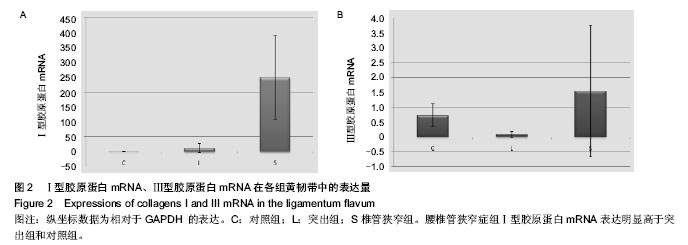
| [1] Sairyo K, Biyani A, Goel VK,et al.Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: A multidisciplinary investigation based on clinical, biomechanical,histologic and biologic assessments.Spine.2005;30:2649-2656.
[2] Schrader P, Grob D, Rahn BA, et al. Histology of the ligamentum flavum in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J.1999;8:323-328.
[3] Fukuyama S, Nakamura T, Tkeda T, et al. The effect of mechanical stress on hypertrophy of the lumbar ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord.1995;8:126-130.
[4] Nakatani T, Marui T, Hitora T, et al.Mechanical stretching force promotes collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum via transforming growth factor-beta1. J Orthop Res.2002;20:1380-1386.
[5] Park JB, Lee JK, Park SJ, et al. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal stenosis associated with increased proteinase inhibitor concentration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(12):2750-2757
[6] Zucherman JF, Hsu KY, Hartjen CA, et al. A prospective randomized multicenter study for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with the X STOP interspinous implant: 1-year results. Eur Spine J.2004;13:22-31.
[7] Takehara K. Growth regulation of skin fibroblasts.J Dermatol Sci.2000;24:70-77.
[8] Shinozaki M, Kawara S, Ilayashi N, et al. Induction of subcutaneous tissue fibrosis in newborn mice by transforming growth factorbeta-simultaneous application with basic fibroblast growth factor causes persistent fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1997;237:292-297.
[9] Mori T, Kawara S, Shinozaki M,et al. Role and interaction of connective tissue growth factor with transforming growth factor-β in persistent fibrosis: a mouse fibrosis model. J Cell Physiol.1999;181:153-139.
[10] 李新奎,王全平,朱锦宇,等.腰椎间盘突出并椎管狭窄症手术失误及再手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,1997,17(5):315.
[11] Fandino J, Botana C, Viladrich A, et al. Reoperation after lumbar disc surgery: results in 130 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien).1993;122(2):102-104.
[12] lgnotz RA, Massague J. Transforming growth factor-p stimulates the expression of fibronection and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:4337-4345.
[13] Reed MJ, Vernon RB, Abrass IB,et al. TGF-01 induces the expression of type I collagen and SPARC, and enhances contraction of collagen gels, by fibroblasts from young and aged donors. J Cell Physiol.1994;158:169-179.
[14] Park JB,Chang H,Lee JK.Quantitative analysis of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in ligamentum flavum of lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Spine. 2001;26: E492-495.
[15] 钟招明,陈建庭.转化生长因子在退变黄韧带中过度表达[J].南方医科大学学报,2009,29(2):316-8.
[16] 付小兵,孙同柱,杨银辉,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和转化生长因子-β在溃疡与增生性瘢痕组织中的表达及其对创面修复的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2000,14(5):271.
[17] Eubanks JD, Lee MJ, Cassinelli E,et al.Prevalence of lumbar facet arthrosis and its relationship to age, sex, and race: an anatomic study of cadaveric specimens. Spine 2007;32(19): 2058-2062.
[18] Eubanks JD, Lee MJ, Cassinelli E, et al. Does lumbar facet arthrosis precede disc degeneration? A postmortem study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464:184-189.
[19] Honsawek S,Poonpukdee J,Chalermpanpipat C, et al. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis is associated with increased bFGF expression. Int Orthop. 2013;37(7):1387-1392.
[20] Finetti G Fewina M. Recombinant human basic- fibroblastic growt h factor: different medical dressing s for clinical application in wound healing. Farmaco.1992;47(6):967.
[21] Satish L, Babu M, Tran KT, et al. Keloid fibroblast responsiveness to epidermal growth factor and activation of downstream intracellular signaling pathways. Wound Repair Regen.2004;12(2):183-192.
[22] Akimoto S, Ishikawa O, Iijima C, et al. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptor by fibroblast, macrophages and mast cells in hypertrophic scar. Eur J Dermatol.1999;9(5):357-362.
[23] Hanasono MM, Kita M, Mikulec AA, et al. Autocrine growth factor production by fetal, keloid, and normal dermal fibroblasts. Arch Facial Plast Surg.2003;5(1):26-30.
[24] Löhr M, Hampl JA, Lee JY, et al. Hypertrophy of the lumbar ligamentum flavum is associated with inflammation-related TGF-β expression.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011;153(1): 134-141.
[25] Okuda T, Baba I, Fujimoto Y, et al. The pathology of ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar disease. Spine. 2004;29:1689-1697.
[26] Chen YT, Wei JD, Wang JP, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human ligamentum flavum: implicating etiology of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(18):E1193-1200.
[27] Kosaka H, Sairyo K, Biyani, et al. Pathomechanism of loss of elasticity and hypertrophy of lumbar ligamentum flavum in elderly patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(25):2805-2811.
[28] Specchia N, Pagnotta A, Gigante A, et al. Characterization of cultured human ligamentum flavum cells in lumbar spine stenosis.J Orthop Res.2001;19(2):294-300. |