Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5536-5542.doi: 10.12307/2025.769
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of high glucose on blood-brain barrier tight junctions in hCMEC/D3 human brain microvascular endothelial cells
Yang Hongtao1, 2, Xu Yongjie1, Zhou Yongjun1, 2, Wang Shuang2, Huang Changyudong1, Zhu Liying2, 3, Pan Wei1, 2
- 1Guizhou Prenatal Diagnosis Center, 3Clinical Laboratory Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-27Accepted:2024-10-16Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-21 -
Contact:Pan Wei, PhD, Professor, Guizhou Prenatal Diagnosis Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China Co-corresponding author: Zhu Liying, PhD, Associate professor, School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Clinical Laboratory Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yang Hongtao, Master candidate, Guizhou Prenatal Diagnosis Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Science Fund Project), No. 82260165 (to PW); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Science Fund Project), No. 82300920 (to XYJ); Guizhou Science and Technology Plan Project, No. ZK[2024]199 (to XYJ); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund Project, No. gzwkj2024-081 (to XYJ); National Natural Science Foundation of Regional Cultivation Program of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, No. gyfyhsfc-2022-37 (to ZLY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Hongtao, Xu Yongjie, Zhou Yongjun, , Wang Shuang, Huang Changyudong, Zhu Liying, Pan Wei, . Effect of high glucose on blood-brain barrier tight junctions in hCMEC/D3 human brain microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5536-5542.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
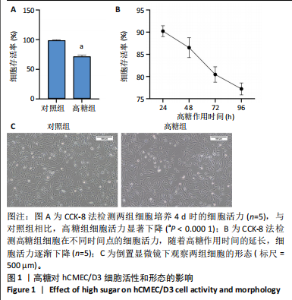
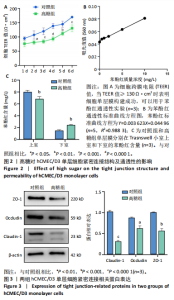
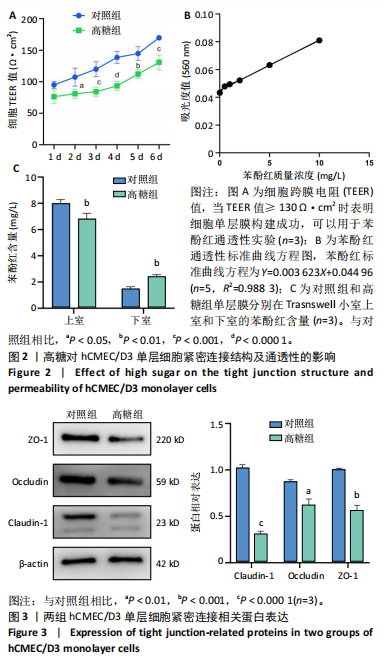
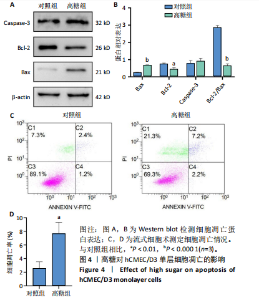
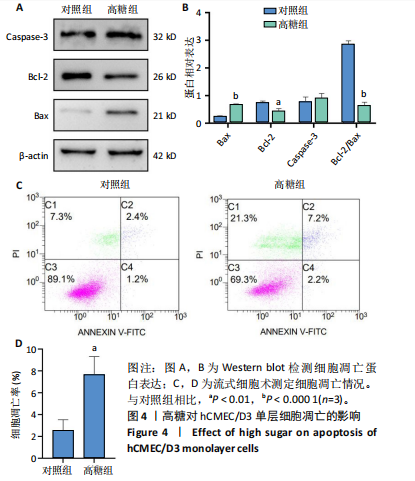
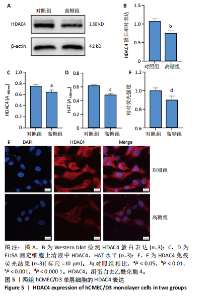
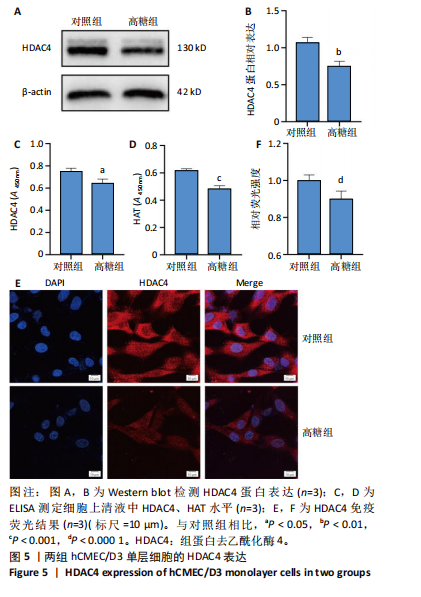
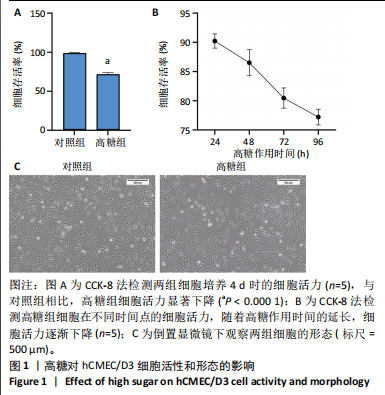
2.1 高糖对hCMEC/D3细胞活力影响 高糖组细胞存活率低于对照组(P < 0.000 1),且随高糖作用时间的延长而逐渐下降,见图1A,B。 2.2 高糖导致hCMEC/D3细胞形态发生改变 倒置显微镜观察显示,对照组细胞生长状态良好,呈典型的扁平状多边形,细胞间彼此间交织成致密网状结构,而高糖组细胞生长状态受抑制,细胞间有较大空隙,细胞间的连接相较于对照组明显减少,细胞碎片增多,见图1C。 2.3 高糖对hCMEC/D3单层细胞TEER值的影响 通过每天记录各组hCMEC/D3细胞TEER值,发现从第2天(P=0.011 5)起高糖组细胞的TEER值低于对照组,见图2A,提示高糖会破坏血脑屏障的紧密连接。 2.4 高糖对hCMEC/D3单层细胞苯酚红通透性的影响 苯酚红通透性实验结果显示加入含0.01 g/L苯酚红的HBSS溶液平衡50 min后,与对照组相比,高糖组Transwell小室上室的苯酚红含量显著下降(P=0.007 434);Transwell小室下室的苯酚红含量显著升高(P=0.002 132),见图2B,C,提示高糖会导致单层细胞的完整性受损。 2.5 高糖对hCMEC/D3单层细胞紧密连接相关蛋白的影响 Western blot检测结果显示,与对照组相比,高糖组细胞紧密连接蛋白ZO-1(P=0.000 216)、Occludin(P=0.002 798)、Claudin-1(P < 0.000 1)的表达量降低,表明高糖会破坏血脑屏障的紧密连接,见图3。 2.6 高糖对hCMEC/D3细胞凋亡的影响 Western blot检测结果显示,与对照组相比,高糖组细胞Caspase-3蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),Bax蛋白表达增加(P < 0.000 1),Bcl-2蛋白表达降低(P=0.007 208),见图4A,B;流式细胞术结果显示,与对照组相比,高糖组hCMECM/D3细胞凋亡率增加(P=0.009 0),见图4C,D。表明高糖可能通过诱导细胞凋亡导致血脑屏障的紧密连接受损。 2.7 高糖对hCMEC/D3单层细胞HDAC4表达的影响 通过Western blot、ELISA、免疫荧光检测结果显示,与对照组相比,高糖组细胞的HDAC4蛋白表达下降(P=0.004 1);HDAC4、HAT活性下降(P=0.019 1,P=0.000 7);HDAC4相对荧光强度下降(P < 0.000 1),见图5,说明高糖可能通过抑制hCMEC/D3单层细胞的HDAC4表达水平诱导细胞凋亡。"
| [1] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. [2] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, WEN Z, et al. Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: abnormal glucose metabolic regulation in the brain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1192602. [3] 段云峰,许永劼,杨婷婷,等.高糖诱导HT-22小鼠海马神经元代谢记忆细胞模型的构建及影响[J].天津医药,2024,52(1):44-50. [4] POPESCU BO, TOESCU EC, POPESCU LM, et al. Blood-brain barrier alterations in ageing and dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2009;283(1-2):99-106. [5] BEI J, MIRANDA-MORALES EG, GAN Q, et al. Circulating Exosomes from Alzheimer’s Disease Suppress Vascular Endothelial-Cadherin Expression and Induce Barrier Dysfunction in Recipient Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;95(3):869-885. [6] NAZARI H, SHRESTHA J, NAEI VY, et al. Advances in TEER measurements of biological barriers in microphysiological systems. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023;234:115355. [7] SUGIYAMA S, SASAKI T, TANAKA H, et al. The tight junction protein occludin modulates blood-brain barrier integrity and neurological function after ischemic stroke in mice. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2892. [8] ZHANG Q, LIU C, SHI R, et al. Blocking C3d+/GFAP+ A1 Astrocyte Conversion with Semaglutide Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Mice after Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2022;13(3):943-959. [9] 刘洋,李嘉民,陈荣,等.白藜芦醇苷对脑缺血再灌注损伤小鼠血脑屏障的保护作用研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2022,28(3):278-283. [10] POP V, SORENSEN DW, KAMPER JE, et al. Early brain injury alters the blood-brain barrier phenotype in parallel with β-amyloid and cognitive changes in adulthood. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(2):205-214. [11] 苏嘉楠,安继仁,孙贵炎,等.基于AMPK/mTOR信号通路探讨中药复方益糖康对db/db小鼠血脑屏障通透性及紧密连接蛋白的影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2024,26(7):10-15. [12] 袁小波,彭小珊,周丽丽,等.荞麦黄酮通过下调HMGB1抑制高糖诱导的人视网膜微血管内皮细胞损伤的研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2023,39(11):2311-2317. [13] FASELIS C, KATSIMARDOU A, IMPRIALOS K, et al. Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):117-124. [14] 王晨曦,王子瑞,俞澜.糖尿病肾病足细胞损伤病理机制及信号通路的研究进展[J].海南医学,2023,34(1):130-135. [15] STODDART P, SATCHELL SC, RAMNATH R. Cerebral microvascular endothelial glycocalyx damage, its implications on the blood-brain barrier and a possible contributor to cognitive impairment. Brain Res. 2022;1780:147804. [16] 杨俊瑶,王前, ZENG LINGFANG.组蛋白去乙酰化酶与血管重建[J].中华高血压杂志,2014,22(5):403-409. [17] LIU Z, HUA W, JIN S, et al. Canagliflozin protects against hyperglycemia-induced cerebrovascular injury by preventing blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption via AMPK/Sp1/adenosine A2A receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;968:176381. [18] ZHU J, JI X, SHI R, et al. Hyperglycemia Aggravates the Cerebral Ischemia Injury via Protein O-GlcNAcylation. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;94(2):651-668. [19] 李双月,刘淇麒,冯馨锐,等.组蛋白去乙酰化酶3与血管内皮细胞的关系[J].吉林医药学院学报,2018,39(3):201-203. [20] SCHADER T, LÖWE O, RESCHKE C, et al. Oxidation of HDAC4 by Nox4-derived H2O2 maintains tube formation by endothelial cells. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101669. [21] WEI Y, ZHOU F, ZHOU H, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells contribute to neovascularization of non-small cell lung cancer via histone deacetylase 7-mediated cytoskeleton regulation and angiogenic genes transcription. Int J Cancer. 2018;143(3):657-667. [22] KANG Y, KIM J, ANDERSON JP, et al. Apelin-APJ signaling is a critical regulator of endothelial MEF2 activation in cardiovascular development. Circ Res. 2013;113(1):22-31. [23] SANDO R 3RD, GOUNKO N, PIERAUT S, et al. HDAC4 governs a transcriptional program essential for synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell. 2012;151(4):821-834. [24] SPALLOTTA F, ROSATI J, STRAINO S, et al. Nitric oxide determines mesodermic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by activating class IIa histone deacetylases: potential therapeutic implications in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. Stem Cells. 2010;28(3):431-442. [25] 许雯,许永劼,刘歆蕾,等. TSA对不同糖浓度下小鼠海马神经元HT-22细胞凋亡的影响[J].天津医药,2021,49(4):349-353. [26] 黄晶晶.基于静电纺纳米纤维膜的Caco-2细胞模型构建及其槲皮素吸收机制研究[D].杭州:浙江工商大学,2019. [27] PARK JS, CHOE K, KHAN A, et al. Establishing Co-Culture Blood-Brain Barrier Models for Different Neurodegeneration Conditions to Understand Its Effect on BBB Integrity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5283. [28] 张翼,杨凯丽,毕嘉谣,等.薄荷醇、苏合香挥发油对川芎嗪纳米粒跨血脑屏障模型转运行为的影响[J].环球中医药,2022,15(2):188-196. [29] 丁怡丹.基于hCMEC/D3细胞单层膜作为血脑屏障模型的地西泮低氧转运研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2020. [30] KADRY H, NOORANI B, CUCULLO L. A blood-brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020;17(1):69. [31] TOTH AE, NIELSEN MS. Sortilins in the blood-brain barrier: impact on barrier integrity. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):549-550. [32] ZAPATA-ACEVEDO JF, MANTILLA-GALINDO A, VARGAS-SÁNCHEZ K, et al. Blood-brain barrier biomarkers. Adv Clin Chem. 2024;121:1-88. [33] ARCHIE SR, AL SHOYAIB A, CUCULLO L. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in CNS Disorders and Putative Therapeutic Targets: An Overview. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(11):1779. [34] COHEN J, MATHEW A, DOURVETAKIS KD, et al. Recent Research Trends in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells. 2024;13(6):511. [35] GUO P, ZHANG WJ, LIAN TH, et al. Alzheimer’s disease with sleep insufficiency: a cross-sectional study on correlations among clinical characteristics, orexin, its receptors, and the blood-brain barrier. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(8):1757-1762. [36] XU Y, LI H, CHEN G, et al. Radix polygoni multiflori protects against hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in diabetic encephalopathy by inhibiting the HDAC4/JNK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113427. [37] GUPTA M, PANDEY S, RUMMAN M, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying hyperglycemia associated cognitive decline. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022;14:57-63. [38] SEBASTIAN MJ, KHAN SK, PAPPACHAN JM, et al. Diabetes and cognitive function: An evidence-based current perspective. World J Diabetes. 2023;14(2):92-109. [39] LEE SWL, ROGOSIC R, VENTURI C, et al. A Human Neurovascular Unit On-a-Chip. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2373:107-119. [40] QI D, LIN H, HU B, et al. A review on in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) based on hCMEC/D3 cells. J Control Release. 2023;358: 78-97. [41] ZHAO Y, GAN L, REN L, et al. Factors influencing the blood-brain barrier permeability. Brain Res. 2022;1788:147937. [42] YUN JH, LEE DH, JEONG HS, et al. STAT3 activation in microglia increases pericyte apoptosis in diabetic retinas through TNF-ɑ/AKT/p70S6 kinase signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;613:133-139. [43] GUO X, SHI Y, DU P, et al. HMGB1/TLR4 promotes apoptosis and reduces autophagy of hippocampal neurons in diabetes combined with OSA. Life Sci. 2019;239:117020. [44] ZHENG X, REN B, GAO Y. Tight junction proteins related to blood-brain barrier and their regulatory signaling pathways in ischemic stroke. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115272. [45] CONG X, KONG W. Endothelial tight junctions and their regulatory signaling pathways in vascular homeostasis and disease. Cell Signal. 2020;66:109485. [46] YIN H, RAN Z, LUO T, et al. BCL-3 Promotes Intracerebral Hemorrhage Progression by Increasing Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability, Inflammation, and Cell Apoptosis via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:1420367. [47] LOCATELLI L, INGLEBERT M, SCRIMIERI R, et al. Human endothelial cells in high glucose: New clues from culture in 3D microfluidic chips. FASEB J. 2022;36(2):e22137. [48] SCHALKWIJK CG, MICALI LR, WOUTERS K. Advanced glycation endproducts in diabetes-related macrovascular complications: focus on methylglyoxal. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023;34(1):49-60. [49] LUO L, AN Y, GENG K, et al. High glucose-induced endothelial STING activation inhibits diabetic wound healing through impairment of angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;668:82-89. [50] CLYNE AM. Endothelial response to glucose: dysfunction, metabolism, and transport. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021;49(1):313-325. [51] LI X, JIN Q, YAO Q, et al. Placental Growth Factor Contributes to Liver Inflammation, Angiogenesis, Fibrosis in Mice by Promoting Hepatic Macrophage Recruitment and Activation. Front Immunol. 2017;8:801. [52] SUN C, XIE K, YANG L, et al. HDAC6 Enhances Endoglin Expression through Deacetylation of Transcription Factor SP1, Potentiating BMP9-Induced Angiogenesis. Cells. 2024;13(6):490. [53] 刘丹,杨锡彤,王光明.组蛋白去乙酰化酶4在缺血性卒中失调的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2021,50(24):4270-4274. [54] SHEN Z, BEI Y, LIN H, et al. The role of class IIa histone deacetylases in regulating endothelial function. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1091794. [55] LIU ZM, WANG X, LI CX, et al. SP1 Promotes HDAC4 Expression and Inhibits HMGB1 Expression to Reduce Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Response after Sepsis. J Innate Immun. 2022;14(4):366-379. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [3] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [4] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [7] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [8] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [9] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [10] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [11] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| [12] | Nigeayi · Aihemaiti, Yilidanna · Dilixiati, An Wei, Maimaitituxun · Tuerdi. Expression of mitochondrial creatine kinase 2 in a rat model of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and its role in inflammation progression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6877-6884. |
| [13] | Wang Ziheng, Wu Shuang. Oxidative stress-related genes and molecular mechanisms after spinal cord injury: data analysis and verification based on GEO database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [14] | Lu Xiuli, Xu Huazhen, Chen Yuxing, Yao Nan, Hu Zixuan, Huang Dane. Mechanism of Jiangu Formula in treating osteoporosis based on osteoclast-osteoblast coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6828-6835. |
| [15] | Lin Shuqian, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Pan Xinghua, Li Zian, Ruan Guangping. Comparison of biological characteristics of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after interference and overexpression of telomere Cajal body protein-1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6616-6624. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||