Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (31): 6674-6680.doi: 10.12307/2025.661
Previous Articles Next Articles
Inhibitory effects of sinomenine hydrochloride in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia CEM cells and transcriptomic analysis
Kang Linzhi1, Liu Zhenshuai1, Wei Jiaxu1, Chang Na2, Zhu Dacheng1
- 1Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Yan'an University, Yan'an 716000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-28Accepted:2024-08-12Online:2025-11-08Published:2025-02-24 -
Contact:Zhu Dacheng, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Kang Linzhi, Doctoral candidate, Lecturer, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:Jiangxi Province “Double First-Class” Discipline (Traditional Chinese Medicine) Construction Project, No. JXYLXK-ZHYI051 (to ZDC); Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Postgraduate Innovation Special Fund Project, No. JZYC22B01 (to KLZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Kang Linzhi, Liu Zhenshuai, Wei Jiaxu, Chang Na, Zhu Dacheng. Inhibitory effects of sinomenine hydrochloride in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia CEM cells and transcriptomic analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6674-6680.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

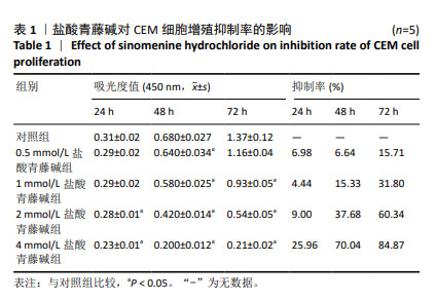
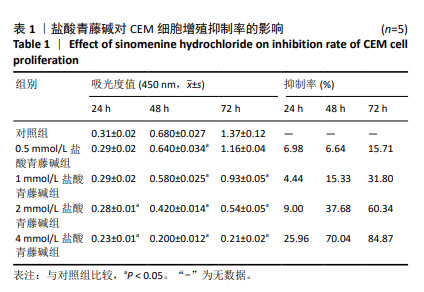
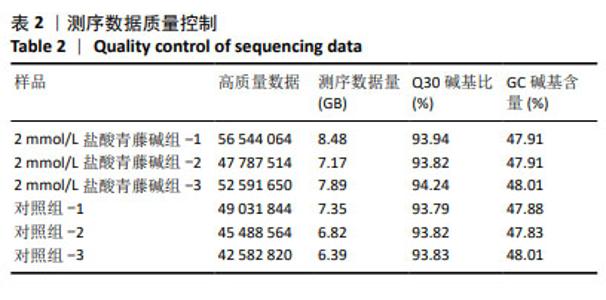
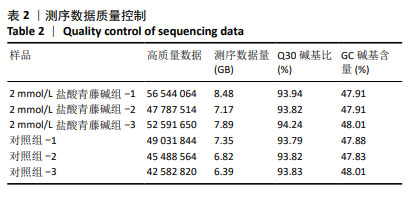
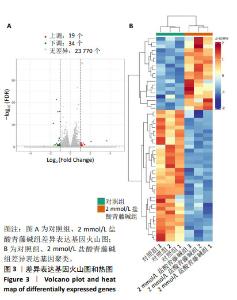
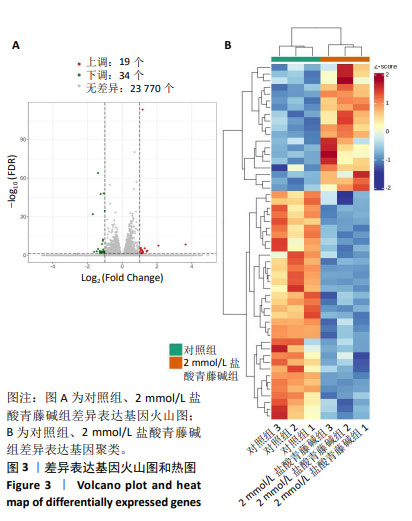
2.3.3 差异表达基因GO功能注释及富集分析 按照生物过程、细胞组分和分子功能进行GO分类,结果见图4。生物学过程主要富集在细胞过程、生物调控、生物过程的调节和代谢过程等;细胞组分主要富集为细胞解剖实体、含蛋白质复合物等;分子功能主要富集在粘连关系、催化活性和分子功能调节等。 2.3.4 差异表达基因KEGG信号通路注释及富集分析 富集结果根据显著性(即Q value)取排名前 20 条通路,见图5。差异表达基因主要富集在矿物质吸收、小细胞肺癌、鞘糖脂生物合成-球蛋白、苯丙氨酸代谢、成熟型糖尿病、鞘糖脂生物合成-乳酸和新乳酸系列、细胞凋亡、酪氨酸代谢、淀粉和蔗糖代谢、丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢等。其中富集程度较高的与肿瘤相关的通路是细胞凋亡,提示凋亡在盐酸青藤碱抑制CEM细胞增殖过程中起重要作用。"
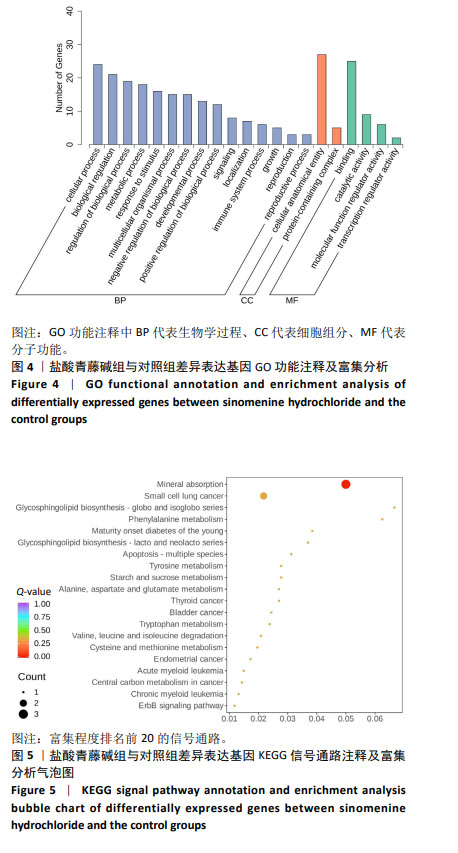
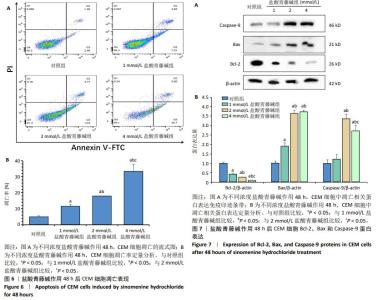
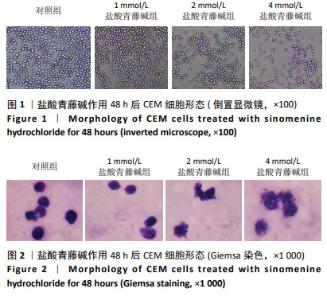
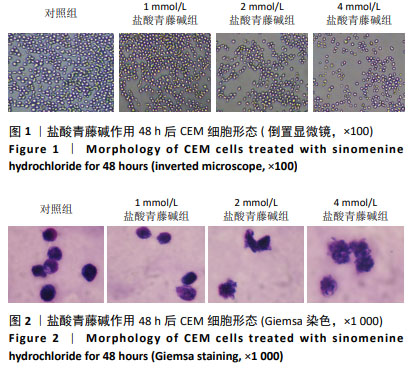
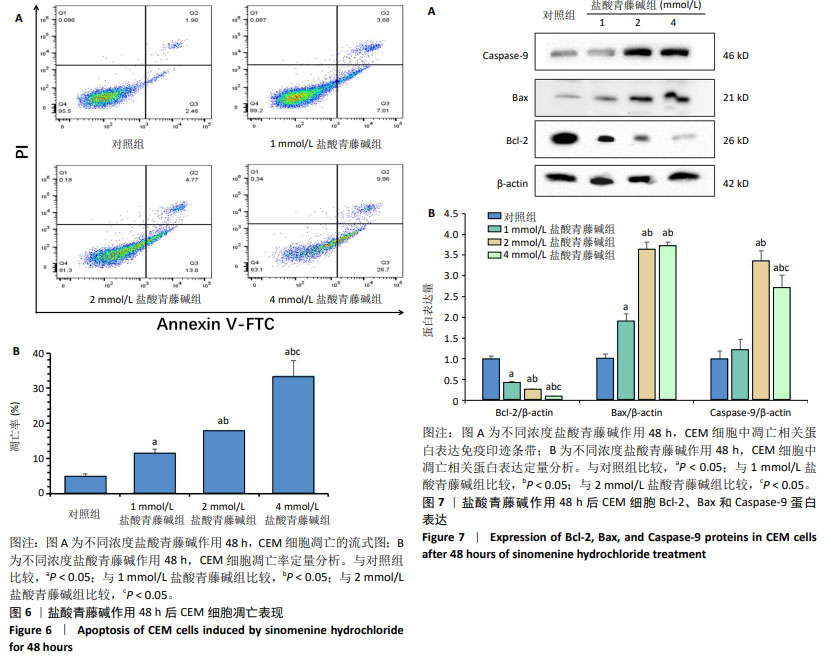
2.4 盐酸青藤碱对CEM细胞凋亡的影响 盐酸青藤碱作用CEM细胞48 h,1,2,4 mmol/L盐酸青藤碱组细胞总凋亡率分别为10.69%,18.57%,36.56%;早期凋亡率为7.01%,13.8%,26.7%;晚期凋亡率为3.68%,4.77%,9.86%。随着给药浓度增加,凋亡率逐渐增加。盐酸青藤碱组与对照组细胞凋亡率比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),不同浓度组间细胞凋亡率有统计学意义,见图6。 2.5 盐酸青藤碱对CEM细胞Bcl-2、Bax、Caspase-9蛋白表达的影响 1,2,4 mmol/L盐酸青藤碱作用48 h后,细胞中Bcl-2蛋白表达水平下降,Bax和Caspase-9蛋白表达水平升高。与对照组比较,各盐酸青藤碱组Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),不同浓度盐酸青藤碱组间Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达有统计学意义。与对照组比较,2,4 mmol/L盐酸青藤碱组Caspase-9蛋白表达差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图7。"
| [1] BAYÓN-CALDERÓN F, TORIBIO ML, GONZÁLEZ-GARCÍA S. Facts and Challenges in Immunotherapy for T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7685. [2] FOLLINI E, MARCHESINI M, ROTI G. Strategies to Overcome Resistance Mechanisms in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3021. [3] 陈玉,蔡恩照,张隽瑜,等.从“毒”论治急性白血病初探[J].中国中医急症,2020,29(5):916-918. [4] KUZILKOVÁ D, BUGARIN C, REJLOVA K, et al. Either IL-7 activation of JAK-STAT or BEZ inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathways dominates the single-cell phosphosignature of ex vivo treated pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Haematologica. 2022;107(6):1293-1310. [5] 肖童,刘嘉,高蕾.靶向药物结合异基因造血干细胞移植治疗急性T淋巴细胞白血病[J].临床内科杂志,2023,40(10):654-658. [6] SHARMA ND, NICKL CK, KANG H, et al. Epigenetic silencing of SOCS5 potentiates JAK-STAT signaling and progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(6):1931-1946. [7] ZHANG Y, BAI L, CHENG Y, et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may improve long-term survival for children with high-risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(8):940-949. [8] SUN W, HUANG X. Role of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the era of immunotherapy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022; 135(8):890-900. [9] CORDO’ V, VAN DER ZWET JCG, CANTÉ-BARRETT K, et al. T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Roadmap to Targeted Therapies. Blood Cancer Discov. 2020;2(1):19-31. [10] 王子健,周春阳,蒋树龙,等.中医药减毒增效作用在肿瘤放射治疗中的应用进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(8):3732-3735. [11] 吕欣妮,杨汪银,钱丽君,等.中医药治疗化疗后骨髓抑制研究进展[J].实用中医内科杂志,2023,37(11):55-58. [12] 高丽娟,李如,李泽光.青风藤不良反应及减毒增效研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,41(4):37-41. [13] 张筠昊,文武龙,张炜烨,等.荧光内窥式共聚焦显微镜下青藤碱固体脂质纳米粒注射治疗类风湿性关节炎的研究[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(14):3786-3792. [14] 张慧敏,刘晓旭,谢佩玲,等.盐酸青藤碱通过抑制bFGF介导的乳腺癌血管新生发挥抑瘤作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2021,42(6):947-952. [15] 王新,张旭,李雅睿,等.盐酸青藤碱通过线粒体凋亡途径诱导胃癌细胞死亡[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020,41(6):854-858+866. [16] 青泓屹,魏寿江,李勋,等.青藤碱对胃癌细胞SGC-7901生物学行为的影响及机制[J].安徽医科大学学报,2020,55(9):1350-1356. [17] 刘斌,杨燚,王福玲,等.青藤碱对HepG2细胞的抑制作用[J].中成药,2023,45(1):237-241. [18] 吕彦霖,朱昌毫,潘耀振,等.青藤碱对体外人胆管癌细胞的抑制作用[J].中成药,2019,41(11):2601-2608. [19] 康林之,朱大诚,刘振帅.青藤碱抗肿瘤作用机制研究现状[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,41(9):184-188. [20] JIANG Y, JIAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Sinomenine Hydrochloride Inhibits the Metastasis of Human Glioblastoma Cells by Suppressing the Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 and Reversing the Endogenous and Exogenous Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(3):844. [21] XIONG M, CHEN X, WANG H, et al. Combining transcriptomics and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of Zuojin capsule improving spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;318(Pt B):117075. [22] 蒋敏,李慧莉,庞盼盼,等.高通量单细胞转录组测序发展与展望[J].生命科学,2020,32(12):1280-1287. [23] 宋新强,张玉,何欢欢,等.单细胞转录组测序在肿瘤研究中的应用进展[J].信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版),2021,34(3):510-516. [24] 李艳荣,李瑞雪,樊慧杰,等.转录组学技术在中医药领域的应用研究进展[J].时珍国医国药,2022,33(4):943-947. [25] YANG Y, YANG Y, SHEN Y, et al. Exploring the pharmacological mechanisms of Shuanghuanglian against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia through network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1):259-270. [26] LIU Y, YANG S, WANG K, et al. Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10):e12894. [27] 颜梦宇,刘芳媛,韩凤娟.中药调控Notch信号通路逆转卵巢癌耐药的研究进展[J].中医药学报,2024,52(5):105-110. [28] 刘学伟,娄彦妮,冯哲,等.从国家自然科学基金资助项目浅谈中医药在恶性肿瘤治疗中的增效减毒作用研究现状[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(1):253-258. [29] 陶智会,仝欣,徐蔚杰,等.中药序贯联合化疗治疗非小细胞肺癌的减毒增效临床观察[J].世界中医药,2021,16(3):477-481+486. [30] 王新,卢朝辉,李雅睿,等.盐酸青藤碱通过C/EBPβ-COX-2通路抑制LPA诱导的肝癌细胞增殖[J].安徽医科大学学报,2021,56(5):786-789. [31] 陈淑瑜,邹勇,黄轶群.盐酸青藤碱对Jeko-1细胞增殖、凋亡的影响及其作用机制研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2017,25(6):1675-1679. [32] LI M. The role of P53 up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) in ovarian development, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Apoptosis. 2021;26(5-6):235-247. [33] GOLDBLATT ZE, CIRKA HA, BILLIAR KL. Mechanical Regulation of Apoptosis in the Cardiovascular System. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(1):75-97. [34] 吴慧婷,朱大诚,徐笑明,等.川楝子醇提物通过线粒体途径诱导白血病CEM细胞的凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(30):4873-4878. [35] SINGH R, LETAI A, SAROSIEK K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(3):175-193. [36] KØNIG SM, RISSLER V, TERKELSEN T, et al. Alterations of the interactome of Bcl-2 proteins in breast cancer at the transcriptional, mutational and structural level. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019;15(12):e1007485. [37] MAES ME, SCHLAMP CL, NICKELLS RW. BAX to basics: How the BCL2 gene family controls the death of retinal ganglion cells. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017;57:1-25. [38] JENNER A, PEÑA-BLANCO A, SALVADOR-GALLEGO R, et al. DRP1 interacts directly with BAX to induce its activation and apoptosis. EMBO J. 2022;41(8):e108587. [39] LIU Y, LIU C, TAN T, et al. Sinomenine sensitizes human gastric cancer cells to cisplatin through negative regulation of PI3K/AKT/Wnt signaling pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 2019;30(10):983-990. [40] BOICE A, BOUCHIER-HAYES L. Targeting apoptotic caspases in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020;1867(6):118688. [41] WU GJ, YANG ST, CHEN RM. Major Contribution of Caspase-9 to Honokiol-Induced Apoptotic Insults to Human Drug-Resistant Glioblastoma Cells. Molecules. 2020;25(6):1450. [42] LI P, ZHOU L, ZHAO T, et al. Caspase-9: structure, mechanisms and clinical application. Oncotarget. 2017;8(14):23996-24008. [43] HOU W, HUANG L, HUANG H, et al. Bioactivities and Mechanisms of Action of Sinomenine and Its Derivatives: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules. 2024;29(2):540. [44] 牟凤林,陈华.青藤碱诱导人红白血病细胞株K562凋亡的实验研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2017,23(10):1387-1390+1396. [45] 范炎峰,荆玲,刘宽浩,等.青藤碱对人急性T淋巴细胞白血病细胞增殖与凋亡的影响及其机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(10): 1199-1203. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [3] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [4] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [7] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [8] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [9] | Zhuo Qiuyan, Jiang Qun, Xia Si, Lu Shiying, Liu Yandi, Dai Mei. Bone marrow hematopoiesis in rats with myelodysplastic syndrome: action mechanism of Huosui Formula in intervening immune checkpoints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7735-7742. |
| [10] | Yu Hui, Yang Yang, Wei Ting, Li Wenli, Luo Wenqian, Liu Bin. Gadd45b alleviates white matter damage in chronic ischemic rats by modulating astrocyte phenotype [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7797-7803. |
| [11] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [12] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [13] | Zhao Nan, Ding Yong, Xiu Hang, Liu Pengfei, Liang Guogang. Extraction and culture of enteric glial cells from C57BL/6 newborn neonatal mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6656-6660. |
| [14] | Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Liu Weipeng, Yang Hui, Luan Zuo, Qu Suqing. Effect of fibronectin on differentiation of human neural stem cells into oligodendrocyte precursor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6661-6666. |
| [15] | Li Jinjie, Xiao Jingxue, Li Nan, Song Zhen, Zhou Yanyun, Ma Jie. Significance of interleukin-18 expression in bone marrow and peripheral blood of rats exposed to hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6681-6687. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||