Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4548-4556.doi: 10.12307/2026.110
Genetic structure of co-morbidity between frailty and rheumatoid arthritis: a genome-wide association analysis
Han Jie1, Yao Guojun2, Huang Yebao3, Xu Zhiwei1, Shao Weigang1, Shang Kebin2, Wu Yachao2, Liao Zhen2
- 1Master of Traditional Chinese Medicine Hall, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine Proctology, Liuzhou People’s Hospital, Liuzhou 545006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-03-19Accepted:2025-06-07Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-05 -
Contact:Han Jie, Master of Traditional Chinese Medicine Hall, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Han Jie, PhD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Master’s supervisor, Master of Traditional Chinese Medicine Hall, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Pilot Project of Guangxi High-level Key Discipline Construction of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. [2023]13 (to HJ); Guangxi Key Research Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. [2023]9 (to HJ); Guangxi Young Qihuang Scholars Cultivation Project, No. [2022]13 (to HJ); “Qihuang Engineering” High-level Talent Team Cultivation Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 202413 (to HJ); 2023 University-level Doctoral Research Innovation Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. YCBXJ2023022 (to XZW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Jie, Yao Guojun, Huang Yebao, Xu Zhiwei, Shao Weigang, Shang Kebin, Wu Yachao, Liao Zhen. Genetic structure of co-morbidity between frailty and rheumatoid arthritis: a genome-wide association analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4548-4556.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
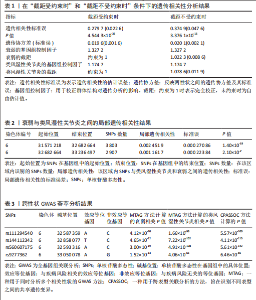
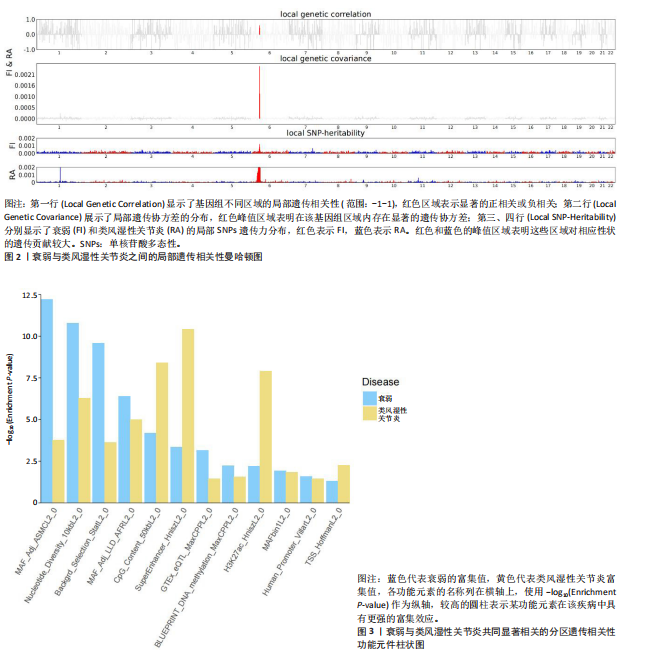
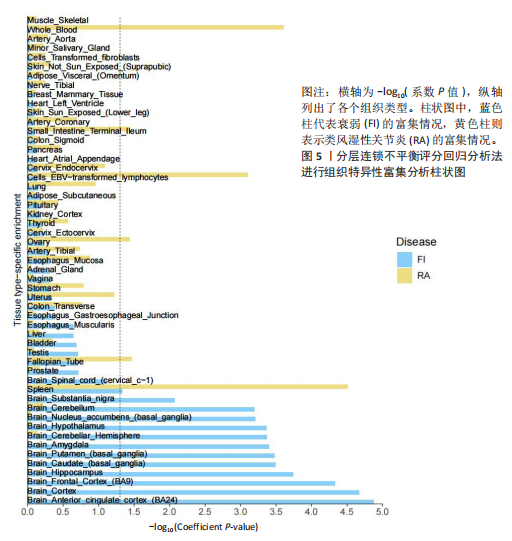
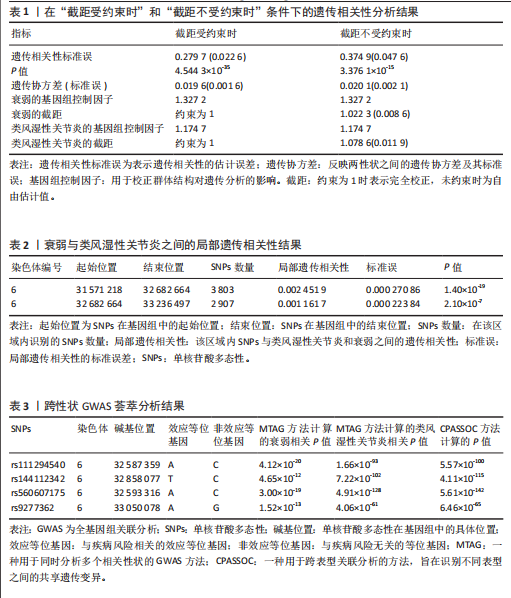
2.1 衰弱与类风湿性关节炎之间的遗传相关性 此次研究采用了LDSC方法,利用SNPs间的连锁不平衡,来评估两种性状间的遗传联系。在不受截距约束的情况下,衰弱的SNPs遗传力估计为11.72%,类风湿性关节炎的SNPs遗传力估计为4.20%。随后,采用双变量LDSC方法估计了衰弱与类风湿性关节炎之间的遗传相关性。结果显示,衰弱与类风湿性关节炎之间存在显著的遗传正相关性(rg=0.28,P=4.54×10-35)。在假设不存在群体分层的情况下,当LDSC截距受约束时,结果仍显著(rg=0.37,P=3.38×10-15)。见表1。 2.2 衰弱与类风湿性关节炎之间的局部遗传相关性 应用ρ-HESS方法确定了衰弱与类风湿性关节炎之间的显著局部遗传相关性。经过多重检验校正后(P < 0.05/1 703),在6p21.32-21.33(chr6:31571218-33236497)这两个特定区域,发现衰弱与类风湿性关节炎之间存在显著的局部相关性,见表2及图2。 2.3 分区遗传相关性 与衰弱部分遗传相关的SNPs在96个功能元件中,有30个功能元件中显示出显著富集,其中最显著的功能元件为GERP.NSL2_0(enrichment=1.962,P=2.88×10-17)。 与类风湿性关节炎相关的SNPs在96功能元件中,有27个类别中表现出显著富集,最显著是SuperEnhancer_HniszL2_0(enrichment=3.703,P=3.85×10-11)。有12个功能类别同时与衰弱和类风湿性关节显著相关,见图3。 2.4 跨性状GWAS荟萃分析 使用MTAG和CPASSO进行的跨性状分析共识别出11个达到全基因组显著性的共享独立SNPs。在对6p21.32-21.33区域SNPs进行筛选时,排除在衰弱与类风湿性关节炎的GWAS中同时显著的SNPs,或与同时显著的SNPs存在连锁(连锁不平衡 r2?≥?0.01)的SNPs后,最终确认有4个SNPs与衰弱和类风湿性关节炎均相关,见表3。SNP rs111294540、rs560607175定位于HLA-DQA1基因,SNP rs9277362定位于HLA-DPA1基因,SNP rs144112342定位于TAP2基因。 2.5 组织特异性富集分析 使用MAGMA进行组织特异性富集分析,结果显示:与衰弱相关的SNPs在9个不同的脑区中特异性富集,其中特异性富集最显著在额叶皮质(BA9)。而类风湿性关节炎则在18个不同的组织中特异性富集,其中特异性富集最显著在脾脏,见图4。此外,进一步使用S-LDSC分析衰弱和类风湿性关节炎在组织水平上的SNPs遗传力富集。结果显示,与衰弱相关的SNPs在12个不同大脑组织及脾脏中表现出明显的富集,其中特异性富集最显著在前扣带皮质(BA24)。与类风湿性关节炎相关的SNPs在5个不同组织中表现出明显的富集,其中特异性富"
| [1] KIM DH, ROCKWOOD K. Frailty in Older Adults. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(6):538-548. [2] COHEN CI, BENYAMINOV R, RAHMAN M, et al. Frailty: A Multidimensional Biopsychosocial Syndrome. Med Clin North Am. 2023;107(1):183-197. [3] DENT E, HANLON P, SIM M, et al. Recent Developments in Frailty Identification, Management, Risk Factors and Prevention: A Narrative Review of Leading Journals in Geriatrics and Gerontology. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;91:102082. [4] O’CAOIMH R, SEZGIN D, O’DONOVAN MR, et al. Prevalence of Frailty in 62 Countries across the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Population-level Studies. Age Ageing. 2021;50(1):96-104. [5] WANG XM, ZHONG WF, LI ZH, et al. Dietary Diversity and Frailty Among Older Chinese People: Evidence from the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023;117(2):383-391. [6] GRAVALLESE EM, FIRESTEIN GS, KOSCAL N, et al. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? N Engl J Med. 2024;390(13):e32. [7] MAISHA JA, El-GABALAWY HS, O’NEIl LJ. Modifiable Risk Factors linked to the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evidence, Immunological Mechanisms and Prevention. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1221125. [8] GRAVALLESE EM, FIRESTEIN GS. Rheumatoid Arthritis - Common Origins, Divergent Mechanisms. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(6):529-542. [9] KIMBROUGH BA, CROWSON CS, DAVIS JM 3RD, et al. Decline in Incidence of Extra-Articular Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024; 76(4):454-462. [10] KIMBROUGH BA, CROWSON CS, DAVIS JM, et al. Decline in Incidence of Extra-Articular Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2024;76(4): 454-462. [11] GU H, YAN D, LI J, et al. Trends and Future Projections of Incidence Rate and Mortality of Rheumatoid Arthritis in China: A Systematic Analysis Based on GBD 2021 Data. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(9):2799-2806. [12] SMITH MH, GAO VR, PERIYAKOIL PK, et al. Drivers of Heterogeneity in Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2023;24(7):1200-1210. [13] KONZETT V, ALETAHA D. Management Strategies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024;20(12):760-769. [14] BĄK E, MŁYNARSKA A, MARCISZ C, et al. Factors that Affect the Assessment of the Quality of Life of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Depending on the Prevalence of Frailty Syndrome. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):216. [15] ZHOU J, ZHANG Y, NI T, et al. Does Autoimmune Diseases Increase the Risk of Frailty? A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 15:1364368. [16] SOBUE Y, SUZUKI M, OHASHI Y, et al. Relationship Between Locomotive Syndrome and Frailty in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients by Locomotive Syndrome Stage. Mod Rheumatol. 2022;32(3):546-553. [17] ATKINS JL, JYLHÄVÄ J, PEDERSEN NL, et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of the Frailty Index Highlights Brain Pathways in Ageing. Aging Cell. 2021;20(9):e13459. [18] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. Finngen Provides Genetic Insights From a Well-Phenotyped Isolated Population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518. [19] CUI G, LI S, YE H, et al. Gut Microbiome and Frailty: Insight from Genetic Correlation and Mendelian Randomization. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(2):2282795. [20] PENG Z, HUANG W, TANG M, et al. Investigating the Shared Genetic Architecture between Hypothyroidism and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2024;14:1286491. [21] XIANG S, XU D, JIN Y, et al. The Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in the Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Depression: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(4): 1839-1848. [22] SONG Z, LI W, HAN Y, et al. Investigating the Shared Genetic Architecture between Frailty and Insomnia. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024;16:1358996. [23] VILKAITIS G, MASEVIČIUS V, KRIUKIENĖ E, et al. Chemical Expansion of the Methyltransferase Reaction: Tools For Dna Labeling and Epigenome Analysis. Acc Chem Res. 2023;56(22):3188-3197. [24] FU W, XU R, BIAN P, et al. Exploring the Shared Genetic Basis of Major Depressive Disorder and Frailty. J Affect Disord. 2024; 366:386-394. [25] LIN D, WU S, LI W, et al. A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Identifies New Susceptibility Genes For Frailty. Front Genet. 2024;15:1404456. [26] HAMANAKA K, YAMAUCHI D, KOSHIMIZU E, et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Tandem Repeats Associated with Splicing Variation Across 49 Tissues In Humans. Genome Res. 2023;33(3):435-447. [27] XUE A, ZHU Z, WANG H, et al. Unravelling the Complex Causal Effects of Substance Use Behaviours on Common Diseases. Commun Med (Lond). 2024;4(1):43. [28] HANLON P, MORTON F, SIEBERT S, et al. Frailty in Rheumatoidrmdopen-2021-002111 Arthritis and Its Relationship with Disease Activity, Hospitalisation and Mortality: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Scottish Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort and Uk Biobank. RMD Open. 2022;8(1):e002111. [29] WEN L, FAN J, SHI X, et al. Causal Association Of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Frailty and the Mediation Role of Inflammatory Cytokines: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024;122:105348. [30] VAN ONNA M, BOONEN A. Challenges in the Management of Older Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(6):326-334. [31] PISHESHA N, HARMAND TJ, PLOEGH HL. A Guide to Antigen Processing and Presentation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022; 22(12):751-764. [32] GFELLER D, LIU Y, RACLE J. Contemplating Immunopeptidomes to Better Predict them. Semin Immunol. 2023;66:101708. [33] PINO LK, BAEZA J, LAUMAN R, et al. Improved Silac Quantification with Data-Independent Acquisition to Investigate Bortezomib-Induced Protein Degradation. J Proteome Res. 2021;20(4):1918-1927. [34] BANUSHI B, JOSEPH SR, LUM B, et al.Endocytosis in Cancer and Cancer Therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023;23(7):450-473. [35] HOSOKAWA H, ROTHENBERG EV. How Transcription Factors Drive Choice of the T Cell Fate. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(3): 162-176. [36] TADROS DM, EGGENSCHWILER S, RACLE J, et al. The Mhc Motif Atlas: A Database of Mhc Binding Specificities and Ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D428-D437. [37] ZHOU X, BROWN BA, SIEGEL AP, et al. Exosome-Mediated Crosstalk between Keratinocytes and Macrophages in Cutaneous Wound Healing. ACS Nano. 2020;14(10):12732-12748. [38] LISCI M, BARTON PR, RANDZAVOLA LO, et al. Mitochondrial Translation is Required for Sustained Killing by Cytotoxic T Cells. Science. 2021;374(6565): eabe9977. [39] YAP CF, NAIR N, DE VRIES A, et al. Hla-Drb1 and Hla-Dqa1 Associated with Immunogenicity to Adalimumab Therapy in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(2): 263-265. [40] LI X, YANG Y, SUN G, et al. Promising Targets and Drugs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Module-Based and Cumulatively Scoring Approach. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(8):501-514. [41] LEE S, SEO J, KIM YH, et al. Enhanced Intra-Articular Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Click-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Loaded with Toll-Like Receptor Antagonizing Peptides. Acta Biomater. 2023;172:188-205. [42] SUN L, WANG Z, LIU T, et al. Tap2 Drives Hla-B*13:01‒Linked Dapsone Hypersensitivity Syndrome Tolerance and Reactivity. J Invest Dermatol. 2023; 143(5):722-730.e1. [43] MEDEIROS FS, DA SILVA MC, DA SILVA NCH, et al. The Antigen Processing-Associated Transporter Gene Polymorphism: Role on Gene and Protein Expression in Hpv-Infected Pre-Cancerous Cervical Lesion. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:979800. [44] ŽILIONYTĖ K, BAGDZEVIČIŪTĖ U, MLYNSKA A, et al. Functional Antigen Processing and Presentation Mechanism as a Prerequisite Factor of Response to Treatment with Dendritic Cell Vaccines And Anti-Pd-1 In Preclinical Murine Llc1 And Gl261 Tumor Models. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022;71(11):2691-2700. [45] CHRISTIANSON JC, JAROSCH E, SOMMER T. Mechanisms of Substrate Processing During Er-Associated Protein Degradation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(11):777-796. [46] DHATCHINAMOORTHY K, COLBERT JD, ROCK KL. Cancer Immune Evasion Through Loss of MHC Class I Antigen Presentation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:636568. [47] CHEN X, GILES J, YAO Y, et al. The path to healthy ageing in China: a Peking University-Lancet Commission. Lancet. 2022;400(10367):1967-2006. [48] FENG Z, GLINSKAYA E, CHEN H, et al. Long-term care system for older adults in China: policy landscape, challenges, and future prospects. Lancet. 2020;396(10259):1362-1372. [49] YUAN B, ZHONG Y, LI S, et al. The degree of population aging and living carbon emissions: Evidence from China. J Environ Manage. 2024;353:120185. |
| [1] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [2] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [3] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [4] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [5] | Lu Liwei, Huang Keqi, Chen Yueping, Zhuo Yinghong, Zhu Naihui, Wei Peng. Bioinformatics-based analysis of shared genes and associations in immune mechanisms between rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4253-4264. |
| [6] | Wu Jun, Zhang Yuzhu, Dong Xiaojie, Wang Kaidi, Sun Bin. Experimental validation of cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway related gene signatures and molecular subtypes in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3145-3155. |
| [7] | Wang Tao, Min Youjiang, Wang Min, Wang Shunpu, Li Le, Zhang Chen, Xiao Weiping, Yu Yiping. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: sample analysis from the IEU Open GWAS Database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3182-3189. |
| [8] | Jiang Kai, Rong Yifa, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Lu Bowen, Liang Xuezhen, Li Gang. Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2629-2640. |
| [9] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [10] | Liu Xiaowu, Liu Jinping, Wu Ting, He Xian, Cai Jianxiong. Antioxidants from different sources and osteoarthritis: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7015-7027. |
| [11] | Luo Weidong, Pu Bin, Gu Peng, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiaohui, Chen Fuhong. Mendelian randomization study on the association between telomere length and 10 common musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 654-660. |
| [12] | Pang Jiahui, Wang Bo, Hu Yingxuan, Hu Ziwei, Wu Wen. Association between dietary preferences and the risk of osteoarthritis in Europeans: analysis of human genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6333-6342. |
| [13] | Sun Pengcheng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Zhengpeng, Li Yongjin, Gao Zhengang, Li Kunjian . Causal relationship between visceral adipose tissue and osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2631-2640. |
| [14] | Yang Jingyan, Ma She, Huang Renjun, Wang Chaoyi, Zhao Yuyang, Yu Dong. Causal relationship between trunk and lower limb fat mass and intervertebral disc degeneration based on a Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5688-5694. |
| [15] | Li Wei, Chai Jinlian, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Sun Tiefeng, Liang Xuezhen. Causal association of micronutrients with osteonecrosis: evidence from a bidirectional Mendelian randomization trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5308-5314. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||