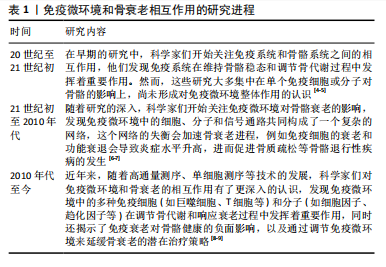
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6509-6519.doi: 10.12307/2025.951
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interaction between immune microenvironment and bone aging and treatment strategies
Wang Jianxu1, Dong Zihao1, Huang Zishuai1, Li Siying2, Yang Guang1
- 1Department of Joint Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China; 2Metabolism and Disease Research Center, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-23Accepted:2024-12-10Online:2025-10-28Published:2025-03-28 -
Contact:Yang Guang, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Joint Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Jianxu, Master candidate, Department of Joint Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jianxu, Dong Zihao, Huang Zishuai, Li Siying, Yang Guang. Interaction between immune microenvironment and bone aging and treatment strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6509-6519.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
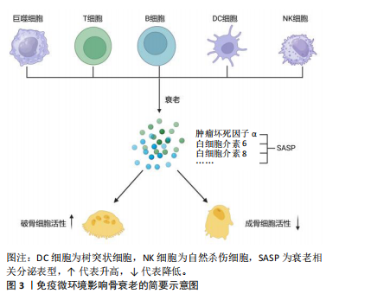
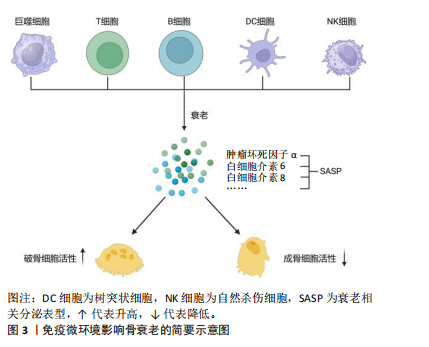
2008年的14.0%上升到2017-2018年的19.6%,男性从2007-2008年的3.7%上升到2017-2018年的4.4%,可见骨质疏松发病率逐渐上升且在女性中更明显[10]。骨质疏松以骨量减少和骨质强度的减弱为特征,增加了骨折风险。由于骨折后的残疾和不活动,髋部骨折一直被认为是最具破坏性的骨质疏松性骨折[11-12]。 老化的骨细胞表现为细胞分裂的停止,从而导致细胞增殖、生长和分化的停止;与此同时,它们还存在不可逆的细胞周期和基因表达的停滞、染色质结构和功能改变、代谢途径中断和分泌表型改变[13]。这些衰老的细胞在其生活的微环境中分泌促炎细胞因子、趋化因子和其他生长因子组成了衰老相关分泌表型(senescence-associated secretory phenotype,SASP)[14]。SASP引起邻近细胞展现出相似的衰老相关特征,因而在细胞衰老和组织功能障碍之间起关键作用[15]。 骨骼微环境是一个复杂的生物系统,由多种细胞类型组成,如骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞以及非细胞成分(如细胞外基质和生长因子等),对于维持骨骼的正常结构和功能具有至关重要的作用[16]。骨微环境中存在多种细胞因子和生长因子,如成纤维细胞生长因子、血小板衍化生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、转化生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白等,通过与各种骨细胞表面的受体结合来调节骨细胞的增殖、分化和功能[17]。另外,骨微环境中的细胞间相互作用对骨细胞的生物学行为有重要影响。骨髓间充质干细胞具有自我更新和多向分化的潜能,能够在特定条件下分化为成骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞等,参与骨组织的修复和重建。成骨细胞主要负责骨质的合成,通过分泌骨基质蛋白以及促进矿化过程来构建和巩固骨骼结构。破骨细胞负责骨骼的吸收和重塑,通过分泌酸性物质和酶来分解骨骼组织,它们之间的相互作用共同维持骨重塑的平衡[18]。骨微环境中的炎症反应也会影响骨细胞的生物学行为。炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1等能够调节破骨细胞的活性和成骨细胞的分化,从而影响骨骼的重塑过程。由此可见,骨细胞在骨微环境中扮演着至关重要的角色,全面了解骨老化过程中发生的微观变化,对于探索减缓衰老进程以及提高生活质量的治疗策略至关重要。 2.2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞 骨髓间充质干细胞的衰老以自我更新和分化能力降低为特征,在骨老化中起着重要作用[19]。衰老骨髓间充质干细胞的自我增殖和更新能力受损通常是由于活性氧的积累和DNA损伤[20]。研究发现,在老化的骨髓中大量骨髓间充质干细胞在G1期停滞,这是由DNA损伤诱导的p53/p21通路积累引起的[21]。 骨髓间充质干细胞衰老导致其向脂肪细胞分化能力的增强[22]。研究表明过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ2是向脂肪形成分化过程的主要调节因子,它与脂肪细胞脂肪酸结合蛋白在衰老的骨髓间充质干细胞中表达上调 [23]。与此同时,骨髓间充质干细胞衰老导致其向成骨细胞分化能力的减弱。研究人员发现,老年人中由于转录因子Runx2、转录因子Sp7和远端非同源盒5的下调,以及主要的骨基质蛋白如骨钙素、骨桥蛋白和骨唾液蛋白的表达降低,成骨能力显著降低[24]。另有研究显示,核小体组装蛋白1样2的表达增加与骨髓间充质干细胞衰老和成骨能力损伤相关[25]。转化生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞和脂肪细胞的分化。转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白信号通路正调控的抑制性Smads——Smad6和Smad7在老年小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中的表达降低。尽管转化生长因子β1 mRNA在老年小鼠中表达增加,但从骨吸收释放的转化生长因子β1可诱导小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3降解,并通过糖原合成酶激酶3β介导β-连环蛋白降解,从而抑制成骨细胞的形成[26]。研究证实,在老年小鼠中,转化生长因子β2、转化生长因子β3及转化生长因子β1受体的mRNA表达降低,控制干细胞向脂肪细胞转化的骨形态发生蛋白4 mRNA表达增加,而控制成骨分化的骨形态发生蛋白受体1B mRNA表达显著降低[27]。此外,在衰老的骨髓间充质干细胞中,重组叉头框蛋白P1的表达降低且与p16INK4A的表达呈负相关,这是通过与免疫球蛋白κJ信号结合蛋白和CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白β/δ复合体相互作用实现的,这2个复合体分别是脂肪形成和成骨形成的关键调节因子[28]。调控骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和影响成骨细胞增殖和成熟的通路(如Wnt信号通路、Notch信号通路和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路)也在衰老过程中发生相应的表达变化,其结果均为促成骨能力的降低。Wnt信号通路包括Wnt6、Wnt10a和Wnt10b,通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,在衰老的个体中该信号通路显著减弱[29]。 2.2.3 成骨细胞 衰老成骨细胞的特征是与年龄相关的细胞增殖障碍(细胞周期停滞)、细胞功能和代谢下降(归因于端粒酶缺陷和端粒缩短、氧化损伤、DNA损伤和DNA损伤反应)、分化减少以及对激素和生长因子的反应性降低[30]。美国德克萨斯大学癌症中心发现了一种名为TAC的小分子化合物,能够恢复端粒酶水平到年轻状态,从而延长端粒并减少细胞衰老和组织炎症[31]。另有研究人员发现一些DNA修复相关蛋白在细胞衰老过程中起到了重要的调控作用,例如,毛细血管扩张性共济失调突变因子和共济失调毛细血管扩张Rad3相关蛋白等DNA损伤感应蛋白可以感知细胞内DNA的损伤信号,并引发一系列的修复反应[32],这些蛋白的功能异常与细胞衰老加速密切相关;此外,一些DNA修复酶如多聚合酶δ和多聚合酶ε等,也在细胞衰老中发挥重要的作用[33]。 研究发现,与年轻人相比,老年人的两种成骨相关基因转录因子Sp7和Runx2以及成骨细胞分化的两种晚期标志物骨桥蛋白和骨钙素的表达减少;此外,miR-93通过在反馈回路中调节转录因子Sp7发挥成骨细胞的调节作用[34]。miR-93直接靶向转录因子Sp7的编码区,影响转录因子Sp7的转录调控,进而影响成骨细胞的功能[35], 然而该调节机制是否随着衰老发生改变需要进一步的实验验证。 雌激素通过雌激素受体刺激Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路,从而促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化。老年女性雌激素水平显著下降,导致成骨细胞增殖和分化受到抑制,细胞凋亡增加[36];而抑制雌激素受体α表达可抑制成骨细胞分化,这阐明了老年女性骨质疏松风险增加的潜在机制[37]。 由衰老引起的慢性炎症已被证实激活重组NLR家族的热蛋白结构域蛋白3炎症小体,从而导致成骨细胞功能障碍[38]。炎症因子白细胞介素1β通过激活核因子κB和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶抑制成骨细胞分化,并且通过抑制骨形态发生蛋白/转化生长因子β信号转导蛋白通路和Runx2的表达同样抑制成骨分化;同时,肿瘤坏死因子α通过上调炎症微环境中Dickkopf-1的表达和白细胞介素6的高表达抑制Wnt通路,共同发挥抗成骨作用,在骨质疏松的发生发展中发挥重要作用[39]。 2.2.4 破骨细胞 衰老影响破骨细胞的机械反应能力。研究表明,细胞的衰老状态改变了破骨细胞对机械刺激的反应,可能对骨骼健康产生负面影响[19]。破骨细胞数量和活性的调控受核因子κB受体活化因子配体、骨保护素和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的影响[40]。核因子κB受体活化因子配体与破骨细胞前体细胞上的核因子κB受体活化因子结合,从而促进破骨细胞相关基因的表达及其本身的成熟。相反,骨保护素竞争性地抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体与核因子κB受体活化因子的结合,因此,核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素比值是骨重塑的重要决定因素。另外,巨噬细胞刺激因子通过促进破骨前体细胞的增殖和分化、促进单核细胞融合和促进破骨细胞存活来刺激破骨细胞成熟[41]。巨噬细胞刺激因子通过增强核因子κB受体活化因子配体与核因子κB受体活化因子的结合,提高破骨细胞对核因子κB受体活化因子配体的敏感性,从而促进破骨细胞分化。衰老主要通过核因子κB受体活化因子/核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素和巨噬细胞刺激因子/集落刺激因子1受体轴参与破骨细胞成熟分化的调控。核因子κB受体活化因子配体和巨噬细胞刺激因子表达的增加,以及骨保护素表达的减少,导致骨重塑失衡,骨吸收大于骨形成,导致老年人骨脆性增加,骨折风险增加[42]。 2.3 免疫微环境影响骨衰老 骨衰老是老年人普遍存在的一种病理状态,以多种生物学过程相互作用为特征,其中免疫因素起着关键作用。随着年龄的增长,免疫细胞的组成和功能发生了显著变化,它们通过分泌细胞因子直接或间接影响骨代谢和骨重塑。免疫系统的慢性低度炎症状态被认为是老年人骨质疏松进展和骨量减少的关键驱动因素[43]。免疫微环境是指存在于特定组织或器官中的由各种免疫细胞、非免疫细胞及其分泌物共同构成的复杂环境,包括多种类型的细胞,如巨噬细胞、树突细胞、T细胞、B细胞和自然杀伤细胞等[44]。非免疫细胞如成纤维细胞、内皮细胞和肿瘤细胞等,通过与免疫细胞的相互作用可以放大或者抑制特定免疫反应,并且作为一个高度动态的复杂网络系统,会根据病原入侵、炎症反应或癌症发展等疾病的动态情况而调整。因此,全面了解免疫微环境与骨衰老之间的相互作用,对开发新的治疗策略具有重要意义。免疫微环境影响骨衰老简要示意图,如图3。"

2.3.1 巨噬细胞 与年龄相关的免疫功能改变被定义为“免疫衰老”。巨噬细胞在先天和获得性免疫中起着至关重要的作用[45]。年龄相关的巨噬细胞功能下降的标志是主要组织相容性复合物Ⅱ类分子表达减少。研究发现,与年轻个体相比,来自老年个体活化的巨噬细胞产生更多的前列腺素E2,从而抑制主要组织相容性复合物Ⅱ类分子的表达和白细胞介素12的产生,导致巨噬细胞的抗原提呈能力下降[46]。实验证实,Fas诱导的巨噬细胞凋亡导致巨噬细胞分泌的促进骨形成细胞因子如骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子减少,从而导致骨皮质和骨小梁骨量减少[47];此外,早期谱系巨噬细胞的消耗导致甲状旁腺激素诱导的小鼠小梁骨合成代谢作用减弱[48]。在衰老状态下,全身低水平的慢性炎症导致循环促炎细胞因子升高,多种细胞因子的存在(如白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18)促进M1型巨噬细胞极化,减弱向具有抗炎作用M2型巨噬细胞的转化。衰老的巨噬细胞更容易被氧化,例如当受到干扰素γ或脂多糖攻击时,衰老的巨噬细胞增加肿瘤坏死因子α、诱导型一氧化氮合酶、白细胞介素1β和干扰素γ的释放,这些都是SASP中常见的促炎因子,最终导致破骨细胞活化增加和成骨细胞形成减少[49]。 巨噬细胞的经典分类可分为组织驻留型巨噬细胞和单核细胞源性巨噬细胞。老年小鼠的组织驻留巨噬细胞表现出细胞体积增大、寿命缩短、分布紊乱、与周围细胞的连接减少以及监测微环境的能力下降[50]。既往研究表明老年人巨噬细胞的吞噬能力降低[51]。有趣的是,另一项研究发现巨噬细胞吞噬功能的降低主要发生在组织内的巨噬细胞中,而骨髓来源的巨噬细胞没有表现出吞噬功能的降低[52]。与年龄相关的吞噬细胞受体,如toll样受体和髓样细胞表达的触发受体2减少与吞噬功能降低相关[53-54]。巨噬细胞经历了与衰老相关的转录组变化,并且表现出组织特异性[55],这些变化最直接的表现是分泌细胞因子的类型和定量浓度改变。衰老巨噬细胞分泌组发生显著变化,分泌大量促炎物质,如白细胞介素(白细胞介素α/β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8)、干扰素、肿瘤坏死因子(肿瘤坏死因子α)、转化生长因子(转化生长因子β)等[56],改变细胞间通讯水平,进而作用于其邻近细胞,加速衰老过程;同时,与年龄相关的巨噬细胞功能降低阻碍了血管化、胶原沉积和趋化因子水平降低,导致创面愈合延迟[57]。 2.3.2 T细胞 T细胞在人体免疫系统中发挥着重要作用,尤其是在适应性免疫中。T细胞根据在免疫应答中的功能分为3个亚群:细胞毒性T细胞、辅助性T细胞(T helper cells,Th)和调节性T细胞。其中细胞毒性T细胞主要具有杀灭某些病毒、肿瘤细胞和其他抗原的能力,细胞毒性T细胞与自然杀伤细胞共同构成人类抗病毒和抗肿瘤免疫的重要防线。Th1细胞受白细胞介素12驱动,可分泌干扰素γ、白细胞介素2和肿瘤坏死因子α。Th2细胞由白细胞介素4驱动并分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素5、白细胞介素10和白细胞介素13,主要影响B淋巴细胞、肥大细胞和粒细胞。巨噬细胞与肿瘤坏死因子α密切相关,可介导巨噬细胞和B细胞核因子κB受体活化因子配体表达增加,从而刺激破骨细胞增殖和分化。在卵巢切除模拟女性衰老的骨质疏松动物模型中发现,阻断Th17细胞和肿瘤坏死因子阳性 T细胞从肠道的输出或它们流入骨髓可防止卵巢诱导的骨质流失[58],因此,阻断肠道T细胞的迁移可能为治疗女性衰老相关骨丢失提供新的方向。 衰老的T淋巴细胞首先具有衰老细胞的一般特征,如SASP的获得,其次CD28表达的缺失被认为是T淋巴细胞中最一致的衰老指标,称为 CD28null T淋巴细胞[59]。实验发现CD28- T细胞表面破骨细胞分化配体——核因子κB受体活化因子配体表达增加,体外诱导破骨细胞生成的能力增强,这可能也是免疫衰老与骨衰老联系的关键点[60]。 2.3.3 B细胞 B细胞是从骨髓中提取的多能干细胞,其典型特征是经过活化转化为浆细胞后能产生并分泌影响细胞分化和炎症反应的抗体和各种细胞因子,在免疫调节中起重要作用。在生理条件下,B细胞产生的骨保护素占骨髓中总量的64%,直接或间接影响骨量。B细胞缺陷小鼠表现为骨质疏松症,B细胞重建可改善骨质疏松症[61]。在炎症条件下,附着在骨髓中央区的B细胞是核因子κB受体活化因子配体的来源,导致骨内膜破骨细胞的活化,从而增强骨吸收能力;此外,这些B细胞释放的粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子可促进绝经后骨质疏松患者破骨细胞前体的活化[62]。 SUN等[63]发现B细胞在类风湿关节炎小鼠模型的软骨和骨髓中富集,并高水平表达成骨细胞抑制剂巨噬细胞炎症蛋白1α和肿瘤坏死因子,它们通过激活细胞外信号调节激酶和核因子κB受体活化因子信号通路抑制成骨细胞分化和骨形成过程。近年来,调节性B细胞成为B细胞与骨免疫代谢研究的热点,但其对成骨细胞功能调控的具体机制仍待深究[64]。调节性B细胞通过分泌白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β抑制单核细胞和树突状细胞分泌炎性因子,抑制Th17细胞分化,促进调节性T细胞分化,从而可能促进成骨前体细胞的成熟和生长,发挥免疫抑制功能。FLORES-BORJA 等[65]发现健康人CD19+CD24+CD38high调节性T细胞(高表达CD38)可能通过产生白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β部分抑制Th1和Th17细胞分化,促进CD25+Foxp3+调节性T细胞的生长和分化。因此,B细胞也可通过调节T细胞的作用间接调节骨重塑过程,B细胞的衰老或功能必将会影响骨质的相应变化。 2.3.4 树突状细胞 经典树突状细胞是CD4和CD8 T淋巴细胞最重要的抗原呈递细胞,它们以髓样和淋巴样标记物的共表达为特征。最新研究表明,浆细胞样树突状细胞不仅是从髓系细胞分化而来,还具有淋巴起源的特点[66]。白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α、前列腺素E2等炎症递质可诱导树突状细胞成熟,通过增加主要组织相容性复合体Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类抗原呈递能力和CD40的上调来增强了指导细胞迁移(黏附分子)和增强T细胞活化至关重要的表面结合分子的表达[67]。 与年轻树突状细胞相比,衰老树突状细胞的吞噬功能降低、抗原呈递减少、后续T和B淋巴细胞活化减少、体外迁移能力受损(对趋化因子巨噬细胞炎症蛋白3β和基质细胞衍生因子1的反应性降低),显著增加脂多糖和单链RNA诱导的肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6分泌[68]。以往研究表明,免疫抑制性细胞因子白细胞介素10水平在老年人群中升高;此外,白细胞介素10可加速成熟树突状细胞的凋亡,从而可能导致与年龄增长相关的免疫功能下降[69]。由于树突状细胞细胞是T淋巴细胞和B淋巴细胞的重要调节因子,并且T细胞和B细胞衰老与年龄相关性骨质流失密切相关,因此,树突状细胞细胞衰老也在骨衰老中发挥作用,其机制有待进一步深究[70]。 2.3.5 自然杀伤细胞 自然杀伤细胞来源于骨髓,是固有免疫和适应性免疫的桥梁。随着年龄的增长,自然杀伤细胞的杀伤能力和细胞因子产生能力显著降低。研究表明,随着年龄的增长,所有性别人群的淋巴细胞总数均显著减少,而自然杀伤细胞总数显著增加且以CD56dim细胞为主[71]。自然杀伤细胞被Th细胞产生的白细胞介素2激活,随着年龄的增长,白细胞介素2分泌水平降低,自然杀伤细胞的反应性也降低[72]。众所周知,全身慢性炎症是衰老的基本标志,许多老年患者遭受骨关节炎引起的疼痛和痛苦。在胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠模型中发现,大量滑膜自然杀伤细胞表达核因子κB受体活化因子配体,表明自然杀伤细胞可能参与骨关节炎的骨侵蚀作用,然而清除这些自然杀伤细胞可以防止骨侵蚀的作用[73]。因此,靶向衰老微环境生态位中增加的自然杀伤细胞可能是治疗与年龄相关的骨骼疾病的潜在方法 [74]。 2.4 抗衰老治疗策略 目前治疗骨衰老药物的使用受到作用时间短、不良反应多的限制,急需寻找更有效的替代药物[75]。现有的药物治疗尽管在一定程度上能改善骨密度,但难以逆转骨骼的衰老过程且对部分患者可能无效,不同个体对治疗方案的反应差异巨大,这使得医生难以制定统一的高效治疗方案,并且长期使用某些药物可能导致肝、肾功能损害,或引发其他健康问题,增加了患者的风险。面对这些风险,科研人员开始探索免疫治疗在骨衰老治疗中的潜力。随着年龄的增长,衰老细胞在骨微环境中蓄积,去除衰老细胞或减少SASP可以预防或减缓骨质疏松的发生,这一策略可能为骨衰老的治疗开辟一个新的范例,并使各种与年龄有关的疾病受益。该部分重点介绍抗衰老疗法和免疫疗法来预防或减轻骨衰老的最新进展(表2),讨论现有治疗骨衰老治疗的一般方法与潜在的新手段。"


2.4.1 清除衰老细胞 抗衰老药物是一类能够选择性去除衰老细胞的药物。衰老细胞是机体衰老的关键驱动因素,其积累会导致多种与年龄相关的疾病。抗衰老药物通常被称为Senolytics,主要作用机制是通过选择性诱导衰老细胞死亡,从而维持机体正常的功能。靶向消除衰老细胞而不伤害非衰老细胞是目前研究中最常见的抗细胞衰老治疗方法之一[76]。与传统抗骨质疏松药物相比,抗衰老药在抑制骨吸收的同时促进骨形成,效果更为明显。第一批抗衰老药物包括达沙替尼、槲皮素、漆黄素和 Navitoclax。迄今为止,已鉴定出46种潜在的抗衰老细胞的化合物[77]。 达沙替尼:是一种酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,抑制衰老细胞的增殖和迁移,诱导细胞凋亡。达沙替尼抑制多种酪氨酸激酶,临床主要用于治疗癌症。最近,达沙替尼也被认为是一种促进骨形成和改善骨骼功能的骨调节剂[78]。低剂量(2-5 nmol/L)达沙替尼治疗已被证明可以增加健康供者和多发性骨髓瘤患者骨髓间充质干细胞中骨形成标志物的表达,如碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ 型胶原a1以及转录因子Runx2/核心结合因子α1和转录因子Sp7[79]。 槲皮素:是一种天然存在的具有多种生物活性的类黄酮[80],能靶向Bcl-2通路触发细胞凋亡,显著减少大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的衰老,同时促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[81]。相对于对照组,20 μmol/L槲皮素处理48 h 后,骨髓间充质干细胞衰老相关标志物β-半乳糖苷酶、P16、P21、组蛋白H2A家族成员X蛋白、人巨噬细胞趋化蛋白1、趋化因子(C-X-C基序)配体1、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6 mRNA均显著降低,成骨诱导21 d后茜素红染色显示钙结节的形成更为明显;腹腔注射槲皮素到骨质疏松小鼠体内时,股骨中P16和P21蛋白表达显著降低,μCT扫描显示骨体积分数和骨小梁数量显著增加[82]。 达沙替尼+槲皮素:达沙替尼和槲皮素在清除衰老细胞中发挥着不同的分子机制。在一项小鼠颅骨缺损模型中发现,联合使用达沙替尼和槲皮素可以提高衰老骨髓间充质干细胞的体外和体内成骨能力[83]。椎间盘退变在老年人群中很常见,是慢性背部疼痛和残疾的主要原因。有研究表明,达沙替尼+槲皮素具有阻止小鼠椎间盘退变随年龄依赖性进展的能力,当给予6,14和18月龄C57BL/6小鼠达沙替尼+槲皮素治疗并随后在23月龄时进行评估时,发现6,14月龄小鼠达沙替尼+槲皮素队列椎间盘退行性变的发生率降低;此外,达沙替尼+槲皮素治疗可使衰老标记物,如p16INK4a、细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶抑制因子2A以及SASP相关分子(包括白细胞介素6和基质金属蛋白酶13)的水平显著降低[84]。目前,达沙替尼+槲皮素疗法也被广泛应用于其他老年性疾病的研究。 目前,抗衰老细胞药物大多处于临床前阶段,主要研究其在骨微环境中的抗细胞衰老作用。尽管Senolytics药物在清除衰老细胞方面取得了显著进展,但仍面临一些局限和挑战:①衰老细胞在体内表现出极大的异质性和动态性[85],导致Senolytics药物在准确性、可控性和广谱活性方面存在显著局限性;②一些Senolytics药物可能会脱靶作用于非衰老细胞,引发不良反应[86],长期治疗后可能出现的耐药性问题也是亟待解决的问题。达沙替尼和槲皮素等毒性作用较小、特异性更强的抗骨质疏松药物的临床试验正在逐步开展,以进一步验证其在人体中的抗骨质疏松作用。 2.4.2 SASP靶向药物 SASP靶向药物是一种抗衰老药物,可抑制衰老细胞中SASP成分的有害作用。鲁索替尼是一种Janus激酶抑制剂,可抑制骨微环境中的各种SASP成分,从而改善小鼠的骨微结构,增强骨强度。在一项使用鲁索替尼治疗22个月雄性C57BL/6小鼠2个月的研究中,与对照组相比,治疗组骨体积分数和骨小梁厚度增加[80]。 需要注意的是,非衰老细胞如巨噬细胞也可以分泌SASP,而SASP抑制剂对SASP分泌的非特异性抑制可能会带来其他不良影响[80],因此,目前不提倡单独将SASP抑制剂用于抗细胞衰老治疗,有望提高其特异性。 雷帕霉素是由吸水链霉菌产生的三十六元环含氮三烯大环内酯类抗生素,可减少细胞衰老、抑制SASP,延长寿命。雷帕霉素被认为是最有效的抗衰老药物之一,并已被证明对骨血管生成以及刺激快速骨组织生成具有积极作用[87-88]。 程序性细胞死亡1抑制剂已在癌症治疗领域出现并得到广泛认可,然而,肿瘤的发展往往与衰老有关。为了验证程序性细胞死亡1是否在衰老中发挥作用,研究人员分析了细胞和小鼠模型中几种免疫检查点蛋白的表达,发现程序性细胞死亡配体1在衰老细胞中显著增加,称为程序性细胞死亡配体1阳性衰老细胞;衰老细胞中程序性细胞死亡配体1 的表达可能导致逃逸免疫监视,并导致衰老细胞随着年龄的增长而积累,研究揭示了程序性细胞死亡配体1表达升高与衰老相关分泌表型水平升高之间的相关性[89]。与此相一致的是,在小鼠体内注射抗程序性细胞死亡1药物后,CD8+ T细胞被激活,导致衰老细胞群中p16+(衰老细胞的标志)细胞的总数和程序性细胞死亡配体1阳性细胞的数量减少,使得各种衰老相关表型得到改善。因此,作为连接衰老和免疫的交叉点,程序性细胞死亡1/程序性细胞死亡配体1被认为是抗衰老治疗的一个有效靶点[90]。 在糖尿病db/db小鼠模型中,皮下注射HCW9218(一种可注射的融合蛋白复合物,通过激活所需的免疫反应来攻击癌细胞,同时阻断不必要的免疫抑制活性,从而驱动抗肿瘤活性的药物)被证明可以减少衰老的胰岛β细胞和SASP,从而改善葡萄糖耐量、胰岛素抵抗和衰老指数;此外,在自然衰老小鼠中连续皮下注射HCW9218显著降低了衰老细胞和SASP的丰度,并且使外周各器官促炎基因的表达减少[91]。表明HCW9218具有中和转化生长因子β 和刺激免疫细胞的双重功能,全身应用于小鼠是安全的,为未来抗衰老治疗提供了新的思路。 SASP靶向药物的疗效和安全性是研发过程中的重要关注点,尽管这些药物在初步研究中显示出一定的疗效,但仍需要更多的临床试验来验证其长期效果和安全性;此外,不同药物之间的相互作用以及药物对特定人群的适用性也需要进一步的研究。例如:如何有效地将药物递送到目标细胞是一个关键问题。长期使用SASP靶向药物可能导致耐药性的产生,未来基于患者特定分子特征或基因型的个体化治疗方案将成为未来SASP靶向药物治疗的重要方向,并且SASP靶向药物与其他抗衰药物的联合治疗将进一步提高疗效,并减少不良反应。 2.4.3 炎症细胞因子靶向治疗 骨衰老和慢性炎症之间的密切关系已被证实[49], 随着年龄的增长,全身炎症水平逐渐升高,这种低度、长期的炎症状态对骨骼健康有负面影响。非类固醇抗炎药、肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂、白细胞介素1阻滞剂等抗炎药物的应用可以有效降低炎症水平,保护骨骼免受炎症损伤。 非类固醇抗炎药种类众多,常用的包括布洛芬、阿司匹林、吲哚美辛、依托考昔、双氯芬酸钠等。非类固醇抗炎药主要集中于骨关节炎的治疗,也被用于骨质疏松症的治疗中,主要通过减少骨骼炎症反应,促进骨骼修复[92]。非类固醇抗炎药的主要不良反应包括胃肠道反应(如恶心、呕吐、腹泻、腹痛等)、肾损伤、心血管风险(如高血压、心肌梗死等)、过敏反应等,长期使用非类固醇抗炎药可能导致胃溃疡、出血等严重并发症。因此,在使用非类固醇抗炎药时需权衡利弊,选择适宜的药物种类和剂量。 临床研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂不仅可以减轻关节炎症,还有助于改善骨密度和结构[93]。针对炎症因子如白细胞介素17或肿瘤坏死因子α的抗体也显示出调节骨重塑平衡的潜力[94]。研究发现肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂可以显著抑制成骨细胞的凋亡,促进骨细胞的增殖和分化,从而改善骨骼的微环境[95]。市场上已有多种肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂药物,如依那西普、英夫利昔单抗、阿达木单抗等,但也存在一些安全性和不良反应问题,例如,肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂可能导致感染、过敏等不良反应[96]。因此,在使用肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂时需要严格掌握用药指征和剂量,密切监测患者的病情变化和不良反应情况。 白细胞介素1阻滞剂在骨衰老治疗中显示出显著疗效,使用白细胞介素1β受体拮抗剂阿纳金拉可以逆转老年小鼠的造血系统衰老,改善血液系统的功能[97]。阻断白细胞介素1β介导的炎症通路有助于恢复骨髓微环境的年轻状态,尽管研究主要在动物模型中进行,但结果显示了白细胞介素1阻滞剂在骨衰老治疗中具有潜在的临床价值。白细胞介素1阻滞剂在骨衰老治疗中的安全性得到了初步验证,例如,Rilonacept是一种已获美国FDA批准用于治疗复发性心包炎的白细胞介素1阻断剂[98]。然而,由于骨衰老是一个复杂的病理过程,涉及多种因素的相互作用,未来研究应继续探索白细胞介素1阻滞剂在骨衰老治疗中的确切作用机制以及优化用药方案和剂量,还需要开展更大规模的临床试验,以验证白细胞介素1阻滞剂的疗效和安全性。 2.4.4 免疫细胞调节疗法 T细胞在调节骨代谢中起着至关重要的作用,尤其是调节性T细胞和Th细胞(如Th17)之间的平衡对骨骼健康至关重要[99]。调节性T细胞通过抑制免疫反应和刺激抗炎细胞因子的产生来保护骨骼;相反,Th17细胞通过分泌白细胞介素17等促炎因子促进骨吸收。针对T细胞的治疗,如扩增调节性T细胞或抑制Th17细胞活性可调节骨代谢,增强骨形成和减少骨吸收。另外,CD153抗原疫苗接种已被证明是一种长期的治疗策略,可以防止衰老T细胞在脂肪组织中的积累,并改善小鼠的肥胖相关表型[100]。T细胞调节疗法在治疗骨衰老方面取得了显著进展,研究者利用表达嵌合抗原受体的工程化T细胞可以使T细胞特异性识别和清除衰老细胞[101],使其具有更强的靶向能力和免疫调节功能。尽管T细胞调节疗法在治疗骨衰老方面具有广阔前景,但其临床应用仍面临一些挑战,例如:T细胞的分离、激活和扩增过程相对复杂,成本较高;基因工程改造T细胞可能存在安全风险,回输T细胞后可能引发免疫反应等。因此,在未来的研究中需要进一步优化T细胞调节疗法的操作流程,提高其安全性和有效性。 巨噬细胞在骨免疫微环境中的作用是多方面的,根据内环境的变化呈现出M1促炎型和M2抗炎型的不同极化状态。巨噬细胞从M1向M2的转化减少了促炎细胞因子的产生、增强了抗炎细胞因子的产生,从而促进骨合成代谢[102]。某些药物,如特异性细胞因子抑制剂或小分子药物(双膦酸盐、他汀类药物、非类固醇抗炎药、巨噬细胞集落刺激因子抑制剂、抗核因子κB受体活化因子配体)已在实验中被用于调节巨噬细胞的活性和极化状态[103-105]。但是如何精确调控巨噬细胞的极化状态,以及如何确定最佳的治疗剂量和时机等也是当前研究面临的挑战,需要深入研究巨噬细胞极化状态的调控机制等,为优化治疗效果和开发新的治疗策略提供理论基础。 2.4.5 NAD+调节疗法 转录因子叉头盒O可以减弱Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导和骨祖细胞的增殖,从而减少骨形 成[106]。研究表明,沉默调节蛋白1是一种依赖于NAD(烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸)+的酶,能够在成骨祖细胞中对叉头蛋白O和β-进行去乙酰化,从而显著提高骨量;此外,NAD+的前体烟酰胺核糖可以有效降低与叉头蛋白O1和β-连环蛋白乙酰化以及细胞衰老相关的标志物,从而增强小鼠衰老细胞的成骨潜能[107]。另外,烟酰胺单核苷酸不仅可以促进骨细胞的生长和分化,增加骨密度,还可以抑制骨吸收,提供抗氧化保护,减少氧化应激对骨细胞的损伤[108]。有研究发现,过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α/β非依赖性线粒体调控通路在衰老过程中发挥作用,过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α/β通路受细胞核NAD+水平的调控,NAD+在衰老过程中失活,导致核和线粒体编码的氧化磷酸化亚基之间出现假缺氧驱动的失衡,这种不平衡可以通过限制热量来预防并通过提高NAD+水平来逆转[109]。衰老细胞通常表现出线粒体功能障碍[110],而NAD+可以调节衰老免疫细胞(如T细胞)的线粒体代谢,使其成为免疫治疗的新候选药物[111]。NAD+调节疗法在治疗骨衰老方面具有广阔的应用前景和潜力,通过补充NAD+或其前体物质可以提高生物体内的NAD+水平,改善细胞代谢、增强能量产生、促进DNA修复和免疫调节等,从而减缓衰老进程并促进组织修复。动物实验和临床前研究已经为这种疗法提供了有力的证据支持,然而长期应用的安全性和有效性仍需进一步验证,并且治疗机制仍需深入探索。 2.4.6 分子治疗 分子治疗可通过靶向骨免疫微环境中的Wnt/β-连环蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β等关键信号通路调节骨生成和吸收。低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5作为参与Wnt信号通路的Wnt配体共受体,可调节骨形成和内环境稳态[112]。研究表明,骨硬化蛋白结合低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5和低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白6可作为Wnt信号的直接拮抗剂,而抗骨硬化蛋白单克隆抗体如罗莫单抗(Romosozumab)通过阻断负调节因子骨硬化蛋白间接激活Wnt信号[113]。核因子κB受体活化因子/因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素信号通路主要调控破骨细胞的分化和成熟[114],简单地说,骨细胞和Th细胞分泌的核因子κB受体活化因子配体与破骨细胞上的核因子κB受体活化因子结合,可以促进破骨细胞的分化和成熟;相反,骨保护素主要由成骨细胞(也由B细胞和树突状细胞)分泌,与核因子κB受体活化因子竞争性结合,从而降低骨吸收。单克隆抗体地诺单抗(Denosumab)能结合并灭活核因子κB受体活化因子配体,阻止核因子κB受体活化因子配体与其受体核因子κB受体活化因子结合,导致功能性破骨细胞数量减少、骨吸收减少[115]。在大鼠和小鼠的衰老过程中,免疫细胞包括巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞的促炎和衰老亚型可在骨髓中积累并分泌丰富的粒钙蛋白[116]。进一步的研究发现,粒钙蛋白与丛状蛋白B2受体结合后部分失活其下游信号通路,从而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的骨形成并促进脂肪生成,一种粒钙蛋白中和抗体被开发出来并被证明可以改善老年小鼠的骨骼健康[117]。 2.4.7 营养和生活方式的调整 营养和生活方式的改变也是通过调节免疫微环境来管理骨衰老的重要方法。微量元素在骨形成过程中扮演着重要角色,钙是骨骼的主要成分,人体中大约99%的钙存在于骨骼和牙齿中,以羟基磷灰石的形式储存,羟基磷灰石负责组织的矿化,对骨骼的矿化和强度有决定性影响。镁作为机体正常运转所必需的元素,参与细胞的多种代谢途径,能够促进钙在骨骼中的吸收和沉淀,防止钙在软组织中沉淀形成结石,从而预防骨质疏松。磷是参与许多生物过程的重要元素,是人体细胞内的一种关键阴离子,参与维持体内酸碱平衡。磷参与神经刺激的传导。羟基磷灰石和磷蛋白是骨构建材料,而焦磷酸盐在骨生成和骨溶解过程中发挥调节作用[118]。另外,微量元素在免疫过程中也发挥着重要作用,硒是一种对健康至关重要的微量矿物质,硒从食物中获得并被肝脏吸收后以硒蛋白的形式在体内执行各种生理功能,硒蛋白以其氧化还原活性和抗炎特性而闻名。硒刺激免疫细胞的激活,对免疫系统的激活很重要[119]。锌是人体第二丰富的必需微量元素,在细胞增殖、转录、凋亡、生长、免疫和创面愈合等许多生理过程中发挥着关键作用。由此可见,及时补充微量元素有利于维持体内骨重塑平衡以及免疫系统的正常运作[120]。这些微量元素还可以通过表面修饰等方式将微量元素引入材料表面,从而在不影响材料性能的同时,增强其免疫调节能力,例如将硒修饰在生物材料表面可以提供持续释放硒的功能,进一步增强材料的免疫调节效果[121]。合理的饮食、适度的体力活动有助于改善骨骼健康,尤其是抗炎饮食,如富含ω-3脂肪酸、抗氧化剂和纤维的地中海饮食,可以有效调节体内炎症状态,支持骨骼健康[122]。 2.4.8 干细胞治疗 关于胚胎干细胞、诱导多能干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞及其分泌因子在骨衰老治疗中的作用的验证文章越来越多,干细胞注射可以通过增加干细胞数量和诱导成骨而在骨衰老治疗中发挥作用[123-124]。另外,干细胞通过旁分泌信号直接将各种生物活性分子释放到局部环境中,促进骨再生,这些分子包括胰岛素样生长因子1、转化生长因子β、血管内皮生长因子、血管生成素、肝细胞生长因子和白细胞介素6,它们作用于成骨细胞和破骨细胞,可以刺激和支持骨形成和重塑过程[125]。尽管干细胞治疗在骨疾病中取得了显著的治疗效果,但其安全性仍存在一些潜在风险,例如干细胞移植后可能发生免疫排斥反应、感染、血栓形成等并发症。因此,在进行干细胞治疗前需要对患者进行全面的评估和监测,确保治疗的安全性和有效性,然而由于临床伦理问题,尚未在人体进行试验观察。未来,干细胞治疗将更加注重个性化治疗和精准医疗的发展,通过基因测序和生物信息学等技术手段来精准识别患者的基因型和表型特征,为患者提供个性化的干细胞治疗方案。 2.4.9 基因调控疗法 疾病的发病通常由基因调控,研究表明骨衰老与表观遗传调控因子miRNAs、长链非编码RNAs和环状RNAs密切相关,它们参与成骨细胞和破骨细胞分化的信号通路和基因表达调控[126]。有实验表明,敲低miR-29a的小鼠骨小梁微结构稀疏,成骨冯库萨染色法染色显示矿化基质沉积减少,并且其DNA甲基化水平上调,衰老相关β-半乳糖苷酶和p16免疫染色增强。了解这些RNA在骨衰老中的作用机制,可以更好地了解这类疾病,并为骨衰老治疗提供新的思路[127]。 2.4.10 肠道菌群调整 有研究发现鼠李糖乳杆菌GG具有成骨作用,其机制是通过调节肠道微生物群和肠道屏障,刺激肠道和骨骼Th17/调节性T细胞平衡,改善雌激素缺乏所致骨质疏松症的雌激素生成功能[128]。由此可见,微生物群与免疫系统密切相关,并参与骨骼老化的过程,因此,肠道微生物群的调节也可能是未来治疗骨骼老化的方法之一。尽管肠道菌群与骨衰老之间的关系已经得到广泛关注和研究,但仍有许多挑战需要克服,目前对肠道菌群影响骨骼健康的机制尚不完全清楚,需要更多的基础研究和临床试验来揭示其内在的机制。"

| [1] CHANDRA A, RAJAWAT J. Skeletal Aging and Osteoporosis: Mechanisms and Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3553. [2] CUI J, SHIBATA Y, ZHU T, et al. Osteocytes in bone aging: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;77:101608. [3] WANG Y, WEHLING-HENRICKS M, WELC SS, et al. Aging of the immune system causes reductions in muscle stem cell populations, promotes their shift to a fibrogenic phenotype, and modulates sarcopenia. FASEB J. 2019;33:1415-1427. [4] HENTGES F. B lymphocyte ontogeny and immunoglobulin production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994;97 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):3-9. [5] SHARP A, KUKULANSKY T, MALKINSON Y, et al. The bone marrow as an effector T cell organ in aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 1990;52(2-3):219-233. [6] GRUVER AL, HUDSON LL, SEMPOWSKI GD. Immunosenescence of ageing. J Pathol. 2007;211(2):144-156. [7] FRANCESCHI C, BONAFÈ M, VALENSIN S, et al. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;908:244-254. [8] PAPPERT M, KHOSLA S, DOOLITTLE M. Influences of Aged Bone Marrow Macrophages on Skeletal Health and Senescence. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(6):771-778. [9] LI H, LIN S, WANG Y, et al. Immunosenescence: A new direction in anti-aging research. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;141:112900. [10] KHANDELWAL S, LANE NE. Osteoporosis: Review of Etiology, Mechanisms, and Approach to Management in the Aging Population. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2023;52(2):259-275. [11] SEELEY DG, BROWNER WS, NEVITT MC, et al. Which fractures are associated with low appendicular bone mass in older women? The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Ann Intern Med 1991;155(11):837-842. [12] GRAVES EJ. Utilization of short-stay hospitals. United States, 1985. Annual summary. Vital Health Stat 13. 1987;(91):1-59. [13] FARR JN, KHOSLA S. Cellular senescence in bone. Bone. 2019;121: 121-133. [14] FANG C-L, LIU B, WAN M. “Bone-SASP” in Skeletal Aging. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;113:68-82. [15] NELSON G, WORDSWORTH J, WANG C, et al. A senescent cell bystander effect: senescence-induced senescence. Aging Cell. 2012;11:345-349. [16] 钟思扬,廖晴,周星宇,等.骨微环境对组织工程骨再生过程的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(15):2452-2460. [17] CAI L, LV Y, YAN Q, et al. Cytokines: The links between bone and the immune system. Injury. 2024;55(2):111203. [18] HADJIDAKIS DJ, ANDROULAKIS II. Bone remodeling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1092:385-396. [19] BOYETTE L, TUAN R. Adult Stem Cells and Diseases of Aging. JCM. 2014; 3:88-134.
[20] CHEN JH, HALES CN, OZANNE SE. DNA damage, cellular senescence and organismal ageing: causal or correlative? Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:7417-7428. [21] KIM HN, CHANG J, SHAO L, et al. DNA damage and senescence in osteoprogenitors expressing Osx1 may cause their decrease with age. Aging Cell. 2017;16:693-703. [22] CALO E, WYSOCKA J. Modification of Enhancer Chromatin: What, How, and Why? Mol Cell. 2013;49:825-837. [23] ZHOU H, YANG X, WANG N, et al. Tigogenin inhibits adipocytic differentiation and induces osteoblastic differentiation in mouse bone marrow stromal cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;270:17-22. [24] CHEN Q, SHOU P, ZHENG C, et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:1128-1139. [25] HU M, XING L, ZHANG L, et al. NAP1L2 drives mesenchymal stem cell senescence and suppresses osteogenic differentiation. Aging Cell. 2022;21:e13551. [26] LI J, AYOUB A, XIU Y, et al. TGFβ-induced degradation of TRAF3 in mesenchymal progenitor cells causes age-related osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2795. [27] Moerman EJ, Teng K, Lipschitz DA, et al. Aging activates adipogenic and suppresses osteogenic programs in mesenchymal marrow stroma/stem cells: the role of PPAR-γ2 transcription factor and TGF-β/BMP signaling pathways. Aging Cell. 2004;3:379-389. [28] LI H, LIU P, XU S, et al. FOXP1 controls mesenchymal stem cell commitment and senescence during skeletal aging. J Clin Invest. 2017; 127:1241-1253. [29] GAO Y, CHEN N, FU Z, et al. Progress of Wnt Signaling Pathway in Osteoporosis. Biomolecules. 2023;13:483. [30] KASSEM M, MARIE PJ. Senescence-associated intrinsic mechanisms of osteoblast dysfunctions: Age-related mechanisms of osteoblast dysfunctions. Aging Cell. 2011;10:191-197. [31] SHIM HS, IACONELLI J, SHANG X, et al. TERT activation targets DNA methylation and multiple aging hallmarks. Cell. 2024;187(15):4030-4042.e13. [32] PEZONE A, OLIVIERI F, NAPOLI MV, et al. Inflammation and DNA damage: cause, effect or both. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(4):200-211. [33] OGI T, LIMSIRICHAIKUL S, OVERMEER RM, et al. Three DNA polymerases, recruited by different mechanisms, carry out NER repair synthesis in human cells. Mol Cell. 2010;37(5):714-727. [34] BECERIKLI M, JAURICH H, SCHIRA J, et al. Age-dependent alterations in osteoblast and osteoclast activity in human cancellous bone. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21:2773-2781. [35] YANG L, CHENG P, CHEN C, et al. miR-93/Sp7 function loop mediates osteoblast mineralization. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27:1598-1606. [36] KOMORI T. Cell Death in Chondrocytes, Osteoblasts, and Osteocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:2045. [37] ZHIVODERNIKOV IV, KIRICHENKO TV, MARKINA YV, et al. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:15772. [38] JIANG N, AN J, YANG K, et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome: A New Target for Prevention and Control of Osteoporosis? Front Endocrinol. 2021; 12:752546. [39] IANTOMASI T, ROMAGNOLI C, PALMINI G, et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Osteoporosis: Molecular Mechanisms Involved and the Relationship with microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:3772. [40] WALSH MC, CHOI Y. Biology of the RANKL–RANK–OPG system in immunity, bone, and beyond. Front Immunol. 2014;5:511. [41] SHARAF-ELDIN WE, ABU-SHAHBA N, MAHMOUD M, et al. The Modulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Osteoclastogenesis. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1-13. [42] CAO JJ, WRONSKI TJ, IWANIEC U, et al. Aging Increases Stromal/Osteoblastic Cell-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Alters the Osteoclast Precursor Pool in the Mouse. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20:1659-1568. [43] LEIMKÜHLER NB, SCHNEIDER RK. Inflammatory bone marrow microenvironment. Hematology. 2019;2019:294-302. [44] HARRIS MA, SAVAS P, VIRASSAMY B, et al. Towards targeting the breast cancer immune microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024;24(8):554-577. [45] VAROL C, MILDNER A, JUNG S. Macrophages: Development and Tissue Specialization. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:643-675. [46] SOLANA R. Innate immunosenescence: Effect of aging on cells and receptors of the innate immune system in humans. Semin Immunol. 2012;24(5):331-341. [47] LI X, LIANG T, DAI B, et al. Excess glucocorticoids inhibit murine bone turnover via modulating the immunometabolism of the skeletal microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(10):e166795. [48] CHO SW, SOKI FN, KOH AJ, et al. Osteal macrophages support physiologic skeletal remodeling and anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone in bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:1545-1550. [49] KUSHIOKA J, CHOW SK, TOYA M, et al. Bone regeneration in inflammation with aging and cell-based immunomodulatory therapy. Inflamm Regener. 2023;43:29. [50] HEFENDEHL JK, NEHER JJ, SU RB, et al. Homeostatic and injuryinduced microglia behavior in the aging brain. Aging Cell. 2014;13(1):60-69. [51] LLOBERAS J, TUR J, VICO T, et al. Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Macrophage Aging// FULOP T, FRANCESCHI C, HIROKAWA K, PAWELEC G, editors. Handbook of Immunosenescence [Internet]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019:1631-1663. [52] LINEHAN E, DOMBROWSKI Y, SNODDY R, et al. Aging impairs peritoneal but not bone marrow-derived macrophage phagocytosis. Aging Cell. 2014;13:699-708. [53] BOYD AR, SHIVSHANKAR P, JIANG S, et al. Age-related Defects in TLR2 Signaling Diminish the Cytokine Response by Alveolar Macrophages during Murine Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Exp Gerontol. 2012;47(7): 507-518. [54] THOMAS AL, LEHN MA, JANSSEN EM, et al. Naturally-aged microglia exhibit phagocytic dysfunction accompanied by gene expression changes reflective of underlying neurologic disease. Sci Rep. 2022; 12(1):19471. [55] BABAGANA M, OH KS, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Hedgehog dysregulation contributes to tissue-specific inflammaging of resident macrophages. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(15):19207-19229. [56] YUE Z, NIE L, ZHANG P, et al. Tissue-resident macrophage inflammaging aggravates homeostasis dysregulation in age-related diseases. Cell Immunol. 2021;361:104278. [57] DANON D, KOWATCH MA, ROTH GS. Promotion of wound repair in old mice by local injection of macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(6):2018-2020. [58] YU M, PAL S, PATERSON CW, et al. Ovariectomy induces bone loss via microbial-dependent trafficking of intestinal TNF+ T cells and Th17 cells. J Clin Invest. 2021;131:e143137. [59] VALLEJO AN. CD28 extinction in human T cells: altered functions and the program of T-cell senescence. Immunol Rev. 2005;205:158-169. [60] FESSLER J, HUSIC R, SCHWETZ V, et al. Senescent T-Cells Promote Bone Loss in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:95. [61] LI Y, TORALDO G, LI A, et al. B cells and T cells are critical for the preservation of bone homeostasis and attainment of peak bone mass in vivo. Blood. 2007;109:3839-3848. [62] TONI R, DI CONZA G, BARBARO F, et al. Microtopography of Immune Cells in Osteoporosis and Bone Lesions by Endocrine Disruptors. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1737. [63] SUN W, MEEDNU N, ROSENBERG A, et al. B cells inhibit bone formation in rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat Commun. 2018;9:5127. [64] CATALÁN D, MANSILLA MA, FERRIER A, et al. Immunosuppressive Mechanisms of Regulatory B Cells. Front Immunol. 2021;12:611795. [65] FLORES-BORJA F, BOSMA A, NG D, et al. CD19 + CD24 hi CD38 hi B Cells Maintain Regulatory T Cells While Limiting TH 1 and TH 17 Differentiation. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(173):173ra23. [66] RODRIGUES PF, TUSSIWAND R. Novel concepts in plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) development and differentiation. Mol Immunol. 2020;126:25-30. [67] UYEMURA K, CASTLE SC, MAKINODAN T. The frail elderly: role of dendritic cells in the susceptibility of infection. Mech Ageing Dev. 2002;123:955-962. [68] AGRAWAL A, AGRAWAL S, CAO JN, et al. Altered Innate Immune Functioning of Dendritic Cells in Elderly Humans: A Role of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Signaling Pathway. J Immunol. 2007;178: 6912-6922. [69] CASTLEAB SC, UYEMURAABC K, CRAWFORD W, et al. Age-related impaired proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with an increase in both IL-10 and IL-12. Exp Gerontol. 1999;34:243-252. [70] CLOWES JA, RIGGS BL, KHOSLA S. The role of the immune system in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:207-227. [71] GOUNDER SS, ABDULLAH BJJ, RADZUANB NEIBM, et al. Effect of Aging on NK Cell Population and Their Proliferation at Ex Vivo Culture Condition. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018;2018:1-6. [72] TEISSIER T, BOULANGER E, COX LS. Interconnections between Inflammageing and Immunosenescence during Ageing. Cells. 2022; 11(3):359. [73] SÖDERSTRÖM K, STEIN E, COLMENERO P, et al. Natural killer cells trigger osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction in arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:13028-13033. [74] SAXENA Y, ROUTH S, MUKHOPADHAYA A. Immunoporosis: Role of Innate Immune Cells in Osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687037. [75] MA M, ZENG H, YANG P, et al. Drug Delivery and Therapy Strategies for Osteoporosis Intervention. Molecules. 2023;28:6652. [76] KIRKLAND JL, TCHKONIA T. Senolytic drugs: from discovery to translation. J Intern Med. 2020;288:518-536. [77] ZHU Y, TCHKONIA T, PIRTSKHALAVA T, et al. The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: from transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell. 2015;14:644-658. [78] ID BOUFKER H, LAGNEAUX L, NAJAR M, et al. The Src inhibitor dasatinib accelerates the differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells into osteoblasts. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:298. [79] GARCIA-GOMEZ A, OCIO EM, CRUSOE E, et al. Dasatinib as a Bone-Modifying Agent: Anabolic and Anti-Resorptive Effects. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34914. [80] FARR JN, XU M, WEIVODA MM, et al. Targeting cellular senescence prevents age-related bone loss in mice. Nat Med. 2017;23:1072-1079. [81] ZHANG D, YU K, YANG J, et al. Senolytic controls bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells fate improving bone formation. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(6):3078-3088. [82] XING X, TANG Q, ZOU J, et al. Bone-targeted delivery of senolytics to eliminate senescent cells increases bone formation in senile osteoporosis. Acta Biomaterialia. 2023;157:352-366. [83] ZHOU Y, XIN X, WANG L, et al. Senolytics improve bone forming potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from aged mice. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6:34. [84] NOVAIS EJ, TRAN VA, JOHNSTON SN, et al. Long-term treatment with senolytic drugs Dasatinib and Quercetin ameliorates age-dependent intervertebral disc degeneration in mice. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5213. [85] DATTA I, BANGI E. Senescent cells and macrophages cooperate through a multi-kinase signaling network to promote intestinal transformation in Drosophila. Dev Cell. 2024;59(5):566-578.e3. [86] LAGOUMTZI SM, CHONDROGIANNI N. Senolytics and senomorphics: Natural and synthetic therapeutics in the treatment of aging and chronic diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;171:169-190. [87] XING Y, LIU C, ZHOU L, et al. Osteogenic effects of rapamycin on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via inducing autophagy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18:129. [88] WU J, WANG A, WANG X, et al. Rapamycin improves bone mass in high-turnover osteoporosis with iron accumulation through positive effects on osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Bone. 2019;121:16-28. [89] LAGES CS, LEWKOWICH I, SPROLES A, et al. Partial restoration of T-cell function in aged mice by in vitro blockade of the PD-1/ PD-L1 pathway. Aging Cell. 2010;9:785-798. [90] Wang TW, Johmura Y, Suzuki N, et al. Blocking PD-L1–PD-1 improves senescence surveillance and ageing phenotypes. Nature. 2022;611:358-364. [91] SHRESTHA N, CHATURVEDI P, ZHU X, et al. Immunotherapeutic approach to reduce senescent cells and alleviate senescence-associated secretory phenotype in mice. Aging Cell. 2023;22:e13806. [92] WANG J, LU HX, WANG J. Cannabinoid receptors in osteoporosis and osteoporotic pain: a narrative update of review. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019;71(10):1469-1474. [93] NIGIL HAROON N, SRIGANTHAN J, AL GHANIM N, et al. Effect of TNF-alpha inhibitor treatment on bone mineral density in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;44:155-161. [94] PATEL JP, KONANUR SRINIVASA NK, GANDE A, et al. The Role of Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Cureus. 2023; 15(1):e33293. [95] ZHENG LW, WANG WC, MAO XZ, et al. TNF-α regulates the early development of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by mediating osteoblast autophagy and apoptosis via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(9):1881-1889. [96] MOCCI G, MARZO M, PAPA A, et al. Dermatological adverse reactions during anti-TNF treatments: focus on inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(10):769-779. [97] MITCHELL CA, VEROVSKAYA EV, CALERO-NIETO FJ, et al. Stromal niche inflammation mediated by IL-1 signalling is a targetable driver of haematopoietic ageing. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25(1):30-41. [98] FAVA AM, REYALDEEN R, LO PRESTI S, et al. Rilonacept for the treatment of recurrent pericarditis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022;22(1): 7-16. [99] BRAGA WMT, ATANACKOVIC D, COLLEONI GWB. The Role of Regulatory T Cells and TH17 Cells in Multiple Myeloma. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012; 2012:1-4. [100] YOSHIDA S, NAKAGAMI H, HAYASHI H, et al. The CD153 vaccine is a senotherapeutic option for preventing the accumulation of senescent T cells in mice. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2482. [101] CARRASCO E, GÓMEZ DE LAS HERAS MM, GABANDÉ-RODRÍGUEZ E, et al. The role of T cells in age-related diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022;22:97-111. [102] KONG L, WANG Y, SMITH W, et al. Macrophages in Bone Homeostasis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14:474-481. [103] FRADE BB, DIAS RB, GEMINI PIPERNI S, et al. The role of macrophages in fracture healing: a narrative review of the recent updates and therapeutic perspectives. Stem Cell Investig. 2023;10:4. [104] BOONYAYOTHIN W, SINNUNG S, SHANMUGARAJ B, et al. Expression and Functional Evaluation of Recombinant Anti-receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Ligand Monoclonal Antibody Produced in Nicotiana benthamiana. Front Plant Sci. 2021;12:683417. [105] HUME DA, MACDONALD KPA. Therapeutic applications of macrophage colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and antagonists of CSF-1 receptor (CSF-1R) signaling. Blood. 2012;119:1810-1820. [106] XIONG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU F, et al. FOXO1 differentially regulates bone formation in young and aged mice. Cell Signal. 2022;99:110438. [107] KIM HN, PONTE F, WARREN A, et al. A decrease in NAD+ contributes to the loss of osteoprogenitors and bone mass with aging. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2021;7:8. [108] SONG J, LI J, YANG F, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide promotes osteogenesis and reduces adipogenesis by regulating mesenchymal stromal cells via the SIRT1 pathway in aged bone marrow. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(5):336. [109] GOMES AP, PRICE NL, LING AJY, et al. Declining NAD+ Induces a Pseudohypoxic State Disrupting Nuclear-Mitochondrial Communication during Aging. Cell. 2013;155:1624-1638. [110] HARRINGTON JS, RYTER SW, PLATAKI M, et al. Mitochondria in health, disease, and aging. Physiol Rev. 2023;103:2349-2422. [111] COVARRUBIAS AJ, PERRONE R, GROZIO A, et al. NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22:119-141. [112] SONG S, GUO Y, YANG Y, et al. Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;237:108168. [113] SHAH AD, SHOBACK D, LEWIECKI EM. Sclerostin inhibition: a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of osteoporosis. Int J Womens Health. 2015:7:565-580. [114] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39:19-26. [115] REID IR, BILLINGTON EO. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet. 2022;399:1080-1092. [116] LI CJ, XIAO Y, SUN YC, et al. Senescent immune cells release grancalcin to promote skeletal aging. Cell Metabolism. 2022;34:184-185. [117] ZOU NY, LIU R, HUANG M, et al. Age-related secretion of grancalcin by macrophages induces skeletal stem/progenitor cell senescence during fracture healing. Bone Res. 2024;12:6. [118] CIOSEK Ż, KOT K, KOSIK-BOGACKA D, et al. The Effects of Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Fluoride, and Lead on Bone Tissue. Biomolecules. 2021;11(4):506. [119] ZHANG F, LI X, WEI Y. Selenium and Selenoproteins in Health. Biomolecules. 2023;13(5):799. [120] WANG B, FANG T, CHEN H. Zinc and Central Nervous System Disorders. Nutrients. 2023;15(9):2140. [121] SONG J, MENG H, DENG G, et al. Sustainable Release Selenium Laden with SiO2 Restoring Peripheral Nerve Injury via Modulating PI3K/AKT Pathway Signaling Pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:7851-7870. [122] KHANDELWAL S, LANE NE. Osteoporosis. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. 2023;52:259-275. [123] PAS HI, WINTERS M, HAISMA HJ, et al. Stem cell injections in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review of the literature. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:1125-1133. [124] LIANG B, BURLEY G, LIN S, et al. Osteoporosis pathogenesis and treatment: existing and emerging avenues. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022; 27:72. [125] ARJMAND B, SARVARI M, ALAVI-MOGHADAM S, et al. Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine in Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:430. [126] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53:40. [127] LIAN WS, WU RW, CHEN YS, et al. MicroRNA-29a Mitigates Osteoblast Senescence and Counteracts Bone Loss through Oxidation Resistance-1 Control of FoxO3 Methylation. Antioxidants. 2021;10:1248. [128] GUO M, LIU H, YU Y, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. 2023;15:2190304. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [4] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [5] | Han Mengjun, Xu Fang. Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization: advantages and disadvantages of different plans and improvements in predictive models and technologies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7863-7871. |
| [6] | Yu Qinghe, Cai Ziming, Wu Jintao, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Wang Yakun, Lin Xiaoqin, Lin Wenping. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation of endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6391-9397. |
| [7] | Fan Jiaxin, Jia Xiang, Xu Tianjie, Liu Kainan, Guo Xiaoling, Zhang Hui, Wang Qian . Metformin inhibits ferroptosis and improves cartilage damage in osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6398-6408. |
| [8] | Zhou Ying, Tian Yong, Zhong Zhimei, Gu Yongxiang, Fang Hao. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [9] | Wang Wanchun, , Yi Jun, Yan Zhangren, Yang Yue, Dong Degang, Li Yumei. 717 Jiedu Decoction remodels homeostasis of extracellular matrix and promotes repair of local injured tissues in rats after Agkistrodon halys bite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [10] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| [11] | Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6474-6481. |
| [12] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| [13] | Zhang Jian, Cai Feng, Li Tingwen, Ren Pengbo. Fatigue gait recognition of athletes based on fish swarm algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6489-6498. |
| [14] | Zhang Zihan¹, Wang Jiaxin¹, Yang Wenyi², Zhu Lei¹. Regulatory mechanism of exercise promoting mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6499-6508. |
| [15] | Zhang Bochun, Li Wei, Li Guangzheng, Ding Haoqin, Li Gang, Liang Xuezhen, . Association between neuroimaging changes and osteonecrosis: a large sample analysis from UK Biobank and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6574-6582. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||