Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4430-4438.doi: 10.12307/2025.824
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of differences in vertebral cortical bone reinforcement on biomechanics of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Fang Wei1, Huang Xinghua1, Qu Bo2, Yang Hongsheng2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Yunyang County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing 404500, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610500, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Accepted:2024-08-26Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-05 -
Contact:Yang Hongsheng, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610500, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Fang Wei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Yunyang County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing 404500, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Wei, Huang Xinghua, Qu Bo, Yang Hongsheng. Effect of differences in vertebral cortical bone reinforcement on biomechanics of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4430-4438.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
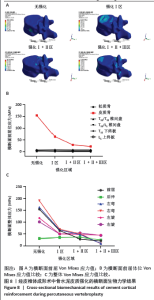
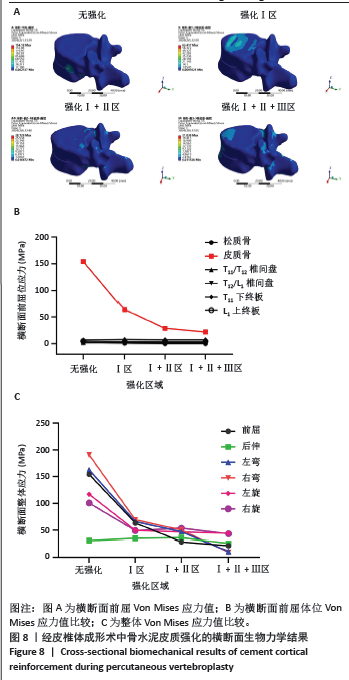
2.1 横断面生物力学结果 在垂直加压作用下,经皮椎体成形术中横断面骨水泥无皮质强化与骨水泥分别强化Ⅰ、Ⅰ+Ⅱ、Ⅰ+Ⅱ+Ⅲ骨皮质区域比较结果提示:在前屈时,随骨皮质强化程度增加,伤椎(T12)椎体皮质骨Von Mises应力值呈下降趋势,在未受皮质强化时为154.18 MPa;而完全强化下,降低为21.84 MPa,见图8A。类似的结果同样发生在左/右侧弯和左旋测试结果中。但随皮质强化程度加重,强化椎体相邻结构(包括T12椎体松质骨、T11/T12椎间盘、T12/L1椎间盘、T11下终板、L1上终板)所受Von Mises应力值变化不明显,即皮质强化后并未对相邻结构应力产生影响,见图8B。同时研究也发现,当人体右旋时,伤椎皮质骨Von Mises应力值整体呈下降趋势,骨水泥强化Ⅰ+Ⅱ区域较强化Ⅰ区Von Mises应力值略大。但皮质强化组Von Mises应力值明显小于无皮质强化组,且皮质强化整个横断面Ⅰ+Ⅱ+Ⅲ皮质区域时伤椎皮质骨Von Mises应力值最小,见图8C。"
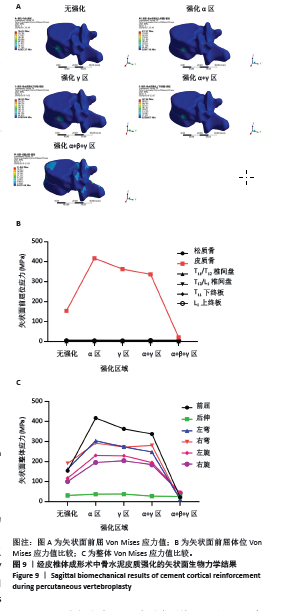
2.2 矢状面生物力学结果 在垂直压缩力作用下,经皮椎体成形术中矢状面骨水泥无皮质强化与骨水泥分别强化骨皮质α区域、强化γ区域、强化α+γ区域、强化α+β+γ皮质区域比较结果提示:在前屈时,随骨皮质纵向强化程度增加,T12椎体皮质骨Von Mises应力值呈下降趋势,但无皮质强化组较强化骨皮质α区域、强化γ区域、强化α+γ区域最大Von Mises应力值减小,较皮质强化α+β+γ皮质区域最大Von Mises应力值明显增大,其中无皮质强化时为154.188 MPa,强化骨皮质α区域时为417.27 MPa,而完全强化时降低为21.838 MPa,见图9A。类似的结果同样发生在左侧弯和左旋转测试结果中。但随皮质强化程度加重,在前屈、后伸、左/右侧弯和左/右轴向旋转不同体位变化下T12椎体松质骨、T11/T12椎间盘、T12/L1椎间盘、T11下终板、L1上终板最大Von Mises应力变化值并不明显,即皮质强化后并未对相邻结构应力产生影响,见图9B。同时研究也发现,当模拟人体右弯时,皮质强化α+γ区域较强化γ区域Von Mises应力值略大;右旋时,皮质α区域较强化γ区域Von Mises应力值略大。但皮质强化组Von Mises应力值整体呈下降趋势,相较强化其他区域组,皮质强化整个矢状面α+β+γ区域组伤椎皮质骨最大Von Mises应力值最小,见图9C。"
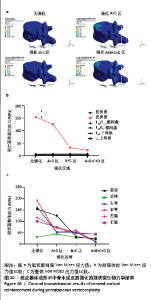
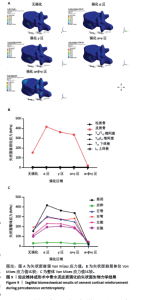
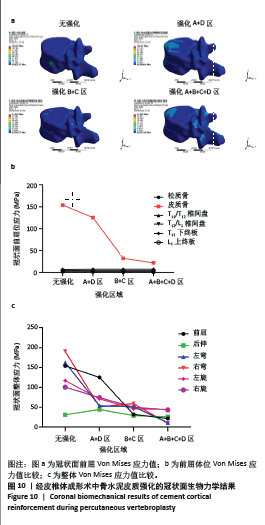
2.3 冠状面生物力学结果 在垂直压缩力作用下,经皮椎体成形术中冠状面骨水泥无皮质强化与骨水泥分别强化A+D区域、强化B+C区域、强化A+B+C+D区域,结果提示,在前屈时,随骨皮质横向强化程度变化,T12椎体皮质骨Von Mises应力值呈下降趋势,在无皮质强化时为154.18 MPa,而完全强化下降低为21.838 MPa,见图10a。类似的结果同样发生在左侧弯和左/右轴向旋转测试结果中。但随皮质强化程度变化,强化椎体的相邻结构(包括T12椎体松质骨、T11/T12椎间盘、T12/L1椎间盘、T11下终板、L1上终板)所受Von Mises应力值变化不明显,即皮质强化后并未对相邻结构应力产生影响,见图10b。同时研究也发现,当人体右弯时,骨水泥强化B+C区域较强化A+D区域Von Mises应力值略大,但伤椎皮质骨Von Mises应力值整体呈下降趋势,相较强化其他区域组,皮质强化整个冠状面A+B+C+D区域组伤椎皮质骨的最大Von Mises应力值最小,见图10c。"
| [1] GRIFFONI C, LUKASSEN JNM, BABBI L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective randomized comparison. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7):1614-1620. [2] 杨智奎,王一公,王德民,等.过伸悬吊复位与PVP协同作用于老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折临床效能分析[J].中国疗养医学, 2023,32(6):626-629. [3] YU H, LI Y, YAO X, et al. Application of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty in treating Kümmell’s patients with different stages and postural correction status. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2020; 17(4):357-364. [4] 田学林,国晓明. 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形术在高龄骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折中的应用效果[J]. 现代养生,2024,24(3):171-173. [5] 姚龚,沈忆新,李敏,等.骨水泥不同弥散方式对椎体成形术后生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2021,34(8):732-737. [6] 谢胜荣,董迎春,李杰,等.双侧分层穿刺与双侧非分层穿刺椎体成形术在治疗OVCF中椎内骨水泥分布及临床疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(4):265-269. [7] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):246-256. [8] CHEVALIER Y, PAHR D, CHARLEBOIS M, et al. Cement distribution, volume, and compliance in vertebroplasty: some answers from an anatomy-based nonlinear finite element study. Spine(Phila Pa1976). 2008;33(16):1722-1730. [9] 赵文韬,秦大平,张晓刚,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体强化术后不同椎体高度对相邻椎体应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(9):1141-114. [10] 蔡明,戚颖,刘肃,等. 骨水泥不同分布对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学影响:三维有限元分析[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2022,39(6):771-777. [11] GALBUSERA F, CASAROLI G, CHANDE R, et al. Biomechanics of sacropelvic fixation: a comprehensive finite element comparison of three techniques. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(2):295-305. [12] ZHOU QK, ZENG FH, TU JL, et al. Influence of cement-augmented pedicle screw instrumentation in an osteoporotic lumbosacral spine over the adjacent segments: a 3D finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):132. [13] 唐冲,吴四军,刘正,等.高黏度骨水泥在单侧经皮椎体成形术中的弥散分布特点[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(10):884-887. [14] 任海江.PVP术后椎体内骨水泥分布区域与疼痛缓解程度的相关性研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2018. [15] ZHOU C, LIAO Y, HUANG S, et al. Effect of cement distribution type on clinical outcome after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the aging population. Front Surg. 2022;9:975832. [16] 王德国,李洋,尹红灵,等. 椎体成形术填充剂最优化分布模式三维有限元分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2021,34(1):26-33. [17] KIM YY, RHYU KW. Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912. [18] XU K, LI YL, SONG F, et al. Influence of the distribution of bone cement along the fracture line on the curative effect of vertebral augmentation. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(9):4505-4513. [19] KIM JM, SHIN DA, BYUN DH, et al. Effect of bone cement volume and stiffness on occurrences of adjacent vertebral fractures after vertebroplasty. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012;52(5):435-440. [20] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):246-256. [21] 代皓文. 单双侧经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学比较[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2023. [22] 谢胜荣,董迎春,李杰,等. 双侧分层穿刺与双侧非分层穿刺椎体成形术在治疗OVCF中椎内骨水泥分布及临床疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(4):265-269. [23] 刘瑞祯,王望任,郝晨,等. 骨水泥分布对单侧穿刺经皮椎体成形治疗单节段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折后相邻椎体骨折的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(28):4498-4504. [24] 贺宝荣,许正伟,郝定均,等.骨水泥在骨质疏松性骨折椎体内分布状态与生物力学性能的关系[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(8):768-773. [25] 任海江.PVP术后椎体内骨水泥分布区域与疼痛缓解程度的相关性研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2018. [26] 麦麦提敏·阿卜力米提.PVP术后骨水泥分布对再发骨折的影响研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2023. [27] ZHANG L, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. Bone cement distribution in the vertebral body affects chances of recompression after percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:431-436. [28] TAN L, WEN B, GUO Z, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on the outcome of percutaneous Vertebroplasty: a case cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):541. [29] 应春宁,陈福宇,唐步顺.高粘度骨水泥弥散程度对绝经后骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后疗效的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2023,38(9):954-956. [30] 张圣飞,张亮,陶玉平.经皮椎体成形二次穿刺骨水泥注入治疗弥散不良的骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].吉林医学,2022,43(3):652-654. [31] ZHANG L, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. Bone cement distribution in the vertebral body affects chances of recompression after percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:431-436. [32] 王浩磊,赵丽.PVP术后骨水泥分布与伤椎再骨折的影响因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2021,42(2):241-243. [33] AN Z, CHEN C, WANG J, et al. Logistic regression analysis on risk factors of augmented vertebra recompression after percutaneous vertebral augmentation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):374. [34] WANG C, ZHANG X, LIU J, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty: Risk Factors for Recollapse of Cemented Vertebrae. World Neurosurg. 2019;130:e307-e315. [35] 冯世波,王蔚,张力,等. 骨水泥弥散、分布及渗漏对PKP术后伤椎再塌陷的影响[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(3):469-471. [36] 阿卜杜吾普尔·海比尔,阿里木江·玉素甫,麦麦提敏·阿卜力米提,等.经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥量和分布对手术椎体及邻近椎体再发骨折的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(10):1586-1591. [37] 张益山.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折PVP术后骨水泥的分布情况对临床预后的影响研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2023. [38] PAN Z, ZHOU Q, YANG M, et al. Effects of distribution of bone cement on clinical efficacy and secondary fracture after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Front Surg. 2023;9:1054995. [39] 李任,唐福宇.骨水泥分布对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折PVP术后邻椎骨折的影响分析[J].广西中医药大学学报,2023,26(6):31-34. [40] 冯世波,王蔚,张力,等.骨水泥弥散、分布及渗漏对PKP术后伤椎再塌陷的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(3):469-471. [41] 王雪峰,刘辉,丁少成.骨水泥分布模式对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折术后临床治疗效果[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2019,8(11):836-841. [42] LIU J, TANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in the Midthoracic Vertebrae (T5-8): A Retrospective Study of 101 Patients with 111 Fractured Segments. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:e1381-e1387. [43] 沈凯,张胜利,谭祖键,等. 经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中骨水泥单侧与双侧弥散对疗效的影响[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2018,34(6):527-533. [44] 刘夏君,王新虎,左春光,等. 骨水泥单侧与双侧分布对椎体后凸成形术疗效影响[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2015,18(2):141-145. [45] 李安明,史国号,王国柱,等. 椎体成形术对相邻椎体生物力学影响的有限元分析[J]. 重庆医学,2021,50(2):215-219. [46] 任亚楠.椎体强化术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学分析[D].天津:天津理工大学,2023. |
| [1] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [2] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [3] | Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002. |
| [4] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichuang, Yang Wen, Ding Guangjiang, Li Peikun, Xiao Zhongyu, Chen Ying, Fang Xue, Zhang Teng. Dispersion effect of bone cement after vertebroplasty using individualized unilateral external pedicle approach and bilateral pedicle approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 800-808. |
| [6] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [7] | Yu Qinghe, Cai Ziming, Wu Jintao, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Wang Yakun, Lin Xiaoqin, Lin Wenping. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation of endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6391-9397. |
| [8] | Zhuang Yan, Wang Xinyu, Cao Yilin, Ding Yuanxin, Wang Jiaqi, Yu Miao, Luan Chunyang, Ding Yuansheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of personalized orthodontic devices for 3D printed maxillary single-rooted rotated tooth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6409-6415. |
| [9] | Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Lu Ming. Repair strategies for nonunion in old osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a case analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 538-546. |
| [10] | Chen Hao, Wu Pigen, Teng Jiaqi, Zhang Liang, Feng Xinmin. Analysis of risk factors for lumbar fascial edema in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6174-6179. |
| [11] | Li Tangbo, Zhang Nan, Hao Guobing, Liu Kun, Qiao Lin, Zhu Zexing, Song Diyu. Bone cement injection during percutaneous curved vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the upper 1/3 of the vertebral body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5977-5984. |
| [12] | Wu Yonghao, Zhu Shuaiqi, Li Yuqiao, Zhang Chenfei, Xia Weiwei, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng. Correction effect of local kyphosis of the spine after percutaneous kyphoplasty in super-aging patients with vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5854-5861. |
| [13] | Ma Jikun, Wang Jianru, Qi Junjie, Liu Haifei. Mechanism by which diabetes exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5907-5913. |
| [14] | Pan Hongyu, Li Hongtao, Xiao Changming, Li Sen. Biomechanical analysis on treatment of different types of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with individualized precise puncture vertebral augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5773-5784. |
| [15] | Xia Zhaoxin, Gao Yichen, Deng Yuyao, Wang Xia, Lan Xiaorong, He Yun, Chen Junliang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of different material implants for replacing single missing anterior tooth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4687-4693. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||