104690. [59] HASEEB A, HAQQI TM. Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis.ClinImmunol. 2013;146(3):185-196. [60] MORADI B, SCHNATZER P, HAGMANN S, et al. CD4⁺CD25⁺/highCD127low/⁻ regulatory T cells are enriched in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis joints--analysis of frequency and phenotype in synovial membrane, synovial fluid and peripheral blood. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R97. [61] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-1499. |
| [1] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [4] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [5] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [6] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [7] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [8] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [9] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [10] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [11] | Zou Gang, Xu Zhi, Liu Ziming, Li Yuwan, Yang Jibin, Jin Ying, Zhang Jun, Ge Zhen, Liu Yi. Human acellular amniotic membrane scaffold promotes ligament differentiation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells modified by Scleraxis in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1037-1044. |
| [12] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [13] | Wang Feng, Zhou Liyu, Saijilafu, Qi Shibin, Ma Yanxia, Wei Shanwen. CaMKII-Smad1 promotes axonal regeneration of peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1064-1068. |
| [14] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||