Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 805-815.doi: 10.12307/2026.549
Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation
Chen Yixian1, Chen Chen2, Lu Liheng2, Tang Jinpeng1, Yu Xiaowei2
- 1Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the Sixth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200233, China
-
Received:2024-10-29Accepted:2024-12-31Online:2026-02-08Published:2025-05-15 -
Contact:Yu Xiaowei, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the Sixth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200233, China -
About author:Chen Yixian, Master candidate, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82372387 (to YXW); Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical-Industrial Cross Fund, No. YG2024ZD19 (to YXW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
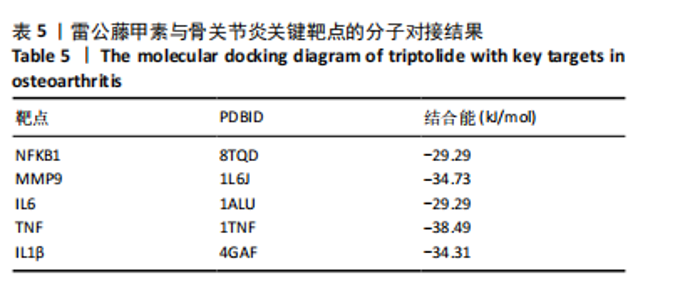
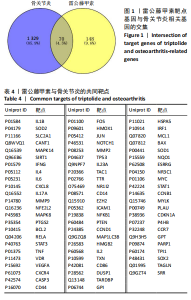
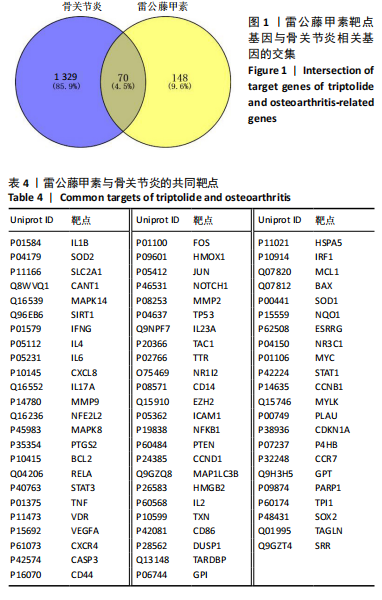
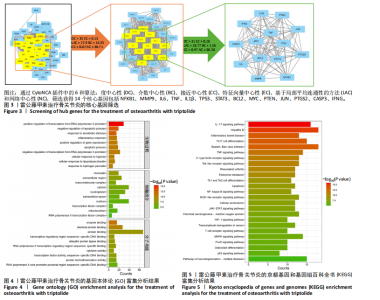
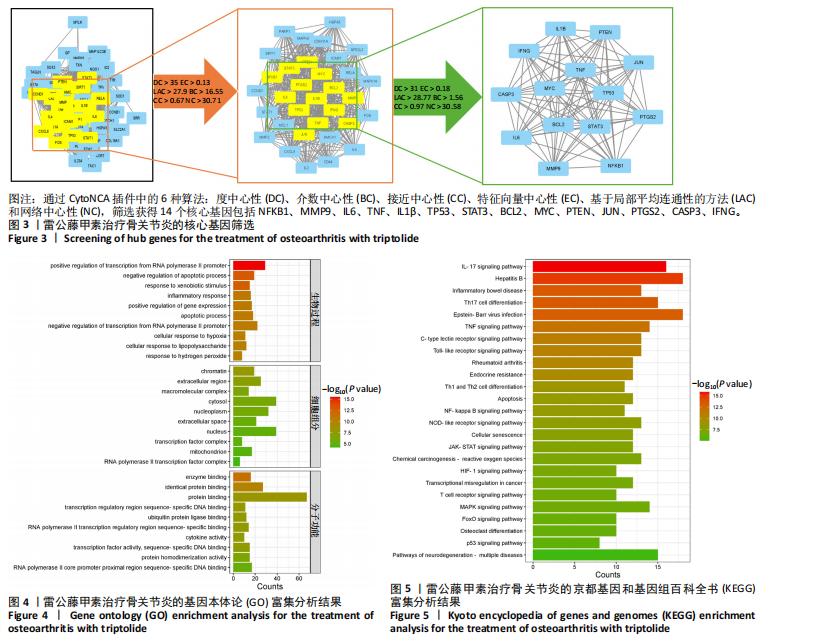
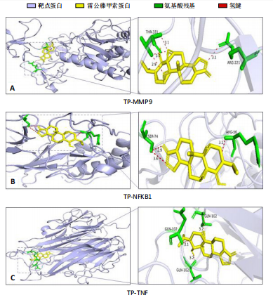
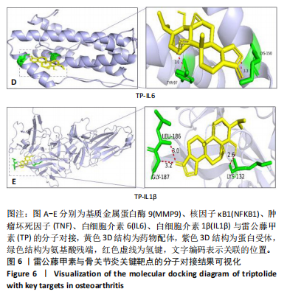
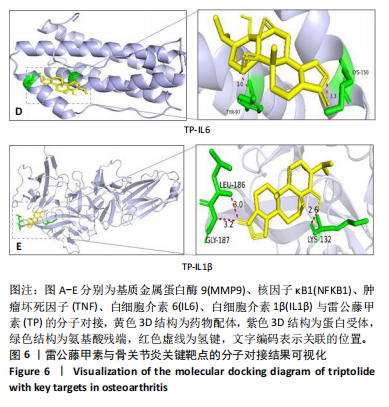
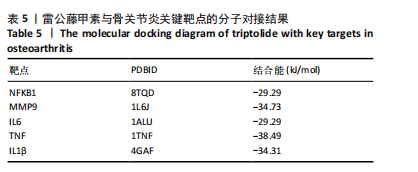
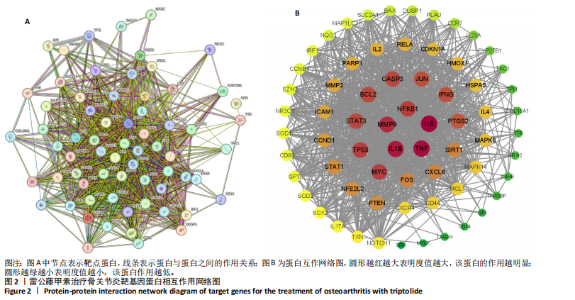
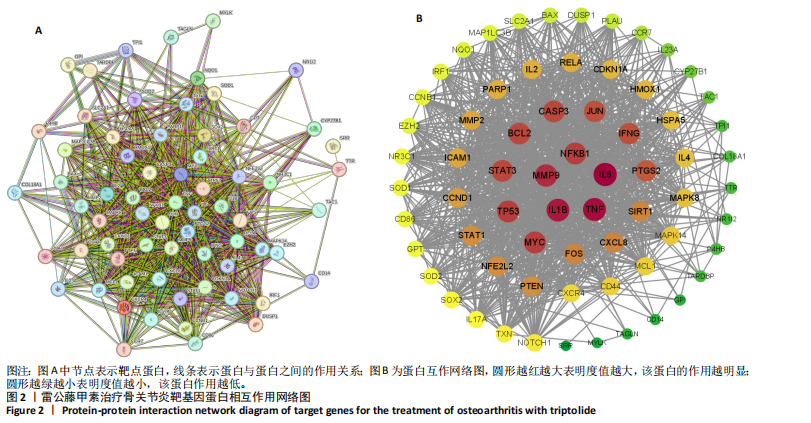
2.2 蛋白相互作用网络图的构建及核心靶点的筛选 将交集靶点导入STRING数据库获得靶点基因对应的蛋白互作网络,见图2A。通过Cytoscape软件将蛋白互作网络进行可视化,得到67个节点和1 084条边,见图2B。采用CytoNCA插件对度中心性、介数中心性、接近中心性、特征向量中心性、基于局部平均连通性的方法和网络中心性进行参数运算以筛选核心靶基因,运算范围为分别大于6个参数的中位数,循环运算2次。最终获得14个核心基因,分别为 NFKB1、MMP9、IL6、TNF、IL1β、TP53、STAT3、BCL2、MYC、PTEN、JUN、PTGS2、CASP3、IFNG,见图3。说明雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎与细胞炎症、细胞凋亡等关系密切。 2.3 GO及KEGG富集分析 通过DAVID数据库获得GO功能400条(P < 0.05),其中生物过程325条、细胞组分29条、分子功能46条。选取排名前10的条目借助微生信平台进行可视化,生成GO功能条形图,见图4。雷公藤甲素可能通过调控细胞凋亡、炎症反应、细胞因子活性、基因表达、聚合酶Ⅱ启动子的转录等方式发挥治疗骨关节炎作用。KEGG富集分析共获得123条通路(P < 0.05),选取其中具有代表性的25条通路进行可视化分析,见图5。雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎主要涉及核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)信号通路、Janus激酶信号转导和转录激活因子(janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription,JAK/STAT)信号通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路、白细胞介素17信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor,TNF)信号通路、Toll样受体通路、核苷酸结合寡聚化域(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain,NOD)样受体通路、缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1)通路、P53通路、T细胞受体通路、C型凝集素受体信号通路等。 2.4 分子对接结果 运用AutoDockTools软件对雷公藤甲素与核心靶点NFKB1、MMP9、IL6、TNF、IL1β进行分子对接,结果显示分子结合能均≤-29.29 kJ/mol,说明雷公藤甲素与骨关节炎的核心靶点具有较好的结合作用,见表5。最后通过PyMOL软件,将对接结果进行可视化分析,见图6。"
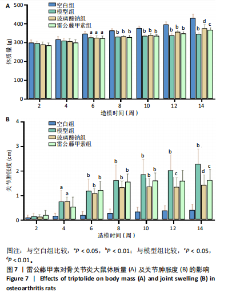
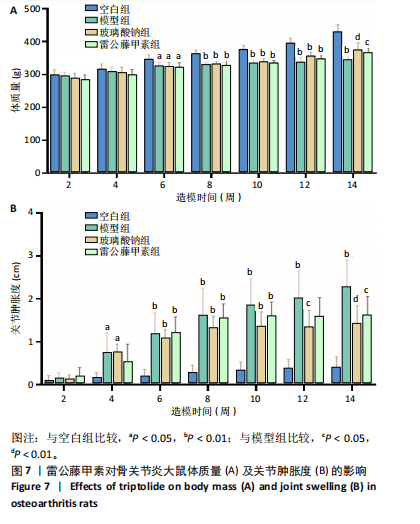
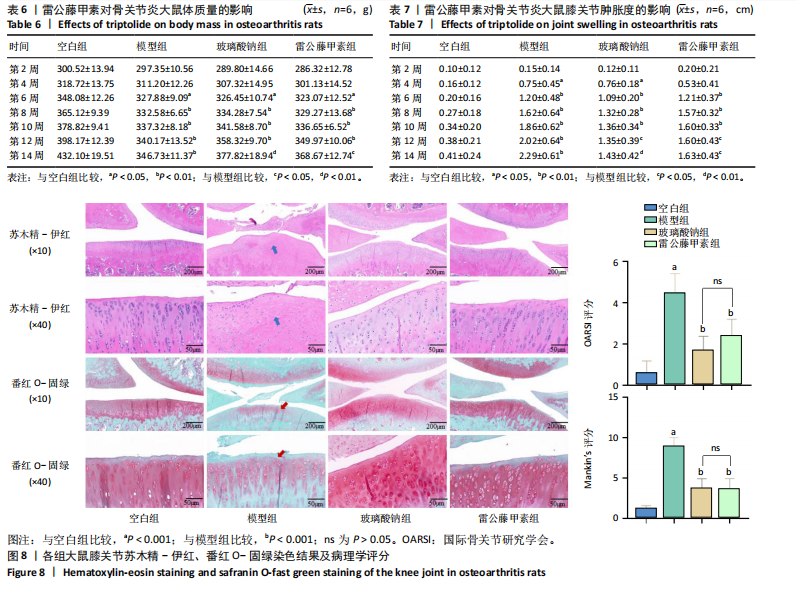
2.5 动物实验结果 2.5.1 对大鼠体质量及关节肿胀度的影响 造模第2,4周,各组大鼠的体质量变化差异不显著(P > 0.05);造模第6,8周,与空白组比较,模型组、玻璃酸钠组及雷公藤甲素组大鼠体质量均显著降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);造模8周后开始进行药物干预,结果显示,第10,12周玻璃酸钠组及雷公藤甲素组较模型组大鼠体质量有一定程度的上升,但差异不显著(P > 0.05),仍显著低于空白组体质量(P < 0.01);第14周,与模型组比较,玻璃酸钠组、雷公藤甲素组大鼠体质量明显增加(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),见图7A及表6。表明雷公藤甲素和玻璃酸钠能够有效抑制骨关节炎大鼠的体质量下降。 造模第2周,各组大鼠同侧膝关节肿胀程度不明显(P > 0.05);造模第4,6,8周,与空白组比较,模型组、玻璃酸钠组及雷公藤甲素组大鼠膝关节肿胀度显著上升(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);给药第10周,玻璃酸钠组、雷公藤甲素组大鼠膝关节肿胀增长程度下降,但较模型组关节肿胀度差异不明显(P > 0.05);给药第12,14周,与模型组比较,玻璃酸钠组、雷公藤甲素组大鼠膝关节肿胀度"
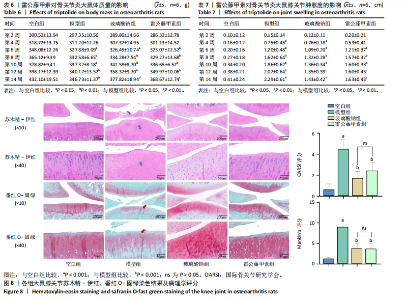
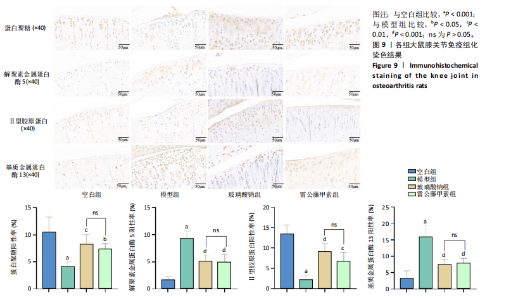
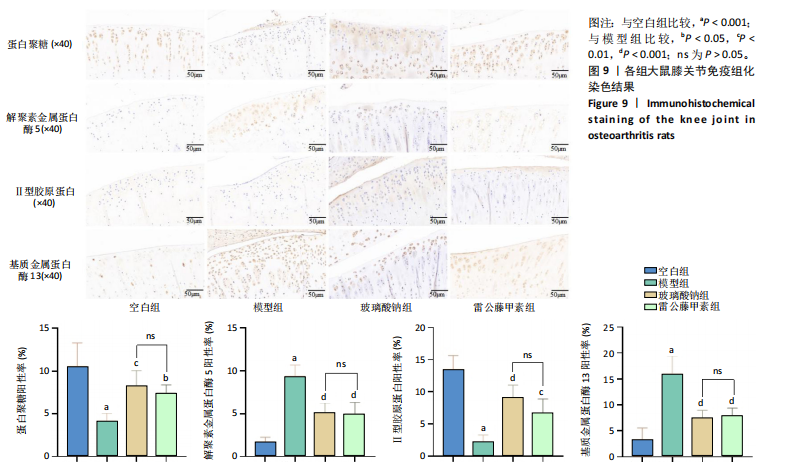
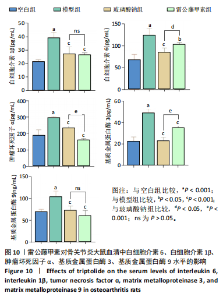
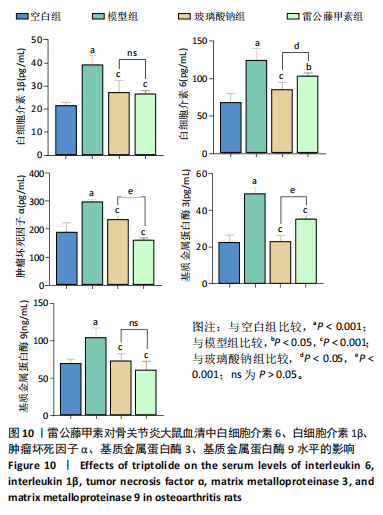
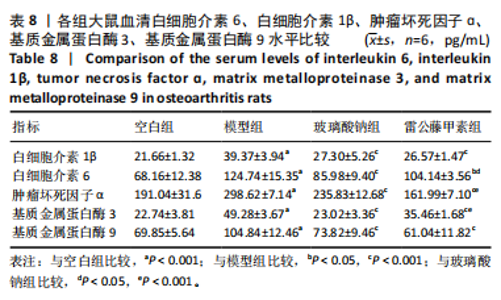
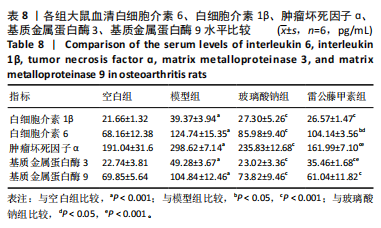
未见组织裂隙及缺损,软骨细胞排列整齐、层次分明,潮线清晰可见,基质着色较均匀,蛋白多糖明显增多,软骨纤维化不明显,见图8。 2.5.3 对大鼠膝关节软骨中蛋白聚糖、ADAMTs5、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白表达的影响 与空白组比较,模型组大鼠关节软骨中蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的蛋白表达均显著降低(P < 0.001),ADAMTs5与基质金属蛋白酶13的蛋白表达均显著增加(P < 0.001);与模型组比较,玻璃酸钠组、雷公藤甲素组大鼠膝关节中蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的蛋白表达均明显增加(P < 0.001,P < 0.01,P < 0.05),ADAMTs5与基质金属蛋白酶13的蛋白表达水平均显著降低(P < 0.001);雷公藤甲素组与玻璃酸钠组大鼠膝关节中此4种蛋白表达水平相比差异不明显(P > 0.05)。见图9。 2.5.4 对大鼠血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶3水平的影响 与空白组比较,模型组大鼠血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶3水平显著升高(均P < 0.001);与模型组比较,玻璃酸钠组和雷公藤甲素组大鼠血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶3水平均显著降低(P < 0.001,"
| [1] HAO HQ, ZHANG JF, HE QQ, et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type II collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 as biomarkers for knee and hip osteoarthritis (OA) diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(5):726-736. [2] GBD 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(9):e508-e522. [3] PESHKOVA M, LYCHAGIN A, LIPINA M, et al. Gender-Related Aspects in Osteoarthritis Development and Progression: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2767. [4] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [5] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [6] 蒋红霞, 伍秋珊, 刘莉, 等. 雷公藤三萜类成分及其药理活性研究进展[J]. 中成药,2022,44(4):1223-1231. [7] CHEN Q, DENG S, DENG M, et al. Therapeutic synergy of Triptolide and MDM2 inhibitor against acute myeloid leukemia through modulation of p53-dependent and -independent pathways. Exp Hematol Oncol.2022;11(1):23. [8] ZHAO X, TANG X, YAN Q, et al. Triptolide ameliorates lupus via the induction of miR-125a-5p mediating Treg upregulation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:14-21. [9] NOEL P, VON HOFF DD, SALUJA AK, et al. Triptolide and Its Derivatives as Cancer Therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019;40(5):327-341. [10] LIU P, LIU H, SANG Y, et al. Triptolide regulates neutrophil function through the Hippo signaling pathway to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis disease progression. J Transl Autoimmun. 2024;8:100242. [11] YANG J, TANG X, KE X, et al. Triptolide Suppresses NF-κB-Mediated Inflammatory Responses and Activates Expression of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Genes to Alleviate Caerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. Int J Mol Sci.2022;23(3):1252. [12] QIAN K, ZHANG L,SHI K. Triptolide prevents osteoarthritis via inhibiting hsa-miR-20b. Inflammopharmacology. 2019;27(1):109-119. [13] LI EQ, ZHANG JL. Therapeutic effects of triptolide from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. on interleukin-1-beta-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;883:173341. [14] ZHOU P, CHEN C, YUE X, et al. Strategy for osteoarthritis therapy: Improved the delivery of triptolide using liposome-loaded dissolving microneedle arrays. Int J Pharm. 2021;609:121211. [15] XIANG C, LIAO Y, CHEN Z, et al. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking to Elucidate the Potential Mechanism of Ligusticum Chuanxiong Against Osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:854215. [16] FANG C, GUO JW, WANG YJ, et al. Diterbutyl phthalate attenuates osteoarthritis in ACLT mice via suppressing ERK/c-fos/NFATc1 pathway, and subsequently inhibiting subchondral osteoclast fusion. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(5):1299-1310. [17] LIU G, WANG L, TUERXUNYIMING M, et al. Triptolide ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating nuclear factor kappa B-mediated inflammatory response. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022:rgab182. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab182. [18] AYTEKIN K, UYSAL M, ŞAHINER GG, et al. Evaluation of different intraarticular injection volumes to assess optimum efficient amount; an experimental study in rat knee joints. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2020;101:106658. [19] YAO N, CHEN GC, LU YY, et al. Bushen Qiangjin capsule inhibits the Wnt/α-catenin pathway to ameliorate papain-induced knee osteoarthritis in rat. J Tradit Chin Med. 2021;41(6):935-942. [20] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18 Suppl 3:S17-23. [21] VAN DER SLUIJS JA, GEESINK RG, VAN DER LINDEN AJ, et al. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992; 10(1):58-61. [22] 卞希贤, 姬翔宇, 陶西雨, 等. 雷公藤多苷片中6个活性成分在正常和佐剂性关节炎大鼠体内药代动力学比较研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2024,49(20):5587-5597. [23] HE C, CHEN J, LIU J, et al. Geranium wilfordii maxim: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and toxicology. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;285:114907. [24] ZHANG Y, MAO X, LI W, et al. Tripterygium wilfordii: An inspiring resource for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(3): 1337-1374. [25] FANG WY, TSENG YT, LEE TY, et al. Triptolide prevents LPS-induced skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting NF-κB/TNF-α and regulating protein synthesis/degradation pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(15): 2998-3016. [26] 王杰, 刘健, 文建庭, 等. 雷公藤甲素抑制类风湿关节炎患者的成纤维样滑膜细胞的炎症和迁移:基于circRNA 0003353/JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2022,42(3):367-374. [27] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [28] PULIK Ł, ŁĘGOSZ P, MOTYL G. Matrix metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: a state of the art review. Reumatologia. 2023;61(3):191-201. [29] 罗媚, 杜信眉, 周学东. 基质金属蛋白酶与骨关节炎发生发展关系的研究进展[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2023,54(1):77-82. [30] LI S, WANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. COL3A1 and MMP9 Serve as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Osteoarthritis and Are Associated With Immune Cell Infiltration. Front Genet. 2021;12:721258. [31] ZHOU Q, REN Q, JIAO L, et al. The potential roles of JAK/STAT signaling in the progression of osteoarthritis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:1069057. [32] 秦庆庆, 谢犇, 王一坤, 等. 骨关节炎中自噬相关信号通路[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2023,29(6):453-457. [33] LU J, ZHANG H, PAN J, et al. Fargesin ameliorates osteoarthritis via macrophage reprogramming by downregulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):142. [34] ZHANG Z, WANG S, LIU X, et al. Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside Ameliorates Osteoarthritis via Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2/ nuclear factor kappa B Pathway: In vitro and in vivo experiments. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;164:114964. [35] WANG LJ, ZENG N, YAN ZP, et al. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis following ACL injury. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):57. [36] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023;64(2):222-238. [37] 许磊, 韩晓强, 张锦涛, 等. 关节软骨细胞周围透明质酸产生、转化和功能特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(5):768-773. [38] WANG H, JIANG Z, PANG Z, et al. Engeletin Protects Against TNF-α-Induced Apoptosis and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Chondrocytes and Alleviates Osteoarthritis in vivo. J Inflamm Res. 2021; 14:745-760. [39] KHADER A, ALQURAN H. Automated Prediction of Osteoarthritis Level in Human Osteochondral Tissue Using Histopathological Images. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(7):764. [40] ZHUANG H, REN X, JIANG F, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid alleviates chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via the AhR/NF-κB axis. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):17. [41] WANG Z, MA J, MIAO Z, et al. Ergothioneine inhibits the progression of osteoarthritis via the Sirt6/NF-κB axis both in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;119:110211. [42] HU Q,ECKER M. Overview of MMP-13 as a Promising Target for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1742. [43] HE L, HE T, XING J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):276. [44] LI T, PENG J, LI Q, et al. The Mechanism and Role of ADAMTS Protein Family in Osteoarthritis. Biomolecules. 2022;12(7):959. |
| [1] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [2] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [3] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [4] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [5] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [6] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [7] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [8] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [9] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [10] | Zou Rongji, Yu Fangfang, Wang Maolin, Jia Zhuopeng. Triptolide inhibits ferroptosis and improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model of cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 873-881. |
| [11] | Yu Shiyu, Yu Sutong, Xu Yang, Zhen Xiangyan, Han Fengxuan. Advances in research and application of tissue engineering therapeutic strategies in oral submucous fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [12] | Zhang Tingting, Li Yalong, Yue Haodi, Li Yanjun, Geng Xiwen, Zhang Yuwei, Liu Xiaozhuan. Protection of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of different mouse ages on radiation-induced lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [13] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [14] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [15] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||