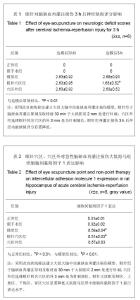
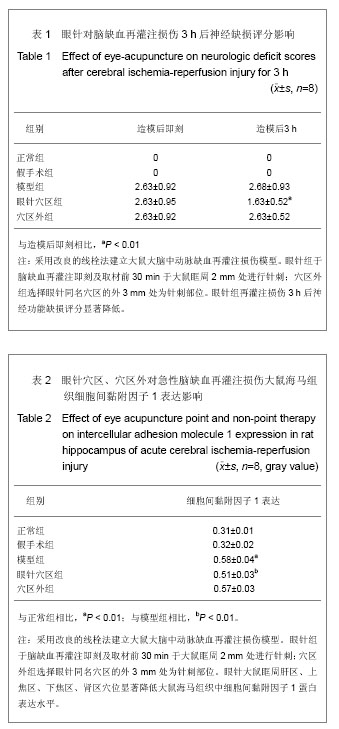
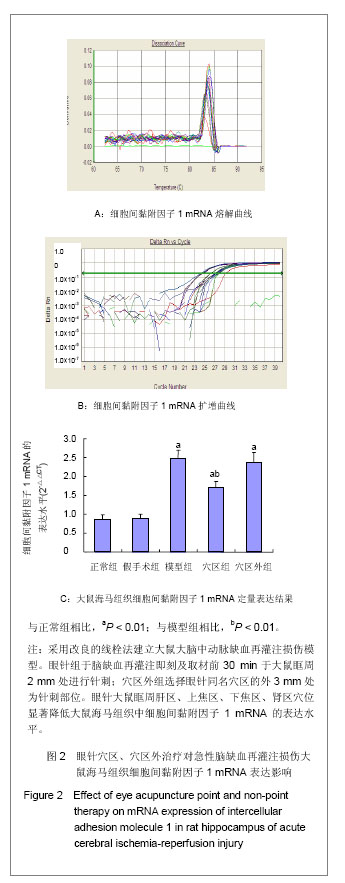
| [1] |
Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi.
Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8.
|
| [2] |
Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang.
Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963.
|
| [3] |
Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi.
Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718.
|
| [4] |
Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi.
Ferroptosis and stroke
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739.
|
| [5] |
Bai Shengchao, Gao Yang, Wang Bo, Li Junping, Wang Ruiyuan.
Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653.
|
| [6] |
Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie.
Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665.
|
| [7] |
Li Xiangze, Bu Xianmin, Li Dongmei, Chi Yulei, Su Qiang, Jin Xintong, Zhao Jian, Zhang Gaotian, Wu Bin, Meng Chunyang .
Stem cells, cytokines, hormones, neuropeptides and genes in traumatic brain trauma to promote fracture healing
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3057-3063.
|
| [8] |
Zhu Shiqiang, Xu Jianfeng, Hei Xiaoyan, Chen Yundong, Tian Xinbao, Zhang Jinchen, Lin Ruizhu.
Effect of internal heat-type acupuncture needle therapy on the expression of type I collagen, matrix metalloproteinase-3 and osteopontin in the subchondral bone of rabbit knee osteoarthritis model
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2636-2642.
|
| [9] |
Yin Yuhui, Zhan Jiawen, Wang Shangquan, Shao Chenchen, Zhou Liang.
Meta-analysis of acupuncture combined with massage in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2719-2726.
|
| [10] |
Zhang Chongfeng, Li Xianlin, Peng Weibing, Jia Hongsheng, Cai Lei.
Treating lumbar disc herniation of blood stasis type with Chinese herbs, acupuncture, moxibustion, and massage: a Bayesian network Meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2781-2788.
|
| [11] |
Zhou Xiaohong, Li Bocun, Li Jia, Peng Rui.
Relationship between joint function and circadian rhythm in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis undergoing acupuncture and moxibustion at acupoints selected based on liver theory
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2192-2198.
|
| [12] |
Wang Donghui, Wu Xin, Sun Ningning, Zhang Han, Gao Jianfeng.
Electroacupuncture intervention on the expression of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampi of mice with radiation-induced brain injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2205-2210.
|
| [13] |
Yu Chenghao, Zhang Yi, Qi Chao, Chen Jinli, Gao Jiake, Yu Tengbo.
Effect of cytokines and platelet-rich plasma on tendon derived stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 133-140.
|
| [14] |
Fei Jing, Zheng Hongdi, Yu Liya, Li Leiji.
Involvement of GDNF/PI3K/AKT pathway in promoting facial
nerve regeneration using electroacupuncture in a rabbit model of facial nerve
crush injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1094-1100.
|
| [15] |
Zhang Jinhuan, Yuan Weiqu, Chen Chen, Huang Xingxian, Yu Haibo.
Different acupuncture therapies for treating periarthritis of the shoulder: overview of systematic reviews and network Meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5723-5732.
|