Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 577-585.doi: 10.12307/2026.545
Previous Articles Next Articles
Endoscopic lumbar canal decompression for upper lumbar spinal stenosis: a comparison of biomechanical stability of three surgical models
Ma Jingbo1, 2, Yang Guangnan2, Liu Jiang2, Jiang Qiang2, Zhang Hanshuo2, Han Jiaheng2, Ding Yu1, 2
- 1Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Sixth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
-
Received:2024-11-16Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-03 -
Contact:Ding Yu, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Sixth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China -
About author:Ma Jingbo, MS, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Sixth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82274637 (to DY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Jingbo, Yang Guangnan, Liu Jiang, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Han Jiaheng, Ding Yu. Endoscopic lumbar canal decompression for upper lumbar spinal stenosis: a comparison of biomechanical stability of three surgical models[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 577-585.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
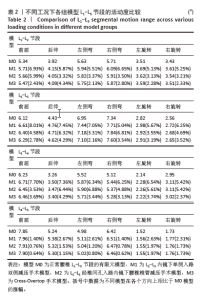
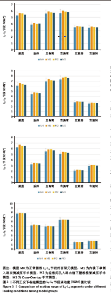
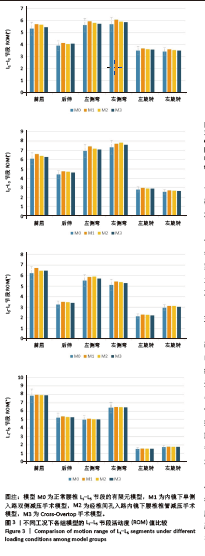
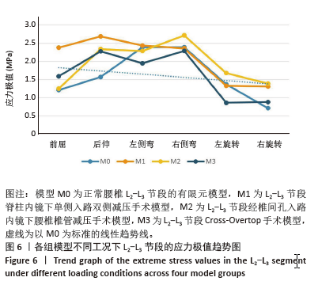
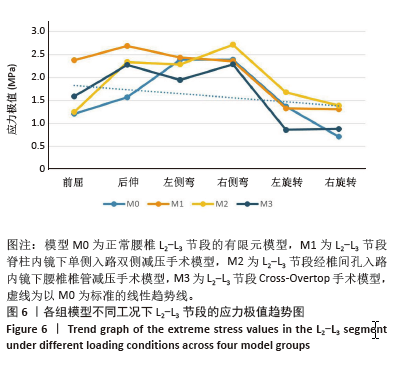
2.1 模型的有效性验证 在成功构建全腰椎节段有限元模型M0之后,模拟了如上6种工况下的腰椎运动表现,并将结果与YAMAMOTO等[17]、CHEN等[18]研究者的实体模型以及有限元模型的生物力学分析结果进行了比较。这一对比验证了此次构建的完整模型M0在上述6种工况下的各节段活动度值与参考文献中的数值和趋势高度一致,表明模型M0具备良好的仿真准确性,能够有效应用于此次研究并进行下一步分析。 2.2 各组模型整体关节活动度值比较 相较于初始的M0模型,手术模型M1、M2、M3在6种不同工况下的各节段活动度值及活动度增长率见表2及图3。从整体来看,所有3种手术模型在这6种工况下的整体关节活动度均有所上升,特别是模型M1和M2在前屈、后伸及右旋转时的活动度增幅较为显著,而在其他工况下的增加幅度均未超过7%,具体见图4。与模型M3相比,模型M1在后伸和左侧弯工况下的整体关节活动度略有提升,但腰椎L1-L5节段仍维持在稳定状态,未出现失稳现象。"
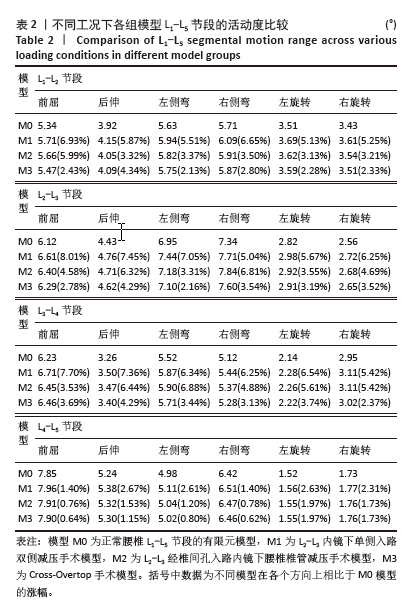

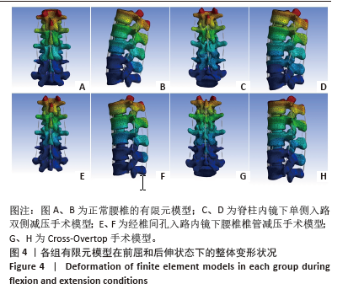
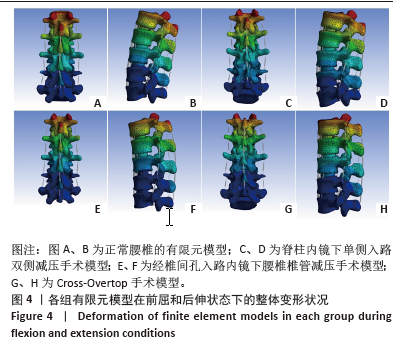
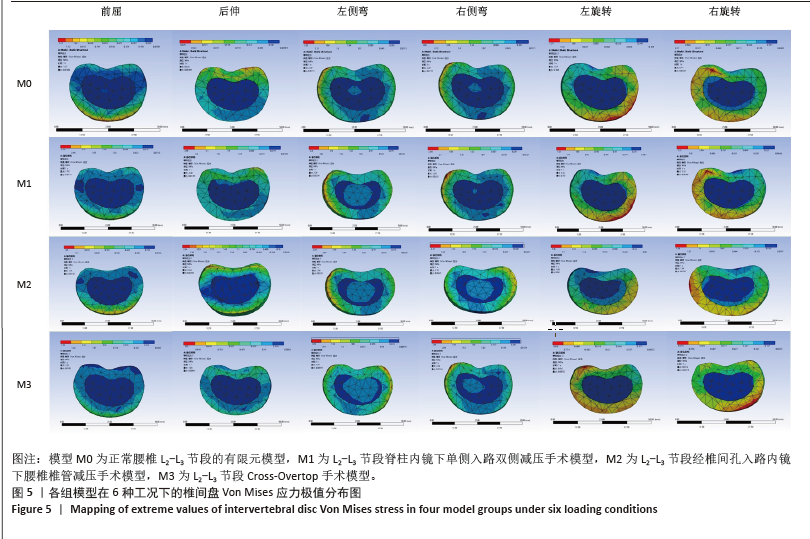
2.3 手术方式的有效性验证 建立的手术模型基于实际临床手术综合评估后的成功减压病例,确保了手术路径和减压范围的一致。根据表2结果显示,所有手术在术后均将腰椎节段的活动度增加控制在9%以内,仅有M1的L2-L3节段活动度在前屈活动中增长8.01%,其余模型在各方向上的活动度均低于8%。这一结果表明,3种术式在实现椎管充分减压的同时,均能有效维持脊柱节段的稳定性,符合微创手术中对于脊柱活动性控制的要求,避免了活动度的过度增加,从而确保了手术的有效性。 2.4 各组模型椎间盘Von Mises应力极值的比较 见图5。 与模型M0相比,模型M1、M2和M3的椎间盘应力极值在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋转及右旋转载荷下都有所增加。与之对应,各纤维环的应变值也有所增大。模型M1的椎间盘应力的极值在前屈和后伸载荷条件下增加最为显著,而在左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋转及右旋转载荷下,增加的幅度都不超过5%,详见图6。"
| [1] JENSEN RK, HARHANGI BS, HUYGEN F, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis. BMJ. 2021;373:n1581. [2] KATZ JN, ZIMMERMAN ZE, MASS H, et al. Diagnosis and management of lumbar spinal stenosis: A review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699. [3] ANDREISEK G, IMHOF M, WERTLI M, et al. A systematic review of semiquantitative and qualitative radiologic criteria for the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(5): W735-W746. [4] KIDO T, OKUYAMA K, CHIBA M, et al. Clinical diagnosis of upper lumbar disc herniation: Pain and/or numbness distribution are more useful for appropriate level diagnosis. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(4):419-424. [5] YÜCE İ, KAHYAOĞLU O, MERTAN P, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and surgical results of upper lumbar disc herniations. Neurochirurgie. 2019;65(4):158-163. [6] KIM DS, LEE JK, JANG JW, et al. Clinical features and treatments of upper lumbar disc herniations. J Korean Neurosurg. 2010;48(2):119-124. [7] WANG Z, JIAN F, WU H, et al. Treatment of upper lumbar disc herniation with a transforaminal endoscopic technique. Front Surg. 2022;9:893122. [8] HEO DH, LEE DK, LEE DC, et al. Fully endoscopic transforaminal lumbar discectomy for upward migration of upper lumbar disc herniation: Clinical and radiological outcomes and technical considerations. Brain Sci. 2020; 10(6): 363. [9] CHOI G, LEE SH, LOKHANDE P, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic approach for highly migrated intracanal disc herniations by foraminoplastic technique using rigid working channel endoscope. Spine. 2008; 33(15): E508-E515. [10] 张晗硕. 内镜下后路椎管减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症不同术式有限元分析及生物力学评价 [D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学,2024. [11] 舒涛, 吴帝求, 沈茂. 不同微创椎管减压术在腰椎管狭窄症中的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(7):895-900. [12] 刘江, 张晗硕, 丁逸苇, 等. 棘突间固定辅助内镜下椎间融合治疗重度腰椎管狭窄症的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(24):3789-3795. [13] CAO L, LIU Y, MEI W, et al. Biomechanical changes of degenerated adjacent segment and intact lumbar spine after lumbosacral topping-off surgery: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):104. [14] SHI Y, XIE YZ, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593. [15] 程莹莹. 基于有限元模拟的腰椎生物力学研究及内固定分析[D]. 北京:北京化工大学,2024. [16] 刘金玉, 丁宇, 蒋强, 等. 全内镜下腰椎板开窗减压有限元模拟建模及生物力学变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(27):4291-4296. [17] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260. [18] CHEN CS, CHENG CK, LIU CL, et al. Stress analysis of the disc adjacent to interbody fusion in lumbar spine. Med Eng Phys. 2001;23(7): 483-491. [19] PARK JH, CHUNG SG, KIM K. Electrodiagnostic characteristics of upper lumbar stenosis: Discrepancy between neurological and structural levels. Muscle Nerve. 2020;61(5):580-586. [20] WILKE HJ, DRUMM J, HÄUSSLER K, et al. Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(8):1049-1056. [21] SRINIVAS GR, KUMAR MN, DEB A. Adjacent disc stress following floating lumbar spine fusion: A finite element study. Asian Spine J. 2017;11(4): 538-547. [22] YUAN H, YI X. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis and Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression: A Narrative Review. J Pain Res. 2023;16:3707-3724. [23] 卢明毅. 脊柱内镜经椎板间单侧入路双侧减压术治疗腰椎管狭窄症的临床研究[D]. 南宁:广西中医药大学,2021. [24] KIM HS, CHOI SH, SHIM DM, et al. Advantages of New Endoscopic Unilateral Laminectomy for Bilateral Decompression (ULBD) over Conventional Microscopic ULBD. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):330-336. [25] ZHAO XB, MA HJ, GENG B, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic unilateral laminotomy and bilateral decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(2):641-650. [26] 姜帅, 孙垂国, 王承夏, 等. 腰椎单侧椎板间开窗双侧减压术后腰椎生物力学改变的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2024,34(6): 629-636. [27] HERMANSEN E, AUSTEVOLL IM, HELLUM C, et al. Comparison of 3 different minimally invasive surgical techniques for lumbar spinal stenosis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(3): e224291. [28] AHN Y. Percutaneous endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2014;11(6):605-616. [29] AHN Y, LEE SH, PARK WM, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for recurrent disc herniation: Surgical technique, outcome, and prognostic factors of 43 consecutive cases. Spine. 2004;29(16): E326-332. [30] SHIN SH, BAE JS, LEE SH, et al. Transforaminal endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: A novel surgical technique and clinical outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:e873-e882. [31] CHEN X, QIN R, HAO J, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic decompression via transforaminal approach for lumbar lateral recess stenosis in geriatric patients. Int Orthop. 2019;43(5):1263-1269. [32] XIE P, FENG F, CHEN Z, et al. Percutaneous transforaminal full endoscopic decompression for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):546. [33] AAEN J, BANITALEBI H, AUSTEVOLL IM, et al. Is the presence of foraminal stenosis associated with outcome in lumbar spinal stenosis patients treated with posterior microsurgical decompression. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2023;165(8):2121-2129. [34] NELLENSTEIJN J, OSTELO R, BARTELS R, et al. Transforaminal endoscopic surgery for symptomatic lumbar disc herniations: A systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(2):181-204. [35] ZHANG B, KONG Q, YAN Y, et al. Degenerative central lumbar spinal stenosis: Is endoscopic decompression through bilateral transforaminal approach sufficient? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):714. [36] AHN Y. Transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: Technical tips to prevent complications. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2012; 9(4):361-366. [37] 张晗硕, 丁宇, 蒋强, 等. 脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压与单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症的生物力学稳定性及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):1981-1986. [38] DING Y, ZHANG H, JIANG Q, et al. Finite element analysis of endoscopic cross-overtop decompression for single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis based on real clinical cases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12: 1393005. [39] SAREMI A, GOYAL KK, BENZEL EC, et al. Evolution of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with key radiographic features. Spine J. 2024;24(6):989-1000. [40] LI C, XU B, ZHAO Y, et al. En bloc resection of the ligamentum flavum for bilateral decompression in unilateral biportal endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: A 2-year follow-up study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):815. [41] ANDERSON B, SHAHIDI B. The Impact of Spine Pathology on Posterior Ligamentous Complex Structure and Function. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2023;16(12):616-626. [42] VAN MIDDENDORP JJ, PATEL AA, SCHUETZ M, et al. The precision, accuracy and validity of detecting posterior ligamentous complex injuries of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a critical appraisal of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):461-474. [43] ZHAO G, WANG L, WANG H, et al. Biomechanical effects of multi-segment fixation on lumbar spine and sacroiliac joints: A finite element analysis. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(10):2499-2508. |
| [1] | Yu Xinlin, Chen Huiyu, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Feng Bin Lin Chengshou, Lin Wang. Finite element analysis of internal fixation with new retrograde intramedullary nail on lateral femur condyle for distal type A2 femur fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 546-552. |
| [2] | Zhao Jingang, Liu Liping, Chen Jianwei, . Finite element analysis comparing lumbar fusion and artificial intervertebral disc replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 553-560. |
| [3] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [4] | Abudusalamu·Tuoheti, Xiao Yang, Wang Yixi, Musitapa·Mijiti, Chen Qihao, Maimaitiming·Saiyiti, Guo Hailong, Paerhati·Rexiti. Effects of three internal fixation techniques on biomechanics of adjacent segment degeneration in lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 586-595. |
| [5] | Shang Depeng, Wei Haiyu, Yang Fan. Finite element analysis for three different types of internal screw fixation in treatment of severe lumbar 1 vertebral body fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 537-545. |
| [6] | Cheng Yanan, Yu Jiazhi, Liu Yinchang, Wu Jie, Yu Tong, Wang Lu, Li Xiaoguang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with clear aligners with different thicknesses and edges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 310-318. |
| [7] | Kang Zirui, Wu Yang, Song Hailong, Yang Qiaoyun, Zang Lixiang, Xu Dongliang. Finite element analysis of implants with different crown-to-implant ratios under different bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 319-328. |
| [8] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [9] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [10] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [11] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [12] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [13] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [14] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [15] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||