Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (29): 6228-6238.doi: 10.12307/2025.767
Previous Articles Next Articles
Du Meridian electroacupuncture inhibits ferroptosis and promotes neurorepair in rats with acute cervical spinal cord injury
Sun Rongyan1, Xu Luchun2, Jiang Guozheng2, Song Jiawei2, Ma Yukun2, Fan Jiaojiao2, Wang Guanlong2, Yang Yongdong2, Yu Xing2
- 1Haidian Hospital of Beijing, Beijing 100080, China; 2Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2024-09-18Accepted:2024-11-09Online:2025-10-18Published:2025-03-07 -
Contact:Yu Xing, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China Co-corresponding author: Yang Yongdong, MD, Associate researcher, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China -
About author:Sun Rongyan, Attending physician, Haidian Hospital of Beijing, Beijing 100080, China Xu Luchun, Doctoral candidate, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China Sun Rongyan and Xu Luchun contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 2024-JYB-JBZD-065 (to YYD); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81973882 (to YX); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Program), No. 81804119 (to YYD); Talent Training Program of Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, No. DZMG-QNGG0010 (to YYD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Rongyan, Xu Luchun, Jiang Guozheng, Song Jiawei, Ma Yukun, Fan Jiaojiao, Wang Guanlong, Yang Yongdong, Yu Xing. Du Meridian electroacupuncture inhibits ferroptosis and promotes neurorepair in rats with acute cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6228-6238.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
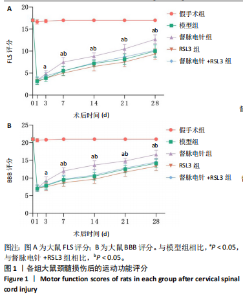
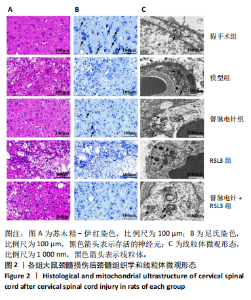
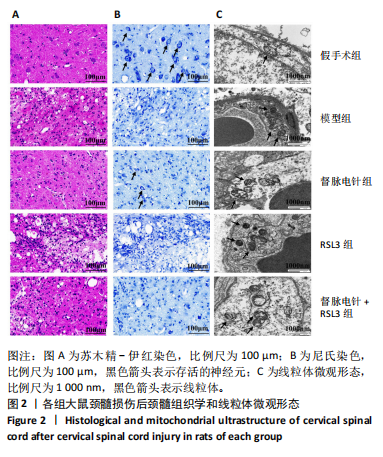
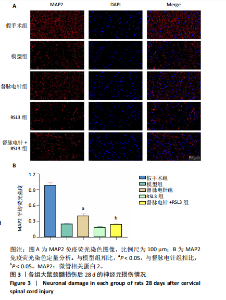
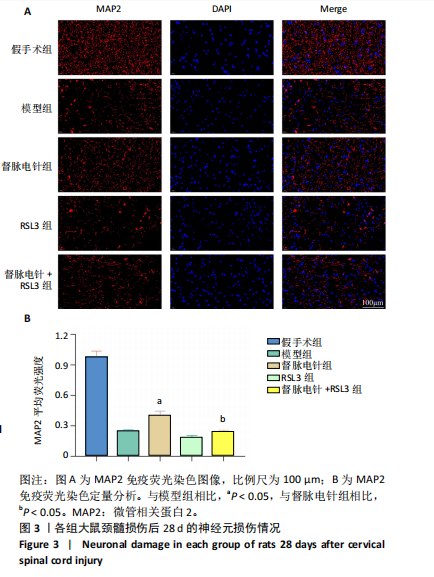
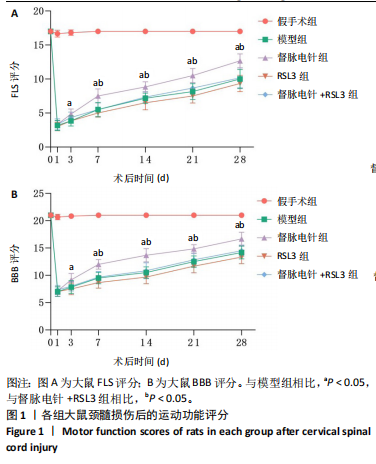
2.1 实验动物数量分析 100只雌性SD大鼠随机分为5组,在颈髓损伤模型构建过程中死亡3只,最后每组随机选取18只,共计90只大鼠完成后续实验。 2.2 各组大鼠颈髓损伤后四肢运动功能 采用FLS评分和BBB评分评估四肢运动功能。除假手术组外,其余各组在术后第1天均表现出严重的运动功能缺陷。从术后3 d开始,督脉电针组的FLS评分和BBB评分开始逐渐恢复,与模型组和督脉电针+RSL3组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图1。结果表明督脉电针促进颈髓损伤后四肢功能恢复,其促进作用可被铁死亡诱导剂RSL3阻断。 2.3 各组大鼠颈髓损伤后组织病理学及线粒体微观形态 苏木精-伊红染色显示,在术后28 d,假手术组大鼠脊髓组织结构正常完整,无水肿;模型组大鼠脊髓组织结构重度异常,水肿严重,大面积组织糜烂,组织间隙增大明显,免疫/炎性细胞广泛浸润;督脉电针组较模型组颈髓结构更为致密,水肿减轻,组织间隙较模型组缩小,免疫/炎性细胞浸润程度降低;督脉电针+RSL3组颈髓结构类似于模型组,存在较大面积组织糜烂与广泛免疫/炎性细胞浸润,见图2A。 尼氏染色显示,在术后28 d,假手术组灰质内存在大量神经元,尼氏体形态规则且呈虎斑状;模型组脊髓周围组织大量溶解,广泛神经元死亡,未见存活神经元,可见散在的细胞碎片和空洞;督脉电针组可见部分存活神经元,溶解性空腔较模型组小;督脉电针+RSL3组颈髓结构类似于模型组,可见大量神经元死亡、细胞碎片和空洞,见图2B。 线粒体形态学的改变是铁死亡的重要标志,因此采用透射电镜观察线粒体的微观形态。模型组线粒体体积变小,基质电子密度升高;督脉电针组线粒体形态明显改善,线粒体体积减少情况较模型组改善,基质电子密度降低,内膜结构趋于完整,嵴清晰可见,显示出一定的保护作用;督脉电针+RSL3组线粒体基质电子密度较督脉电针组升高,嵴结构部分更加模糊,表明RSL3逆转了督脉电针对线粒体的保护性,进一步支持GPX4在铁死亡中的关键作用,见图2C。 组织学和线粒体的微观形态表明,督脉电针可有效减轻颈髓损伤后铁死亡。 2.4 各组大鼠颈髓损伤后神经元继发性损伤及胶质瘢痕形成情况 采用微管相关蛋白2和胶质纤维酸性蛋白免疫荧"
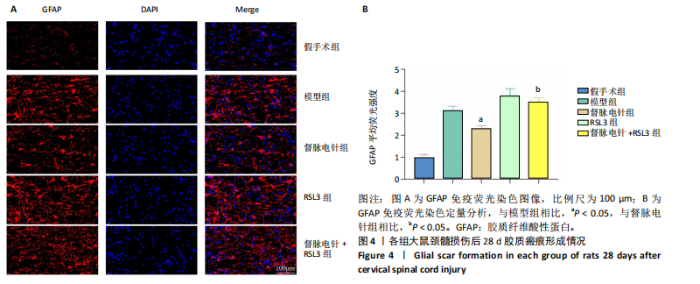
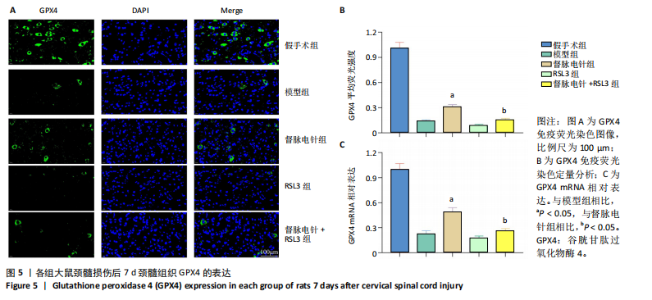
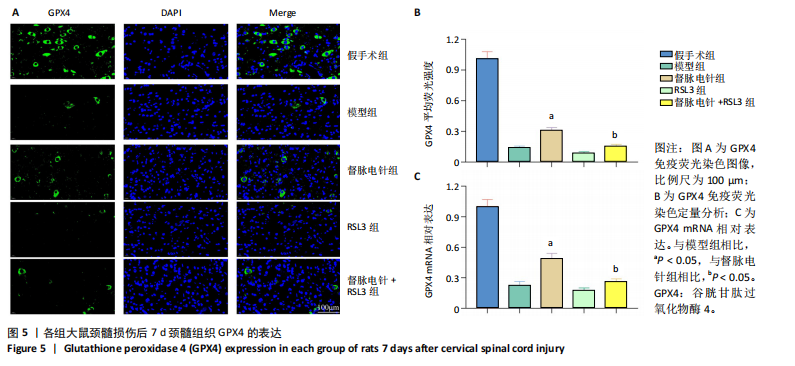
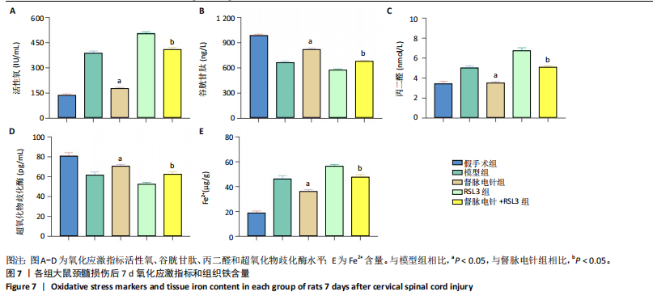
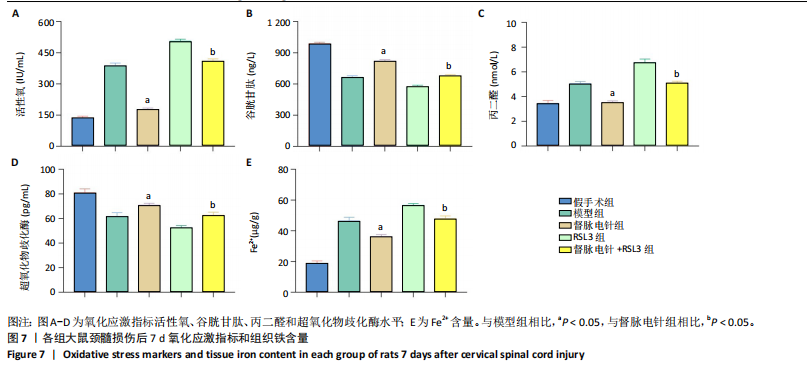
以通过抑制铁死亡减少颈髓损伤后神经元继发性损伤及胶质瘢痕形成。 2.5 各组大鼠颈髓损伤后GPX4和ACSL4的表达 采用免疫荧光染色和RT-PCR检测GPX4和ACSL4水平。结果显示,督脉电针能提高颈髓损伤后GPX4的表达(P < 0.05),降低ACSL4的表达(P < 0.05)。此外,GPX4抑制剂RSL3减弱了督脉电针对GPX4和ACSL4的作用,见图5和图6。这表明GPX4可能是督脉电针抑制颈髓损伤后铁死亡的重要靶点。 2.6 各组大鼠颈髓损伤后氧化还原指标和Fe2+含量 督脉电针组活性氧、丙二醛和Fe2+含量较模型组和督脉电针+RSL3组显著减少(P < 0.05),而谷胱甘肽和超氧化物歧化酶水平较模型组和督脉电针+RSL3组显著增加(P < 0.05),见图7。这提示督脉电针可以通过GPX4/ACSL4轴维持颈髓损伤后氧化还原平衡,抑制铁死亡。"

| [1] SKINNIDER MA, GAUTIER M, TEO AYY, et al. Single-cell and spatial atlases of spinal cord injury in the Tabulae Paralytica. Nature. 2024; 631(8019):150-163. [2] LORACH H, GALVEZ A, SPAGNOLO V, et al. Walking naturally after spinal cord injury using a brain-spine interface. Nature. 2023;618(7963):126-133. [3] XU L, ZHAO H, YANG Y, et al. The application of stem cell sheets for neuronal regeneration after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of pre-clinical studies. Syst Rev. 2023;12(1):225. [4] QIU W, ZHOU B, LUO Y, et al. An Optimized Decellularized Extracellular Matrix from Dental Pulp Stem Cell Sheets Promotes Axonal Regeneration by Multiple Modes in Spinal Cord Injury Rats. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024:e2402312. [5] XU L, YANG Y, ZHONG W, et al. Comparative efficacy of five most common traditional Chinese medicine monomers for promoting recovery of motor function in rats with blunt spinal cord injury: a network meta-analysis. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1165076. [6] 许卢春,杨永栋,赵赫,等.非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用和机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(33):5404-5412. [7] JAFFER H, ANDRABI SS, PETRO M, et al. Catalytic antioxidant nanoparticles mitigate secondary injury progression and promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury model. J Control Release. 2023;364:109-123. [8] ORTEGA MA, FRAILE-MARTINEZ O, GARCÍA-MONTERO C, et al. A comprehensive look at the psychoneuroimmunoendocrinology of spinal cord injury and its progression: mechanisms and clinical opportunities. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):26. [9] RYAN F, BLEX C, NGO TD, et al. Ferroptosis inhibitor improves outcome after early and delayed treatment in mild spinal cord injury. Acta Neuropathol. 2024;147(1):106. [10] SHI T, CHEN Y, ZHOU L, et al. Carboxymethyl cellulose/quaternized chitosan hydrogel loaded with polydopamine nanoparticles promotes spinal cord injury recovery by anti-ferroptosis and M1/M2 polarization modulation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;275(1):133484. [11] ZHENG Q, WANG D, LIN R, et al. Pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and autophagy in spinal cord injury: regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(10):2787-2806. [12] HU X, ZHANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Emerging role of STING signalling in CNS injury: inflammation, autophagy, necroptosis, ferroptosis and pyroptosis. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):242. [13] LI QS, JIA YJ. Ferroptosis: a critical player and potential therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):506-512. [14] LAN T, SUN TT, WEI C, et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Ferroptosis in Central Nervous System Diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(7):3584-3599. [15] BAI XY, LIU XL, DENG ZZ, et al. Ferroptosis is a new therapeutic target for spinal cord injury. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1136143. [16] LIU Y, WAN Y, JIANG Y, et al. GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023;1878(3):188890. [17] ZHANG W, LIU Y, LIAO Y, et al. GPX4, ferroptosis, and diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;174:116512. [18] MA T, DU J, ZHANG Y, et al. GPX4-independent ferroptosis-a new strategy in disease’s therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):434. [19] DING K, LIU C, LI L, et al. Acyl-CoA synthase ACSL4: an essential target in ferroptosis and fatty acid metabolism. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023; 136(21):2521-2537.
[20] JIA B, LI J, SONG Y, et al. ACSL4-Mediated Ferroptosis and Its Potential Role in Central Nervous System Diseases and Injuries. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(12):10021. [21] LIU G, DENG B, HUO L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in spinal cord injury by regulating GPX4/ACSL4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;977:176710. [22] 许卢春,杨永栋,赵赫,等.颈髓损伤动物模型的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(9):836-842. [23] WEBB AA, MUIR GD. Sensorimotor behaviour following incomplete cervical spinal cord injury in the rat. Behav Brain Res. 2005;165(2):147-159. [24] 罗联忠,周逸敏,张俐.基于督脉枢机不利探讨脊髓损伤与血脊髓屏障[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(8):4515-4518. [25] 吴明莉,冯晓东.基于督脉理论探讨“通督益髓”针法治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国民族民间医药,2024,33(14):72-75. [26] 赵亚莉,姚海江,李志刚,等.督脉电针对脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓神经连接蛋白1和神经丝蛋白200的影响[J].针刺研究,2023,48(9):906-913. [27] 叶青,李志刚,时素华,等.督脉电针联合重复经颅磁刺激对脊髓损伤后大鼠脊髓BDNF及其受体TrkB和p75NTR表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2022,38(8):57-65. [28] XU L, YANG Y, JIANG G, et al. Buyang Huanwu decoction promotes angiogenesis and improves hemorheological parameters after cervical spinal cord injury. J Tradit Chin Med Sci. 2024;11(4):456-465. [29] KANG Y, ZHU R, LI S, et al. Erythropoietin inhibits ferroptosis and ameliorates neurological function after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(4):881-888. [30] SINGH A, KRISA L, FREDERICK KL, et al. Forelimb locomotor rating scale for behavioral assessment of recovery after unilateral cervical spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurosci Methods. 2014;226:124-131. [31] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21. [32] ZIPSER CM, CRAGG JJ, GUEST JD, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(7):659-670. [33] MORITZ C, FIELD-FOTE EC, TEFERTILLER C, et al. Non-invasive spinal cord electrical stimulation for arm and hand function in chronic tetraplegia: a safety and efficacy trial. Nat Med. 2024;30(5):1276-1283. [34] PENG H, LIU Y, XIAO F, et al. Research progress of hydrogels as delivery systems and scaffolds in the treatment of secondary spinal cord injury. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1111882. [35] ZHU J, LIU Z, LIU Q, et al. Enhanced neural recovery and reduction of secondary damage in spinal cord injury through modulation of oxidative stress and neural response. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):19042. [36] VERSTAPPEN K, AQUARIUS R, KLYMOV A, et al. Systematic Evaluation of Spinal Cord Injury Animal Models in the Field of Biomaterials. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(6):1169-1179. [37] HU M, CAO Z, JIANG D. The Effect of miRNA-Modified Exosomes in Animal Models of Spinal Cord Injury: A meta-Analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;9:819651. [38] KO CC, LEE PH, LEE JS, et al. Spinal decompression surgery may alleviate vasopressor-induced spinal hemorrhage and extravasation during acute cervical spinal cord injury in rats. Spine J. 2024;24(3):519-533. [39] PIECZONKA K, NAKASHIMA H, NAGOSHI N, et al. Human Spinal Oligodendrogenic Neural Progenitor Cells Enhance Pathophysiological Outcomes and Functional Recovery in a Clinically Relevant Cervical Spinal Cord Injury Rat Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2023;12(9):603-616. [40] YAO S, PANG M, WANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell attenuates spinal cord injury by inhibiting mitochondrial quality control-associated neuronal ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2023;67:102871. [41] XUAN Y, PENG K, ZHU R, et al. Hmox1 is Identified as a Ferroptosis Hub Gene and Associated with the M1 Type Microglia/Macrophage Polarization in Spinal Cord Injury: Bioinformatics and Experimental Validation. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(12):7151-7165. [42] BAO J, YANG S. ScRNA analysis and ferroptosis-related ceRNA regulatory network investigation in microglia cells at different time points after spinal cord injury. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):701. [43] SONG QF, CUI Q, WANG YS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells, extracellular vesicles, and transcranial magnetic stimulation for ferroptosis after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(9):1861-1868. [44] DIXON SJ, OLZMANN JA. The cell biology of ferroptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(6):424-442. [45] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282. [46] KIM JW, LEE JY, OH M, et al. An integrated view of lipid metabolism in ferroptosis revisited via lipidomic analysis. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(8): 1620-1631. [47] CUI C, YANG F, LI Q. Post-Translational Modification of GPX4 is a Promising Target for Treating Ferroptosis-Related Diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:901565. [48] DAR NJ, JOHN U, BANO N, et al. Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Neurodegeneration: the Underlying Role of Master Regulator Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(3):1507-1526. [49] HUSSAIN S, GUPTA G, SHAHWAN M, et al. Non-coding RNA: A key regulator in the Glutathione-GPX4 pathway of ferroptosis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024;9(4):1222-1234. [50] BOUCHAOUI H, MAHONEY-SANCHEZ L, GARÇON G, et al. ACSL4 and the lipoxygenases 15/15B are pivotal for ferroptosis induced by iron and PUFA dyshomeostasis in dopaminergic neurons. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;195:145-157. [51] LI R, YAN X, XIAO C, et al. FTO deficiency in older livers exacerbates ferroptosis during ischaemia/reperfusion injury by upregulating ACSL4 and TFRC. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):4760. [52] SHI J, XUE X, YUAN L, et al. Amelioration of White Matter Injury Through Mitigating Ferroptosis Following Hepcidin Treatment After Spinal Cord Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(6):3365-3378. [53] DAVAANYAM D, LEE H, SEOL SI, et al. HMGB1 induces hepcidin upregulation in astrocytes and causes an acute iron surge and subsequent ferroptosis in the postischemic brain. Exp Mol Med. 2023; 55(11):2402-2416. [54] LI S, MA S, WANG L, et al. ATF3 as a response factor to regulate Cd-induced reproductive damage by activating the NRF2/HO-1 ferroptosis pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;285:117114. [55] MA H, XING C, WEI H, et al. Berberine attenuates neuronal ferroptosis via the AMPK-NRF2-HO-1-signaling pathway in spinal cord-injured rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;142(Pt B):113227. [56] RODENCAL J, KIM N, HE A, et al. Sensitization of cancer cells to ferroptosis coincident with cell cycle arrest. Cell Chem Biol. 2024;31(2): 234-248.e13. [57] JIANG W, YU L, MU N, et al. MG53 inhibits ferroptosis by targeting the p53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway to alleviate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;223:224-236. [58] LIU N, LIN Q, HUANG Z, et al. Mitochondria-Targeted Prodrug Nanoassemblies for Efficient Ferroptosis-Based Therapy via Devastating Ferroptosis Defense Systems. ACS Nano. 2024;18(11):7945-7958. [59] WANG LL, MAI YZ, ZHENG MH, et al. A single fluorescent probe to examine the dynamics of mitochondria-lysosome interplay and extracellular vesicle role in ferroptosis. Dev Cell. 2024;59(4):517-528.e3. [60] ZHONG S, CHEN W, WANG B, et al. Energy stress modulation of AMPK/FoxO3 signaling inhibits mitochondria-associated ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2023;63:102760. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Zhao Nannan, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhu Bochao, Ding Huimin, Xu Zhenhua. Changes in ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons of vascular dementia model rats treated with Tongmai Kaiqiao Pill [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [3] | Zhang Mingyang, Yang Xinling. Verbascoside inhibits Erastin-induced ferroptosis of dopaminergic nerve cell line MN9D cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1408-1413. |
| [4] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [7] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [8] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [9] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [10] | Wang Chen, Zhang Weinan, Shen Jining, Liu Fan, Yuan Jishan, Liu Yake. Inhibitory effect of ferroptosis inhibitor toxicity induced by cobalt nanoparticles through reactive oxygen species [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7310-7317. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [12] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [13] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [14] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [15] | Pan Yu, Zhao Renfeng, Li Xingping, Zhang Chengdong, Shi Feng, Pu Chao, Luo Xuwei, Xiao Dongqin. Iron overload induces ferroptosis in osteoblast precursor cells and inhibits osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6381-6390. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||