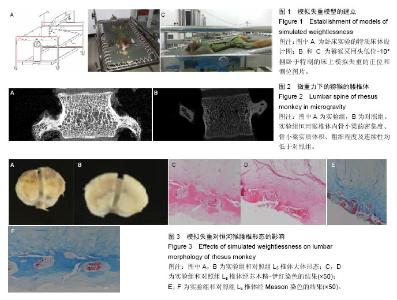
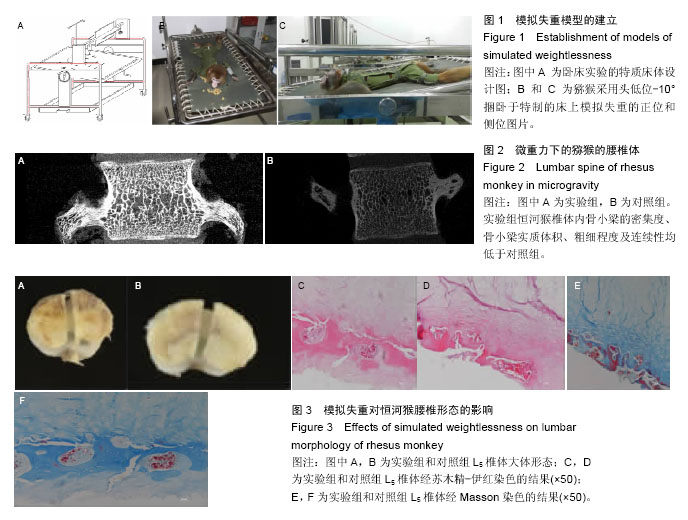
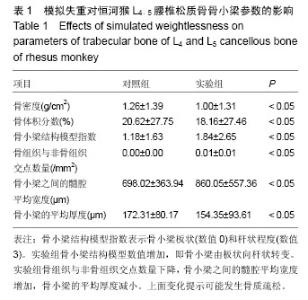
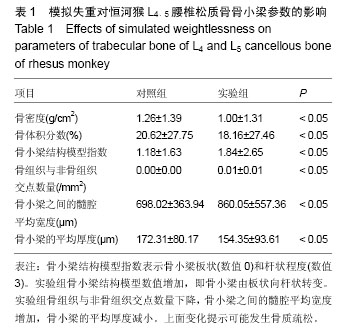
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (26): 3843-3848.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.26.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of simulated weightlessness on biomechanics of motion unit of rhesus monkey lumbar vertebra
Wang Xiao-ping1, Lu Ming1, Ma Pei2, Chen Zhi-ming1, Yuan Wei1, Zhao Fu-jiang1, Zhao Hao1,Ren Dong-yun1, Ma Hua-song1, Wu Zhi-hong2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the 306th Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100101, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing 100730, China
-
Revised:2016-04-23Online:2016-06-24Published:2016-06-24 -
Contact:Ma Hua-song, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, the 306th Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100101, China -
About author:Wang Xiao-ping, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the 306th Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100101, China Lu Ming, Department of Orthopedics, the 306th Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100101, China Wang Xiao-ping and Lu Ming contributed equally to this paper.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xiao-ping, Lu Ming, Ma Pei, Chen Zhi-ming, Yuan Wei, Zhao Fu-jiang, Zhao Hao,Ren Dong-yun, Ma Hua-song, Wu Zhi-hong. Effects of simulated weightlessness on biomechanics of motion unit of rhesus monkey lumbar vertebra[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3843-3848.
share this article
| [1] Convertino VA, Koenig SC, Krotov VP, et al. Effects of 12 days exposure to simulated microgravity on central circulatory hemodynamics in the rhesus monkey. Acta Astronaut. 1998;42(1-8):255-263. [2] Fulzele K, Riddle RC, DiGirolamo DJ, et al. Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates postnatal bone acquisition and body composition. Cell. 2010;142(2):309-319. [3] Kneser U, Schaefer DJ, Polykandriotis E, et al. Tissue engineering of bone: the reconstructive surgeon's point of view. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10(1):7-19. [4] Holguin N, Muir J, Rubin C, et al. Short applications of very low-magnitude vibrations attenuate expansion of the intervertebral disc during extended bed rest. Spine J. 2009;9(6):470-477. [5] Styf JR, Ballard RE, Fechner K, et al. Height increase, neuromuscular function, and back pain during 6 degrees head-down tilt with traction. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1997;68(1):24-29. [6] Lee SU, Hargens AR, Fredericson M, et al. Lumbar spine disc heights and curvature: upright posture vs. supine compression harness. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2003;74(5):512-516. [7] Lee NK, Sowa H, Hinoi E, et al. Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell. 2007;130(3):456-469. [8] Hinoi E. Pivotal role of skeletal tissues in the regulation mechanisms for physiological functions mediated by multiple organ networks. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012; 132(6): 721-725. [9] Yoshikawa Y, Kode A, Xu L, et al. Genetic evidence points to an osteocalcin-independent influence of osteoblasts on energy metabolism. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(9):2012-2025. [10] Ferron M, Hinoi E, Karsenty G, et al. Osteocalcin differentially regulates beta cell and adipocyte gene expression and affects the development of metabolic diseases in wild-type mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(13):5266-5270. [11] Abdallah BM, Ditzel N, Laborda J, et al. DLK1 Regulates Whole-Body Glucose Metabolism: A Negative Feedback Regulation of the Osteocalcin-Insulin Loop. Diabetes. 2015;64(9):3069-3080. [12] Klaman LD, Boss O, Peroni OD, et al. Increased energy expenditure, decreased adiposity, and tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 20(15):5479-5489. [13] Hinoi E. Control of bone remodeling by nervous system. Regulation of glucose metabolism by skeleton. - Tangent point with nervous system. Clin Calcium. 2010;20(12):1814-1819. [14] Rached MT, Kode A, Silva BC, et al. FoxO1 expression in osteoblasts regulates glucose homeostasis through regulation of osteocalcin in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010; 120(1):357-368. [15] Kimura S, Steinbach GC, Watenpaugh DE, et al. Lumbar spine disc height and curvature responses to an axial load generated by a compression device compatible with magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(23):2596-2600. [16] Wisleder D, Werner SL, Kraemer WJ, et al. A method to study lumbar spine response to axial compression during magnetic resonance imaging: technical note. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(18):E416-420. [17] Momken I, Stevens L, Bergouignan A, et al. Resveratrol prevents the wasting disorders of mechanical unloading by acting as a physical exercise mimetic in the rat. FASEB J. 2011;25(10):3646-3660. [18] Hutton WC, Yoon ST, Elmer WA, et al. Effect of tail suspension (or simulated weightlessness) on the lumbar intervertebral disc: study of proteoglycans and collagen. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(12):1286-1290. [19] Shackelford LC, LeBlanc AD, Driscoll TB, et al. Resistance exercise as a countermeasure to disuse-induced bone loss. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004;97(1):119-129. [20] Tilton FE, Degioanni JJ, Schneider VS. Long-term follow-up of Skylab bone demineralization. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1980;51(11):1209-1213. [21] Yu H, VandeVord PJ, Mao L, et al. Improved tissue-engineered bone regeneration by endothelial cell mediated vascularization. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(4):508-517. [22] Chiu LL, Radisic M. Scaffolds with covalently immobilized VEGF and Angiopoietin-1 for vascularization of engineered tissues. Biomaterials. 2010;31(2):226-241. [23] Chiu LL, Weisel RD, Li RK, et al. Defining conditions for covalent immobilization of angiogenic growth factors onto scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(1):69-84. [24] Shen YH, Shoichet MS, Radisic M. Vascular endothelial growth factor immobilized in collagen scaffold promotes penetration and proliferation of endothelial cells. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(3):477-489. [25] Odedra D, Chiu LL, Shoichet M, et al. Endothelial cells guided by immobilized gradients of vascular endothelial growth factor on porous collagen scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(8):3027-3035. [26] Leslie-Barbick JE, Moon JJ, West JL. Covalently-immobilized vascular endothelial growth factor promotes endothelial cell tubulogenesis in poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2009;20(12):1763-1779. [27] Kanczler JM, Barry J, Ginty P, et al. Supercritical carbon dioxide generated vascular endothelial growth factor encapsulated poly(DL-lactic acid) scaffolds induce angiogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;352(1):135-141. [28] Grieb G, Groger A, Piatkowski A, et al. Tissue substitutes with improved angiogenic capabilities: an in vitro investigation with endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;191(2):96-104. [29] Patel ZS, Ueda H, Yamamoto M, et al. In vitro and in vivo release of vascular endothelial growth factor from gelatin microparticles and biodegradable composite scaffolds. Pharm Res. 2008;25(10):2370-2378. [30] Chae JK, Kim I, Lim ST, et al. Coadministration of angiopoietin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor enhances collateral vascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(12):2573-2578. [31] Yu H, Vandevord PJ, Gong W, et al. Promotion of osteogenesis in tissue-engineered bone by pre-seeding endothelial progenitor cells-derived endothelial cells. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(8):1147-1152. [32] Fuchs S, Ghanaati S, Orth C, et al. Contribution of outgrowth endothelial cells from human peripheral blood on in vivo vascularization of bone tissue engineered constructs based on starch polycaprolactone scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(4):526-534. [33] Kim JY, Jin GZ, Park IS, et al. Evaluation of solid free-form fabrication-based scaffolds seeded with osteoblasts and human umbilical vein endothelial cells for use in vivo osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 16(7):2229-2236. [34] Sahar DE, Walker JA, Wang HT, et al. Effect of endothelial differentiated adipose-derived stem cells on vascularity and osteogenesis in poly(D,L-lactide) scaffolds in vivo. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(3): 913-918. [35] Roh JD, Brennan MP, Lopez-Soler RI, et al. Construction of an autologous tissue-engineered venous conduit from bone marrow-derived vascular cells: optimization of cell harvest and seeding techniques. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42(1):198-202. [36] Hao Z, Feng W, Hao T, et al. Study on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived osteoblasts and endothelial cells compound with chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffold to construct vascularized tissue engineered bone. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;26(4):489-494. [37] Li T, Wang J, Yang H. A research on ectopic osteogenesis and vascularization of tissue engineered bone promoted by 1,25-(OH)2D3. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007;21(10):1142-1146. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||