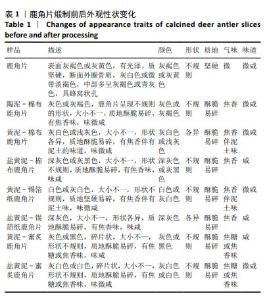
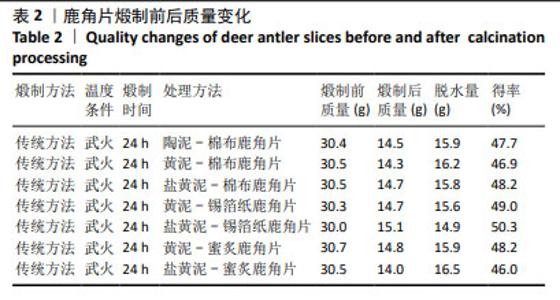
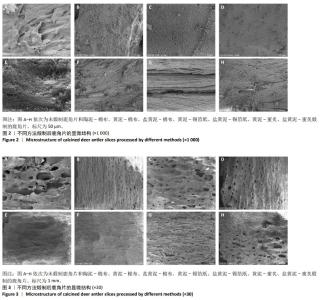
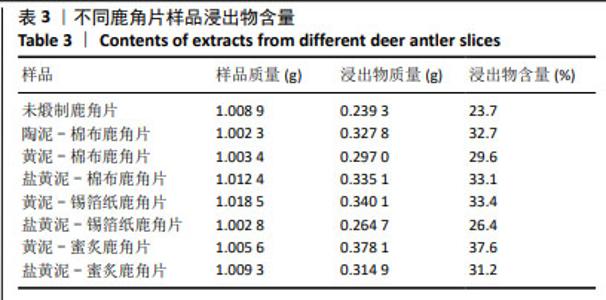
[1] 周晶晶,周洁,窦霞,等.不同炮制方法对甘草化学成分及药理作用的影响研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2024,42(5):244-249.
[2] 秦伟瀚,魏江平,张小梅,等.基于炎症大鼠代谢组学的马钱子炮制减毒存效机制研究[J].天然产物研究与开发,2024,36(5):825-837.
[3] 陈淼芬,黄子豪,周栋,等.炮制对黄精蛋白氨基酸组成及营养价值的影响[J].食品与发酵工业,2024,50(12):170-177.
[4] 谢静,穆中林,温远珍,等.不同炮制工艺鲜竹沥多糖的化学特征及体外抗氧化活性比较[J].中国现代中药,2023,25(12):2540-2548.
[5] 潘凉.分析中药炮制对中药化学成分及药理作用的影响[J].生命科学仪器,2022,20(z1):514.
[6] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典:四部[S].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020:66.
[7] 杜沁圆,秦聪聪,张义敏,等.全蝎炮制历史考证及现代炮制研究进展[J].中成药,2024,46(2):542-548.
[8] 隋利强,吴追乐,陈玉鹏.基于SPME-GC-MS分析探讨炮制对6种动物药挥发性成分的影响[J].中药材,2019,42(5):1030-1037.
[9] 邓雨娇,张定堃,刘倩,等.动物药腥臭气味形成机制及掩味技术研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(10):2353-2359.
[10] 范红.动物药腥臭气物质分析与水蛭炮制矫臭初探[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2023.
[11] 李绍烁,顾一丹,尹恒,等.基于网络药理学方法分析“龟板-鹿角”药对活性成分治疗骨质疏松症的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(35):5668-5674.
[12] 于大猛.鹿角胶传统炮制工艺探讨[J].陕西中医,2020,41(6):827-830.
[13] 李娜,胡亚楠,王晓雪,等.鹿角胶化学成分、药理作用及质量控制研究进展[J].中药材,2021,44(7):1777-1783.
[14] 高志惠,孙铁锋,王平,等.星点设计-效应面法优化鹿角胶-脱蛋白骨制备工艺[J].中成药,2016,38(8):1838-1841.
[15] 王平,张会敏,李刚.鹿角多肽对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(12):5644-5647.
[16] YANG B, LUO QL, WANG N, et al. HPF Modulates the Differentiation of BMSCs into HLCs and Promotes the Recovery of Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5686.
[17] LU GD, CHENG P, LIU T, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomal miR-29a Promotes Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020; 8:608521.
[18] YANG H, WU L, DENG H, et al. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting the TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in spinal microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):154.
[19] GUO Y, JIA X, CUI Y, et al. Sirt3-mediated mitophagy regulates AGEs-induced BMSCs senescence and senile osteoporosis. Redox Biol. 2021;41:101915.
[20] CHENG S, XU X, WANG R, et al. Chondroprotective effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2024;56(1):31-44.
[21] ZHANG Y, JIAO Z, WANG S. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Release miR-378a-5p-Carried Extracellular Vesicles to Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Innate Immun. 2023;15(1):893-910.
[22] HUANG Z, WEI H, WANG X, et al. Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by upregulating BMAL1 expression via BMP signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(3):1590-1596.
[23] 魏珍珍,方晓艳,苗明三.胶类中药的特点及现代研究分析[J].中国现代应用药学,2019,36(14):1842-1849.
[24] LI H, WANG C, YAO J, et al. Circ_0114581 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via the MiR-155-5p/HNRNPA3 axis. Life Sci. 2023;333:122127.
[25] TANG T, CHEN L, ZHANG M, et al. Exosomes derived from BMSCs enhance diabetic wound healing through circ-Snhg11 delivery. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024;16(1):37.
[26] LI M, TANG Q, LIAO C, et al. Extracellular vesicles from apoptotic BMSCs ameliorate osteoporosis via transporting regenerative signals. Theranostics. 2024;14(9):3583-3602.
[27] ZHANGDI H, GENG X, LI N, et al. BMSCs alleviate liver cirrhosis by regulating Fstl1/Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Heliyon. 2023;9(11):e21010.
[28] ZHANG K, QIU W, LI H, et al. MACF1 overexpression in BMSCs alleviates senile osteoporosis in mice through TCF4/miR-335-5p signaling pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2023;39:177-190.
[29] WU Z, ZHU J, WEN Y, et al. Hmga1-overexpressing lentivirus protects against osteoporosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. FASEB J. 2023;37(9):e22987.
[30] SU W, NONG Q, WU J, et al. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by BMSCs attenuates silica-induced acute pulmonary inflammation by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in macrophages. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 3):126651.
[31] 郁红礼,张元斌,刘冰冰,等.模拟醋制法研究狼毒(月腺大戟)主要萜类效应成分醋制过程结构转化机制[J].中国中药杂志, 2022,47(24):6596-6606.
[32] 邓畅,成铭,薛蓉,等.淡附片炮制前后色泽及水煎液中化学成分变化研究[J].中成药,2022,44(10):3382-3385.
[33] 宋志前,曾林燕,王淳,等.鲜地黄加工炮制后新成分含量变化研究[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2014,16(2):346-351.
[34] 吴旭,欧阳楠.炮制工艺对矿物药赤石脂有害重金属元素的影响考察[J].中国药师,2022,25(2):364-368.
[35] 刘铭超.何首乌炮制前后含药血清及主要化学成分对BMSCs的影响及机制研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2014.
[36] ZHANG Y, FENG X, ZHENG B, et al. Regulation and mechanistic insights into tensile strain in mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Bone. 2024;187:117197. |