Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (14): 3694-3701.doi: 10.12307/2026.106
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different preparation methods of silk fibroin and its application in the construction of small-diameter tissue-engineered blood vessels
Yang Lei1, Liu Xinfang1, Luo Sidong1, Zhang Hongan1, Wang Yeyang1, Chen Weijian2
- 1Guangdong Second People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University, Guangzhou 510317, Guangdong Province, China; 2Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-22Accepted:2025-06-06Online:2026-05-18Published:2025-09-12 -
Contact:Wang Yeyang, MD, Master’s supervisor, Guangdong Second People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University, Guangzhou 510317, Guangdong Province, China Chen Weijian, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yang Lei, MS, Guangdong Second People’s Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University, Guangzhou 510317, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan City-School Joint Project, No. 2023A03J0266 (to WYY); Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 202102020108 (to WYY); Special Fund Project of Guangdong Second People’s Hospital, No. TJGC-2023009 (to WYY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Lei, Liu Xinfang, Luo Sidong, Zhang Hongan, Wang Yeyang, Chen Weijian. Different preparation methods of silk fibroin and its application in the construction of small-diameter tissue-engineered blood vessels[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3694-3701.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
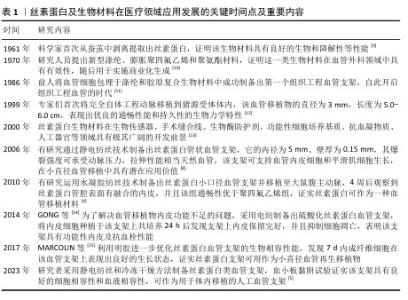
2.1 丝素蛋白及生物材料在医疗领域应用发展的历程 见表1。 2.2 丝素蛋白的特性 2.2.1 丝素蛋白的种类、成分和分子结构 蚕丝是昆虫和蛛形纲节肢动物生产的生物聚合物[16],根据食物来源可分为桑蚕和非桑蚕,桑蚕存在于五湖四海中,但非桑蚕受地理位置限制[17]。蚕丝的主要成分有75%丝素蛋白、25%丝胶蛋白、蜡质、色素和无机物[18]。丝素蛋白的初级结构有重链(分子质量350 kD)和轻链(分子质量25 kD),并以二硫键形式相连。丝素蛋白的二级结构包括丝素蛋白Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ,丝素蛋白Ⅰ是由α-螺旋和随机线圈构成,在甲醇作用下可转化为丝素Ⅱ结构;丝素蛋白Ⅱ为反平行β片结构,具有良好的稳定性和力学性;丝素蛋白Ⅲ可用于区分亲水性丝氨酸残基和疏水性丙氨酸残基的二级结构[19]。因此,合理调整丝素蛋白的分子结构比例可获得理想的材料力学性能。"
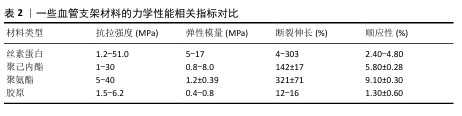
2.2.2 丝素蛋白的生物性能 机械性能:丝素蛋白的力学强度明显优于其他生物材料,因而被应用于医用外科缝合线与组织工程血管支架等领域[20]。表2总结归纳一些常见高分子材料的力学性能指标,相较于常用生物材料,丝素蛋白支架表现出优良的柔韧性,可以维持移植物在体内的通畅[21]。弹性模量可反映血管支架的耐疲劳性。研究发现,电纺丝素蛋白血管支架的弹性模量数值为5-17 MPa,明显高于天然血管,说明丝素蛋白支架具有较好的弹性变形能力,以促进血管移植物再生。研究表明,丝素蛋白力学性能与支架的形式、结晶程度及β-片结构等因素有着密切联系[22],因此,可根据应用需求调整丝素蛋白的制备方式、聚合物浓液结晶度等制备出理想的小口径组织工程血管。 生物相容性:研究表明,丝素蛋白材料的生物相容性要好于其他生物材料,如聚乳酸、聚己内酯和胶原蛋白,丝素蛋白已获得美国药物管理局批准应用于整形外科缝合材料[23]。近年,ZOU等[24]报道多种类型丝素蛋白生物材料,如颗粒、薄膜、纤维垫、3D支架等,证明了该材料可合理调控细胞行为、改善组织再生。CHEN等[25]利用气体发泡技术制备出丝素蛋白类支架,发现该支架上的细胞呈快速生长和迁移现象,并且该支架可改善细胞外基质和血管再生。虽然大量研究证实丝素蛋白具有良好的生物形容性,但该生物材料的体内长期安全性问题依然不明确。 生物降解性:支架的降解性能是组织工程血管移植物最具有挑战性的难题之一,生物降解速率应与组织再生保持一致性,这对于血管重塑至关重要。丝素蛋白在体内外均可发生降解,并且1周内降解率为10%左右,而聚乳酸、聚己内酯、聚氨酯和胶原蛋白1周内的降解率分别为3%,1.5%,1.2%和5.2%,这充分说明丝素蛋白材料具有良好的降解性,可用于小口径血管组织工程中[26]。研究发现,丝素蛋白的降解时间随着丝素蛋白Ⅱ中β-片结构数量的增加而延长,证实了其降解速率与β-片的结构数量呈正相关[27]。另外,丝素蛋白的降解速率还与结晶度、孔隙度、孔径、形态、分子质量、植入部位及生物学条件密切相关。 免疫原性:免疫反应是生物材料植入体内后宿主体产生的防御性保护机制,受生物材料形态和生化结构的影响[28]。另外,炎症巨噬细胞的表型转换对于血管重塑极其关键,血管移植物植入后,巨噬细胞发生极化,即早期为促炎型,后期是抗炎型,这一改变有利于促进组织愈合[29]。丝素蛋白材料的不同形式或加工技术均会影响到材料的力学强度和降解性能,进而影响免疫反应[30]。相比于其他生物材料如聚己内酯、聚氨酯和胶原蛋白等,丝素蛋白材料在体内发生的免疫炎症程度较轻(表3)。 "

2.3 丝素蛋白提取工艺 ROCKWOOD等[35]全面归纳了丝素蛋白经各种水溶剂或有机溶剂处理后获得了水凝胶、薄膜和复合材料的过程。通常,从蚕茧提取出丝素蛋白生物材料需进行脱胶和溶解处理,常用的脱胶溶剂有碳酸钠、酒石酸、碱性溶液脱胶,其中碳酸钠溶液是最常见、有效[36]。将生蚕茧放置于0.02 mol/L碳酸钠缓冲液中并煮沸60 min,纯净水反复洗涤干净,丝素蛋白溶液无需透析处理,直接冻干处理并保存。不同的脱胶法对丝素蛋白的降解性能和力学强度有着不同影响。为了保持丝素蛋白结构的稳定性,LIU等[37]采用酶脱胶法制备了丝素蛋白,脱胶后丝素蛋白纤维溶解于水溶剂或有机溶剂(中如氯化钙/乙醇/水溶液、六氟异丙醇溶液和甲酸溶液)直至重塑成不同形态的丝素蛋白,应用于组织工程血管中[38]。 "

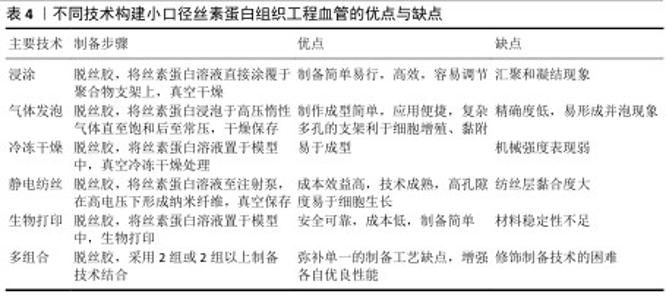
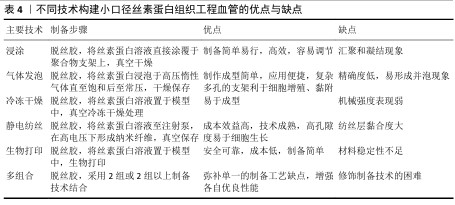
2.4 丝素蛋白构建小口径组织工程血管的技术 丝素蛋白人工血管支架的制备应具有便捷、高效生产、低成本和类似于天然血管细胞外基质等特点。运用浸涂法、气体发泡法、静电纺丝、冷冻干燥法和生物打印等技术制备出满意的丝素蛋白支架材料,在小口径组织工程血管领域具有非凡的意义。 2.4.1 浸涂法 浸涂工艺是一种制备简单、操作容易和效果显著的技术,可制备出良好孔径的小口径人工血管[39]。为了制备出合理孔隙率的支架,研究者采用不同浓度丝素蛋白得到了多孔微管,实验结果显示高孔隙率丝素蛋白支架可改善细胞的迁移行为[40]。ZHAN等[41]在紫外光照射下通过丝素蛋白浸渍涂覆于聚乙二醇接枝膨胀聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯血管移植物,证明未经修饰聚乙二醇接枝膨胀聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯的表面亲水性差,难以内皮化,而丝素蛋白修饰后的聚乙二醇接枝聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯表面更易于细胞增殖、黏附和快速内皮化。另外,适当修饰人工血管移植物可改善丝素蛋白血管支架在体内的通畅性能,研究者采用编织技术制备丝素蛋白血管移植物并涂覆丝素蛋白海绵,体内移植4周后发现实验组中人工血管通畅率是100.0%,而聚四氟乙烯血管移植物组人工血管通畅率为80.0%,表明丝素蛋白可作为小口径血管的候选材料之一[42]。尽管运用浸涂方法制作血管支架较为简便、高效和易调节,但该工艺易使血管支架形态结构发生汇聚与凝结现象,因此,在今后研究中需重点关注如何来改变血管支架的物理结构。 2.4.2 气体发泡法 发泡技术主要分为物理发泡和化学发泡,其中,物理发泡是指添加氢气、二氧化碳或其他惰性气体诱导气泡,而化学发泡是采用化学过程如偶氮二甲酰胺、碳酸氢钠形成气泡,该技术有应用便捷和成型快等优点。高孔隙率结构的血管移植物能促进血管重建,例如,MANIGLIO等[43]通过喷嘴和小直径针加压氧化亚氮气体制备了易调节的多孔丝素蛋白血管支架,实验结果显示该支架具有稳定的形状结构且孔隙尺寸与气体压力呈正比,可改善血管组织再生。同样,LEE等[44]采用气体泡沫制备出具有理想体积及合理纳米纤维结构的丝素蛋白类纳米纤维支架,可用于小口径人工血管中。然而,发泡技术模具加压的高饱和强度容易形成高密度泡孔,较快的降压速度会引起并泡现象,而过慢的降温速度形成凝固。 2.4.3 冷冻干燥法 冷冻干燥是指真空条件下诱导丝素蛋白水溶液升华为多孔结构的支架,聚合物浓度、黏度、冻结时间和温度等参数都影响到支架的孔径,因此,适当调整这些指标可改善支架的微观结构。近期,ZHU等[45]基于冷冻干燥方法开发出一种多孔丝素蛋白支架,皮下植入4周后观察到丝素蛋白支架孔隙中有宿主细胞浸润,并且生成了新生毛细血管。WANG等[46]采用冷冻干燥法在脱胶酶作用下制备了丝素蛋白支架,免疫荧光染色结果显示接种于该支架上复合培养3,7 d的内皮细胞数量明显高于其他对照组,并且支架表面的且细胞分布均匀,形状呈纺锤状,证实丝素蛋白支架可诱导细胞增殖行为,可作为组织工程支架。运用冷冻干燥手段可较好地改善人工血管机械强度,科学家报道了运用该方法制成的丝素蛋白类血管移植物爆破强度非常接近于自体移植物(如大隐静脉),可用于小口径人造血管支架中[47]。虽然,通过冷冻干燥法制备的丝素蛋白组织工程血管支架容易成型,但存在力学强度不足的缺点,这一缺点需要科研者们逐步突破。 2.4.4 静电纺丝技术 静电纺丝技术制备的小口径丝素蛋白血管移植物,可模拟天然细胞外基质纳米纤维结构。静电纺丝技术的原理是:在强电场高压电作用下,带电溶液喷射至收集器,蒸发的溶剂形成不同形状的纳米纤维[48]。调整电纺参数(固化距离、电压、流速和温度等)及纺丝液(浓度、黏度和溶剂等)可改变丝素蛋白纤维的形貌和直径,从而影响细胞增殖黏附行为[49]。YANG等[50]利用电纺设备制作出4种直径的丝素蛋白类小口径血管支架,发现4种直径支架材料表面的间充质干细胞表现出不同的增殖与黏附行为,均具有具有良好的细胞相容性。DURáN-REY等[51]发现丝素蛋白膜、多孔膜和电纺薄膜都能改善人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖行为,其中随机取向电纺膜上的细胞增殖行为更好。有研究表明,多层丝素蛋白管状血管支架有利于内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞和成纤维细胞的生长[52]。有研究发现采用静电纺丝技术制备了丝素蛋白双层组织工程血管,负载肝素及内皮生长因子后该支架在体内的血流速度接近于天然血管,组织学观察显示支架表面有着分布均匀的内皮细胞[53]。 此外,良好的机械强度是小口径血管支架的先决条件之一,而静电纺丝技术可改善支架的特性。ALKAZEMZ等[54]运用静电纺丝技术制备了丝素蛋白类血管移植物,该移植物的刚度和最大抗拉强度相似于天然血管。大量研究证实,静电纺丝血管移植物可诱导血管内皮细胞再生,进而形成完整性内皮层,以减少血栓和内膜增生形成。FILIPE等[55] 采用静电纺丝技术制备了丝素蛋白血管移植物,植入大鼠主动脉24周后仍保持良好的通畅性能,并可快速内皮化。与此同时,也有研究将直径1.8 mm丝素蛋白电纺移植物移植于鼠动脉,结果显示该移植物具有完整的内皮化,为制备出具有长期通畅性能的支架提供了理论性依据[56]。然而,运用静电纺丝技术制备的人工血管依然面临一些问题,如应怎样改善支架表面的性能、纺丝层黏合度及力学强度等,这都有待研究者需进一步解决。 2.4.5 生物打印技术 生物打印技术是指在计算机辅助下定制重建出具有高清复杂的血管结构,其中主要发展方向以生物材料和细胞为墨水打印成人工血管,该技术不局限于3D打印,还包括4D打印、5D打印和6D打印[57],该技术受流变、膨胀比和表面张力等因素影响[58]。目前生物打印的墨水材料有天然衍生材料、高分子材料和复合材料,应用丝素蛋白材料制备出的生物打印血管支架具有可加工性、易调节性、机械性强及模拟天然微环境结构,可以促进组织再生[59]。丝素蛋白的流变性可通过调节生物墨水的纯度和浓缩性而改变,但它的黏度较低,难以单独打印,因而常把丝素蛋白生物墨水与其他生物材料相结合以满足3D打印的不同要求。LI等[60]利用海藻酸盐和丝素蛋白组合成复合生物墨水,运用3D生物打印出海藻酸盐/丝素蛋白血管支架,该支架的微通道相互连接,并具有较高的渗透性,在血管组织工程方面具有巨大的潜力。WANG等[61]通过嵌入式3D打印和调聚电解质复合物相结合构建了微通道网络的多功能支架,发现该微通道有三维分层结构以允许自由质量/氧运输,证实该支架可促进细胞基质沉积,有利于生理相关组织如细胞化和血管化的形成。然而,生物打印在小口径人工血管领域中仍面临许多挑战,存在如何选择有限的材料、如何设计细胞类型、制备成本过高及结构稳定性等问题,需要在以后工作研究中来解决。 2.4.6 多组合技术 近些年,随着科学研究的飞跃进展,单一制备技术手段常无法满足血管移植物的性能要求,因而研究者常采用2种或2种以上制备方式来充分弥补各自的缺点,从而构建出理想的人造血管移植物。GUPTA等[62]采用模具铸造和静电纺丝结合新方法设计出双层小口径丝素蛋白支架,它的高孔隙内层允许细胞渗透,致密的电纺纳米纤维外层展示出良好的机械性能,实验表明该支架上可形成新生组织且没有动脉瘤形成,证实了该支架在血管组织工程中具有应用潜力。也有研究通过静电纺、气体发泡、原位交联和冷冻干燥相结合手段制备了丝素蛋白类双层纳米复合支架,该支架的高程度交联方式可显著性增强丝素蛋白类支架的力学强度,如弹性模量、拉伸强度和断裂伸长率大小[63]。SONG等[64]采用静电纺丝和涂层技术制备出高孔聚乳酸/丝素蛋白纤维复合支架,结果表明丝素蛋白包覆在多孔聚乳酸纤维膜上显著增强了支架表面平滑肌细胞的黏附、增殖能力及亲水性和力学性能,该支架具有潜在的临床应用价值。开发出一种安全、有效、长期通畅良好的小口径血管移植是非常值得深入探索。KUANG等[65]通过共轭静电纺丝技术和冷冻干燥相结合的方法制备了复合纳米材料,核心纤维为聚L-丙交酯-己内酯并包覆肝素和丝素蛋白凝胶,移植体内2个月后,高分辨超声可见该血管移植物移植仍保持良好的通畅性(通畅率为100%),8个月后丝素蛋白类复合材料的血流量相似于天然血管,表明该移植物可保持长期通畅性并在体内促进血管组织重塑。尽管结合多种制备手段可极大改善人工血管的性能,但如何选择最佳的制备技术组合方构建理想的小口径组织工程血管,这一问题需进一步探索研究。 不同技术构建小口径丝素蛋白组织工程血管的优点与缺点,见表4。 "

2.5 丝素蛋白在小口径组织工程血管的最新应用进展 小口径组织血管移植物的构建一直是研究者追寻的热点问题,以丝素蛋白为基础材料的人工血管支架近年来备受广大科研人员的关注[66]。人造血管支架必备的条件为良好的力学性与生物相容性[67]。LIU等[68]研究证实丝素蛋白支架具有良好的理化特性。小口径血管支架体内移植早期失败的原因是形成血栓,从而引起血管堵塞[69]。合适的人工血管支架应拥有抗血栓性,众多研究证明丝素蛋白的血液相容性良好,这同它优良的理化结构特性有关联[70]。然而,丝素蛋白类人造血管存在过度的细胞增殖等问题,是引起血栓形成的原因之一,因此,可采用抗凝药物如阿司匹林、肝素钠及华法林等相结合以改善血管支架的抗血栓性能。 ALMASI-JAF等[71]报道通过冷冻干燥与静电纺丝技术及交联法制备了小口径肝素化丝素蛋白类双层血管移植物,血小板黏附试验显示该支架材料表面的血小板形态呈球形或圆形,血小板数量少且具有内皮层形成,证实了该支架可成为血管移植应用的理想候选者。 制备出具有血管内皮化完全再生与重塑能力的血管支架,在小口径人工血管移植物中显得尤为重要[72],功能性内皮层可优化支架的血液相容性,从而降低形成血栓的风险性。研究发现丝素蛋白类血管移植物表面可生成再生融合的内皮层,这是血管在体内移植成功的关键,也是评估该支架作为自体血管代替品的重要标志。FUKUDA等[73]通过编织和涂层手段制备出薄、厚两种类型的丝素蛋白血管移植物,并将其与鼠尾腔静脉置换,实验结果显示静脉置换4周后丝素蛋白血管移植可形成内皮化结构,术后2周观察该两组的通畅率分别为50%和88%,说明该移植物是一种有前途的用于中型哺乳动物腹腔静脉系统替代的组织工程支架。RIZZI等[74]使用低速滚动将内皮细胞接种于丝素蛋白类支架管腔表面,以形成完整的内皮单层用于移植或疾病模型的完整血管结构建立,该工作克服了血管移植物制造中缺乏内皮细胞层的仿生学问题。然而,基于丝素蛋白类血管移植物的内皮化生成主要位于吻合口,该支架中心部位的内皮细胞比较少见[75],因此,如何改善丝素蛋白类血管移植物内皮化完整性问题需要进一步深入探索。 "

| [1] BACKER CL, JACOBS JP. Proceedings of the 8th Scientific Meeting of the World Society for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery (WSPCHS) at the 8th World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery (WCPCCS). World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2024;15(3):263-264. [2] TSAO CW, ADAY AW, ALMARZOOQ ZI, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation.2022;145(8):e153-e639. [3] BUŁDAK Ł. Cardiovascular Diseases-A Focus on Atherosclerosis, Its Prophylaxis, Complications and Recent Advancements in Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4695. [4] WANG Y, KESHAVARZ M, BARHOUSE P, et al. Strategies for Regenerative Vascular Tissue Engineering. Advanced Biology. 2023;7(5):e2200050. [5] CHEN J, ZHANG D, WU LP, et al. Current Strategies for Engineered Vascular Grafts and Vascularized Tissue Engineering. Polymers. 2023;15(9):2015. [6] 杨磊,李霞飞,董玉珍,等.小口径组织工程血管支架:如何产生一种具有生理重塑活性的材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(22):3579-3586. [7] LI MX, WEI QQ, MO HL, et al. Challenges and advances in materials and fabrication technologies of small-diameter vascular grafts. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):91. [8] LI G, SUN S. Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2757. [9] DASTAGIR K, DASTAGIR N, LIMBOURG A, et al. In vitro construction of artificial blood vessels using spider silk as a supporting matrix. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;101:103436. [10] BOBADILLA JL. From ebers to EVARs: a historical perspective on aortic surgery. Aorta (Stamford). 2013;1(2):89-95. [11] HU K, LI Y, KE Z, et al. History, progress and future challenges of artificial blood vessels: a narrative review. Biomater Transl. 2022;3(1):81-98. [12] THOTTAPPILLIL N, NAI RPD. Scaffolds in vascular regeneration: current status. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2015;11:79-91. [13] 蔡佳丽,陈菲菲,蒋鸣谦,等.丝素蛋白在生物材料领域的应用[J].广东蚕业, 2021,55(3):5-7. [14] GONG X, LIU H, DING X, et al. Physiological pulsatile flow culture conditions to generate functional endothelium on a sulfated silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffold. Biomaterials. 2014;35(17):4782-4791. [15] MARCOLIN C, DRAGHI L, TANZI M, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin-gelatin composite tubular matrices as scaffolds for small diameter blood vessel regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(5):80. [16] JANANI G, KUMAR M, CHOUHAN D, et al. Insight into Silk-Based Biomaterials: From Physicochemical Attributes to Recent Biomedical Applications. ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2019;2(12):5460-5491. [17] SAHOO JK, HASTURK O, FALCUCCI T, et al. Silk chemistry and biomedical material designs. Nat Rev Chem. 2023;7(5): 302-318. [18] AHSAN F, ANSARI TM, USMANI S, et al. An Insight on Silk Protein Sericin: From Processing to Biomedical Application. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2018;68(6):317-327. [19] GUPTA P, MANDAL BB. Silk biomaterials for vascular tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2021;134:79-106. [20] 匙峰,梁帅,王倩,等.丝素蛋白在骨组织工程领域的应用研究进展[J].西华师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022, 43(2):137-143. [21] BUCCIARELLI A, MOTTA A. Use of Bombyx mori silk fibroin in tissue engineering: From cocoons to medical devices, challenges, and future perspectives. Biomater Adv. 2022;139:212982. [22] ALKAZEMI H, CHAI J, ALLARDYCE BJ, et al. Glycerol-plasticized silk fibroin vascular grafts mimic key mechanical properties of native blood vessels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2025;113(1):e37802. [23] MICHELI L, PARISIO C, LUCARINI E, et al. Restorative and pain-relieving effects of fibroin in preclinical models of tendinopathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;148:112693. [24] ZOU S, YAO X, SHAO H, et al. Nonmulberry silk fibroin-based biomaterials: Impact on cell behavior regulation and tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022;153: 68-84. [25] CHEN Y, JIA Z, SHAFIQ M, et al. Gas foaming of electrospun poly(L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofiber scaffolds to promote cellular infiltration and tissue regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;201:111637. [26] BOJEDLA SSR, CHAMEETTACHAL S, YELESWARAPU S, et al. Silk fibroin microfiber-reinforced polycaprolactone composites with enhanced biodegradation and biological characteristics. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(7):1386-1400. [27] LU Y, HUANG X, YUTING L, et al. Silk Fibroin-Based Tough Hydrogels with Strong Underwater Adhesion for Fast Hemostasis and Wound Sealing. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(1):319-331. [28] LI Z, TAN G, XIE H, et al. The Application of Regenerated Silk Fibroin in Tissue Repair. Materials (Basel). 2024;17(16):3924. [29] GRANEY PL, BEN-SHAUL S, LANDAU S, et al. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaay6391. [30] MA L, DONG W, LAI E, et al. Silk fibroin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1381838. [31] LI H, WANGY, SUN X, et al. Steady-State Behavior and Endothelialization of a Silk-Based Small-Caliber Scaffold In Vivo Transplantation. Polymers (Basel). 2019; 11(8):1303. [32] ZHAO L, LI X, YANG L, et al. Evaluation of remodeling and regeneration of electrospun PCL/fibrin vascular grafts in vivo. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111441. [33] JIA W, LI M, LIU L, et al. Fabrication and assessment of chondroitin sulfate-modified collagen nanofibers for small-diameter vascular tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;257:117573. [34] BUSCEMI S, PALUMBO VD, MAFFONGELLI A, et al. Electrospun PHEA-PLA/PCL Scaffold for Vascular Regeneration: A Preliminary in Vivo Evaluation. Transplant Proc. 2017; 49(4):716-721. [35] ROCKWOOD DN, PREDA RC, YÜCEL T, et al. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat Protoc. 2011;6(10): 1612-1631. [36] ANAND P, PANDEY JP, PANDEY DM. Study on cocoonase, sericin, and degumming of silk cocoon: computational and experimental. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021;19(1):32. [37] LIU X, HUANG Q, PAN P, et al. Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(16):3383. [38] WANG HY, WEI ZG, ZHANG YQ. Dissolution and regeneration of silk from silkworm Bombyx mori in ionic liquids and its application to medical biomaterials. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143:594-601. [39] DE GIORGIO G, MATERA B, VURRO D, et al. Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11(2):167. [40] FUEST S, SMEETS R, GOSAU M, et al. Layer-by-Layer Deposition of Regenerated Silk Fibroin horizontal line An Approach to the Surface Coating of Biomedical Implant Materials. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(12):6644-6657. [41] ZHAN C, XIA C, WANG P, et al. Modulation of neo-endothelialization of vascular graft materials by silk fibroin. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2021;66(6):573-580. [42] KIRITANI S, KANEKO J, ITO D, et al. Silk fibroin vascular graft: a promising tissue-engineered scaffold material for abdominal venous system replacement. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):21041. [43] MANIGLIO D, BONANI W, MIGLIARESI C, et al. Silk fibroin porous scaffolds by N(2)O foaming. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(5):491-506. [44] LEE S, LEE J, BAEK J, et al. Design of Volumetric Nanolayers via Rapid Proteolysis of Silk Fibroin for Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2022;23(12):4995-5006. [45] ZHU M, WANG K, MEI J, et al. Fabrication of highly interconnected porous silk fibroin scaffolds for potential use as vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2014-2023. [46] WANG M, WANG Y, PAN P, et al. A high molecular weight silk fibroin scaffold that resists degradation and promotes cell proliferation. Biopolymers. 2023;114(7):e23554. [47] MALEKI S, SHAMLOO A, KALANTARNIA F. Tubular TPU/SF nanofibers covered with chitosan-based hydrogels as small-diameter vascular grafts with enhanced mechanical properties. Scientific Reports. 2022;12(1):6179. [48] CHEN N, JIN W, GAO H, et al. Sequential intervention of anti-inflammatory and osteogenesis with silk fibroin coated polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligaments for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Mater Chem B. 2023; 11(34):8281-8290. [49] HODGE J G, QUINT C. Improved porosity of electrospun poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic) scaffolds by sacrificial microparticles enhances cellular infiltration compared to sacrificial microfiber. J Biomater Appl. 2022;37(1):77-88. [50] YANG L, WANG X, XIONG M, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin/fibrin vascular scaffold with superior mechanical properties and biocompatibility for applications in tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):3942. [51] DURÁN-REY D, BRITO-PEREIRA R, RIBEIRO C, et al. Development of Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Vascular Repair. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(3):1121-1130. [52] ALESSANDRINO A, CHIARINI A, BIAGIOTTI M, et al. Three-Layered Silk Fibroin Tubular Scaffold for the Repair and Regeneration of Small Caliber Blood Vessels: From Design to in vivo Pilot Tests. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:356. [53] 刘月,蒋紫仪,李晶晶,等.聚左旋乳酸己内酯/丝素蛋白小口径人工血管细胞共培养及体内生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22):3505-3513. [54] ALKAZEMI H, CHAI J, ALLARDYCE BJ, et al. Glycerol-plasticized silk fibroin vascular grafts mimic key mechanical properties of native blood vessels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2025;113(1):e37802. [55] FILIPE EC, SANTOS M, HUNG J, et al. Rapid Endothelialization of Off-the-Shelf Small Diameter Silk Vascular Grafts. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2018;3(1):38-53. [56] LIU J, CHEN D, ZHU X, et al. Development of a decellularized human amniotic membrane-based electrospun vascular graft capable of rapid remodeling for small-diameter vascular applications. Acta Biomater. 2022;152:144-156. [57] XU Y, WANG C, YANG Y, et al. A Multifunctional 3D Bioprinting System for Construction of Complex Tissue Structure Scaffolds: Design and Application. Int J Bioprint. 2022;8(4): 617. [58] XIAO M, YAO J, SHAO Z, et al. Silk-Based 3D Porous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024; 10(5):2827-2840. [59] LI X, LI N, FAN Q, et al. Silk fibroin scaffolds with stable silk I crystal and tunable properties. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;248: 125910. [60] LI H, LI N, ZHANG H, et al. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Perfusable Hierarchical Microchannels with Alginate and Silk Fibroin Double Cross-linked Network. 3D Print Addit Manuf. 2020; 7(2):78-84. [61] WANG H, ZHOU X, WANG J, et al. Fabrication of channeled scaffolds through polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) printed sacrificial templates for tissue formation. Bioact Mater. 2022;17: 261-275. [62] GUPTA P, LORENTZ KL, HASKETT DG, et al. Bioresorbable silk grafts for small diameter vascular tissue engineering applications: In vitro and in vivo functional analysis. Acta Biomater. 2020;105:146-158. [63] HAJIABBAS M, ALEMZADEH I, VOSSOUGHI M. A porous hydrogel-electrospun composite scaffold made of oxidized alginate/gelatin/silk fibroin for tissue engineering application. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;245:116465. [64] SONG J, CHEN Z, MURILLO LL, et al. Hierarchical porous silk fibroin/poly(L-lactic acid) fibrous membranes towards vascular scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;166: 1111-1120. [65] KUANG H, WANG Y, SHI Y, et al. Construction and performance evaluation of Hep/silk-PLCL composite nanofiber small-caliber artificial blood vessel graft. Biomaterials. 2020;259:120288. [66] CORDELLE J, MANTERO S. Insight on the endothelialization of small silk-based tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(10):631-644. [67] RODRIGUEZ M, KLUGE JA, SMOOT D, et al. Fabricating mechanically improved silk-based vascular grafts by solution control of the gel-spinning process. Biomaterials. 2020;230:119567. [68] LIU X, OUYANG Q, YAO X, et al. A facile nanopattern modification of silk fibroin electrospun scaffold and the corresponding impact on cell proliferation and osteogenesis. Regen Biomater. 2024; 11:rbae117. [69] CALDIROLI A, PEDERZANI E, PEZZOTTA M, et al. Hybrid fibroin/polyurethane small-diameter vascular grafts: from fabrication toin vivopreliminary assessment. Biomed Mater.2022;17(5).doi:10.1088/1748-605X/ac885a. [70] GUPTA P, MANDAL BB. Fabrication of Small-Diameter Tubular Grafts for Vascular Tissue Engineering Applications Using Mulberry and Non-mulberry Silk Proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2022; 2375:125-139. [71] ALMASI-JAF A, SHAMLOO A, SHAYGANI H, et al. Fabrication of heparinized bi-layered vascular graft with PCL/PU/gelatin co-electrospun and chitosan/silk fibroin/gelatin freeze-dried hydrogel for improved endothelialization and enhanced mechanical properties. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt2):126807. [72] CHAN AHP, FILIPE EC, TAN RP, et al. Altered processing enhances the efficacy of small-diameter silk fibroin vascular grafts. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17461. [73] FUKUDA K, KANEKO J, KIRITANI S, et al. Thick silk fibroin vascular graft: A promising tissue-engineered scaffold material for abdominal vein grafts in middle-sized mammals. Int J Artif Organs. 2024;47(3):190-197. [74] RIZZI S, MANTERO S, BOSCHETTI F, et al. Luminal endothelialization of small caliber silk tubular graft for vascular constructs engineering. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022; 9:1013183. [75] FUKAYAMA T, OZAI Y, SHIMOKAWATOKO H, et al. Evaluation of endothelialization in the center part of graft using 3 cm vascular grafts implanted in the abdominal aortae of the rat. J Artif Organs. 2017;20(3):221-229. |
| [1] | Liu Yang, Liu Donghui , Xu Lei, Zhan Xu, Sun Haobo, Kang Kai. Role and trend of stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels in precise myocardial infarction therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [2] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [3] | Shi Xiaonan, Wu Xuan, Zhang Daxu, Hu Jingjing, Zheng Yazhe, Liu Yutong, Zhao Shuo, Li Weilong, Ye Shujun, Wang Jingyi, Yan Li. Preparation and characterization of 3D printed microstructured silk fibroin scaffold for liver injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3618-3625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

