Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (31): 6697-6707.doi: 10.12307/2025.614
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction
Tian Yushi1, Fu Qiang1, Li Ji2
- 1School of Basic Medicine, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Accepted:2024-06-27Online:2025-11-08Published:2025-02-25 -
Contact:Li Ji, PhD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Postdoctoral instructor, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Tian Yushi, PhD candidate, School of Basic Medicine, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81874426 (to LJ); Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation “Millions of Talents” Project (Qihuang Project) Qihuang Scholars Project (Guozhong Medicine Ren Jiaohan [2018] No. 284) (to LJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
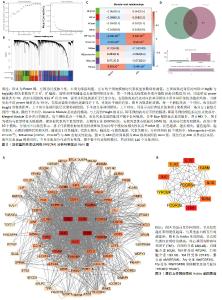
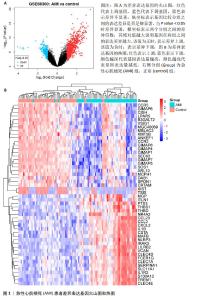
2.2 急性心肌梗死特征基因模块鉴定结果 WGCNA分析可进一步识别急性心肌梗死数据集GSE66360的特征基因模块,探索基因网络与表型之间的关联性。结果显示,第一个到达无标度拓扑拟合指数(0.8)的数值为14,因此选择power值为14,数值开始持平,表明网络的连通性好。在GSE66360数据集中共识别出10个模块,其中Blue模块包含4 992个基因,是最大的基因模块。将急性心肌梗死的差异基因和Blue模块基因上传至Venny 2.1.0平台,共获得116个交集基因,见图2。 2.3 特征基因的PPI分析结果 为进一步识别116个基因中的核心,将116个基因上传至STRING平台后,共得到116个节点,604条边线,下载tsv文件并导入至Cytoscape 3.9.1软件中进行可视化分析。利用CytoHubba插件筛选出排名前10位的核心靶点基因,分别为肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素1B、白细胞介素6、Toll样受体4 (Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)、白细胞介素10、Toll样受体2(Toll-like receptor 2,TLR2)、整合素αM(integrin subunit alpha M,ITGAM)、Fcγ受体IIIa(Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIIa,FCGR3A)、Fcγ受体IIIb(FCGR3B,Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIIb)和跨膜免疫信号配体TYROBP(transmembrane immune signaling adaptor TYROBP,TYROBP),见图3。"

2.4 特征基因的富集分析结果 将交集靶点基因导入DAVID数据进行GO和KEGG富集分析。GO分析共得到81个条目(P < 0.05),其中BP共有49个条目,主要涉及炎症反应、肿瘤坏死因子产生的正调控、细胞表面受体信号通路等;CC共有18个条目(P < 0.05),主要涉及三级颗粒膜、质膜外层、质膜等;MF共有14个条目(P < 0.05),主要涉及免疫球蛋白G结合、跨膜信号受体活性、趋化因子活性等;KEGG分析共得到31条通路(P < 0.05),主要为肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、白细胞介素17信号通路和核转录因子κB信号通路等,见图4。 2.5 急性心肌梗死中差异线粒体基因的鉴定结果 将116个核心急性心肌梗死差异表达基因与1 136个人类线粒体基因上传至Venny 2.1.0平台,明确急性心肌梗死中差异线粒体基因的特征和变化趋势,最终获得8个交集基因,分别为佛波醇-12-肉豆酸酯-13-乙酰基诱导蛋白1(phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein1,PMAIP1)、BCL2-相关蛋白A1 (BCL2 related protein A1,BCL2A1)、溶质载体家族25成员37(solute carrier family 25 member 37,SLC25A37)、脱氧核糖核酸聚合酶β(deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase beta,POLB)、F-box和富亮氨酸的重复蛋白4(F-box and leucine rich repeat protein 4,FBXL4)、锌结合醇脱氢酶结构域2(zinc binding alcohol dehydrogenase domain containing 2,ZADH2)、线粒体核糖体蛋白S30(mitochondrial ribosomal protein S30,MRPS30)及心磷脂合酶1(cardiolipin synthase 1,CRLS1)。与空白组相比,差异线粒体基因PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37,POLB,FBXL4和ZADH2表达下降,而MRPS30及CRLS1表达上升,见图5。 "


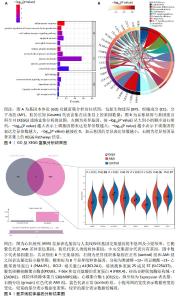
2.6 LASSO-cox分析结果 运用LASSO-cox回归分析进一步筛选8个差异线粒体基因中对急性心肌梗死有重要影响的特征基因,最终获得4个特征基因分别为PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37和POLB,见图6。 2.7 GSEA分析结果 对4个特征基因进行单基因的GSEA分析,以确定PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37和POLB的基因功能和途径。结果显示,PMAIP1主要涉及12个通路,其中最显著的是肿瘤蛋白53(tumor protein 53,p53)信号通路;BCL2A1主要涉及1个通路即氧化磷酸化途径;SLC25A37主要涉及1个通路即硫代谢途径;POLB主要涉及1个通路即甘油磷脂代谢,见图7。 2.8 ROC分析结果 为明确4个差异线粒体基因是否具有预测诊断急性心肌梗死的意义,采用外部数据集GSE12288对PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37和POLB进行ROC分析,以明确判断最佳特征基因作为疾病特征基因的准确度,计算AUC,AUC值越接近1,表示预测性能越好。结果显示,在GSE12288数据集中PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37和POLB与空白组相比表达显著升高,其中PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37和POLB的AUC值分别为0.801 4,0.910 3,0.737 7,0.816 3,表明PMAIP1,BCL2A1,SLC25A37和POLB可作为急性心肌梗死的线粒体功能障碍的诊断标志,见图8。"


2.9 免疫浸润分析结果 采用CIBERSORT算法对GSE66360数据集的对照组和空白组样本进行免疫浸润分析,探究两组之间不同免疫细胞浸润水平的差异。结果显示,空白组样本中幼稚B细胞、T细胞滤泡辅助细胞表达增高(P < 0.05),急性心肌梗死组记忆性静息CD4+T细胞、静息树突状细胞表达显著升高(P < 0.05),见图9;免疫浸润细胞相关性分析显示浆细胞与嗜酸性粒细胞具有最高的正相关性(r=0.48),幼稚CD4+T细胞与活化树突状细胞具有最高的负相关性(r=-0.46)。对差异线粒体基因与免疫细胞之间的相关性进行计算,结果显示PMAIP1与静息树突状细胞呈负相关性(r=-0.40,P < 0.01),BCL2A1与静息树突状细胞(r=-0.55,P < 0.01)、幼稚B细胞(r=-0.33,P < 0.05)呈负相关,SLC25A37与静息树突状细胞呈负相关性(r=-0.48,P < 0.01),POLB与静息树突状细胞呈负相关性(r=-0.57,P < 0.01),见图10。 "

| [1] WANG X, ChEN D, ZOU P, et al. Understanding adaptive tasks in cardiac rehabilitation among patients with acute myocardial infarction: a qualitative study. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2311227. [2] WANG X, XU L, LEE G, et al. Development of an integrated cardiac rehabilitation program to improve the adaptation level of patients after acute myocardial infarction. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1121563. [3] WANG L, LIU J, FANG H, et al. Factors associated with participation in cardiac rehabilitation in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cardiol. 2023; 46(11):1450-1457. [4] 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告》2021(冠心病部分内容)[J].心肺血管病杂志,2022, 41(12):1205-1211. [5] HEUSCH G, ANDREADOU I, BELL R, et al. Health position paper and redox perspectives on reactive oxygen species as signals and targets of cardioprotection. Redox Biol. 2023;67:102894. [6] AKHTAR KH, KHAN MS, BARON SJ, et al. The spectrum of post-myocardial infarction care: From acute ischemia to heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;82:15-25. [7] HAUSENLOY DJ, CHILIAN W, CREA F, et al. The coronary circulation in acute myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury: a target for cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(7):1143-1155. [8] YOU H, DONG M. Identification of immuno-inflammation-related biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction based on bioinformatics. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16: 3283-3302. [9] CAI S, ZHAO M, ZHOU B, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in macrophages promotes inflammation and suppresses repair after myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2023; 133(4):e159498. [10] MALET-PEREZL J, BELAIDI E. Interplay between hypoxia inducible factor-1 and mitochondria in cardiac diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;221:13-22. [11] GUPTA L, THOMAS J, RAVICHANDRAN R, et al. Inflammation in cardiovascular disease: a comprehensive review of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cureus. 2023;15(9):e45483. [12] CHEN L, YANG X, WANG K, et al. Humanin inhibits lymphatic endothelial cells dysfunction to alleviate myocardial infarction-reperfusion injury via BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Free Radic Res. 2024; 58(3):180-193. [13] KUZNETSOV AV, JAVADOV S, MARGREITER R, et al. The role of mitochondria in the mechanisms of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(10):454. [14] LI H, JIA Y, YAO D, et al. Rhein alleviates myocardial ischemic injury by inhibiting mitochondrial division, activating mitochondrial autophagy and suppressing myocardial cell apoptosis through the Drp1/Pink1/Parkin pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):266. [15] ZHANG M, YANG Y, ZHU Z, et al. Implications of activating the ANT2/mTOR/PGC-1α feedback loop: insights into mitochondria-mediated injury in hypoxic myocardial cells. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45(11): 8633-8651. [16] NAOI M, WU Y, SHAMOTO-NAGAI M, et al. Mitochondria in neuroprotection by phytochemicals: bioactive polyphenols modulate mitochondrial apoptosis system, function and structure. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(10):2451. [17] CHANG X, LIU R, LI R, et al. Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial quality control in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(2):426-448. [18] BEREZHNOV AV, FEDOTOVA EI, NENOV MN, et al. Disturbance of calcium homeostasis, activation of Ca2+-dependent phospholipases, and mitochondrial energetics collapse. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(20):7461. [19] BERTERO E, POPOIU TA, MAACK C. Mitochondrial calcium in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024;119(4):569-585. [20] BALACHANDER K, VIJAYASHREE PRIYADHARSINI J, PARAMASIVAM A. Role of exosomal mitochondria in cardiovascular diseases. Hypertens Res. 2023;46(3): 812-813. [21] YU Y, YAN Y, NIU F, et al. Ferroptosis: a cell death connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):193. [22] HEUSCH G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(12): 773-789. [23] JIANG S, ZHANG S. Differentiation of cardiomyocytes from amniotic fluid‑derived mesenchymal stem cells by combined induction with transforming growth factor β1 and 5‑azacytidine. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16(5):5887-5893. [24] FU JH, ZHAO M, LIN YR, et al. Degradable chitosan-collagen composites seeded with cells as tissue engineered heart valves. Heart Lung Circ. 2017;26(1):94-100. [25] RAZAVI ZS, SOLTANI M, MAHMOUDVAND G, et al. Advancements in tissue engineering for cardiovascular health: a biomedical engineering perspective. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1385124. [26] JARRELL DK, VANDERSLICE EJ, VEDEPO MC, et al. Engineering myocardium for heart regeneration-advancements, considerations, and future directions. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:586261. [27] WHO CVD RISK CHART WPRKING GROUP. World Health Organization cardiovascular disease risk charts: revised models to estimate risk in 21 global regions. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(10):e1332-e1345. [28] CHEN G, WESTRA J, YANG X, et al. A simple angio-based coronary flow assessment of culprit vessels in primary percutaneous coronary intervention is associated with long-term prognosis after ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2024;409:132199. [29] ZHOU YM, SUN B. Immediate versus staged complete revascularization in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome and multivessel coronary disease without cardiac shock: a study-level meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. doi:10.1007/s10557-024-07597-7. [30] VALIKESERLIS I, ATHANASIOU AA, STAKOS D. Cellular mechanisms and pathways in myocardial reperfusion injury. Coron Artery Dis. 2021;32(6):567-577. [31] FENG M, ZHANG L, YIN A, et al. Peptide PDRPS6 attenuates myocardial ischemia injury by improving mitochondrial function. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;974:176570. [32] ZHANG T, ZHONG Y, SHI Y, et al. Multi-omics reveals that 5-O-methylvisammioside prevention acute liver injury in mice by regulating the TNF/MAPK/NF-κB/arachidonic acid pathway. Phytomedicine. 2024;128:155550. [33] LING T, YIN A, CAO Y, et al. Purinergic astrocyte signaling driven by tnf-α after cannabidiol administration restores normal synaptic remodeling following traumatic brain injury. Neuroscience. 2024;545:31-46. [34] AKKAYA FIRAT A, ÖZEL A, DAVUTOGLU EA, et al. Maternal serum interleukin-1β, FoxO1 and Sestrin2 levels in predicting preterm delivery. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2024;37(1):2295807. [35] ABDULLA MH, ALMARABEH S, BOLGER T, et al. Effects of intrarenal pelvic infusion of tumour necrosis factor-α and interleukin 1-β on reno-renal reflexes in anaesthetised rats. J Hypertens. 2024;42(6):1027-1038. [36] WANG H, ZHANG Y, ZHAO C, et al. Serum IL-17A and IL-6 in paediatric mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: implications for different endotypes. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024;13(1):2324078. [37] XU H, DU Z, LI Z, et al. MUC1-EGFR crosstalk with IL-6 by activating NF-κB and MAPK pathways to regulate the stemness and paclitaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Med. 2024;56(1): 2313671. [38] SCHWAB AD, WYATT TA, NELSON AJ, et al. Lung-delivered IL-10 therapy elicits beneficial effects via immune modulation in organic dust exposure-induced lung inflammation. J Immunotoxicol. 2024; 21(1):2332172. [39] YANG C, ZHANG Y, WANG R, et al. IL-10+CD19+ regulatory B cells induce CD4+Foxp3+regulatory T cells in serum of cervical cancer patients. Autoimmunity. 2024;57(1):2290909. [40] XIA YM, GUAN YQ, LIANG JF, et al. TAK-242 improves sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in rats by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Ren Fail. 2024; 46(1):2313176. [41] MA L, WANG T, LIU M, et al. Xiaoer niuhuang qingxin powder alleviates influenza a virus infection by inhibiting the activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;328:118000. [42] LIN L, WANG L, LI A, et al. CircDiaph3 aggravates H/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation through miR-338-3p/SRSF1 axis. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2024;56(3):235-245. [43] SAEED A, FAROUK MM, SABRI NA, et al. Effect of pentoxifylline on endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in STEMI patients. Future Sci OA. 2024;10(1):FSO967. [44] MORADI A, ASLANI MR, MIRSHEKARI JAHANGIRI H, et al. Protective effects of 4-methylumbelliferone on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through inhibition of oxidative stress and downregulation of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397(7):5015-5027. [45] CAO Y, LUO F, PENG J, et al. KMT2B-dependent RFK transcription activates the TNF-α/NOX2 pathway and enhances ferroptosis caused by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;173:75-91. [46] KROTT KJ, REUSSWIG F, DILLE M, et al. Platelets induce cell apoptosis of cardiac cells via fasl after acute myocardial infarction. Biomedicines. 2024;12(5):1077. [47] KIM Y, NURAKHAYEV S, NURKESH A, et al. Macrophage polarization in cardiac tissue repair following myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2715. [48] GRANEY PL, BlEN-SHAU S, LANDAU S, et al. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaay6391. [49] CHAI R, YE Z, XUE W, et al. Tanshinone IIA inhibits cardiomyocyte pyroptosis through TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway after acute myocardial infarction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1252942. [50] YUAN H, YANG G, LI S, et al. Calcium sensing receptor involving in therapy of embryonic stem cell transplantation alleviates acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020;23(10):1353-1359. [51] IWATA A, MORGAN-STEVENSON V, SCHWARTZ B, et al. Extracellular BCL2 proteins are danger-associated molecular patterns that reduce tissue damage in murine models of ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9103. [52] GUO M, ZHUANG Y, WU Y, et al. The cell fate regulator DACH1 modulates ferroptosis through affecting P53/SLC25A37 signaling in fibrotic disease. Hepatol Commun. 2024; 8(3):e0396. [53] ZHANG R, DI C, GAO H, et al. Identification of iron metabolism-related genes in the circulation and myocardium of patients with sepsis via applied bioinformatics analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10:1018422. [54] LU C, LUO J, LIU Y, et al. The oxidative stress responses caused by phthalate acid esters increases mRNA abundance of base excision repair (BER) genes in vivo and in vitro. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;208:111525. [55] WU Y, JIANG T, HUA J, et al. Integrated bioinformatics-based analysis of hub genes and the mechanism of immune infiltration associated with acute myocardial infarction. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:831605. [56] QI Z, PU Y, GUO H, et al. Identification and subtype analysis of biomarkers associated with the solute carrier family in acute myocardial infarction. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(49):e36515. [57] YANG X, LI J, HU X, et al. Identification of PFKFB2 as a key gene for the transition from acute to old myocardial infarction in peripheral blood. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:993579. [58] 韦丽娥,卢梦歌,杨秋月,等.生物信息学分析揭示与急性心肌梗死有关的线粒体功能障碍基因[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2023,44(21):2007-2016. [59] 壮婷,杨帆.急性心肌梗死患者外周血NO-PGC1α线粒体生物合成通路相关基因的表达及其临床意义[J].中国现代医学杂志,2022,32(12):78-83. [60] LI SP, LIU B, SONG B, et al. miR-28 promotes cardiac ischemia by targeting mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) in mus musculus cardiac myocytes. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(5):752-758. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [7] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [8] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [9] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [10] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [11] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [12] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [13] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [14] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [15] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||