Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2054-2062.doi: 10.12307/2026.563
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immune inflammatory microenvironment mechanisms in peri-implantitis
Chen Haojie, Wang Dai, Shen Shan
- School of Stomatology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-12Accepted:2025-02-06Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-24 -
Contact:Shen Shan, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Haojie, MS, School of Stomatology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Municipality-University Institute Joint Funding Scheme of Guangzhou Science and Technology Program, No. 202201020031 (to SS); Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Project, No. B2022134 (to SS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Haojie, Wang Dai, Shen Shan. Immune inflammatory microenvironment mechanisms in peri-implantitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
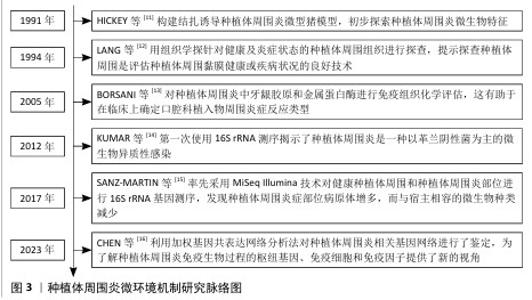
2.1 种植体周围炎微环境机制研究脉络 在过去的30年里,种植体周围炎已成为口腔科的主要疾病负担,针对种植体周围炎的研究在不断进展。1991年,HICKEY等[11]构建了一种结扎诱导种植体周围炎微型猪模型,初步探索种植体周围炎微生物特征。1994年,LANG等[12]用组织学探针对健康及炎症状态的种植体周围组织进行探查,提示探查种植体周围是评估种植体周围黏膜健康或疾病状况的良好技术。2005年,BORSANI等[13]对种植体周围炎中牙龈胶原和金属蛋白酶进行免疫组织化学评估,这有助于在临床上确定口腔科植入物周围炎症反应类型。2012年,KUMAR等[14]第一次使用16S焦磷酸测序,揭示了种植体周围炎是一种以革兰阴性菌为主的微生物异质性感染。2017年,SANZ-MARTIN等[15]率先采用MiSeq Illumina技术对健康种植体周围和种植体周围炎部位进行16S rRNA基因测序,发现种植体周围炎症部位病原体增多,而与宿主相容的微生物种类减少。2023年,CHEN等[16]利用加权基因共表达网络分析法对种植体周围炎相关基因网络进行了鉴定,为了解种植体周围炎免疫生物过程的枢纽基因、免疫细胞和免疫因子提供了新的视角。种植体周围炎微环境机制研究脉络图见图3。"
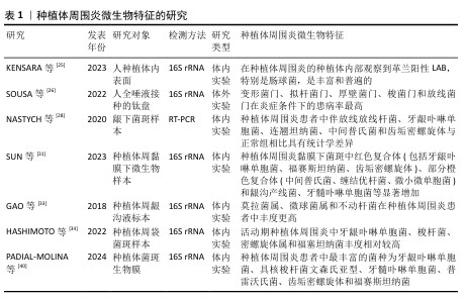
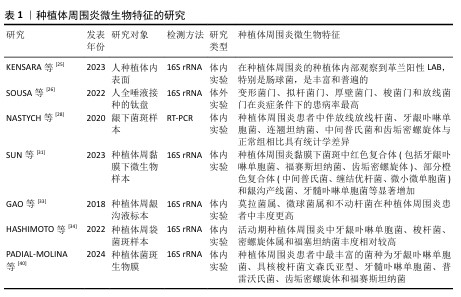
2.2 种植体周围炎相关微生物特征 2.2.1 菌斑生物膜 菌斑生物膜是指口腔微生物在自然牙齿和黏膜表面或人工植入物表面形成的固定群落,这些微生物嵌入其分泌的细胞外基质中,形成的一种膜状结构[17]。牙菌斑生物膜中的细菌及其代谢产物是引发牙周炎和种植体周围炎的关键始动因素,能通过多种机制间接或直接参与炎症的全过程。菌斑生物膜中细菌过度增殖并产生毒力因子,可使种植体周围软硬组织发生炎症病变,导致种植体周围炎的发生[18]。与浮游状态的细菌相比,菌斑生物膜中的细菌具有更强的产酸、耐酸能力和黏附力。菌膜对其中的细菌起到渗透屏障的作用,使细菌对抗菌药物的抗性和对宿主免疫系统的逃避能力增强,继而导致顽固性感染。对种植体周围炎的微生物学特征进行深入分析,对于制定有效的预防和治疗策略至关重要。目前健康种植体及种植体周围炎植体表面细菌的多样性和相关微生物群的组成尚无定论[19]。 2.2.2 种植体周菌群定植过程 微生物定植于硬组织(包括天然牙和种植体)上形成生物膜涉及一系列步骤,包括黏附、生长和成熟[6],定植在植体的整个生命周期中都存在,在植体植入后几分钟内即可发生[20]。通过静电吸引作用,细菌实现对种植体表面的黏附,随后分泌胞外聚合物。细菌聚集引起宿主组织的炎症反应,并且胞外聚合物能使细菌对于抗菌药物具有一定的抗性[6-21]。相关研究表明,细菌于种植体植入口腔30 min后开始定植于种植体表面,定植的细菌在1 h内能被检出,2周内就可形成复杂的菌斑生物膜,3个月左右菌落结构趋于稳定,根据细菌黏附于获得性膜表面的时间可分为早、中、晚期定植细菌,因为不是所有的细菌都能直接黏附于获得性膜表面[22]。SILVA-BOGHOSSIAN等[23]研究表明,口内龈下种植体表面在种植体植入6 d后即可表现出多样的微生物群,6个月后,龈下种植体周围微生物物种水平与天然牙相似。 2.2.3 种植体周围炎黏膜菌群 种植体周围炎微生物群是高度多样化的,健康种植体的微生物群组成与发生种植体周围炎种植体的微生物群组成显著不同,存在丰富度及多样性的差异[24-26]。种植体周围炎没有特异性的细菌[27],相关研究表明,种植体周围炎相关菌群主要包括革兰阳性需氧菌、革兰阴性厌氧菌、梭形杆菌及螺旋体等[25-28],在种植体周围炎中检出的关键致病菌主要有牙龈卟啉单胞菌、齿垢密螺旋体、福赛斯坦纳菌、金黄色葡萄球菌等,均属于红色复合体的一部分[26-29],与种植体周围炎的发生密切相关。另一项研究也指出,红色复合体与种植体周围炎和严重的牙周疾病关系密切,具有强大的诱导组织炎症的能力,被认为是主要病原体[30]。除红色复合体外,橙色复合体的部分成员也是种植体周围炎的病原体,如中间普氏菌、缠结优杆菌和微小微单胞菌[31]。此外,有文献表明,中间普氏菌(Prevotella intermedia)、牙周假单胞菌(Centipeda periodontii)、具核梭杆菌(Fusobacterium nucleatum)、结节真杆菌(Eubacterium nodatum)、龈沟产线菌(Filifactor alocis)等与种植体周围炎联系密切[24-25,32]。莫拉菌属、微球菌属和不动杆菌在种植体周围炎患者中的丰度更高[15,33-34]。 16S rRNA测序和宏基因组学的发展,提供了更详细和准确的种植体周围微生物群特征[30],更多与种植体周围炎有关的微生物被检出,如莫拉氏菌属、微球菌属、链球菌和梭杆菌。其中,具核梭杆菌是传统的牙周致病菌中与种植体周围炎密切相关的菌群,不仅在菌斑生物膜的形成中起到关键作用,还携带有多种毒力因子,这些因子能够导致牙周组织的破坏[29,35-36]。具核梭杆菌还可以通过表达多种黏附素促进牙菌斑生物膜的形成,在早期和晚期定植菌之间充当“桥梁”,增强生物膜的稳定性[37]。KENSARA等[25]通过16S rRNA基因测序发现,种植体周围炎内表面的核心革兰阳性LAB,特别是肠球菌,十分丰富和普遍。福赛斯坦纳菌是一种革兰阴性厌氧杆菌,在严重牙周病及种植体周围炎中检出率高,证明它与种植体周围炎之间有着高度相关性[29-31]。 此外,种植体周围炎临床指标与其致病菌群的改变具有相关性。研究表明,种植体周探诊深度的增加与微生物生态失调水平有显著关联,随着探诊深度的增加,生物群落多样性显著降低,表明种植体周袋越浅其物种丰富度越高,反之亦然。奈瑟氏球菌、韦荣氏球菌、红杆菌科、奇异劳托氏菌、溶囊奥里杆菌在样品中随着探诊深度的增加而显著降低[38]。SUN等[31]采用统计学方法确定了与探诊深度加深存在显著相关的9种细菌,其中与探诊深度加深呈显著负相关的是空间罗氏菌,而齿垢密螺旋体、福赛斯坦纳菌、依赖杆菌属、脱硫球菌属、龈沟产线菌、苛求依赖杆菌、牙龈卟啉单胞菌和牙髓卟啉单胞菌与探诊深度呈正相关。密螺旋体HMT-257与种植体周围炎的严重程度密切相关,与放射学骨丢失、探诊深度和化脓显著相关[39]。同时,固有层中的黑色素瘤缺乏因子2与增效菌门相关,固有层中的NLRP3与增效菌门和特纳菌门相关,上皮中的白细胞介素1β与弯曲菌门(Campylobacterota)相关,表明菌群种类与白细胞介素1β和某些炎性小体的表达有关[40]。微生物群会随着种植体周围炎进展的变化而变化,活动性种植体周围炎中牙龈卟啉单胞菌属、齿垢密螺旋体属、福赛斯坦纳菌属较缓解性种植体周围炎多,而在缓解期,乳酸杆菌及双歧杆菌比例上升[34]。 文章列举了关于种植体周围炎微生物特征的研究,见表1。种植体周围炎是一种混合感染,由多种细菌共同作用导致的,包括难以培养的革兰厌氧阳性杆菌和革兰阴性杆菌和牙周致病菌以及机会性致病菌(如葡萄球菌和肠杆菌科),有利于复杂生物膜的形成和疾病的进展,其中红色复合体和橙色复合体部分成员在种植体周围炎的发生发展中起着重要作用。得益于先进微生物学技术,包括二代测序、聚合酶链式反应、DNA-DNA棋盘式杂交等分子分析技术,使得人们对种植体周围炎微生物的多样性认识更加全面,识别这些微生物并了解其在种植体周围炎发生发展中的作用,有利于更好地制定预防和治疗策略。 "
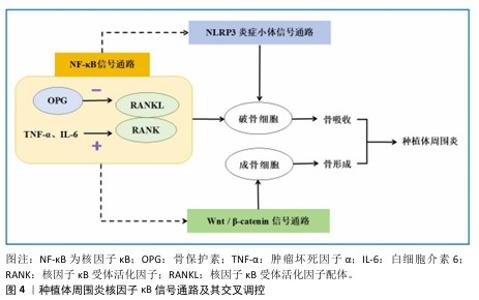
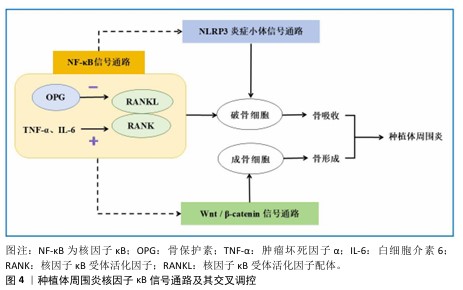
2.3 种植体周围炎相关免疫应答机制 2.3.1 种植体骨结合过程 种植体骨结合,即骨组织与有负荷的种植体表面直接接触,无纤维组织等非骨组织介入种植体与骨组织之间,被定义为一种异物反应,其中界面骨的形成是一种防御反应[41]。种植体骨结合过程按发生先后顺序可分为4期,分别为凝血期、炎症期、增殖期、骨改建期[42],种植体植入后,血液迅速包裹植体,随后蛋白质等快速吸附于植体表面,血浆中的血小板和凝血级联反应被激活,在种植体表面形成血凝块[43]。随后进入炎症期,机体释放大量的细胞因子,包括血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β和生长因子等,中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞分别参与急性和慢性炎症反应,随着炎症反应的发展,成纤维细胞和新生血管开始增殖,形成肉芽组织,这种新生组织逐渐取代种植体周围的血凝块,为后续的骨结合奠定基础。增殖期的骨祖细胞分化为成骨细胞,在种植体表面形成编织骨,随后免疫细胞诱导的破骨细胞在种植体与种植窝之间压力较大的地方发挥作用,使机械稳定性向生物稳定性转变,伴随一定程度的骨吸收和新骨生成。种植体植入约3个月后骨结合初步形成。 2.3.2 种植体周围炎的免疫应答反应 种植体在颌骨内形成稳定的骨结合后,在咬合因素、吸烟、种植体周生物膜的形成及局部不良刺激等因素的作用下,种植体周围发生进行性骨吸收,甚至破坏骨结合。宿主免疫反应在种植体周围炎的病理发展过程中起着重要作用[44]。免疫细胞通过释放调节因子影响成骨细胞与破骨细胞的生成,参与骨的生理和病理过程,进而调控骨再生。机体受到抗原刺激后,免疫细胞会对抗原分子进行识别,随后活化、增殖及分化并产生免疫产物,发挥特异性免疫效应,这个过程体现了免疫系统各部分的综合功能,机体得以维持内环境的稳定。根据识别机制、获得方式以及作用机制,免疫应答可分为适应性免疫和固有免疫两大类[45]。 适应性免疫又称为特异性免疫,指的是机体内抗原特异性T淋巴细胞与B淋巴细胞在接收到特定抗原刺激之后,经历激活、增殖及分化等过程转变为效应细胞,并引发一系列生物学效应的过程,表现为高度特异性的抗原反应并形成长期记忆[43]。T/B淋巴细胞通过调节促炎细胞因子、抗炎细胞因子等调控种植体周围炎的炎症进展和骨改建过程。T淋巴细胞具有多种分化状态,成熟T淋巴细胞可分为CD4+辅助性细胞(滤泡辅助性T细胞、辅助性T细胞1、辅助性T细胞2、辅助性T细胞17和调节性T细胞)和CD8+杀伤细胞,在种植体周围炎中起重要作用[16,46]。辅助性T细胞1细胞释放的CD40L和干扰素γ能刺激巨噬细胞的活化,使巨噬细胞分泌白细胞介素12和白细胞介素18,主要发挥促炎作用[47]。辅助性T细胞17可分泌多种细胞因子,如白细胞介素17、白细胞介素21和干扰素γ等,这些因子在加剧骨吸收过程中扮演重要角色[48-49],并可通过产生白细胞介素21及白细胞介素23等细胞因子参与介导与牙槽骨破坏相关的炎症反应[50]。另外,辅助性T细胞17细胞不仅可以通过表达核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)直接激活破骨细胞,其分泌的白细胞介素17还具有双重作用:一方面,白细胞介素17可以直接作用并激活破骨细胞;另一方面,白细胞介素17还具有促进炎症反应的作用,可诱导其它免疫细胞产生肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1,从而形成有利于破骨细胞活性的炎性微环境[49]。调节性T细胞具有免疫抑制功能,可以通过阻止巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL的产生抑制破骨细胞的产生,与抑制骨吸收有关[51],并且在辅助性T细胞17的诱导作用下,能抑制维甲酸相关孤儿受体γT,促进调节性T细胞分化[52]。FOXP3分别是辅助性T细胞17细胞和调节性T细胞分化过程中不可或缺的特异性转录因子[50]。研究表明,在种植体周围炎发生时,种植体周围组织内的维甲酸相关孤儿受体γT与FOXP3基因表达水平均有所增加,辅助性T细胞17/调节性T细胞之间的比例升高致使RANKL过度表达,引起牙槽骨的丢失[49,53-54]。 B细胞是体液免疫反应的主要参与者,在炎症组织中大量浸润并能够分泌多种细胞因子和抗体,对骨平衡起到重要的调节作用[55]。研究显示,特定类型的记忆B细胞(即CD27+CD38-记忆B细胞)能通过促进RANKL的表达,从而增加破骨细胞的生成[56]。将B细胞内的RANKL基因敲除,不仅B细胞会出现发育异常,同时其抗体分泌及抗原提呈的功能也会完全丧失,这说明上调的RANKL表达与B细胞自身发育成熟密切相关[57-58]。 B10细胞是一种调节性B细胞,主要分泌白细胞介素1,而白细胞介素10则主要由辅助性T细胞2及调节性T细胞表达,说明T细胞与B细胞之间具有一定的相互作用关系。研究发现,B10细胞的激活可以促进调节性T细胞的活化,同时能够抑制辅助性T细胞17的局部增殖,调节宿主的局部免疫反应,抑制牙槽骨的炎症性吸收[50,54,58]。Toll样受体4是脂多糖的膜受体,参与了B细胞介导的体液免疫,是参与非特异性免疫的一类重要蛋白质分子[50],可通过调节免疫B细胞浸润、RANKL/骨保护素表达比例和差异炎症因子的产生介导种植体周围炎骨丢失[59]。与此同时,有研究表明,RANKL/骨保护素比值可能是决定骨吸收的关键因素,骨保护素下调和RANKL上调可能会导致骨丧失[60]。 参与固有免疫应答的细胞主要有巨噬细胞、单核细胞、中性粒细胞、朗格汉斯细胞等,它们能立即识别外来物质,激发非特异性炎症反应[43]。巨噬细胞在炎症反应和宿主防御中发挥着关键作用,特别是在非特异性免疫反应中。这些细胞能够根据体内外的不同刺激展现出显著的功能差异,并在M1型和M2型巨噬细胞之间进行动态转换。M1型为促炎性巨噬细胞,分泌白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎细胞因子[61],使种植体骨结合的界面过度纤维化,甚至造成种植体骨整合的失败。M2型巨噬细胞是具有抗炎和促修复功能的细胞,主要通过分泌多种抗炎细胞因子(如白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10等)来抑制炎症反应,并促进组织愈合和成骨分化[20,54]。在种植体植入后,其微生物群和代谢产物可诱导巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞、树突细胞等产生促炎细胞因子如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17、肿瘤坏死因子α、巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1和巨噬细胞趋化蛋白1,导致RANKL表达增加[24,62-63],RANKL与前体破骨细胞表面的核因子kB受体活化因子结合,从而促进破骨细胞的增殖、分化与成熟,引起骨的破坏吸收[54]。巨噬细胞还可吞噬小于10 μm的钛颗粒,吞噬后巨噬细胞将有更大概率向M1表型极化分化,导致破骨细胞活化,进而造成种植体周骨丧失;而对于较大的钛颗粒,炎症细胞能转化为多核巨细胞吞噬颗粒[64-65]。树突细胞作为一种抗原呈递细胞,是固有免疫与适应性免疫之间的媒介,其成熟程度决定了树突细胞在免疫反应中的具体功能,未成熟树突细胞主要通过分泌白细胞介素10等抑炎细胞因子来抑制炎症反应,而成熟树突细胞则通过分泌白细胞介素12和干扰素γ等促炎细胞因子来增强免疫应答。中性粒细胞能促进促炎性细胞因子白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α的释放,进而激活种植体周围炎中的溶骨和炎性组织损伤[66]。中性粒细胞促进RANKL诱导的骨髓巨噬细胞分化为破骨细胞,可以通过分泌弹性蛋白酶降解骨保护素,从而促进破骨细胞的生成[67]。 综上所述,固有免疫应答和适应性免疫应答在种植体周围炎的免疫反应中相互协作,共同调控炎症进程,固有免疫不仅在初期识别并应对病原体,还为适应性免疫提供了必要的信号和支持,而适应性免疫则通过高度特异性的机制进一步增强对病原体的清除能力和炎症调控能力,两者协同作用,共同调控种植体周围炎的发展。种植体自身的材料种类、表面形貌及生物活性等因素,显著影响其介导的免疫反应类型和范围,这些因素不仅决定了种植体与周围组织的相互作用方式,还对长期的生物学反应和种植体的成功率具有重要影响。相比于亲水材料,疏水材料更能促进免疫细胞的黏附,从而引起植入位点的局部免疫反应。就表面电荷而言,阳离子通过影响信号传导促进炎症反应。种植体材料的表面粗糙度可影响免疫细胞的黏附和扩散,调节炎性细胞因子和趋化因子的释放。通过药物、生长因子、蛋白质等修饰种植体表面、模拟纳米形貌及介导巨噬细胞的增殖活化可调节局部微环境,控制炎症,促进骨再生。因此,通过种植体材料的定向修饰、调控免疫反应以创造利于骨结合和骨再生的局部免疫微环境,对种植体周围炎的预防和治疗具有重要意义。 2.4 相关信号通路 种植体周病的发生发展与多条信号转导通路的调控密切相关,深入剖析各条信号通路的调控作用及其交互调控机制,对揭示种植体周病的调控机制、发掘新的具有特异性的靶向治疗方法具有重要意义[68]。在种植体周围炎进展过程中,发挥重要作用的信号转导通路主要有Wnt/β-catenin信号通路、核因子κB信号通路、NLRP3炎症小体信号通路等。 Wnt信号转导通路分为经典β-catenin依赖性途径和非经典β-catenin非依赖性通路,经典和非经典Wnt信号通路在正常组织损伤中起着重要作用[69]。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化、成骨细胞和破骨细胞的增殖分化及功能密切相关[70]。APPELMAN-DIJKSTRA等[70]通过喂养鼠李糖乳杆菌GG给小鼠,对其骨髓和肠道中的调节性T细胞进行诱导扩增,刺激其CD8+T细胞上调并与调节性T细胞相互作用,增加Wnt10b(Wnt信号配体)的分泌,从而激活Wnt/β-catenin通路,促进小鼠骨量增加。 ZHANG等[71]通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术分析了接受种植体修复患者以及患有种植体周围炎患者的牙龈组织样本,结果显示种植体周围炎患者牙龈组织样本中Wnt5a的表达水平显著升高;进一步的体外实验揭示,在被牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染的巨噬细胞内Wnt5a的表达量同样增加,并且当利用基因敲除技术降低Wnt5a表达后,与种植体周围炎症相关的几种生物标志物(包括白细胞介素1β、基质金属蛋白酶2及单核细胞趋化蛋白1)表达水平均呈现下降趋势。SUI等[72]通过构建一种破骨细胞中β-catenin过表达的小鼠模型,进行CT断层扫描和组织形态学分析发现,这些小鼠表现出生长迟缓和骨量减少的现象,实验结果表明,在破骨细胞中激活β-catenin能够促进破骨细胞的形成,进而导致小鼠出现骨质流失的情况。Wnt/β-catenin还可通过调节骨保护素的表达,从而调控骨代谢[60]。 核因子κB信号通路作为一条经典的炎症反应路径,在骨免疫系统以及破骨细胞与成骨细胞之间的动态平衡中扮演着关键角色,尤其在骨微环境中具有重要意义[54-68]。研究表明,种植体周围炎患者龈沟液中的白细胞介素1β过表达可能是通过激活核因子κB信号传导途径实现的。特别地,RANKL/核因子κB受体活化因子/骨保护素系统在调控破骨细胞功能方面发挥着核心作用。RANKL与位于破骨细胞表面或其前体细胞上的核因子κB受体活化因子结合后,能够激活并促进破骨细胞的分化过程;而骨保护素则通过竞争性地阻断RANKL与核因子κB受体活化因子的结合,抑制破骨细胞进一步分化和成熟的过程[73]。另外,炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的表达水平升高,能引起RANKL/骨保护素的比率增加[50],这进一步加剧了种植体周围炎的炎症进展。 NLRP3炎症小体是一种存在于细胞质中的多蛋白复合体,在维持免疫平衡和调控炎症进程中发挥着关键作用。当牙周组织发生炎症时,炎症小体调节蛋白的表达减少,导致NLRP3及其下游效应分子白细胞介素1β的表达增加[74]。研究进一步表明,当NLRP3炎症小体的表达受到抑制时,诸如白细胞介素1β等促炎细胞因子的表达也会相应减少,这种变化削弱了机体对抗病原体的能力,为菌斑生物膜提供了逃逸局部免疫监视并持续引发炎症反应的机会[75]。李小红等[76]通过实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应和蛋白质印迹法对531例行牙种植修复术患者的NLRP3、caspase-1、白细胞介素1β的表达进行检测,发现种植体周围炎和种植体周围黏膜炎患者龈沟液中的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、NLRP3、caspase-1、白细胞介素1β mRNA和蛋白水平均高于非感染组患者,并且与种植体周围黏膜炎患者相比,种植体周围炎患者龈沟液中的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6水平更高。GALINDO--MORENO等[77]收集了21例患者(33个种植体)以及15例牙周健康患者的牙龈组织,通过免疫组化检测发现NLRP3和黑色素瘤缺乏因子2炎性体活化诱导的白细胞介素1β/caspase-1在种植体周围炎的发生发展中起着重要作用。这说明NLRP3炎症小体激活参与了种植体周围感染后的免疫防御过程,有助于临床上辅助诊断种植体修复术后细菌感染及评估种植体周围炎的发生、发展情况。 综上所述,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路、核因子κB信号通路及NLRP3炎症小体信号通路在种植体周围炎的发生与发展过程中扮演了重要角色,不仅参与了炎症反应,还调控着骨改建的过程;此外,这些信号通路并非独立运作,而是通过复杂的相互作用和正负反馈调节机制共同影响骨代谢的平衡。其中,核因子κB信号通路与其他两条信号通路之间存在紧密联系,在特定条件下,抑制核因子κB信号通路能够提升β-catenin和Runx2的表达水平,从而促进骨形成[78];阻断核因子κB的磷酸化过程能减少NLRP3、白细胞介素1β及白细胞介素18前体的表达,有效抑制NLRP3炎症小体的激活[79],这表明核因子κB不仅在局部或全身炎症反应中发挥关键作用,还在多条信号通路的交互调控中起到桥梁作用。因此,针对核因子κB信号通路的干预措施在调节骨代谢和控制炎症反应方面具有重要意义。种植体周围炎核因子κB信号通路及其交叉调控见图4。深入探索各条信号通路在种植体周围炎中的发生发展中的作用,将有利于为种植体周围炎的治疗提供新途径。"
| [1] GUGLIELMOTTI MB, OLMEDO DG, CABRINI RL. Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontol 2000. 2019; 79(1):178-189. [2] BLANCO C, LIñARES A, DOPICO J, et al. Peri-implantitis, systemic inflammation, and dyslipidemia: a cross-sectional biochemical study. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021;51(5):342-351. [3] DIAZ P, GONZALO E, VILLAGRA LJG, et al. What is the prevalence of peri-implantitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):449. [4] CATON JG, ARMITAGE G, BERGLUNDH T, et al. A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions – Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;89(S1):S1-S8. [5] NG E, TAY JRH, BALAN P, et al. Metagenomic sequencing provides new insights into the subgingival bacteriome and aetiopathology of periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2021; 56(2):205-218. [6] BANU RAZA F, VIJAYARAGHAVALU S, KANDASAMY R, et al. Microbiome and the inflammatory pathway in peri-implant health and disease with an updated review on treatment strategies. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(2):84-91. [7] SHI Y, TONG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Microbial profiles of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: Submucosal microbial dysbiosis correlates with disease severity. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(2):172-183. [8] LI Y, LI X, GUO D, et al. Immune dysregulation and macrophage polarization in peri-implantitis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1291880. [9] 刘官娟,宋娜,安哲庆,等.宏基因组学与种植体周围炎[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(34):5511-5516. [10] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(10):626-642. [11] HICKEY JS, O’NEAL RB, SCHEIDT MJ, et al. Microbiologic characterization of ligature-induced peri-implantitis in the microswine model. J Periodontol. 1991;62(9):548-553. [12] LANG NP, WETZEL AC, STICH H, et al. Histologic probe penetration in healthy and inflamed peri-implant tissues. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994;5(4):191-201. [13] BORSANI E, SALGARELLO S, MENSI M, et al. Histochemical and immunohistochemical evaluation of gingival collagen and metalloproteinases in peri-implantitis. Acta Histochem. 2005;107(3):231-240. [14] KUMAR PS, MASON MR, BROOKER MR, et al. Pyrosequencing reveals unique microbial signatures associated with healthy and failing dental implants. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(5):425-433. [15] SANZ-MARTIN I, DOOLITTLE-HALL J, TELES RP, et al. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(12):1274-1284. [16] CHEN LW, JIN SH, LU Q, et al. Identification of immunological bioprocesses involved in peri-implantitis using weighted gene co-expression network analysis. J Periodontol. 2023;94(9):1078-1089. [17] JAKUBOVICS NS, GOODMAN SD, MASHBURN-WARREN L, et al. The dental plaque biofilm matrix. Periodontol 2000. 2021;86(1):32-56. [18] 文言,王宇蓝.菌斑生物膜与种植体周围炎相关研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2024, 32(9):730-736. [19] DE MELO F, MILANESI FC, ANGST PDM, et al. A systematic review of the microbiota composition in various peri-implant conditions: data from 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Arch Oral Biol. 2020; 117:104776. [20] ALVES CH, RUSSI KL, ROCHA NC, et al. Host-microbiome interactions regarding peri-implantitis and dental implant loss. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):425. [21] CHOUDHARY P, SINGH S, AGARWAL V. Microbial Biofilms. 2020. doi:10.5772/intechopen.90790. [22] WANG CW, ASHNAGAR S, GIANFILIPPO RD, et al. Laser-assisted regenerative surgical therapy for peri-implantitis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2021; 9(23):378-388. [23] SILVA-BOGHOSSIAN CM, DUARTE PT, SILVA DGD, et al. Colonization dynamics of subgingival microbiota in recently installed dental implants compared to healthy teeth in the same individual: a 6-month prospective observational study. J Appl Oral Sci. 2023;31:e20230134. [24] KENSARA A, HEFNI E, WILLIAMS MA, et al. Microbiological Profile and Human Immune Response Associated with Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J Prosthodont. 2021; 30(3):210-234. [25] KENSARA A, SAITO H, MONGODIN EF, et al. Microbiological profile of peri-implantitis: Analyses of microbiome within dental implants. J Prosthodont. 2023;32(9): 783-792. [26] SOUSA V, SPRATT D, DAVRANDI M, et al. Oral Microcosm Biofilms Grown under Conditions Progressing from Peri-Implant Health, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(21):14088. [27] BERGLUNDH T, ARMITAGE G, ARAUJO MG, et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45 Suppl 20:S286-s291. [28] NASTYCH O, GONCHARUK-KHOMYN M, FOROS A, et al. Comparison of Bacterial Load Parameters in Subgingival Plaque during Peri-implantitis and Periodontitis Using the RT-PCR Method. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2020;54(1):32-43. [29] GAZIL V, BANDIAKY ON, RENARD E, et al. Current Data on Oral Peri-Implant and Periodontal Microbiota and Its Pathological Changes: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms. 2022;10(12):2466. [30] DI SPIRITO F, GIORDANO F, DI PALO MP, et al. Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms. 2024;12(6):1137. [31] SUN F, LIU J, LI SQ, et al. [Profiles and differences of submucosal microbial in peri-implantitis and health implants: A cross-sectional study]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023;55(1):30-37. [32] HEREKAR M, SETHI M, PRITHVIRAJ DR, et al. A Clinical Study Evaluating Changes in the Microbial Flora Around Dental Implants During Various Stages of Implant Restoration. Implant Dent. 2015;24(5): 527-532. [33] GAO X, ZHOU J, SUN X, et al. Diversity analysis of subgingival microbial bacteria in peri-implantitis in Uygur population. Medicine Baltimore). 2018;97(5):e9774. [34] HASHIMOTO Y, OKADA S, YASUDA K, et al. Microbial differences between active and remission peri-implantitis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):5284. [35] BANU RAZA F, VIJAYARAGAVALU S, KANDASAMY R, et al. Microbiome and the inflammatory pathway in peri-implant health and disease with an updated review on treatment strategies. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(2):84-91. [36] DE ANDRADE KQ, ALMEIDA-DA-SILVA CLC, COUTINHO-SILVA R. Immunological Pathways Triggered by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum: Therapeutic Possibilities? Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:7241312. [37] BRENNAN CA, GARRETT WS. Fusobacterium nucleatum - symbiont, opportunist and oncobacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019; 17(3):156-166. [38] KRöGER A, HüLSMANN C, FICKL S, et al. The severity of human peri-implantitis lesions correlates with the level of submucosal microbial dysbiosis. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(12):1498-1509. [39] BELIBASAKIS GN, MANOIL D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1): 21-28. [40] PADIAL-MOLINA M, MONTALVO-ACOSTA S, MARTíN-MORALES N, et al. Correlation between Inflammasomes and Microbiota in Peri-Implantitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(2):961. [41] ALBREKTSSON T, WENNERBERG A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019; 21 Suppl 1:4-7. [42] SARTORETTO SC, CALASANS-MAIA J, RESENDE R, et al. The Influence of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Surface in the Early Stages of Osseointegration: A Multiparameter Animal Study in Low-Density Bone. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15: 8803-8817. [43] MARIANI E, LISIGNOLI G, BORZì RM, et al. Biomaterials: Foreign Bodies or Tuners for the Immune Response? Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):636. [44] CHEN X, ZHAO Y. Genetic Involvement in Dental Implant Failure: Association With Polymorphisms of Genes Modulating Inflammatory Responses and Bone Metabolism. J Oral Implantol. 2019;45(4): 318-326. [45] 尹昭懿,李效宇,王子璇,等.免疫反应在种植体周围炎中的作用研究进展[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2022,36(1):46-50. [46] SARAVIA J, CHAPMAN NM, CHI H. Helper T cell differentiation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(7):634-643. [47] MANSOORI MN, SHUKLA P, KAKAJI M, et al. IL-18BP is decreased in osteoporotic women: Prevents Inflammasome mediated IL-18 activation and reduces Th17 differentiation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33680. [48] YOU L, CHEN L, PAN L, et al. SOST Gene Inhibits Osteogenesis from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inducing Th17 Cell Differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):1030-1040. [49] ZHU L, HUA F, DING W, et al. The correlation between the Th17/Treg cell balance and bone health. Immun Ageing. 2020;17:30. [50] 吴东潮,何东宁,余飞燕,等.种植体周围炎免疫应答机制的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2024,25(5):371-377,388. [51] 钱治,仲泽远,崔元斌,等.T细胞与骨代谢[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(11):7. [52] SUN L, FU J, ZHOU Y. Metabolism Controls the Balance of Th17/T-Regulatory Cells. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1632. [53] CAFFERATA EA, CASTRO-SAAVEDRA S, FUENTES-BARROS G, et al. Boldine inhibits the alveolar bone resorption during ligature-induced periodontitis by modulating the Th17/Treg imbalance. J Periodontol. 2021; 92(1):123-136. [54] 廖安琪,杨仁丽,杨醒眉.种植体周围炎的免疫应答机制及其影响因素的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2021,41(12):1143-1147. [55] TSAI DY, HUNG KH, CHANG CW, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of B cell responses and the implication in B cell-related diseases. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):64. [56] HAN Y, JIN Y, MIAO Y, et al. Improved RANKL expression and osteoclastogenesis induction of CD27+CD38- memory B cells: A link between B cells and alveolar bone damage in periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54(1):73-80. [57] FUJIWARA Y, PIEMONTESE M, LIU Y, et al. RANKL Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand) Produced by Osteocytes Is Required for the Increase in B Cells and Bone Loss Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Mice. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(48):24838-24850. [58] 林晓萍,韩亚琨.B细胞骨免疫在牙周炎中的作用[J].口腔疾病防治,2020,28(4): 205-213. [59] 韦雨杏,董皓,韦惠平,等.种植体周围炎炎性组织差异表达基因的筛选及验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30): 4844-4849. [60] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:6910312. [61] GALARRAGA-VINUEZA ME, OBREJA K, RAMANAUSKAITE A, et al. Macrophage polarization in peri-implantitis lesions. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(4):2335-2344. [62] CHENG X, ZHOU X, LIU C, et al. Oral Osteomicrobiology: The Role of Oral Microbiota in Alveolar Bone Homeostasis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:751503. [63] THEODORIDIS C, DOULKERIDOU C, MENEXES G, et al. Comparison of RANKL and OPG levels in peri-implant crevicular fluid between healthy and diseased peri-implant tissues. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2022; 26(1):823-836. [64] CALLEJAS JA, GIL J, BRIZUELA A, et al. Effect of the Size of Titanium Particles Released from Dental Implants on Immunological Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7333. [65] ZHOU F, ZHANG G, WU Y, et al. Inflammasome Complexes: Crucial mediators in osteoimmunology and bone diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022; 110:109072. [66] BASERI M, RADMAND F, HAMEDI R, et al. Immunological Aspects of Dental Implant Rejection. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020: 7279509. [67] SUGISAKI R, MIYAMOTO Y, YOSHIMURA K, et al. Possible involvement of elastase in enhanced osteoclast differentiation by neutrophils through degradation of osteoprotegerin. Bone. 2020;132:115216. [68] 霍花,宋斌,廖健.种植体周病的相关信号通路机制及其交互调控作用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2024,4(5):310-314. [69] HU L, CHEN W, QIAN A, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling components and mechanisms in bone formation, homeostasis, and disease. Bone Res. 2024;12(3):469-501. [70] APPELMAN-DIJKSTRA NM, PAPAPOULOS SE. Clinical advantages and disadvantages of anabolic bone therapies targeting the WNT pathway. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(10):605-623. [71] ZHANG Q, LIU J, MA L, et al. Wnt5a is involved in LOX-1 and TLR4 induced host inflammatory response in peri-implantitis. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(2):199-208. [72] SUI X, DENG S, LIU M, et al. Constitutive Activation of β-Catenin in Differentiated Osteoclasts Induces Bone Loss in Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2091-2102. [73] AMIN N, BOCCARDI V, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(3):363-371. [74] ARAL K, BERDELI E, COOPER P, et al. Differential expression of inflammasome regulatory transcripts in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2019;91:606-616. [75] 李碧榕,孟维艳.NLRP3炎症小体在种植体周围炎中的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2022,38(12):1119-1123. [76] 李小红,郝志军,许应宏,等.牙种植修复术后感染对NLRP3信号通路及炎症细胞因子水平的影响[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2022,32(8):1185-1188. [77] GALINDO-MORENO P, MONTALVO-ACOSTA S, MARTíN-MORALES N, et al. Inflammasomes NLRP3 and AIM2 in peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2023;34(12):1342-1353. [78] XU W, LU Y, YUE J, et al. Occlusal trauma inhibits osteoblast differentiation and bone formation through IKK-NF-κB signaling. J Periodontol. 2020;91(5):683-692. [79] YAO L, HUANG C, DAI J. Staphylococcus aureus enhances osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by stimulating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(11):9395-9403. |
| [1] | Yang Qiongqiong, Liu Wei. Comparison of performance and clinical effects of zirconia and titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2063-2071. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||