Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 3145-3155.doi: 10.12307/2026.323
Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental validation of cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway related gene signatures and molecular subtypes in rheumatoid arthritis
Wu Jun1, Zhang Yuzhu2, Dong Xiaojie1, Wang Kaidi1, Sun Bin3
- 1Medical Cosmetic and Plastic Surgery Center, 2Department of Intensive Care Medicine, 3Second Ward of the Trauma Center, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-21Accepted:2025-06-26Online:2026-04-28Published:2025-09-30 -
Contact:Sun Bin, MS, Associate chief physician, Second Ward of the Trauma Center, Linyi People's Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wu Jun, PhD candidate, Attending physician, Medical Cosmetic and Plastic Surgery Center, Linyi People's Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Jun, Zhang Yuzhu, Dong Xiaojie, Wang Kaidi, Sun Bin. Experimental validation of cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway related gene signatures and molecular subtypes in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3145-3155.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
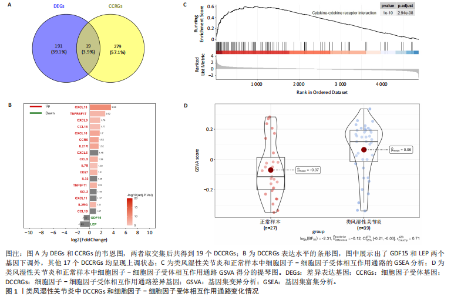
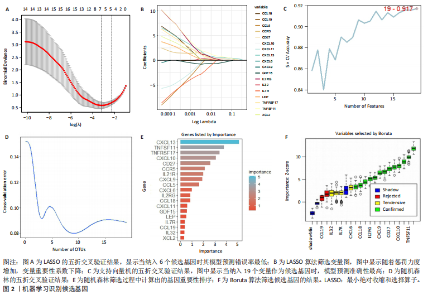
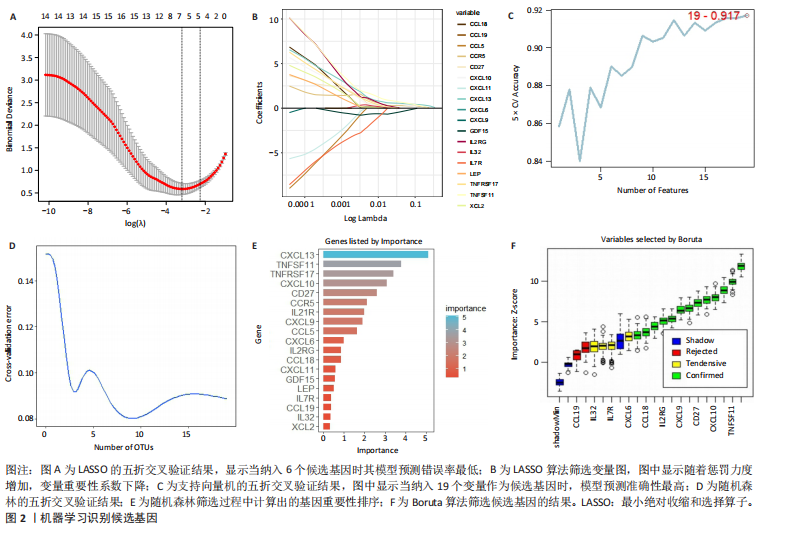
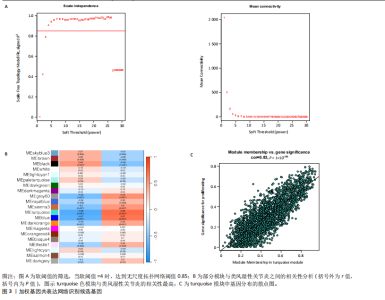
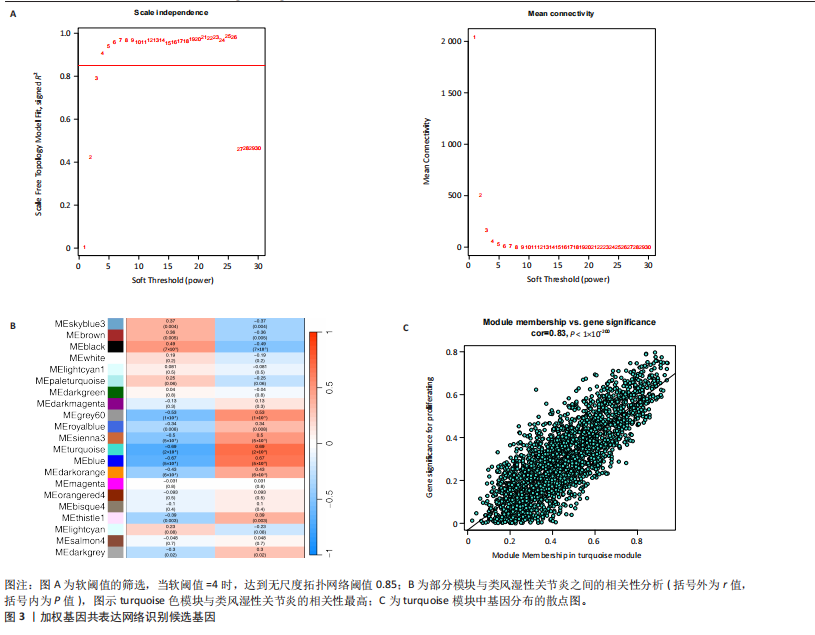
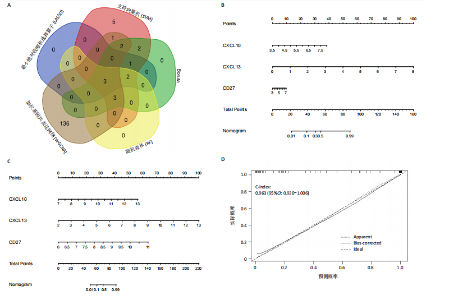
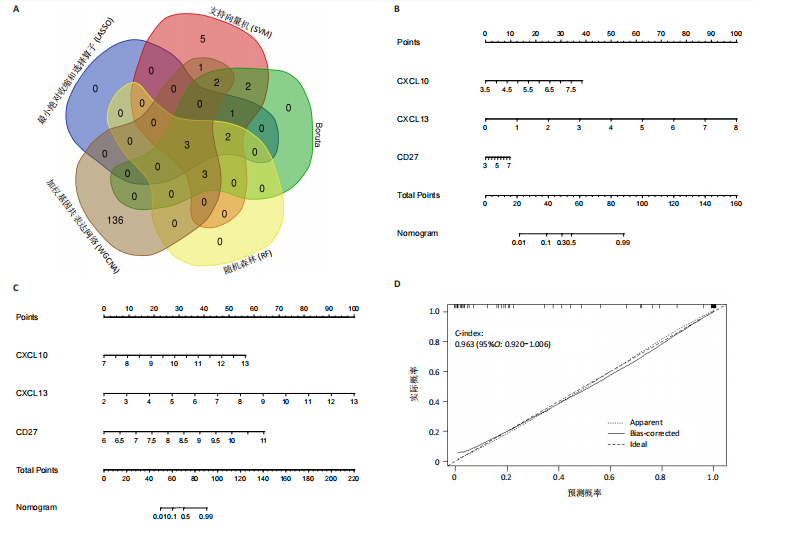
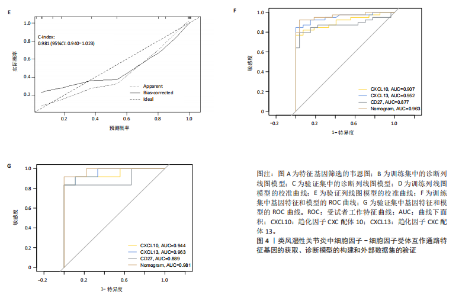
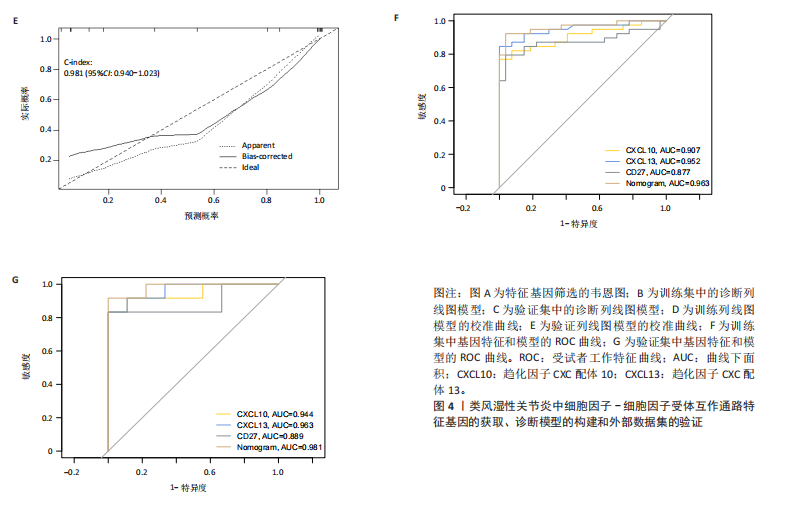
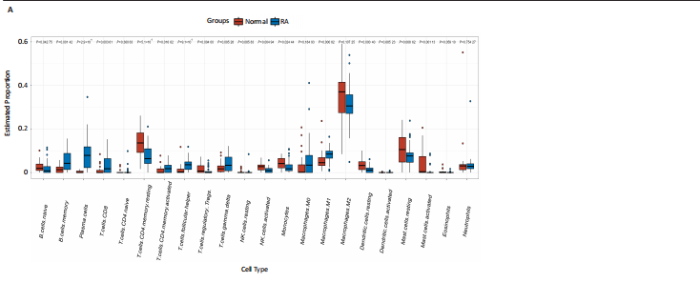
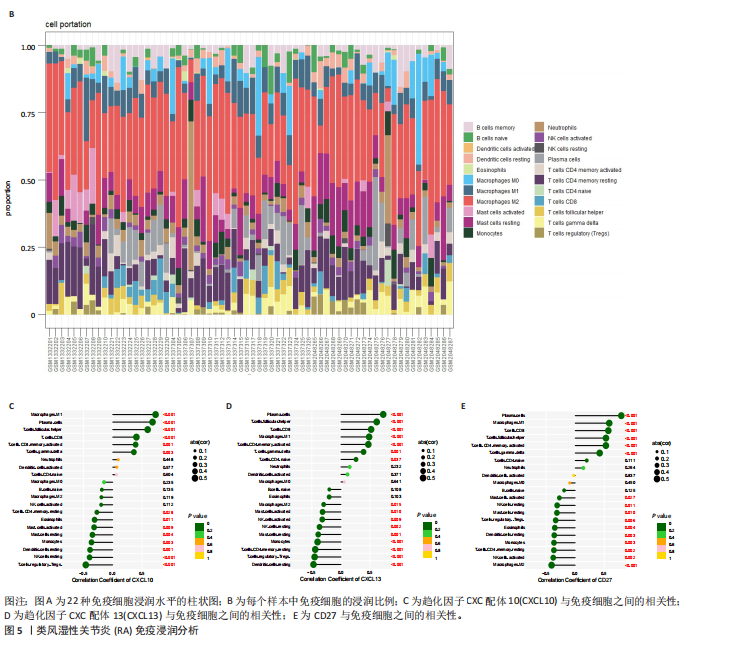
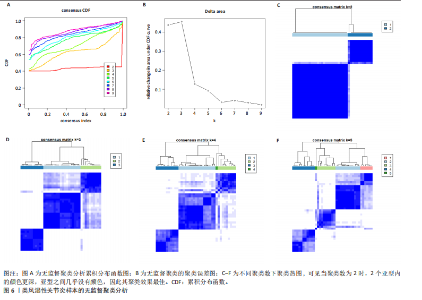
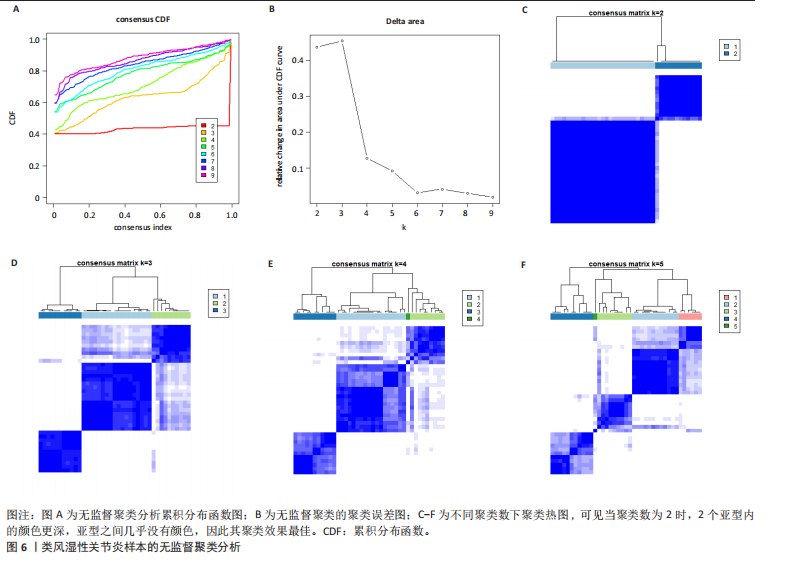
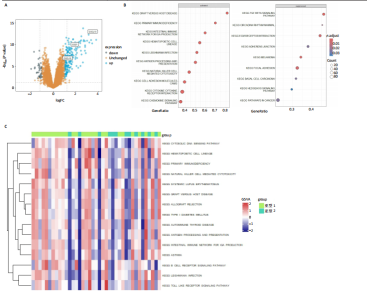
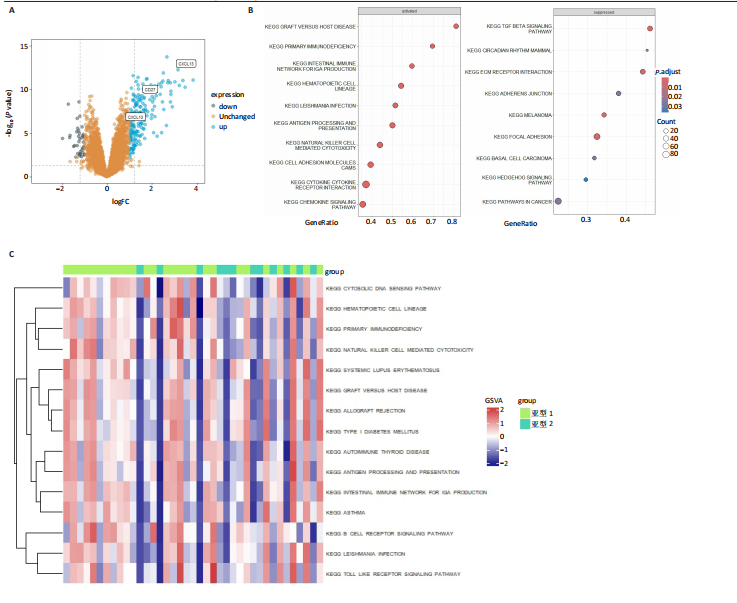
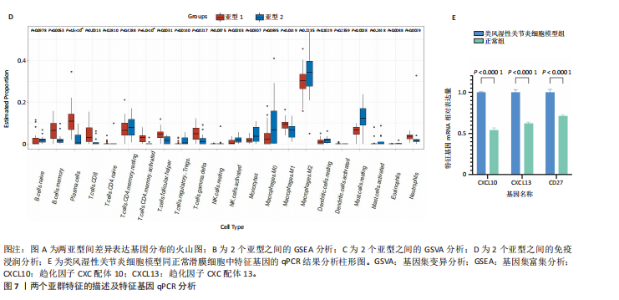
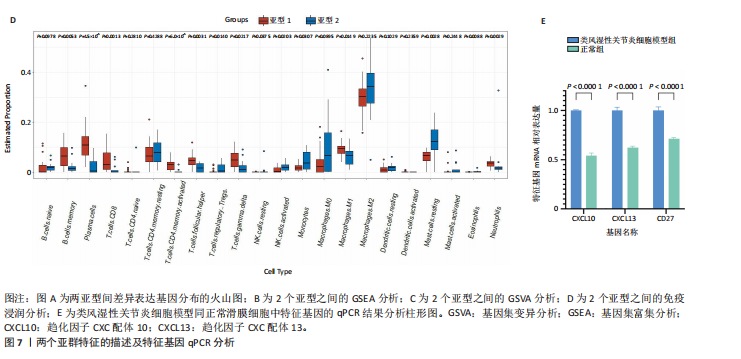
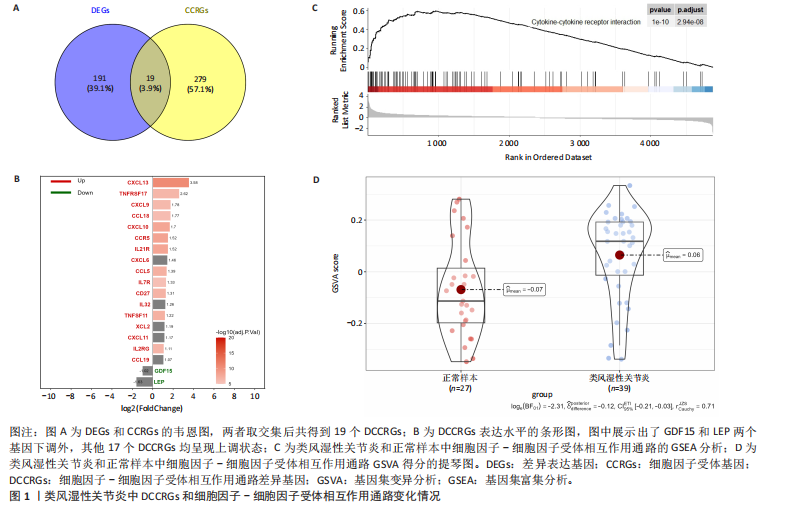
2.1 类风湿性关节炎中DCCRGs和细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用通路变化情况 将训练集差异分析获得210个DEGs同298个CCRGs取交集后共获得19个DCCRGs(图1A)。19个DCCRGs中,17个上调基因,2个下调基因(图1B)。通过对训练集进行基因集富集分析发现,细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用途径在类风湿性关节炎中显著上调(图1C)。基因集变异分析结果显示A样本中该通路得分显著高于正常样本,说明在类风湿性关节炎样本中该通路处于异常激活的状态(图1D)。基于此,作者认为细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用通路的异常激活同类风湿性关节炎的发生、发展密切相关,筛选该通路相关的特征基因可以为类风湿性关节炎的治疗提供新的方向。 2.2 机器学习识别候选基因 LASSO算法通过五折交叉验证筛选发现当将CXCL13、CXCL10、趋化因子受体5(chemokine C-C motif receptor 5,CCR5)、CD27、肿瘤坏死因子(配体)超家族成员11(tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily,member 11,TNFSF11)和生长分化因子15(growth differentiation factor 15,GDF15)作为候选基因纳入评价时,模型的预测错误率最低为0.041(图2A,B)。支持向量机经过十折交叉验证筛选发现当纳入19个基因作为特征,对模型进行评价时其预测准确性最高(0.917)(图2C)。随机森林法则通过筛选获得了8个候选基因(图2D),通过其内置的算法函数计算获得19个DCCRGs的重要性,并根据重要程度进行可视化(图2E)。最后Boruta算法通过筛选得到了10个候选基因,如图2F所示。 2.3 WGCNA识别候选基因 通过对样本表达量的聚类分析,共发现7个离群样本,将其筛除后,共有59个样本进入下一步的WGCNA分析。当软阈值选择为4时,网络达到无尺度拓扑阈值0.85(图3A)。随后基于基因的皮尔逊系数,经过动态树切割、融合,共获得40个模块,其中turquoise色模块与类风湿性关节炎的相关性最高(r=0.69,P ≤ 2×10-10)(图3B)。根据上文设定的模块相关性 > 0.8的标准,在turquoise模块中筛选获得了144个候选基因(图3C)。 2.4 特征基因的获取、诊断模型的构建和外部数据集的验证 将4种机器学习算法和WGCNA算法筛选得到的候选基因取交集后,获得了3个同类风湿性关节炎密切相关通路特征基因即:CXCL10、CXCL13和CD27(图4A)。通过“rms”包,基于3个特征基因的表达量,分别在训练集和验证集中构建了类风湿性关节炎的列线图诊断模型(图4B,C)。接着通过构建诊断模型的校准曲线进一步评估诊断模型预测准确性同实际情况的贴合程度,发现无论在训练集还是在验证集中诊断模型均表现出了同实际结果较为一致的预测趋势(图4D,E)。最后,通过使用受试者工作曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)对特征基因及诊断模型的诊断特异度和灵敏度进行了评估,经过评估发现无论是特征基因还是诊断模型均具有较好的临床诊断特异度和灵敏度(图4F,G)。 2.5 免疫浸润分析 通过对训练集进行CIBERSORT分析显示,类风湿性关节炎样本中的记忆B细胞、浆细胞、CD8+ T细胞、活化CD4+ T细胞、滤泡辅助T细胞、Tregs细胞和M1巨噬细胞浸润程度显著高于正常滑膜组织(P < 0.05)(图5A)。相反,B细胞、静息CD4+记忆T细胞、静息树突状细胞和活化肥大细胞的浸润水平显著低于正常滑膜样本(P < 0.05)。图5B为每个样本中免疫细胞浸润程度的柱状图,通过对特征基因和免疫细胞的相关性分析发现:所有3个特征基因的表达量均与浆细胞、CD8+ T细胞、活化CD4+ T细胞、滤泡辅助T细胞和M1巨噬细胞呈正相关;同时,它们与静息CD4+记忆T细胞、活化肥大细胞、静息肥大细胞、单核细胞、静息树突状细胞、静息自然杀伤细胞和Treg细胞呈负相关(图5C-E)。 2.6 基于DCCRGs使用无监督聚类分析识别类风湿性关节炎亚型 临床治疗过程中部分类风湿性关节炎患者对治疗不敏感,因此推测类风湿性关节炎患者中可能存在不同的亚型。而上述结果表明,细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用通路的上调同类风湿性关节炎的进展密切相关。因此,拟基于DCCRGs的表达通过无监督聚类方法尝试对类风湿性关节炎进行亚型的区分。设置9为最大聚类类别,通过不断的交叉验证获得了聚类分析的累积分布函数图和聚类误差图。累积分布函数图显示当聚类数为2时,该曲线最平缓,样本分布趋向更为均匀,聚类效果最好(图6A),聚类误差图显示当聚类数超过3时,聚类误差开始减小,表明增加聚类数对模型性能的提升效果减弱,因此选择2为最佳聚类数目(图6B)。为了进一步确定聚类数为2时模型的聚类效果,对不同聚类数下的模型分辨程度进行了可视化,可见当聚类数为2时,2个亚型内的颜色更深,亚型之间几乎没有颜色,因此其聚类效果最佳(图6C-F)。 2.7 两个亚群特征的描述及特征基因qPCR结果分析 对类风湿性关节炎2个亚群进行差异分析共识别出了217个DEGs,3个特征基因在亚群1中均呈现高表达趋势(图7A)。基因集富集分析及基因集变异分析结果均显示,免疫和炎症递质相关的通路在亚型1中被激活,而转化生长因子β和细胞外基质受体相互作用等通路则被抑制(图7B,C)。免疫浸润结果显示(图7D),与亚型2相比,亚型1的记忆B细胞、浆细胞、CD8+ T细胞、活化CD4+ T细胞、滤泡辅助T细胞、M1巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞浸润水平显著增高(P < 0.05)。相反,活化自然杀伤细胞、单核细胞、M0巨噬细胞、M2巨噬细胞和静息肥大细胞的浸润水平显著低于亚型2(P < 0.05)。通过对比发现,高表达特征基因的亚群1免疫浸润结果与上文提及的类风湿性关节炎样本整体免疫浸润结果高度相似。据此推断,当前对甲氨蝶呤类药物治疗敏感性较高的患者可能主要集中于亚群1(即特征基因高表达患者)。对于亚群2患者而言,因其失调的通路和免疫浸润程度与亚群1完全相反,故可能对甲氨蝶呤类要求治疗产生抵抗,进而成为难治性类风湿性关节炎患者。最后,通过构建类风湿性关节炎的细胞模型,对3个特征基因进行了qPCR水平的验证:3个特征基因qPCR均在类风湿性关节炎中呈现高表达趋势,同生信分析结果一致(图7E)。"
| [1] ZHOU S, LU H, XIONG M. Identifying Immune Cell Infiltration and Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12726747. [2] WU YK, LIU CD, LIU C, et al. Machine learning and weighted gene co-expression network analysis identify a three-gene signature to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1387311. [3] YU F, HU G, LI L, et al. Identification of key candidate genes and biological pathways in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2022; 23(6):368. [4] BRZUSTEWICZ E, BRYL E. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis--Practical and potential application of cytokines as biomarkers and targets of personalized therapy. Cytokine. 2015;76(2):527-356. [5] SULLIVAN DI, ASCHERMAN DP. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD): Update on Prevalence, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Therapy. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024;26(12):431-449. [6] DINARELLO CA. The IL-1 family of cytokines and receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(10):612-632. [7] BROWN P, PRATT AG, HYRICH KL. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. Bmj. 2024;384:e070856. [8] LIU X, PING G, JI D, et al. Reclassify High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Patients Into Different Molecular Subtypes With Discrepancy Prognoses and Therapeutic Responses Based on Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Enriched Prognostic Genes. Biomed Eng Comput Biol. 2024;15:11795972241274024. [9] DU G, CHEN J, ZHU X, et al. Bioinformatics analysis identifies TGF-β signaling pathway-associated molecular subtypes and gene signature in diabetic foot. iScience. 2024; 27(3):109094. [10] ZHAO J, HE K, DU H, et al. Bioinformatics prediction and experimental verification of key biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease based on transcriptome sequencing in mice. Peer J. 2022;10:e13932. [11] KANG J, CHOI YJ, KIM IK, et al. LASSO-Based Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in T1 Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2021;53(3):773-783. [12] LV JH, HOU AJ, ZHANG SH, et al. WGCNA combined with machine learning to find potential biomarkers of liver cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(50):e36536. [13] SANZ H, VALIM C, VEGAS E, et al. SVM-RFE: selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(1):432. [14] HAMIDI F, GILANI N, ARABI BELAGHI R, et al. Identifying potential circulating miRNA biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of ovarian cancer using machine-learning approach: application of Boruta. Front Digit Health. 2023;5:1187578. [15] LIU K, CHEN S, LU R. Identification of important genes related to ferroptosis and hypoxia in acute myocardial infarction based on WGCNA. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):7950-7963. [16] CHEN T, HUA W, XU B, et al. Robust rank aggregation and cibersort algorithm applied to the identification of key genes in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Math Biosci Eng. 2021;18(4):4491-4507. [17] WANG Q, GAO QC, WANG QC, et al. A compendium of mitochondrial molecular characteristics provides novel perspectives on the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):561. [18] RADU AF, BUNGAU SG. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857. [19] CONFORTI A, DI COLA I, PAVLYCH V, et al. Beyond the joints, the extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(2):102735. [20] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHÜLKE S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880. [21] GUO D, ZHANG B, WU D, et al. Identification of PRTN3 as a novel biomarker for the diagnosis of early gastric cance. J Proteomics. 2023;277:104852. [22] ZHOU Y, LIN Z, XIE S, et al. Interplay of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and colorectal cancer development: unravelling the mediating role of fatty acids through a comprehensive multi-omics analysis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):587. [23] ZHOU Z, ZHOU X, JIANG X, et al. Single-cell profiling identifies IL1B(hi) macrophages associated with inflammation in PD-1 inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2107. [24] LARAGIONE T, BRENNER M, SHERRY B, et al. CXCL10 and its receptor CXCR3 regulate synovial fibroblast invasion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(11):3274-3283. [25] PAN Z, ZHU T, LIU Y, et al. Role of the CXCL13/CXCR5 Axis in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2022;13:850998. [26] BUGATTI S, MANZO A, VITOLO B, et al. High expression levels of the B cell chemoattractant CXCL13 in rheumatoid synovium are a marker of severe disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(10):1886-1895. [27] STARZER AM, BERGHOFF AS. New emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy: CD27 (TNFRSF7). ESMO Open. 2020;4(Suppl 3): e000629. [28] MERINO-VICO A, FRAZZEI G, VAN HAMBURG JP, et al. Targeting B cells and plasma cells in autoimmune diseases: From established treatments to novel therapeutic approaches. Eur J Immunol. 2023;53(1):e2149675. [29] DI BENEDETTO P, RUSCITTI P, VADASZ Z, et al. Macrophages with regulatory functions, a possible new therapeutic perspective in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(10):102369. [30] GENSOUS N, CHARRIER M, DULUC D, et al. T Follicular Helper Cells in Autoimmune Disorders. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1637. [31] LI Y, BAI S, ZHANG J, et al. [T follicular helper cells and their related molecules in rheumatoid arthritis: A review]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;35(3):281-286. |
| [1] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [2] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [3] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [4] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [5] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [6] | Guan Yujie, Zhao Bin. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [7] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [8] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [9] | Qi Xiang, Cao Shan, Chen Jian, Zhang Yijia, Liu Keke, Xu Zifu, Liu Wang, Fu Xiaoxiao, Yin Xiaolei. Screening of genes related to mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis in atherosclerosis and target prediction of regulatory traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2641-2652. |
| [10] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [11] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [12] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [13] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [14] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [15] | Chen Ying, Guo Xiaojing, Mo Xueni, Ma Wei, Wu Shangzhi, Li Xiangling, Xie Tingting. Analysis of diagnostic biomarkers for ischemic stroke and experimental validation of targeted cuproptosis related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7562-7570. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||