Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4529-4536.doi: 10.12307/2025.199
Previous Articles Next Articles
Opposing needling acupuncture combined with preemptive analgesia in treatment of pain after initial unilateral total knee arthroplasty
Xu Minglan1, Hu Xiaoxue1, Shen Jun2, Xiang Zheng2, Zhang Chengbo2, Xiao Lianbo2, 3
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, 2Department of Orthopedics Surgery, Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; 3Institute of Arthritis Research in Integrated Medicine, Shanghai Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China
-
Received:2024-04-04Accepted:2024-06-11Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-06 -
Contact:Xiao Lianbo, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics Surgery, Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; Institute of Arthritis Research in Integrated Medicine, Shanghai Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China -
About author:Xu Minglan, Associate chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation Project/General Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No. 22ZR1453000 (to SJ); Medical Innovation Research Special General Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No. 22Y11923200 (to SJ); Medical Innovation Research Special General Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No. 21Y11921500 (to XLB); Shanghai Municipal Health Commission, Shanghai Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Standardization Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2023JS03 (to XLB); Shanghai Scientific Research Project of Changning District Health Commission, No. 20214Y020 (to XML)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Minglan, Hu Xiaoxue, Shen Jun, Xiang Zheng, Zhang Chengbo, Xiao Lianbo. Opposing needling acupuncture combined with preemptive analgesia in treatment of pain after initial unilateral total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4529-4536.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
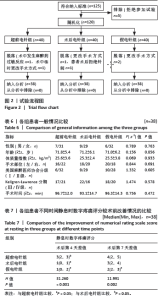
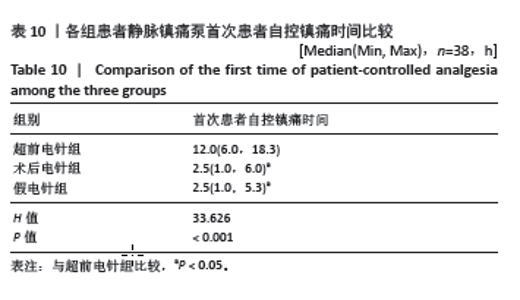
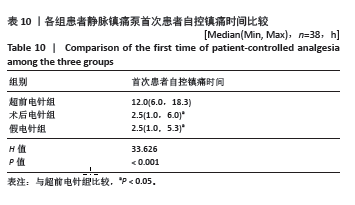
2.1 参与者数量分析 此次试验招募过程中,共有125例研究对象符合纳入标准,其中5例拒绝加入此次试验予以排除,共计入组120例患者进入随机化分组,超前电针组、术后电针组和假电针组各40例。试验进行阶段,超前电针组脱落2例:1例患者因术中发生麻醉药过敏反应,1例患者术中临时更改手术方式;术后电针组脱落2例:1例更改手术方式,1例患者术后拒绝针刺,自行退出研究;假电针组因更改手术方式脱落2例。最终3组共纳入患者114例,每组38例。脱落人数未超过纳入人数的20%,符合试验样本数标准。 2.2 试验流程图 见图2。 2.3 基线资料比较 各组患者性别、年龄、体质量指数、手术部位、ASA分级、K-L分期、手术时间相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表6。 2.4 术后第4,7天静息数字疼痛评分较术前改善情况 各组患者术后第4,7天静息数字疼痛评分较术前显著改善(P < 0.05);其中与超前电针组比较,术后第4天术后电针组和假电针组患者静息数字疼痛评分差值明显降低 (P < 0.05);与超前电针组比较,术后第7天术后电针组静息数字疼痛评分差值无显著变化(P > 0.05),假电针组静息数字疼痛评分差值明显降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。说明超前电针组可以有效缓解全膝关节置换术后急性静息疼痛,且在术后第4天效果优于术后电针组,见表7。"
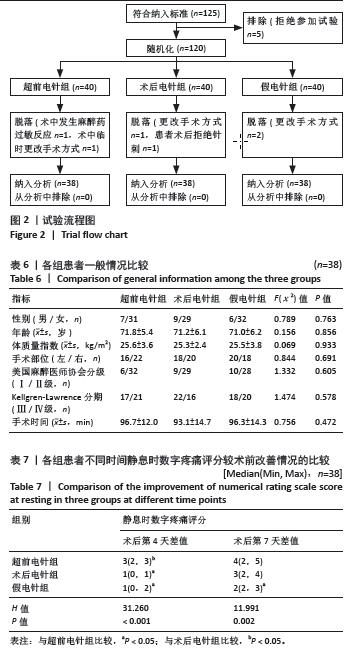
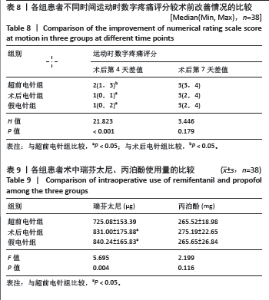
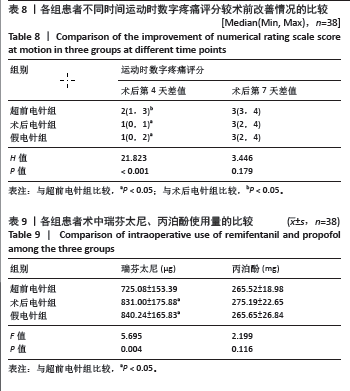
2.5 术后第4,7天运动数字疼痛评分较术前改善情况 3组患者术后第4天运动数字疼痛评分较术前改善情况比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);其中与超前电针组比较,术后电针组和假电针组患者术后第4天运动数字疼痛评分差值明显降低(P < 0.05)。3组患者术后第7天运动数字疼痛评分较术前改善情况比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),说明超前电针组可以有效缓解全膝关节置换术后急性运动疼痛,且在术后第4天效果优于术后电针组,见表8。 2.6 术中瑞芬太尼和丙泊酚使用量 各组患者术中瑞芬太尼使用量比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);其中与超前电针组比较,术后电针组和假电针组患者术中瑞芬太尼用量明显增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。3组患者术中丙泊酚用量相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表9。"
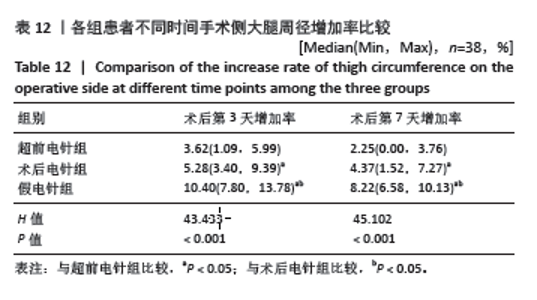
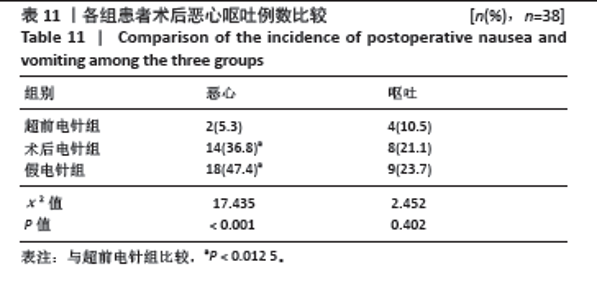
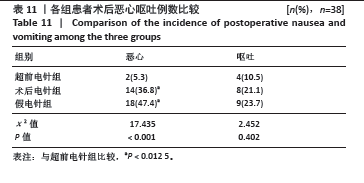
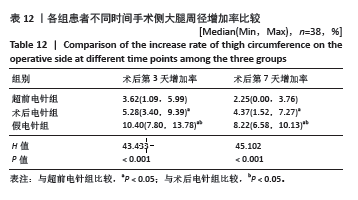
2.9 术后第3,7天手术侧大腿周径增加率 各组患者术后第3,7天手术侧大腿周径增加情况比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。其中与超前电针组比较,术后电针组和假电针组患者术后第3,7天大腿周径增加率明显增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与术后电针组比较,假电针组患者术后第3,7天大腿周径增加率明显增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。说明超前电针组和术后电针组均可以有效降低全膝关节置换术后大腿周径,且超前电针组效果更优,见表12。 2.10 电针实施盲法成功率 超前电针组盲法成功率为87%(33/38),术后电针组盲法成功率为76%(29/38),假电针组盲法成功率为66%(25/38),3组患者电针实施盲法成功率比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.110 > 0.05)。 2.11 植入物与宿主的生物相容性 3组患者均未观察到明显的植入物和宿主不良反应发生,例如植入物周围感染、过敏反应、免疫反应及排斥反应等。"
| [1] KANG K, TIEN T, LEE M, et al. Suitability of Metal Block Augmentation for Large Uncontained Bone Defect in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA). J Clin Med. 2019;8(3):384. [2] CARR AJ, ROBERTSSON O, GRAVES S, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2012;379(9823):1331-1340. [3] LAVAND’HOMME PM, KEHLET H, RAWAL N, et al. Pain management after total knee arthroplasty: Procedure Specific Postoperative Pain Management recommendations. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2022;39(9):743-757. [4] RAMLALL Y, ANDRION JJD, CAMERON HU, et al. Examining pain before and after primary total knee replacement (TKR): A retrospective chart review. Int J of Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2019;34:43-47. [5] SZÖTS K, PEDERSEN PU, HØRDAM B, et al. Physical health problems experienced in the early postoperative recovery period following total knee replacement. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2015;19(1):36-44. [6] 周宗科,廖刃,唐佩福,等.中国骨科手术加速康复围手术期疼痛管理指南[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(12):929-938. [7] 刘娅楠,侯怀晶,薛建军,等.全膝关节置换术后疼痛机制与针刺镇痛研究进展[J].西部中医药,2020,33(4):146-150. [8] SHAH S, GODHARDT L, SPOFFORD C. Acupuncture and Postoperative Pain Reduction. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022;26(6):453-458. [9] 孙若晗,徐赟赟,胡汉通,等.巨刺的理论基础及应用时机探讨[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(4):1972-1974. [10] MENGHAN L, YAN Y, SHIZHE D, et al. Contralateral needling at the foot of unaffected side combining with rehabilitation treatment for motor dysfunction of hand after ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023;43(5):1034-1039. [11] XUAN C, YAN W, WANG D, et al. Efficacy of preemptive analgesia treatments for the management of postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2022;129(6):946-958. [12] GONÇALVES DE FREITAS ATA, LEMONICA L, DE FAVERI J, et al. Preemptive Analgesia with Acupuncture Monitored by c-Fos Expression in Rats. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2016;9(1):16-21. [13] LISZKA H, ZAJĄC M, GĄDEK A. Pre-emptive analgesia with methylprednisolone and gabapentin in total knee arthroplasty in the elderly. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):2320. [14] ZHOU Y, LIU X, DING C, et al. Positive Preemptive Analgesia Effectiveness of Pregabalin Combined with Celecoxib in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Controlled Randomized Study. Pain Res Manag. 2023;2023: 1-10. [15] YANG EJ, KOO ST, KIM YS, et al. Contralateral electroacupuncture pretreatment suppresses carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain via the opioid-mu receptor. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31(6):725-730. [16] 樊子娟,王桂杉,李川,等.《中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)》解读和评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(6):621-627. [17] 中华中医药学会骨伤科分会膝痹病(膝骨关节炎)临床诊疗指南制定工作组. 中医骨伤科临床诊疗指南·膝痹病(膝骨关节炎)[J].康复学报,2019,29(3):1-7. [18] 谭亚芹,马昕婷,王琦,等.国家标准《腧穴名称与定位》(GB/T 12346-2006)使用情况调查研究[J].中国针灸,2016,36(8):871-874. [19] 李冰,赵占强,柳舒扬,等.经皮穴位电刺激对腹腔镜胆囊切除术后应激反应及胃肠功能的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2023,39(4): 379-383. [20] PINSORNSAK P, ROJANAVIJITKUL S, CHUMCHUEN S. Peri-articular tranexamic acid injection in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. 2016;17(1):313. [21] LIU Z, XU H, CHEN Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture for women with pure stress urinary incontinence: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14(1):315. [22] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [23] LIU Y, XIAO S, YANG H, et al. Postoperative pain-related outcomes and perioperative pain management in China: a population-based study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023;39:100822. [24] SMALL C, LAYCOCK H. Acute postoperative pain management. Br J Surg. 2020;107(2):e70-e80. [25] DE LADOUCETTE A. Management of perioperative pain after TKA. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023;109(1):103443. [26] XUAN C, YAN W, WANG D, et al. Efficacy of preemptive analgesia treatments for the management of postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2022;129(6):946-958. [27] 李蔚,赵华,吴君怡,等.针灸在手术超前镇痛中的临床应用进展[J].中医药导报,2016,22(16):93-95. [28] BRINCK E, TIIPPANA E, HEESEN M, et al. Perioperative intravenous ketamine for acute postoperative pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;12(12):CD012033. [29] 闫向彪,韩学昌,邢群智,等.电针内麻点和内关穴与硬膜外神经阻滞在胸科手术患者超前镇痛的对比研究[J].中国针灸,2021, 41(1):59-64. [30] SCHIFF E, ATTIAS S, MATTER I, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine interventions for perioperative symptoms: A comparative effectiveness study. Complement Ther Med. 2019;44:51-55. [31] ACAR HV. Acupuncture and related techniques during perioperative period: A literature review. Complement Ther Med. 2016;29:48-55. [32] 权隆芳,贾小强,李东冰,等.不同时间电针对直肠癌开腹手术患者围术期应激反应和免疫功能的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2020, 39(3):330-338. [33] ZHU J, LI S, WU W, et al. Preoperative electroacupuncture for postoperative nausea and vomiting in laparoscopic gynecological surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Acupunct Med. 2022;40(5): 415-424. [34] PIRES MC, BARROS GAMD, FONSECA LGF, et al. Effects of Preoperative Acupuncture on Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting and Plasma Serotonin Values in the Hysterectomy Postoperative Period: a Randomized Clinical Trial. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2022;15(5):300-306. [35] ZHANG C, YAN CH, CHAN PK, et al. A Randomized Controlled Study on the Use of Tourniquet in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(6): 698-706. [36] 刘玥,安冬卫.针刺配合推拿手法治疗骨折后期肢体肿胀的疗效分析[J].山西医药杂志,2021,50(5):837-839. [37] WU MS, CHEN KH, CHEN IF, et al. The Efficacy of Acupuncture in Post-Operative Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150367. [38] XU Z, ZHU Y, SHEN J, et al. Pain Relief Dependent on IL-17–CD4+ T Cell–β-Endorphin Axis in Rat Model of Brachial Plexus Root Avulsion After Electroacupuncture Therapy. Front Neurosci. 2021;14: 596780. [39] 赵翅,许辉,康冰心,等.基于数据挖掘分析针灸治疗全膝关节置换术后急性疼痛的选穴规律[J].西部中医药,2023,36(4):63-67. [40] 康冰心,肖涟波,赵翅,等.电针联合塞来昔布治疗全膝关节置换术后疼痛的疗效观察[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2022,42(10): 1169-1174. |
| [1] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [2] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [3] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [6] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [7] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [8] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [9] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [10] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [11] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [12] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [13] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [14] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [15] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||