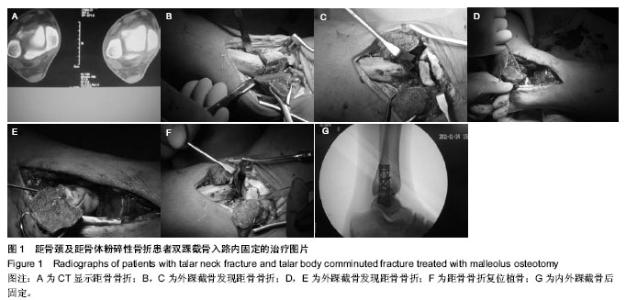
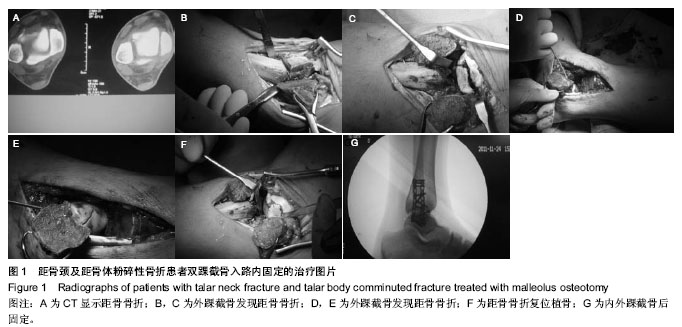
| [1] Thomas FH, Michael RB. Diagnosis and treatment of fracture of the talus:a comprehensive review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int.1999;20:595-605.
[2] Rammelt S, Zwipp H. Talar neck and body fractures. Injury. 2009;2:120-135.
[3] 张长青,张伟,主译.骨折手术技巧图解[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2011:7357-7371.
[4] 彭湘晖.螺旋CT重建在距骨骨折诊断中的价值[J].华西医学, 2009,14(4): 843-844.
[5] Magid D, Fishman EK. Imaging of muscul osketeal trauma in three dimensions-an integrated two-dimensional/ three-dimensional approach with computed tomography. RCNA.1989;27: 945-956.
[6] Hawkins LG. Fractures of the neck of the talus. J Bone Joint Surg ( Am).1970;52: 991.
[7] 卢世璧,主译.坎贝尔骨科手术学[M]. 11版.北京:人民军医出版社, 2009: 55-56.
[8] 卢绍燊,余海波.经内踝截骨空心钉内固定治疗HaokinsII和II型距骨骨折的疗效[J].广东医学,2013,34(2):270-271.
[9] 隋爱萍,孙芬兰,于仙娟.改良前入路治疗复杂踝关节骨折脱位的护理及康复训练指导[J].中医正骨,2012,24(5):66-67.
[10] Fullerson EW,Egol KA. Timing issues in fracture management: a review of current concepts. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;1: 58-67.
[11] 马睿,舒衡生.距骨颈骨折治疗方法及疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(10):894-896.
[12] 王琨,朱琪.距骨侧位形态分析附175例X线照片及10例足标本观察[J].实用放射学杂志.1998.14(3):618-619.
[13] 黄昌林,丁志海.距骨骨折脱位手术入路的解剖研究与临床应 用[J].中华骨科杂志,1994,14(12):736-738.
[14] Crenshaw AH. Campbell 's Orthopaedics. 8thver. Mosby- Year Book,Inc. St Louis, 1992: 2892.
[15] 王荣诗,黄迅,谭伦.距骨颈骨折手术内固定远期疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(6): 560-561.
[16] Cronier P,Talha A,Massin P. Central talar fractures-therapeutic considerations. Injury. 2004;35( S2):10-22.
[17] 陈勇忠,周清碧,戴晓明,等.经内踝截骨手术人路治疗复杂的距骨骨折[J].广东医学,2006,27(10):1518-1519.
[18] 李京生,李绍光,孙天胜,等.经内外踝截骨入路可吸收螺钉固定治疗复杂距骨体部骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(10): 749-750.
[19] 黄林昌,崔明华,黄涛,等.距骨骨折脱位手术入路的解剖研究与临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,1994,14(12): 736-738.
[20] 李祖明.距骨骨折手术疗效的影响因素分析研究[J].当代医学, 2012,18(17):107.
[21] 李元洲,杨茂伟,冯博.距骨血液供应的解剖学研究[J].中国医学工程,2012,20(1):86-88.
[22] Ziran BH,Abidi NA,Scheel MJ.Medial malleolar osteotomy for exposure of complex talar body fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(7): 513.
[23] 刘鸿程,邹玉莲,赖优良.经内外踝低位截骨入路治疗复杂距骨骨折脱位[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(2):185.
[24] Nabil A,Ebraheim VP,Christopher O,et al. Clinical outcomes of fractures of the talar body. Inter Othop. 2008;6:773-777.
[25] 余全胜.距骨颈骨折行闭合复位经皮空心螺钉内固定治疗的临床价值[J].中国伤残医学,2012,20(12):36-37.
[26] Lin S,Hak DJ. Management of talar neck fractures. Orthopedics. 2014;3(90):715-727.
[27] Sproule JA, Glazebrook MA, Younger AS.Varus hindfoot deformity after talar fracture.Foot Ankle Clin. 2012;17(10): 117-125.
[28] 陈学强,俞立新.采用Herbert钉内固定急诊手术治疗距骨骨折也取得较好疗效[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(2): 186-188.
[29] 胡力,周忠,陈学明,等.内固定结合骨诱导活性材料治疗HawkinsⅡ、Ⅲ型距骨颈骨折[J].创伤外科杂志, 2013, 15(4):331-334.
[30] Ly PN, Falat LM. Transchondral fractures of the talus :A review of 64 surgical cases. Foot Ankle Surg. 1993;4:352.
[31] 张勇,贾斌,曹国庆.可吸收钉结合硫酸钙治疗距骨体粉碎性骨折22例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,5(11):3746-3747.
[32] 王荣诗,黄迅,谭伦.距骨颈骨折手术内固定远期疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(6): 560-561.
[33] 刘立峰,蔡锦方,梁进,等.可吸收螺钉固定治疗移位的距骨颈骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2003,17(5):367-369.
[34] Jukkala PK,Pohjonen T,Laitinen O,et al.Biodegradation and strength retention of poly-L-lactides clews in vivo.An experimental long•term study sheep.Ann Chir Gynaecol. 2001;90(3):219-223.
[35] 王卫国,蔡锦方,曹学成.可吸收螺钉治疗关节部位骨折的临床体会[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2004,19(1):63-65.
[36] Sneppen O,Bunl O.Fracture of the talus.a study of its genesis and morphology.based upon cases with associated ankle fracture. Acta Orthop Scand. 1974;45(2):307-309.
[37] 张驰,顾文奇,施忠民.经外踝截骨锁定钢板固定的胫距跟关节融合术的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(4):309-312.
[38] Ohl X,Harisboure A,Hemery X,et al.Long-term follow-up after surgical treatment of talar fractures: twenty cases with an average follow-up of 7.5 years. Int Orthop. 2011;1:93-99.
[39] Vaillier HA,Nork SE,Barei DP,et al.Talar neck fracture: results and outcomes.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;8:1616-1624.
[40] 李泽龙,蔡习炜,刘发平,等.距骨骨折的基础研究及临床治疗进展[J].创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(4):377.
[41] 施忠民,顾文奇,梅国华.双切口接骨板内固定治疗距骨颈粉碎性骨折的临床效果[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,5(4): 310-314.
[42] Kely FB Jr. Fracture of the neck of the talus:Long terme-valuation of 71 eases. J Bone Joint Surg(Am).1978; 60(2):143-156.
[43] 杨勇,朱守荣,主译.骨科标准手术技术丛书[M]. 2版,沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社,2004:469.
[44] 胡畔,何锦泉,张英泽.距骨颈骨折治疗进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2013, 33(4):419-422.
[45] 刘宏波,田清叶,何正,等.距骨严重骨折脱位的外科治疗[J].山东医药,2013,53(8):67-68.
[46] 王岩,武勇,龚晓峰,等. SneppenII型距骨体骨折的手术技巧及疗效分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(5):435-437.
[47] Mei-Dan O, Hetsroni I, Mann G, et al. Prevention of avascular necrosis in displanced talar neck fractures by hyperbaric oxygenation therapy; a dual case report. J Postgrad Med. 2008;54(2):140-143. |