Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4602-4611.doi: 10.12307/2025.812
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of external stent fixation and internal plate fixation for treatment of comminuted distal radius fractures
Lin Qing1, Liu Huan2, Cheng Yongzhong3, Jiang Junjie2, Li Yongyao3, Li Guangyao1
- 1Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100020, China; 2Institute of Clinical Basic Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100010, China; 3First Department of Trauma, Wangjing Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2024-04-10Accepted:2024-07-06Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-07 -
Contact:Cheng Yongzhong, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, First Department of Trauma, Wangjing Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100020, China -
About author:Lin Qing, Master candidate, Physician, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100020, China -
Supported by:Research and Transformation Application of Clinical Characteristic Diagnosis and Treatment Technology in Capital, No. Z221100007422075 (to CYZ); Special Project Independently Selected by Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, No. WJYY-ZZXT-2022-10 (to CYZ); Key Project of Science and Technology Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, No. CI2021A02008 (to CYZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Qing, Liu Huan, Cheng Yongzhong, Jiang Junjie, Li Yongyao, Li Guangyao. Meta-analysis of external stent fixation and internal plate fixation for treatment of comminuted distal radius fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4602-4611.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
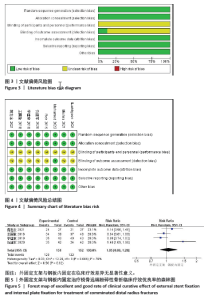
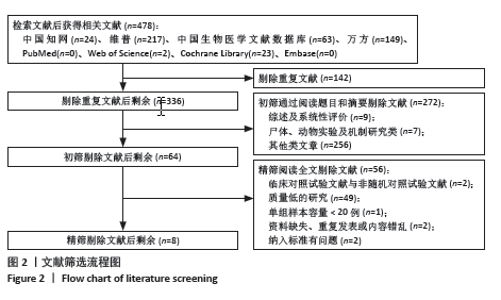
2.2 纳入研究文献方法学质量评价结果 纳入的8个研究均采用随机数字表法[18-25],采用分配隐藏,评价为低风险;1个研究描述了测量盲法[25],评价为低风险,其余研究均未描述是否采取分配盲法、测量盲法,评价为不清楚;4个研究存在退出失访情 况[18,22-23,25],均将退出失访人员剔除研究,其余研究不存在退出失访情况,均评价为低风险。所有研究不存在选择性报告研究结果,评价为低风险。所有研究基线数据均具有可比性,其他偏倚来源均评价为低风险。详见图3,4。 2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 临床疗效 4个研究报告了临床疗效优良率[19-21,24],临床疗效总优良率=(优+良)/总人数×100%,均属于粉碎性关节内骨折。统计学异质性显著(I2=76%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示,差异无显著性意义[RR=1.05,95%CI(0.86,1.29),P=0.62],见图5。"
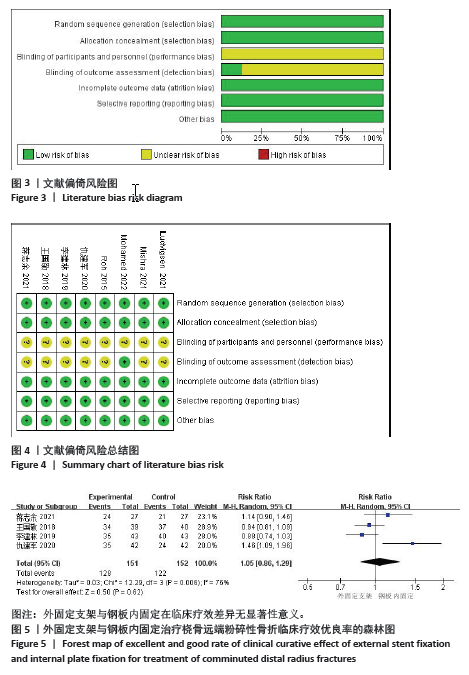
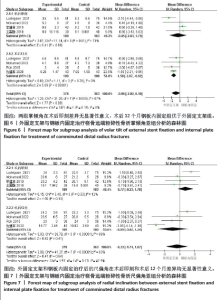
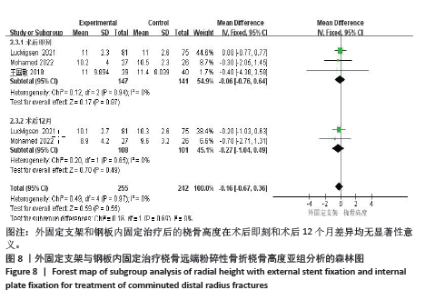
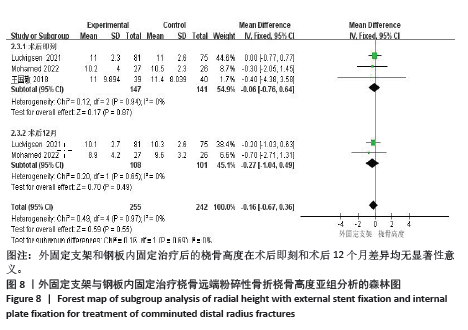
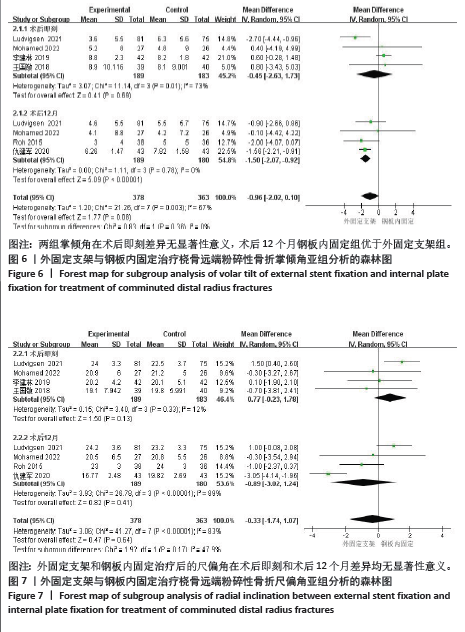
2.3.2 影像学相关指标 (1)掌倾角:6个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的掌倾角(单位:°)[18-21,23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后即刻和术后12个月的掌倾角。统计学异质性显著(I2=67%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后即刻,差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.45,95%CI(-2.63,1.73),P=0.69];术后12个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-1.50,95%CI(-2.07,-0.92), P < 0.000 01],见图6。 (2)尺偏角:6个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的尺偏角(单位:°)[18-21,23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后即刻和术后12个月的尺偏角。统计学异质性显著(I2=83%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后即刻,差异无显著性意义[MD=0.77,95%CI(-0.23,1.78),P=0.13];术后12个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.89,95%CI(-3.02,1.24),P=0.41],见图7。 (3)桡骨高度:3个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的桡骨高度(单位:mm)[19,23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后即刻和术后12个月的桡骨高度。统计学异质性不显著(I2=0%),采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示术后即刻,差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.06,95%CI(-0.76,0.64),P=0.87];术后12个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.27,95%CI(-1.04,0.49),P=0.49],见图8。"
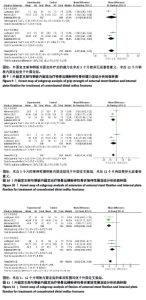
2.3.3 握力 2个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的握力(单位:kg)[22-23],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的握力。统计学异质性显著(I2=86%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-4.31,95%CI(-9.36,0.75),P=0.09];术后12个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-4.59,95%CI(-7.52,-1.65), P=0.002],见图9。 2.3.4 腕关节活动范围 (1)背伸:3个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的背伸范围(单位:°)[22-23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的背伸范围。统计学异质性显著(I2=62%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-4.94,95%CI (-8.21,-1.68),P=0.003];术后12个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-4.43, 95%CI(-9.28,0.42),P=0.07],见图10。 (2)掌屈:3个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的掌屈范围(单位:°)[22-23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的掌屈范围。统计学异质性不显著(I2=26%),采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-5.16,95%CI(-6.59,-3.72),P < 0.000 01];术后12个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-2.76,95%CI(-4.55,-0.97),P=0.003],见图11。"
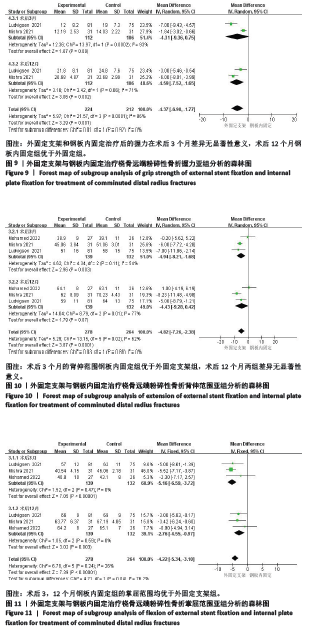
(3)旋前:3个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的旋前范围(单位:°)[22-23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的旋前范围。统计学异质性显著(I2=62%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-2.96,95%CI(-6.64,0.72),P=0.12];术后12个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-1.45,95%CI(-2.85,-0.04),P=0.04],见图12。 (4)旋后:3个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的旋后范围(单位:°)[22-23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的旋后范围。统计学异质性不显著(I2=48%),采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-3.97,95%CI(-6.13,-1.80),P=0.000 3];术后12个月,差异有显著性意义[MD=-2.80,95%CI(-4.67,-0.94),P=0.003],见图13。 (5)桡偏:2个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的桡偏范围(单位:°)[23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的桡偏范围。统计学异质性显著(I2=88%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-3.23,95%CI(-10.57,4.12),P=0.39];术后12个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-1.17,95%CI(-4.89,2.56),P=0.54],见图14。"
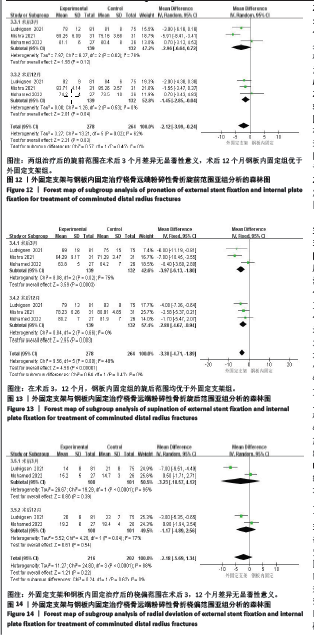
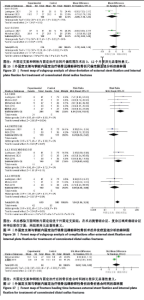
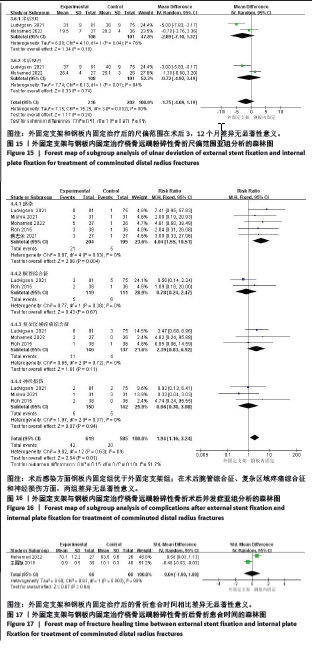
(6)尺偏:2个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的尺偏范围(单位:°)[23,25],根据随访时间的不同进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后3,12个月的尺偏范围。统计学异质性显著(I2=80%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示术后3个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-2.89,95%CI(-7.10,1.32),P=0.18];术后12个月,差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.72,95%CI(-4.92,3.49),P=0.74],见图15。 2.3.5 安全性评价 5个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的不良反应发生率[18,22-25],根据术后不良反应的症状进行亚组分析,分别比较了术后感染、腕管综合征、复杂区域疼痛综合征和神经损伤。统计学异质性不显著(I2=0%),采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示术后感染方面,差异有显著性意义[RR=4.04,95%CI(1.55,10.51),P=0.004];术后腕管综合征方面,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.78,95%CI(0.24,2.47),P=0.67];术后复杂区域疼痛综合征方面,差异无显著性意义[RR=2.39,95%CI(0.83,6.92),P=0.11];术后神经损伤方面,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.96,95%CI(0.30,3.08),P=0.94],见图16。 2.3.6 骨折愈合时间 2个研究报告了外固定与内固定治疗粉碎性桡骨远端骨折的骨折愈合时间[19,25],统计学异质性显著(I2=88%),采用随机效应模型分析,结果显示,差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.04,95%CI(-1.00,1.08),P=0.94],见图17。 2.4 异质性分析 此次Meta分析有较多异质性较大的结果,通过一一剔除纳入文献检验异质性进行敏感性分析,未发现明显导致异质性高的文献来源。因此,异质性高的原因可能与医生手术经验、护理康复经验、医院设施不一致等临床异质性有关。 2.5 发表偏倚评价 此次纳入文献8篇,未超过10篇,不需要制作漏斗图以检测其是否存在发表偏倚。"
| 1] 黄晓夏, 彭聪, 艾科拜尔·喀迪尔, 等. 三种入路掌侧钢板置入治疗不稳定桡骨远端骨折的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(24):3867-3872. [2] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组, 中华医学会骨科学分会外固定与肢体重建学组, 余斌, 等. 中国成人桡骨远端骨折诊疗指南(2023)[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2023,25(1):6-13. [3] 徐志国, 张超, 曹聪, 等. 桡骨远端骨折手术治疗及术后并发症[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2013,34(3):178-181. [4] 伏治国, 张曦, 董启榕, 等. 背侧双锁定加压钢板治疗桡骨远端伸直型不稳定骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2013,29(6):532-535. [5] 刘锋, 陈凯奇. 尺骨茎突骨折内固定对桡骨远端骨折合并尺骨茎突骨折治疗结果的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2024, 32(2):60-66. [6] 程文静, 丁国正, 谢家兵, 等. 桡骨远端骨折掌侧钢板内固定后关节僵硬的危险因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(27):4374-4378. [7] 廖禄田, 糜菁熠. 桡骨远端骨折畸形愈合对下尺桡关节的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(8):705-709. [8] 卓金, 王莎莎, 陈其强, 等. C型桡骨远端骨折患者腕关节功能及骨折复位质量:克氏针辅助外固定架、外固定架及掌侧入路钢板内固定的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5126-5132. [9] 李海波, 马宝通. 老年桡骨远端骨折保守治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2023,29(3):406-410. [10] 罗德素, 刘培来, 苗壮. 分期外固定架牵引联合铰链膝假体置换术治疗复杂创伤性膝关节炎1例[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版),2022,60(1):121-124. [11] 宋建伟, 马延彬, 路训明, 等. 侧卧屈膝牵引器辅助髓内钉钢板固定胫腓骨骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(14): 1323-1326. [12] 刘安, 盛伟. 关节镜辅助下静态牵引综合治疗桡骨远端关节内骨折的临床疗效观察[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2023, 20(3):27-31. [13] LEE DJ, ELFAR JC. External Fixation Versus Open Reduction With Locked Volar Plating for Geriatric Distal Radius Fractures. Geriatr Orthop Surge Rehabil. 2014;5(3):141-143. [14] PATEL S, DESHMUKH A, YADAV P, et al. Assessment of Functional and Radiological Outcomes of Comminuted Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fracture Treated With Locking Compression Plate. Cureus. 2022; 14(1):e21398. [15] 唐聪, 颜志文, 池开宇, 等. 保留旋前方肌小切口掌侧解剖锁定钢板辅助复位内固定治疗不稳定桡骨远端骨折疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2024, 39(1):37-42. [16] 陈孝均, 罗焘, 欧昌良, 等. 外架辅助复位锁定钢板内固定与单纯锁定钢板内固定治疗C型桡骨远端骨折的对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(33):5315-5320. [17] KARIMI NM, SHAYESTEH AM, FAZEL MS, et al. Success Rate and Complications of Comminuted Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fracture Treatment via Closed Reduction and Use of a Mini-External Fixator. Trauma Mon. 2015;20(4):e18885. [18] ROH YH, LEE BK, BAEK JR, et al. A randomized comparison of volar plate and external fixation for intra-articular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2015; 40(1):34-41. [19] 王国敬. 有限切开锁定加压钢板内固定与闭合复位外固定架治疗桡骨远端C2型骨折的疗效比较[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2018. [20] 李建林, 吴文侠, 云丽媛. 万向锁定钢板内固定对老年C型桡骨远端粉碎性骨折的疗效分析[J]. 河北医药,2019,41(12): 1813-1816. [21] 仇建军, 邹翰林, 石文俊, 等. 背侧钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端背侧粉碎性骨折的疗效分析[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2020, 41(6):376-381. [22] MISHRA RK, SHARMA BP, KUMAR A, et al. A comparative study of variable angle volar plate and bridging external fixator with K-wire augmentation in comminuted distal radius fractures. Chin J Traumatol. 2021; 24(5):301-305. [23] LUDVIGSEN T, MATRE K, GUDMUNDSDOTTIR RS, et al. Surgical Treatment of Distal Radial Fractures with External Fixation Versus Volar Locking Plate: a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021; 103(5):405-414. [24] 蒋志余, 张波, 孙印明. 桡骨远端不稳定型骨折3种疗法的疗效比较[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2021,25(4):96-99. [25] MOHAMED MA, ABDEL-WANIS ME, SAID E, et al. Dorsal bridge plating versus bridging external fixation for management of complex distal radius fractures. Injury. 2022; 53(10):3344-3351. [26] JAFARI D, BIRJANDINEJAD A, DALIRI M, et al. Treatment outcomes of applying external fixator on distal radius fractures: a randomized clinical trial to compare between two directions of force exertion in parallel to radius shaft and perpendicular to the distal radius articular surface. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):283. [27] XIE X, XIE X, QIN H, et al. Comparison of internal and external fixation of distal radius fractures. Acta Orthop. 2013;84(3): 286-291. [28] GOU Q, XIONG X, CAO D, et al. Volar locking plate versus external fixation for unstable distal radius fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):433. [29] BROGAN DM, RICHARD MJ, RUCH D, et al. Management of Severely Comminuted Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2015;40(9):1905-1914. [30] WANG J, LU Y, CUI Y, et al. Is volar locking plate superior to external fixation for distal radius fractures? A comprehensive meta-analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018; 52(5):334-342. [31] DARIO P, MATTEO G, CAROLINA C, et al. Is it really necessary to restore radial anatomic parameters after distal radius fractures? Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 6:S21-S26. [32] DÜNDAR A, CANKAYA D, KARAKUŞ D, et al. Volar-locking plate versus external fixator in the management of distal radius fractures: An isokinetic study. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022;28(8):1156-1163. [33] BEYER J, WYNKOOP E, LIU J, et al. Interventions for Distal Radius Fractures: A Meta-analysis of Comparison Studies. J Wrist Surg. 2021;10(5):440-457. [34] 袁术鹏, 张兴平, 孙研, 等. 外固定架与切开复位内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折Meta分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2021,34(5):429-437. [35] 杨召, 苑珍珍, 马剑雄, 等. 切开复位内固定与外固定治疗不稳定桡骨远端骨折远期疗效的荟萃分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2017,97(41):3269-3272. [36] RICHARD MJ, WARTINBEE DA, RIBOH J, et al. Analysis of the complications of palmar plating versus external fixation for fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 2011; 36(10):1614-1620. |
| [1] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [2] | Huang Haobo, Liang Xinyuan, Ye Guozhong, Xie Qingxiang, Su Boyuan. Suture tape and headless compression screws in treatment of Lisfranc injury with comminuted fractures of the first and second proximal metatarsal bones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1803-1809. |
| [3] | Zhang Hao, Wang Qing, Zhang Jian, Li Guangzhou, Wang Gaoju. Comparison of posterior C2-3 fixation combined with bucking bar technique and posterior C2-3 fixation alone in treatment of unstable Hangman fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1848-1854. |
| [4] | Su Lintao, Jiang Jianfeng, Ma Jun, Huang Liangliang, Lei Changyu, Han Yaozheng, Kang Hui. Precise application of O-arm navigation system in thoracolumbar fractures with developmental pedicle stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1855-1862. |
| [5] | Gao Zhenyang, Zeng Xiuan, Yang Qibing, Kou Xianshuai, Wang Kejing, Li Meng. Computer-simulated repositioning combined with pelvic reduction frame for treatment of anteroposterior compression-III pelvic fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1870-1875. |
| [6] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| [7] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [8] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [9] | Yu Ming, Wang Wen. Posterior cruciate ligament tibial attachment point avulsion fracture: materials, implants, and internal fixation techniques in arthroscopic treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 872-880. |
| [10] | Sheng Wenbo, Liu Bingli, Li Sibo, Ao Rongguang, Yu Baoqing. Cement-augmented short-segment percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for the stage II Kümmell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7286-7292. |
| [11] | Wang He, Yu Shaohong, . Meta-analysis of transcranial direct current stimulation in improving lower limb motor dysfunction in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6556-6565. |
| [12] | Li Zhenggang, Shang Xuehong, Wu Zhang, Li Hong, Sun Chaojun, Chen Huadong, Sun Zhe, Yang Yi. Finite element analysis of three internal fixation modalities for treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures under different loading conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 455-463. |
| [13] | Wang Jianlei, He Peiliang, Sun Yongjian. A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of intravenous glucocorticoids before lower limb joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 599-607. |
| [14] | Hu Liuchao, Luo Yiwen, Wu Zhifang. Fracture line map characteristics of distal radius fractures involving dorsal articular surface: effective fixation with screws for postoperative displacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 524-530. |
| [15] | Liu Xiaoyin, Zhang Jianqun, Chen Zhen, Liang Simin, Wang Zhiqiang, Ma Zongjun, Ma Rong, Ge Zhaohui. Short-term efficacy of oblique lateral interbody fusion combined with lateral plate fixation in treatment of single-level lumbar degenerative disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 531-537. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||