Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (26): 3849-3855.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.26.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Safety of screw placement for severe spinal deformity with the use of O-arm three-dimensional computer-assisted navigation system
Wang Tao, Wang Hui, Song Yan-li, Yang Da-long, Wei Hai-kun, Liu Feng-yu, Ding Wen-yuan
- Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2016-04-06Online:2016-06-24Published:2016-06-24 -
Contact:Ding Wen-yuan, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Wang Tao, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China Wang Tao, Wang Hui and Song Yan-li contributed equally to this paper. -
Supported by:the Key Project of Medical Science Research in Hebei Province in 2015, No. 20150279
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Tao, Wang Hui, Song Yan-li, Yang Da-long, Wei Hai-kun, Liu Feng-yu, Ding Wen-yuan. Safety of screw placement for severe spinal deformity with the use of O-arm three-dimensional computer-assisted navigation system[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3849-3855.
share this article
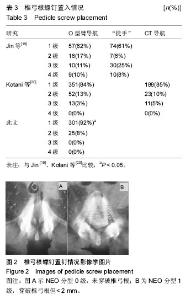
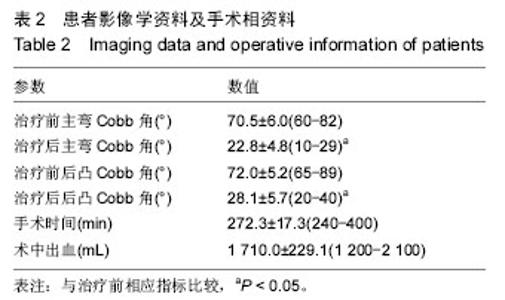
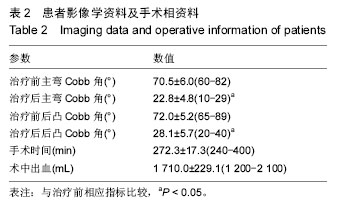
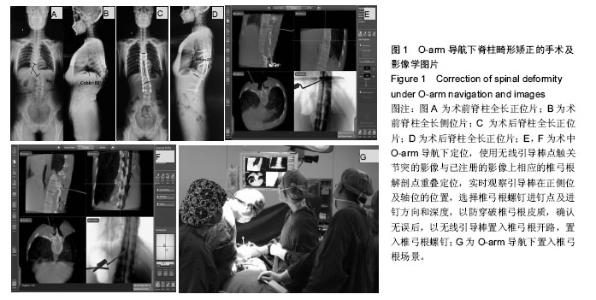
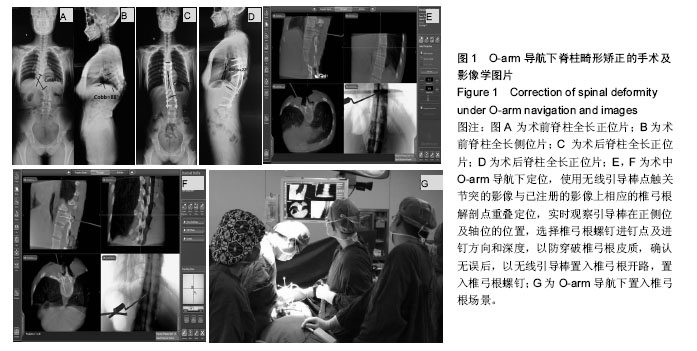
2.3 O-arm导航下置钉情况 共置入326枚椎弓根螺钉,其中T3 8枚,T4 12枚,T5 20枚,T6 22枚,T7 28枚,T8 30枚,T9 30枚,T10 32枚,T11 30枚,T12 28枚,L1 20枚,L2 22枚,L3 20枚,L4 16枚,L5 8枚;根据NEO分级,0级即没有穿破椎弓根皮质有280枚(92%),1级即穿破椎弓根皮质,但< 2 mm有44枚(8%),2级即穿破椎弓根皮质> 2 mm,但< 4 mm有0枚(0%),3级即穿破椎弓根皮质> 4 mm有0枚(0%),见表3及图2。25例患者矫形术后随访6-18个月。 2.4 手术相关情况 所有患者均安全完成置钉手术,未发生术中、术后并发症。手术时间为240-300 min,平均(272.3±17.3) min;术中出血为1 200-2 100 mL,平均(1 710.0±229.1) mL,见表2。 2.5 不良事件 治疗及随访过程中均未发生不良事件。"

| [1] Lenke LG, Kuklo TR, Ondra S, et al. Ratio-nale behind the current state-of-the-art treatment of scoliosis (in the pedicle screw era). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33: 1051-1054. [2] Halm H, Niemeyer T, Link T, et al. Segmental pedicle screw instrumentation in idiopathic thoraco-lumbar and lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2000;9:191-197. [3] Hamill CL, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. The use of pedicle screw fixation to improve correction in the lumbar spine of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Is it warranted? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21:1241-1249. [4] Lonstein JE, Denis F, Perra JH, et al. Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:1519-1528. [5] Minor ME, Morrissey NJ, Peress R, et al. Endovascu-lar treatment of an iatrogenic thoracic aortic injury after spinal instrumentation: case report. J Vasc Surg. 2004;39:893-896. [6] Papin P, Arlet V, Marchesi D, et al. Unusual presentation of spinal cord compression related to misplaced pedicle screws in thoracic sco-liosis. Eur Spine J. 1999;8:156-159. [7] West JL 3rd, Ogilvie JW, Bradford DS. Complications of the variable screw plate pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16:576-579. [8] Sembrano JN, Santos ER, Polly DW Jr.New generation intraoperative three-dimensional imaging (O-arm) in 100 spine surgeries: does it change the surgical procedure. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(2):225-231. [9] Vrtovec T, Pernus F, Likar B. A review of methods forquantitative evaluation of spinal curvature. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(5): 593-607. [10] 宋维通,李忠,李旭明,等.全脊柱DR与CR成像质量的对比分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2008,24(7):973-975. [11] 孙涛,卢光,陶蔚.O型臂引导下经皮椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2015,15(20):3926-3929. [12] Neo M, Sakamoto T, Fujibayashi S, et al. The clinical risk of vertebral artery injury from cervical pedicle screws inserted in degenerative vertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30:2800-2805. [13] 张永刚,王岩,刘郑生,等.数字化三维重建技术定量评估青少年特发性脊柱侧弯胸椎椎弓根的形态变化[J].中国临床康复,2015,9(22):13-15. [14] Hicks JM, Singla A, Shen FH, et al. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in scoliosis surgery: a sys-tematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35:E465-470. [15] Kotani Y, Abumi K, Ito M, et al. Accuracy analysis of pedicle screw placement in posterior scoliosis surgery: comparison between conventional fluoroscopic and computer-assisted technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32:1543-1550. [16] Takahashi J, Hirabayashi H, Hashidate H, et al. Accuracy of multilevel registration in image-guided pedicle screw insertion for adolescent idio-pathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35:347-352. [17] Sakai Y, Matsuyama Y, Nakamura H, et al. Segmental pedicle screwing for idiopathic scoliosis using computer-assisted surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008; 21:181-186. [18] 刘亚军,田伟,刘波,等.术中即时三维导航辅助微创经关节突关节螺钉寰枢椎内固定的临床研究[J].山东医药,2010, 50(28):42-43. [19] Jin M,Liu Z,Liu X, et al. Does intraoperative navigation improve the accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the apical region ofdystrophic scoliosis secondary to neurofibromatosis type I: comparison between O-arm navigation and free-handtechnique.Eur Spine J.2015. [Epub ahead of print] [20] Kotani T, Akazawa T, Sakuma T, et al. Accuracy of Pedicle Screw Placement in Scoliosis Surgery: A Comparison between Conventional Computed Tomography-Based and O-Arm-Based Navigation Techniques.Asian Spine J. 2014;8(3);331-338. [21] Theologis AA,Burch S.Safety and Efficacy of Reconstruction of Complex Cervical Spine Pathology Using Pedicle Screws Inserted with Stealth Navigation and 3D Image-Guided (O-Arm) Technology.Spine (Phila Pa1976).2015;40(18):1397-1406. [22] Su AW,Luo TD,McIntosh AL,et al. Switching to a Pediatric Dose O-Arm Protocol in Spine Surgery Significantly Reduced Patient Radiation Exposure.J Pediatr Orthop.2015. [Epub ahead of print] [23] Grelat M,Zairi F,Quidet M. Assessment of the surgeon radiation exposure during a minimally invasive TLIF: Comparison between fluoroscopy and O-arm system. Neurochirurgie.2015;61(4):255-259. [24] Epstein NE.Commentary: Utility of the O-Arm in spinal surgery. Surg Neurol Int.2014;5(Suppl 15):S517-519. [25] Qureshi S,Lu Y,McAnany S,et al. Three-dimensional Intraoperative Imaging Modalities in Orthopaedic Surgery: A Narrative Review. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(12):800-809. [26] Rivkin MA,Yocom SS.Thoracolumbar instrumentation with CT-guided navigation (O-arm) in 270 consecutive patients: accuracy rates and lessons learned. Neurosurg Focus.2014;36(3):E7. [27] Hsu AR,Lee S.Evaluation of tarsal navicular stress fracture fixation using intraoperative O-arm computed tomography. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014;7(6):515-521. [28] Kim TT,Drazin D,Shweikeh F, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of minimally invasive percutaneous pedicle screw placement with intraoperative CT (O-arm) image guidance navigation. Neurosurg Focus.2014;36(3):E1. [29] Hur JW,Kim JS,Cho DY, et al. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery under O-arm navigation system guidance for the treatment of thoracic disk herniations: surgical techniques and early clinical results.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg.2014;75(6):415-421. [30] Hellström PA,Katisko J,Finnilä P, et al. Sacral nerve stimulation lead implantation using the O-arm. BMC Urol.2013;13:48. [31] Attia W,Orief T,Almusrea K, et al.Role of the O-arm and Computer-assisted Navigation of Safe Screw Fixation in Children with Traumatic Rotatory Atlantoaxial Subluxation. Asian Spine J.2012;6(4):266-273. [32] Karahalios DG,Mansour NH,Girardot EA, et al. Overcoming challenges associated with upright imaging of the cervicothoracic junction: a case report involving a novel repurposing of the O-arm. Int J Med Robot.2013;9(2):148-151. [33] Castro J,Rodino Padín J,Pinzón Millán A, et al. Posterior lumbar fusion using the O-arm surgical imaging system: initial experience. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2013;24(1):1-8. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||