Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (22): 4720-4730.doi: 10.12307/2025.455
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films
Hu Chen1, Jiang Ying2, Chen Jia3, Qiao Guangwei1, Dong Wen1, Ma Jian1
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Xuzhou Stomatological Hospital, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Orthodontics, Stomatological Hospital, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-04-24Accepted:2024-07-05Online:2025-08-08Published:2024-12-06 -
Contact:Ma Jian, Chief physician, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Hu Chen, Master, Attending physician, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China Jiang Ying, Master, Physician, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Xuzhou Stomatological Hospital, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Ningxia Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2021AAC03357 (to HC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
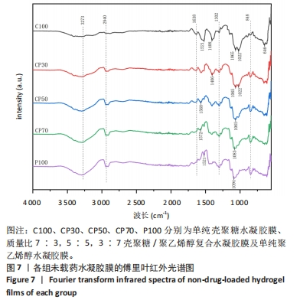
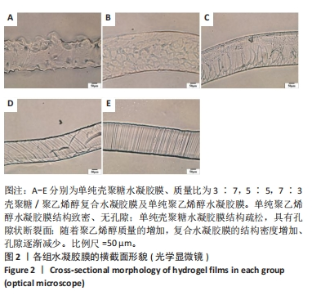
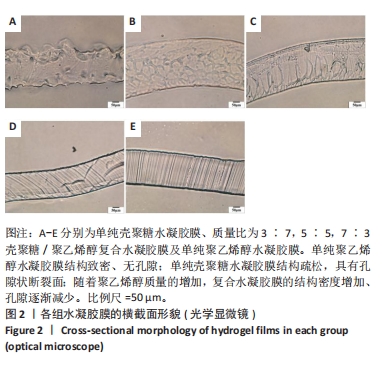
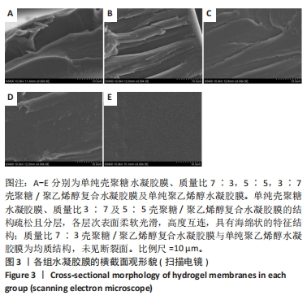
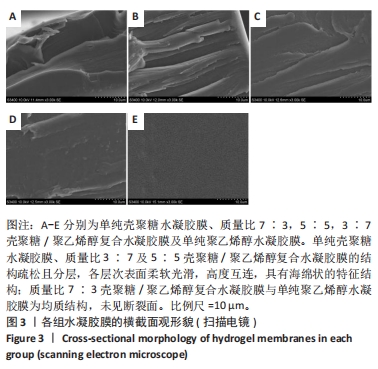
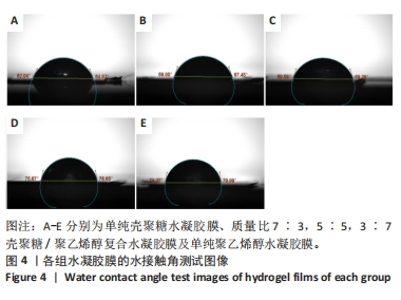
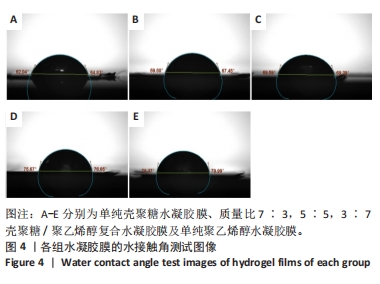
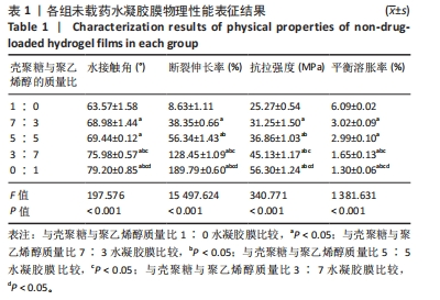
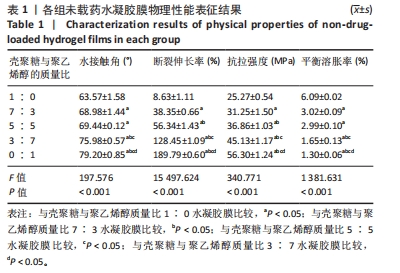
2.5 各组未载药水凝胶膜的傅里叶红外光谱测试结果 如图7所示,在P100组红外光谱图中,波数为3 273 cm-1峰为羟基-OH伸动峰,波数为2 940 cm-1峰为亚甲基中C-H键伸缩振动峰,1 521 cm-1峰为C-OH弯曲振动峰,1 302 cm-1峰为-OH变形振动峰,1 094 cm-1峰归属于C-O键伸缩振动峰,848 cm-1峰为亚甲基中C-H键面外摇摆振动。在C100组外光谱图中,3 273 cm-1弱峰为氨基与羟基中-OH与N-H键伸缩振动峰,由于峰较弱,这表明该样品分子链内与链间存在大量的氢键,1 638 cm-1峰为酰胺Ⅰ带C=O键伸缩振动峰,1 521 cm-1峰为酰胺Ⅱ带中N-H键弯曲振动峰,1 408,1 302 cm-1峰为亚甲基中C-H键弯曲振动峰,1 065,1 022 cm-1峰为C-O键伸缩振动峰,646 cm-1峰为壳聚糖的结晶敏感峰。在CP70组红外光谱图中,波数为3 273 cm-1附近的羟基的伸缩振动峰强度强于C100组的羟基峰强度且峰宽度变宽,这说明聚乙烯醇与壳聚糖之间形成了氢键。在CP30组中,1 065,1 022 cm-1处壳聚糖中C-O键的特征峰得以保留,这说明在这个比例壳聚糖的结构较为完整。在CP50组、CP70组中1 065,1 022 cm-1峰处壳聚糖中C-O键的特征峰明显降低,646 cm-1处的结晶敏感峰逐渐消失,进一步说明了随着聚乙烯醇比例的增加,壳聚糖链的规整性逐渐被破坏且结晶度降低。3种复合水凝胶膜的红外光谱图基本相似,与单独的组分相比无明显特征峰出现,说明两种材料的混合只是物理混合,在CP50组红外光谱图中3 273 cm-1处峰更宽、强度更大,说明氢键缔合更加紧密。"
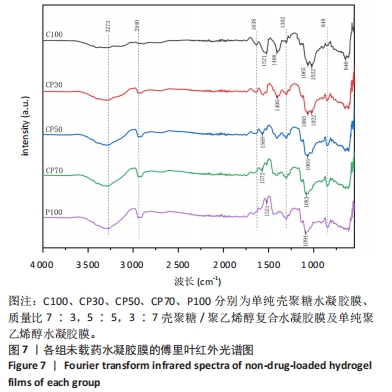
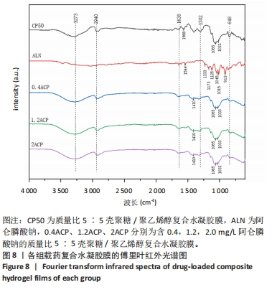
2.6 各组载药复合水凝胶膜的傅里叶红外光谱测试结果 如图8所示,在CP50组红外光谱图中,波数为3 273 cm-1峰为羟基-OH伸缩振动峰,波数为2 940 cm-1峰为亚甲基中C-H键伸缩振动峰,848 cm-1峰为亚甲基中C-H键面外摇摆振动,三者为聚乙烯醇的特征峰,1 638 cm-1峰为酰胺Ⅰ带C=O键伸缩振动峰,1 302 cm-1峰为亚甲基中C-H键弯曲振动峰,两者为壳聚糖的特征峰。在阿仑膦酸钠的红外光谱图中,波数为1 544 cm-1峰为N-H键弯曲振动峰,1 233 cm-1峰为C-N键伸缩振动峰,1 173,1 125 cm-1峰分别归属于PO2反对称伸缩振动与对称伸缩振动峰,1 245,1 015 cm-1峰为C-O键伸缩振动峰,913 cm-1峰为P-OH键伸缩振动峰。在0.4ACP组、1.2ACP组、2ACP组红外光谱中,1 065,1 033 cm-1峰分别归属于为P-OH键的反对称伸缩振动峰和对称伸缩振动峰,相较于CP50组1 065,1 021 cm-1峰的伸缩振动加强,P-OH键特征峰变宽,P-OH键含量增大,说明阿仑膦酸钠药物成功加载到了复合水凝胶膜上。913 cm-1处P-OH键伸缩振动峰消失说明该官能团与别的结构形成了氢键,与聚乙烯醇或壳聚糖中的某种结构进行了整合。另外,在0.4ACP组、1.2ACP组、2ACP组红外光谱图中,3 273,2 940,848 cm-1峰为聚乙烯醇的特征峰,1 638,1 302 cm-1峰为壳聚糖的特征峰,说明不同浓度阿仑膦酸钠的加入均没有破坏CP50的结构。"
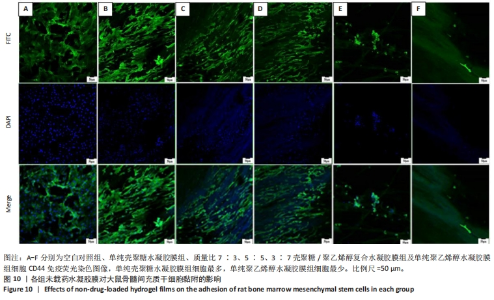
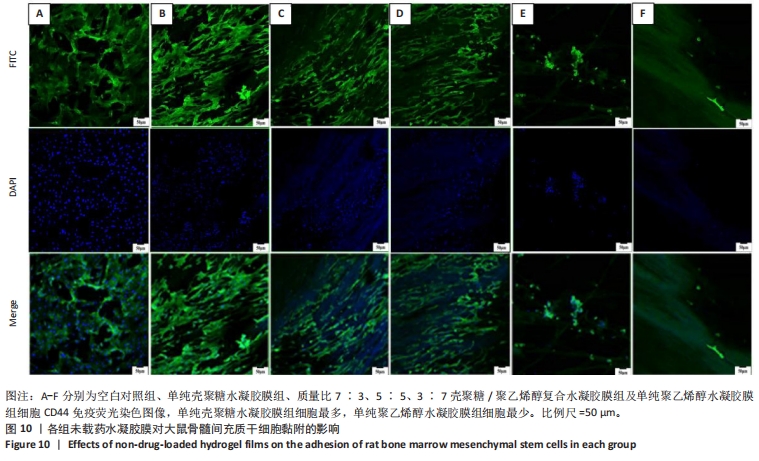
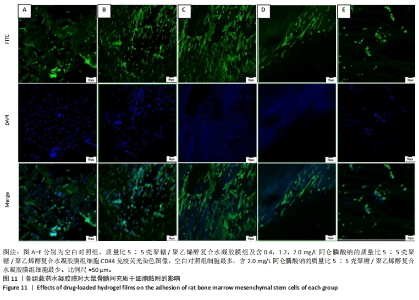
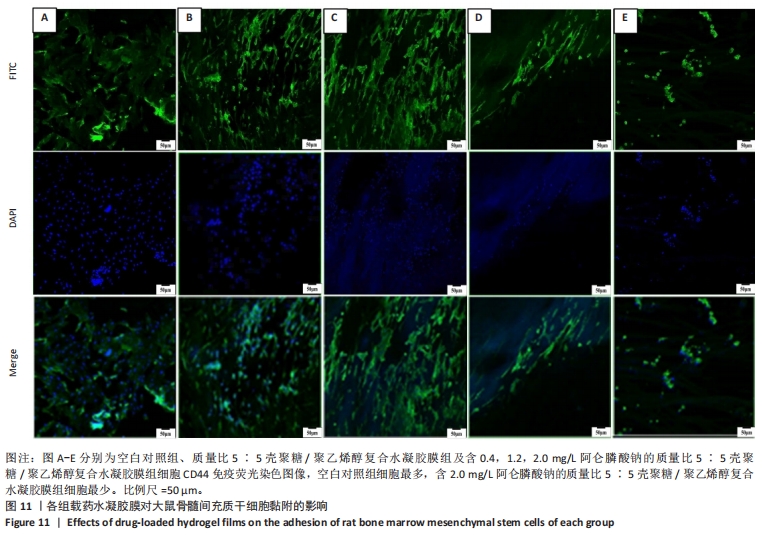
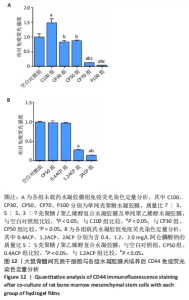
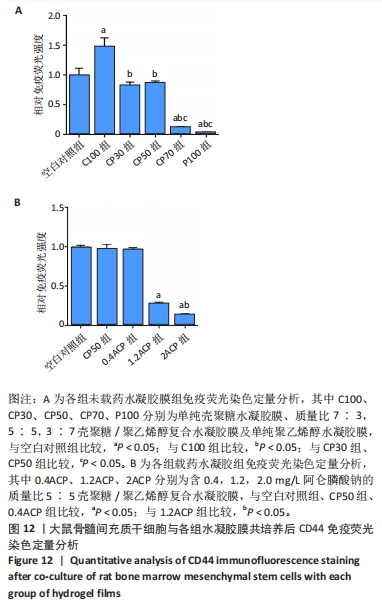
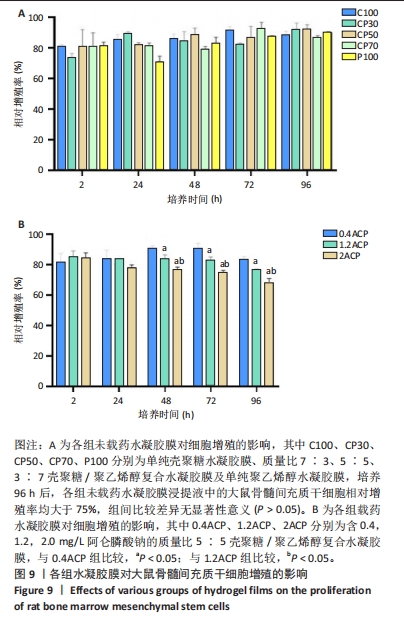
2.7 各组水凝胶膜对细胞增殖的影响 图9A显示了各组未载药水凝胶膜浸提液中大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的相对增殖率,结果显示:培养96 h后,各组未载药水凝胶膜浸提液中的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞相对增殖率均大于75%,组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。图9B显示了各组载药复合水凝胶膜浸提液中大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的相对增殖率,结果显示:0.4ACP组、1.2ACP组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的相对增殖率均大于75%;培养48,72,96 h,2ACP组细胞相对增殖率低于0.4ACP组、1.2ACP组(P < 0.05),1.2ACP组细胞相对增殖率低于0.4ACP组(P < 0.05),说明2ACP有轻度细胞毒性。"
| [1] D’AMBROSIO F, AMATO A, CHIACCHIO A, et al. Do Systemic Diseases and Medications Influence Dental Implant Osseointegration and Dental Implant Health? An Umbrella Review. Dent J (Basel). 2023; 11(6):146. [2] 金夏悦,顾迎新.骨质疏松对口腔种植修复影响的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2023,21(1):81-86. [3] KOCIJAN R, KLAUSHOFER K, MISOF BM. Osteoporosis Therapeutics 2020. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2020;262:397-422. [4] TAKAHATA M, SHIMIZU T, YAMADA S, et al. Bone biopsy findings in patients receiving long-term bisphosphonate therapy for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022;40(4): 613-622. [5] GOSSIEL F, PAGGIOSI MA, NAYLOR KE, et al. The effect of bisphosphosphonates on bone turnover and bone balance in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: The T-score bone marker approach in the TRIO study. Bone. 2020;131:115158. [6] RUGGIERO SL, DODSON TB, AGHALOO T, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons’ Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws—2022 Update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022; 80(5):920-943. [7] OTSURU M, FUJIKI Y, SOUTOME S, et al. Risk factors for dental findings of the development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Investigation of 3734 teeth in cancer patients receiving high dose antiresorptive agents. J Dent Sci. 2024;19(1):203-210. [8] OHBAYASHI Y, NAKAI F, IWASAKI A, et al. Symposium: Imaging modalities for drug-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (6), assessment of mandibular metabolism due to long-term administration of an anti-resorptive agent by bone scintigraphy (secondary publication). Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2019;55(1):51-57. [9] 鲍宏宇,吕冬梅,何芸,等.颌骨和股骨缺损模型大鼠注射唑来膦酸后骨坏死发生率的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(11): 1699-1704. [10] CUAIRAN C, CAMPBELL PM, KONTOGIORGOS E, et al. Local application of zoledronate enhances miniscrew implant stability in dogs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;145(6):737-749. [11] YING G, BO L, YANJUN J, et al. Effect of a local, one time, low-dose injection of zoledronic acid on titanium implant osseointegration in ovariectomized rats. Arch Med Sci. 2016;12(5):941-949. [12] PETROVIC Z, SARIC A, DESPOTOVIC I, et al. Surface Functionalisation of Dental Implants with a Composite Coating of Alendronate and Hydrolysed Collagen: DFT and EIS Studies. Materials (Basel). 2022; 15(15):5127. [13] ZHANG J, BAI H, BAI M, et al. Bisphosphonate-incorporated coatings for orthopedic implants functionalization. Mater Today Bio. 2023;22: 100737. [14] TAOKAEW S, KAEWKONG W, KRIANGKRAI W. Recent Development of Functional Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Gels. 2023;9(4):277. [15] ALMAJIDI YQ, GUPTA J, SHERI FS, et al. Advances in chitosan-based hydrogels for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: A comprehensive review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 6):127278. [16] NATHAN KG, GENASAN K, KAMARUL T. Polyvinyl Alcohol-Chitosan Scaffold for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Application: A Review. Mar Drugs. 2023;21(5):304. [17] NIU Y, WU J, KANG Y, et al. Recent advances of magnetic chitosan hydrogel: Preparation, properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;247:125722. [18] TIAN B, HUA S, TIAN Y, et al. Chemical and physical chitosan hydrogels as prospective carriers for drug delivery: a review. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(44):10050-10064. [19] KITASATO S, TANAKA T, CHAZONO M, et al. Local application of alendronate controls bone formation and beta-tricalcium phosphate resorption induced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(3):528-536. [20] RUMIAN L, WOLF-BRANDSTETTER C, ROSSLER S, et al. Sodium alendronate loaded poly(l-lactide- co-glycolide) microparticles immobilized on ceramic scaffolds for local treatment of bone defects. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(3):293-302. [21] 陈艳平,龙明立.UV法测定复方阿仑膦酸钠肠溶片中阿仑膦酸钠的含量[J].解放军药学学报,2008,24(2):171-173. [22] SIONKOWSKA A, SKOPINSKA-WISNIEWSKA J, PLANECKA A, et al. The influence of UV irradiation on the properties of chitosan films containing keratin. Polym Degrad Stab. 2010;95(12):2486-2491. [23] HOFFMAN AS. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:18-23. [24] MANTHA S, PILLAI S, KHAYAMBASHI P, et al. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials (Basel). 2019; 12(20):3323. [25] PEERS S, MONTEMBAULT A, LADAVIÈRE C. Chitosan hydrogels incorporating colloids for sustained drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;275:118689. [26] ISLAM MT, LAING RM, WILSON CA, et al. Fabrication and characterization of 3-dimensional electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/keratin/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;275: 118682. [27] ABU-SAIED MA, WYCISK R, ABBASSY MM, et al. Sulfated chitosan/PVA absorbent membrane for removal of copper and nickel ions from aqueous solutions-Fabrication and sorption studies. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;165:149-158. [28] BHATTARAI N, GUNN J, ZHANG M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(1):83-99. [29] ALI A, BANO S, POOJARY S, et al. Effect of cellulose nanocrystals on chitosan/PVA/nano beta-TCP composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering application. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022;33(1):1-19. [30] LIU L, WU D, TU H, et al. Applications of Hydrogels in Drug Delivery for Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases. Gels. 2023;9(2):146. [31] NARAYANASWAMY R, TORCHILIN VP. Hydrogels and Their Applications in Targeted Drug Delivery. Molecules. 2019;24(3):603. [32] XIA Y, MA Z, WU X, et al. Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Chitosan Hydrogels for Drug Delivery Systems. Macromol Biosci. 2024;24(5): e2300399. [33] ARYANI T, BUDIATIN AS, SAMIRAH, et al. The administration of bovine hydroxyapatite-alendronate implant accelerates bone defect healing in an osteoporotic rat. Technol Health Care. 2023;31(5):1747-1757. [34] SUN Y, ZHAO YQ, ZENG Q, et al. Dual-Functional Implants with Antibacterial and Osteointegration-Promoting Performances. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(40):36449-36457. [35] KANDAROVA H, POBIS P. The “Big Three” in biocompatibility testing of medical devices: implementation of alternatives to animal experimentation-are we there yet? Front Toxicol. 2023;5:1337468. [36] HU X, ZHANG L, YAN L, et al. Recent Advances in Polysaccharide-Based Physical Hydrogels and Their Potential Applications for Biomedical and Wastewater Treatment. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(9):e2200153. [37] ZHANG M, WANG G, ZHANG X, et al. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan and Polyvinyl Alcohol/Ag@MOF Bilayer Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(18):3151. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [4] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [5] | Wang Zilin, Mu Qiuju, Liu Hongjie, Shen Yuxue, Zhu Lili. Protective effects of platelet-rich plasma hydrogel on oxidative damage in L929 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 771-779. |
| [6] | Zhao Hongxia, Sun Zhengwei, Han Yang, Wu Xuechao , Han Jing. Osteogenic properties of platelet-rich fibrin combined with gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 809-817. |
| [7] | Zhao Zengbo, Li Chenxi, Dou Chenlei, Ma Na, Zhou Guanjun. Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/leonurine hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [8] | Dong Meilin, Du Haiyu, Liu Yuan. Quercetin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [9] |
Zhang Bo, Zhang Zhen, Jiang Dong.
Tannic acid modified interpenetrating network hydrogel promotes tissue remodeling of ruptured Achilles tendon after surgery#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 721-729.
|
| [10] | Zhang Yuhang, Zeng Yuning, Zeng Jindi, Lu Yixuan, Ye Hui, Ji Jianxin. Accuracy of modified implant template of assisted implantation in missing second molars [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 738-744. |
| [11] | Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277. |
| [12] | Yin Hang, Song Kui. Effect of crocin hydrogel on chondrocytes and MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7293-7300. |
| [13] | Wang Chen, Zhang Weinan, Shen Jining, Liu Fan, Yuan Jishan, Liu Yake. Inhibitory effect of ferroptosis inhibitor toxicity induced by cobalt nanoparticles through reactive oxygen species [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7310-7317. |
| [14] | Li Ruotong, Wu Yuening, Deng Yunyi, Chen Shichao, Lan Xiaorong, Li Shiting, Li Guangwen. Preparation and antibacterial evaluation of nanosilver-reduced graphene oxide/polydopamine/methacrylated gelatin@Gap19 hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7333-7343. |
| [15] | Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||