Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (31): 4637-4643.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.31.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Digital three-dimensional measurement and design of proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric femoral fractures
Chen Shao-ming, Lu Bin, Yang Zhi-qiang, Zhou Xue-li, Chen Xiao-hua
- Second Department of Orthopedics, Changyi People’s Hospital, Changyi 261300, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2016-06-15Online:2016-07-22Published:2016-07-22 -
About author:Chen Shao-ming, Master, Attending physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Changyi People’s Hospital, Changyi 261300, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Shao-ming, Lu Bin, Yang Zhi-qiang, Zhou Xue-li, Chen Xiao-hua. Digital three-dimensional measurement and design of proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric femoral fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4637-4643.
share this article
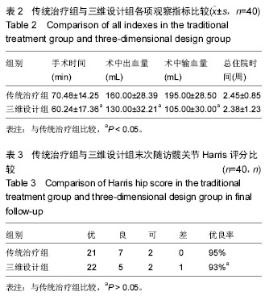
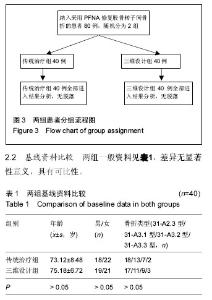
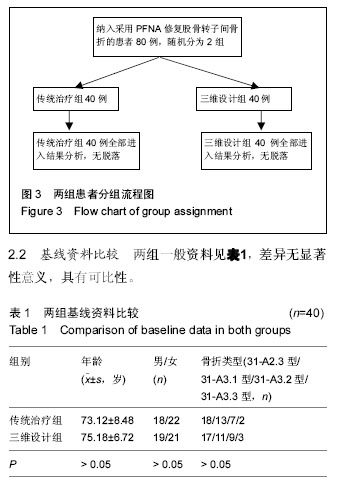
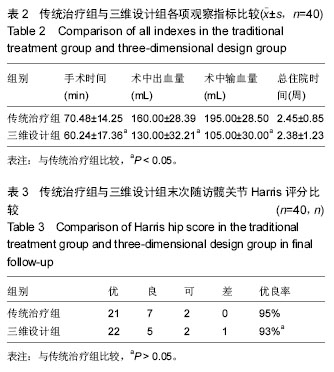
2.3 两组手术情况及住院时间比较 2组病例手术均获得成功,手术顺利,其中传统治疗组手术时间显著长于三维设计组,2组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);传统治疗组术中出血及术中输血均显著大于三维设计组,2组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);传统治疗组总住院时间显著长于三维设计组,但两组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),详见表2。 2.4 两组髋关节Harris评分比较 所有患者均获得随访,随访时间10-22个月。术后伤口均一期愈合,至研究结束时,未发现断钉,断棒情况发生。至末次随访时,传统治疗组髋关节功能Harris评分优良率为95%,三维设计组优良率为93%,2组优良率比较差异无显著性意义(见表3)。 2.5 不良事件 文中三维设计组1例患者术后髋关节Harris评分较低,为68分,该患者由车祸致右侧髋臼及转子间骨折分别进行髋臼切开复位内固定及转子间骨折术前数字化三维测量及设计PFNA治疗,术后Harris评分较低考虑与髋臼骨折有关。此病例说明文章纳入与排除标准设计不严谨,没有排除可能对结果造成影响的所有因素,最终可能造成研究结果的误差,但就80例病例仅出现此1例不良事件来看,造成试验结果误差的概率较低,结果在可接受范围。"
| [1] Shawky A, Al-Sabrout AM, El-Meshtawy M, et al. Thoracoscopically assisted corpectomy and percutaneous transpedicular instrumentation in management of burst thoracic and thoracolumbar fractures.Eur Spine J. 2013;22(10):2211-2218. [2] Hu X, Lieberman IH.What is the learning curve for robotic-assisted pedicle screw placement in spine surgery?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(6):1839-1844. [3] Neal B, Gray H, MacMahon S, et al.Incidence of heterotopic bone formation after major hip surgy.ANZ J Surg.2012;72:808. [4] Pechlivanis I, Kiriyanthan G, Engelhardt M, et al. Percutaneous placement of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine using a bone mounted miniature robotic system: first experiences and accuracy of screw placement.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 34(4):392-398. [5] Stockle U ,Konig B,Dahne M,et al.Computer assisted pelvic and acetabular surgery. Clin Exp Ind. 2013;105: 886-892 . [6] Jiang-Jun Z, Min Z, Ya-Bo Y, et al. Finite element analysis of a bone healing model: 1-year follow-up after internal fixation surgery for femoral fracture.Pak J Med Sci. 2014;30(2):343-347. [7] Heidari SM, Soltani H, Hashemi SJ, et al. Comparative study of twoanesthesia methods according to postoperative complications and one month mortanity rate in the candidates of hip surgery. Res Med Sci. 2011;16(3):323-330. [8] Rohlmann A, Boustani HN, Bergmann G, et al.A probabilistic finite element analysis of the stresses in the augmented vertebral body after vertebroplasty.Eur Spine J. 2010; 19(9):1585-1595. [9] Letoumel E, Judet R. Fractures of the Acetabulum. 2nd ed. New York: Springer Verlag,2013:535-563. [10] 李志刚.带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折53例并发症原因分析[J].陕西医学杂志,2012,41(9):1198-1199,1211. [11] Kaempffe FA,Bone LB,Border JR. Open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures: heterotopic ossification and other complications of treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;5(4):439-442. [12] Tian W, Han X, Liu B, et al.A robot-assisted surgical system using a force-image control method for pedicle screw insertion. PLoS One. 2014; 9(1):e86346. [13] Haidudewych GJ,Scaduto J,Herscovici D Jr. lartogenic nerve injury in acetabular fracture surgery :a comparison of monitored and unmonitored procedures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;16(5):297-301. [14] 蒋协远,王大伟.骨科临床疗效评价标准[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:260. [15] Levi D, Rampa F, Barbieri C,et al.True 3D reconstruction for planning of surgery on malformed skulls. Childs Nerv Syst. 2012;18(12):705-706. [16] Sugimoto Y, Tanaka M, Nakanishi K, et al. Safety of atlantoaxial fusion using laminar and transarticular screws combined with an atlas hook in a patient with unilateral vertebral artery occlusion (case report).Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(1):25-27. [17] 李辉,彭阿钦.老年股骨转子间骨折术后隐性失血的分析[J].河北医药,2013,35(10):1505-1506. [18] Lu J, Ni H, Wang Z, et al.Validation study on precision of digitized custom-made radial head prosthesis by three-dimensional visualization of virtual surgery. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013; 27(9):1065-1069. [19] He Q, Jiang W, Luo J. Investigation on biomechanics behavior using three-dimensional finite element analysis for femur shaft fracture treated with locking compression plate].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2014; 31(4):777-781, 792. [20] Digioia AM. What is computer assisted orthopaedic surgery ? Clin Orthop, 2013;354: 2-4. [21] Pennal GF, Davidsion J, Garside H, et al. Results of treatment of acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;(151):115-123. [22] Heeg M,Klasen HJ,Visser JD. Operative treatment for acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2010; 72(3):383-386. [23] Ziran BH. Acetabular reconstructionrfixation methods in simple fracture Pattems//Smith WR, Ziran BH,Morgan SJ. Fraetures of the Pelvis and acetabulum.1th ed.New York rlnforma Healtheare, 2014: 112-116. [24] Rodt T, Schlesinger A, Schramm A, et al. 3D visualization and simulation of frontoorbital advancement in metopic synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007; 23(11):1313-1317. [25] 钟世镇.转化医学理念对数字医学的启迪[J].中华消化外科杂志, 2012,11(2):99-100. [26] Metzger MC, Hohlweg-Majert B, Schön R, et al. Verification of clinical precision after computer-aided reconstruction in craniomaxillofacial surgery.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2012; 104(4): e1-10. [27] Chang JK, Gill SS, Zura RD,et al. Comparative strength of three methods of fixation of transverse acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; (392): 433-441. [28] Bain GI, Ashwood N, Baird R, et al.Management of Mason type-III radial head fractures with a titanium prosthesis, ligament repair, and early mobilization. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 87 Suppl 1(Pt 1):136-147. [29] Mullis BH,Sagi HC.Minimum 1-yea rfollow-up for patients with vertical shear sacroiliac joint dislocation streated with iliosacral screws:does joint ankylosis or anatomic reduction contribute to functional outcome? J Orthop Trauma. 2013;22(5):293-298. [30] Zentrum MC,Charite-Universitatsmedizin B, Campus VK. Clinical applications-pelvis. Injur Int Care Injur. 2014;35: 46-56. [31] Pring ME, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME,et al. Intraoperative electromyographic monitoring during periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop. 2012;(400): 158-164. [32] Li WY, Zhang BS, Zhang L, et al.Comparative study of antegrade and retrograde intramedullary nailing for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009; 22(3):199-201. [33] Kurup H, Hossain M, Andrew JG. Dynamic compression plating versus locked intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (6): CD005959. [34] Lin YC,Chen CH,Huang HT,et al.Pereutaneous antegrade screwing for anterior column fracture of acetabulum with fluoroscopic-based computerized navigation.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;128(2): 223-226. [35] Moed BR, Maxey JW. The effect of indomethacin on heterotopic ossification following acetabular fracture surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;7(1):33-37. [36] Reinhold M, Knop C, Beisse R, et al. Operative treatment of traumatic fractures of the thorax and lumbar spine. Part II: surgical treatment and radiological findings. Unfallchirurg. 2009;112(2):149-167. [37] Gay SB,Sistrom C,Wang GJ,et al. Percutaneous srew fixation of acetabular fracture with CT guidancerrpreliminary results of a new teachnique. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;158:819. [38] Letournel E, Judet R. Fractures of the Acetabulum.2nd ed.New York:Springer Verlag, 2013: 535-563. [39] Rosenthal R, Gantert WA, Scheidegger D,et al.Can skills assessment on a virtual reality trainer predict a surgical trainee's talent in laparoscopic surgery? Surg Endosc. 2010; 20(8): 1286-1290. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||