Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (33): 7072-7079.doi: 10.12307/2025.855
Previous Articles Next Articles
A three-dimensional finite element modal analysis on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Ye Xiaolong1, Zhang Yuxuan2, Fu Rongchang2, Liu Yun3, Yusanjiang·Wuhuer3, Escar·Aimer3, Ma Yuan3
- 1Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2College of Intelligent Manufacturing and Modern Industry (School of Mechanical Engineering), Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830092, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830092, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-08-16Accepted:2024-10-23Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-04-12 -
Contact:Ma Yuan, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830092, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Ye Xiaolong, Doctoral candidate, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82260446 (to MY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ye Xiaolong, Zhang Yuxuan, Fu Rongchang, Liu Yun, Yusanjiang·Wuhuer, Escar·Aimer, Ma Yuan. A three-dimensional finite element modal analysis on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7072-7079.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
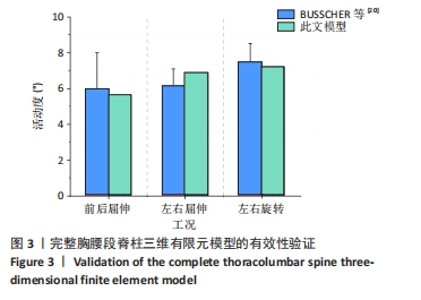
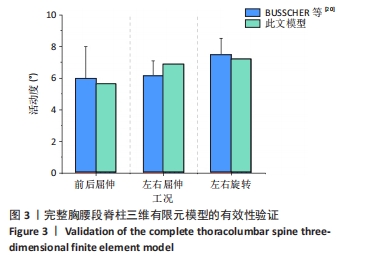
2.1 有限元模型有效性验证 目前国内外针对全胸腰椎生物力学特性的实验报道,普遍无法直接对完整胸腰段脊柱三维有限元模型进行验证,故此文建立完整的胸腰椎段脊椎模型,采用脊柱分段模型进行加载验证。选取胸椎T1-4节段模型进行验证[19],在ANSYS 19.2 Workbench模块中先限制T4下表面6个方向的自由度,对T1上表面均匀施加4 N·m力矩,模拟前屈、后伸、左侧屈、右侧屈、左旋、右旋运动,然后将模型进行计算。通过计算求解出T1相对于T4在不同工况下的活动度,并将所得加载结果与BUSSCHER等[20]的实验结果进行比较,从而验证模型的有效性。通过求解可得,此模型在屈伸、左右侧屈、左右旋转工况下的活动度如图所示。结果表明,此模型活动度与BUSSCHER等[20]的实验结果有一定偏差,此偏差可能是由于后者的实验对象选用正常人体,而此文T1-4节段模型本身就存在一定程度畸形而造成。但总体上,此模型仿真结果与BUSSCHER等[20]的实验结果具有较好一致性,详见图3。因此,此模型的有效性得到了验证。"

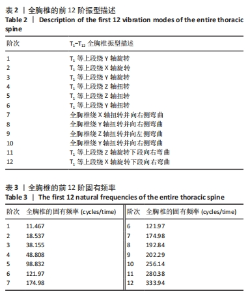
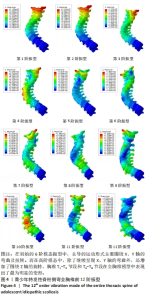
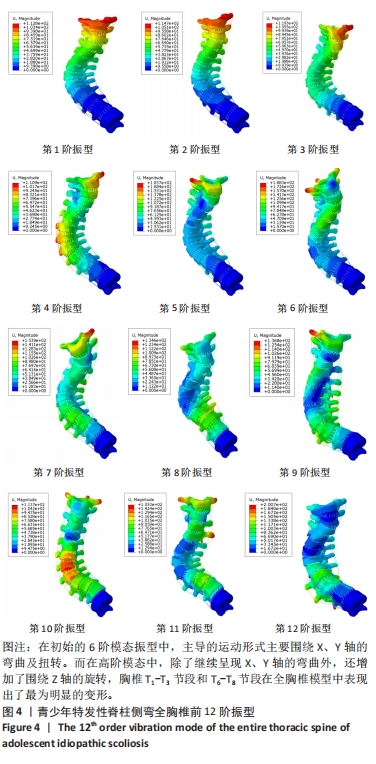
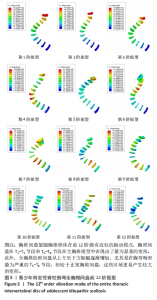
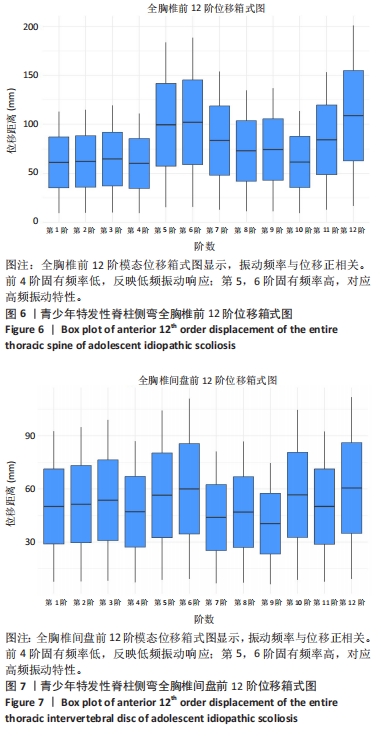
全胸椎和椎间盘的前12阶模态位移的箱式图如图6,7所示。从中可以观察到,随着振动频率的逐渐升高,振动位移也相应增大。前4阶的固有频率相对较低,它们主要反映了全胸椎结构在低频振动下的响应特性。这些低阶模态可能与人体日常活动中的常见振动频率相接近,因此长期暴露于这些频率的振动环境下可能对全胸椎产生累积性损伤。第5阶和第6阶的固有频率相对较高,对应于全胸椎在高频振动下的响应特性。虽然这些高阶模态在日常活动中可能不常出现,但在某些特定情况下如剧烈运动等,这些高频振动可能对全胸椎造成较大的冲击和损伤。特别值得注意的是,在低频振动的第5阶和第6阶,以及高频振动的第12阶,椎体和椎间盘的振动位移达到了近似水平。综合模态分析的结果,发现当全胸椎和椎间盘在低阶模态下,且固有频率长期集中在98.832-121.97 cycles/s这一范围内时,这种频率的长期暴露会对胸椎和椎间盘造成较大的损伤风险。在此需要指出的是,由于cycles/time的单位未明确给出,假设其为cycles/s,即每秒内的周期数,这与赫兹(Hz)单位等价。因此,当固有频率长期暴露于上述范围内时,应引起足够的重视,以避免潜在的脊柱健康问题。"
| [1] KUZNIA AL, HERNANDEZ AK, LEE LU. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(1):19-23. [2] CHUNG CL, KELLY DM, SAWYER JR, et al. Mechanical Testing of a Novel Fastening Device to Improve Scoliosis Bracing Biomechanics for Treating Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2018;2018:7813960. [3] ENGELBERT RH, UITERWAAL CS, VAN DER HULST A, et al. Scoliosis in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: influence of severity of disease and age of reaching motor milestones. Eur Spine J. 2003;12:130-134. [4] LENKE LG, SIDES BA, KOESTER LA, et al. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(3):687-699. [5] 蔡振宁,朱泽章,邱勇.Lenke 1型和2型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸选择性胸弯融合术后腰弯自发性纠正的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(3):270-273. [6] FAN W, ZHAO D, GUO LX. A finite element model of the human lower thorax to pelvis spinal segment: Validation and modal analysis. Biomed Mater Eng. 2021;32(5):267-279. [7] GOEL VK, PARK H, KONG W. Investigation of vibration characteristics of the ligamentous lumbar spine using the finite element approach. J Biomech Eng. 1994;116(4):377-383. [8] JIA S, LI Y, XIE J, et al. Differential response to vibration of three forms of scoliosis during axial cyclic loading: a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):370. [9] BRINCKMANN P, FROBIN W, BIGGEMANN M, et al. Quantification of overload injuries to thoracolumbar vertebrae and discs in persons exposed to heavy physical exertions or vibration at the work-place The shape of vertebrae and intervertebral discs - study of a young, healthy population and a middle-aged control group. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1994;9 Suppl 1:S3-S83. [10] LI S, PATWARDHAN AG, AMIROUCHE FM, et al. Limitations of the standard linear solid model of intervertebral discs subject to prolonged loading and low-frequency vibration in axial compression. J Biomech. 1995;28(7):779-790. [11] XU M, YANG J, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite element method-based study for effect of adult degenerative scoliosis on the spinal vibration characteristics. Comput Biol Med. 2017;84:53-58. [12] GOULD SL, CRISTOFOLINI L, DAVICO G, et al. Computational modelling of the scoliotic spine: A literature review. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(10):e3503. [13] LERCHL T, NISPEL K, BAUM T, et al. Multibody Models of the Thoracolumbar Spine: A Review on Applications, Limitations, and Challenges. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(2):202. [14] LIAO JC, CHEN WP, WANG H. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by short-segment pedicle screw fixation using a combination of two additional pedicle screws and vertebroplasty at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):262. [15] ZHANG W, ZHAO J, LI L, et al. Modelling tri-cortical pedicle screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae under osteoporotic condition: A finite element analysis based on computed tomography. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;187:105035. [16] WANG TN, WU BL, DUAN RM, et al. Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures Through Different Short Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation Techniques: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):601-608. [17] 富荣昌,杨骁峥,李现政.最佳Halo重力牵引治疗Lenke3型脊柱侧凸的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(18):2901-2905. [18] DONG R, ZHU S, CHENG X, et al. Study on the biodynamic characteristics and internal vibration behaviors of a seated human body under biomechanical characteristics. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2024;23(5):1449-1468. [19] XIN DQ, HU XM, HANDY, et al. Parameter modification and validation of the finite element model of Lenke type 3 adult idiopathic scoliosis. Chin Tissue Eng Res. 2017;21(31):4975-4982. [20] BUSSCHER I, VAN DIEËN JH, KINGMA I, et al. Biomechanical characteristics of different regions of the human spine: an in vitro study on multilevel spinal segments. Srine. 2009;34(26):2858-2864. [21] PENG Y, WANG SR, QIU GX, et al. Research progress on the etiology and pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(4):483-493. [22] LI P, FU R, YANG X, et al. Finite element method-based study for spinal vibration characteristics of the scoliosis and kyphosis lumbar spine to whole-body vibration under a compressive follower preload. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2024:1-10. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2024.2333925. [23] GUO LX, ZHANG YM, ZHANG M. Finite element modeling and modal analysis of the human spine vibration configuration. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2011;58(10):2987-2990. [24] TANG SJ, DONG RC, CHENG X, et al. Effect of anteroposterior vibration frequency on the risk of lumbar injury in seated individuals. Ergonomics. 2024:1-13. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2024.2391591. [25] CARREAU JH, BASTROM T, PETCHARAPORN M, et al. Computer-Generated, Three-Dimensional Spine Model From Biplanar Radiographs: A Validity Study in Idiopathic Scoliosis Curves Greater Than 50 Degrees. Spine Deform. 2014;2(2):81-88. [26] SELEVICIENE V, CESNAVICIUTE A, STRUKCINSKIENE B, et al. Physiotherapeutic Scoliosis-Specific Exercise Methodologies Used for Conservative Treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis, and Their Effectiveness: An Extended Literature Review of Current Research and Practice. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(15):9240. [27] KAWCHUK GN, HARTVIGSEN J, EDGECOMBE T, et al. Structural health monitoring (vibration) as a tool for identifying structural alterations of the lumbar spine: a twin control study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22974. [28] SHU D, DAI S, WANG J, et al. Impact of Running Exercise on Intervertebral Disc: A Systematic Review. Sports Health. 2024;16(6):958-970. [29] LI N, CAVAGNARO MJ, XIONG K, et al. The Multi-Modal Risk Analysis and Medical Prevention of Lumbar Degeneration, Fatigue, and Injury Based on FEM/BMD for Elderly Chinese Women Who Act as Stay-Home Grandchildren Sitters. Front Public Health. 2021;9:700148. [30] MACEDO LG, NOGUCHI KS, DE OLIVEIRA LA, et al. The association between whole body vibration exposure and spine degeneration on imaging: A systematic review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2022; 35(4):691-700. [31] GUO LX, TEO EC. Influence prediction of injury and vibration on adjacent components of spine using finite element methods. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(2):118-124. [32] BOVENZI M, SCHUST M. A prospective cohort study of low-back outcomes and alternative measures of cumulative external and internal vibration load on the lumbar spine of professional drivers. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2021;47(4):277-286. [33] COMTE N, PUJADES S, COURVOISIER A, et al. Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(7):874. [34] OVERBERGH T, SEVERIJNS P, BEAUCAGE-GAUVREAU E, et al. Development and validation of a modeling workflow for the generation of image-based, subject-specific thoracolumbar models of spinal deformity. J Biomech. 2020;110:109946. [35] WEI W, ZHANG T, HUANG Z, et al. Finite element analysis in brace treatment on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022;60(4):907-920. [36] IDE K, NARITA K, YAMATO Y, et al. Effect of corrective stresses on rods in adult spinal deformity surgery-finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2024;29(3):711-717. [37] JIA S, LIN L, YANG H, et al. The influence of the rib cage on the static and dynamic stability responses of the scoliotic spine. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):16916. [38] PIERCE KE, HORN SR, JAIN D, et al. The Impact of Adult Thoracolumbar Spinal Deformities on Standing to Sitting Regional and Segmental Reciprocal Alignment. Int J Spine Surg. 2019;13(4):308-316. [39] JIA S, LIN L, YANG H, et al. Biodynamic responses of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis exposed to vibration. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023; 61(1):271-284. [40] YANG Y, LIU Y, YUAN X, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution on short implants with different bone conditions and osseointegration rates. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):220. |
| [1] | Zheng Xiaodong, Gao Shan, Han Wenjin, Liu Lijun, Jia Menglong, Yu Longtan. Visual analysis of treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 645-653. |
| [2] | Zhang Juanjuan, Jiang Nannan, Wu Yajun, Gu Qian, He Linfei, Ji Yongxin, Liu Su. Schroth therapy combined with core strength training improves scoliosis angle in patients with mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5876-5882. |
| [3] | Wang Xia, Xue Boshi, Yang Chen, Zhou Zhipeng, Zheng Liangliang. Influence of neuromuscular function on the risk of biomechanical injury in landing manoeuvres in patients undergoing anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5556-5562. |
| [4] | Liu Jing, Xu Chunxin, Lu Yangyang, Qu Qinquan, Zhu Qi, Guo Yulan, Shen Min. Correlation of gait parameters and muscle parameters with imaging in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4477-4485. |
| [5] | Yue Bo, Cao Zhenhua, Zhang Yunfeng, Xu Yangyang, Jin Feng, Su Baoke, Wang Lidong, Wang Xing, Tong Ling, Liu Qinghua, Fang Yuan, Sha Lirong, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe, Li Zhijun. Biomechanical characteristics of different orthopedic modalities for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis based on finite element simulation analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3129-3137. |
| [6] | Wu Maodong, Su Qinglun, Huang Yiming, Shen Longying, Lu Yu, Zhao Qin. Correlation between coronal pressure variation and coronal imbalance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 852-856. |
| [7] | Hou Yutong, Huang Chenglan, Yang Yunxiao, Li Ya, Guo Peiwu, Yu Wenqiang, Zhao Yu, Wang Zanbo, Zeng Hong, Ma Zhenjiang, Lu Dezhi, Wang Jinwu. Correlation between lumbar spine and pelvic parameters in Lenke type 5 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5753-5758. |
| [8] | Chang Ying, Xia Yuan, Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Xiong Wenjuan, Zhao Xianghu. Effectiveness of different specific exercise therapies in treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5899-5904. |
| [9] | Huang Yangyang, Wang Shiyu, Liu Hao, Yang Li, Wang Penglai, Yuan Changyong. Effect of sagittal overcorrection design on displacement and stress of mandibular anterior teeth intrusion using clear aligners [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4593-4598. |
| [10] | Hou Zhaomeng, Su Shaoting, Chen Longhao, Wei Guikang, Zhou Honghai. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and trends in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3424-3430. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinqin, Cui Jian, Gao Xiaolin, Shi Yongjin, Zhu Chao, Huang Peng. The landing error scoring system as a screening tool for non-contact injury risk in college soccer athletes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1641-1646. |
| [12] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [13] | Xin Xiaoming, Gao Mingxuan, Zhang Fan, Chi Fei, Feng Junchao, Luo Wenyuan. Application of orthopedic robot-assisted screw placement in the correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5790-5794. |
| [14] | Peng Lu, Duan Zhili, Li Zhenyu, Li Junhui, Li Yunhong, Wang Song, Liu Weiqiang. Research status and progress of establishment and validation of finite element model of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4393-4400. |
| [15] | Wang Shuai, Wang Liancheng, Zhang Shuhao, Li Fuli, Dong Jiaxing, Zhang Yajie. Correlation of the electromyography ratio of the paraspinal muscles on the convex and concave sides with Cobb angle, apical vertebra translation, and coronal balance distance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1402-1406. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||