Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1905-1912.doi: 10.12307/2025.141
Previous Articles Next Articles
Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis
Han Haihui1, 2, 3, Ran Lei1, 2, 3, Meng Xiaohui1, 2, 3, Xin Pengfei1, 2, 3, Xiang Zheng1, 2, 3, Bian Yanqin1, 2, 3, Shi Qi1, 2, 3, Xiao Lianbo1, 2, 3
- 1Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; 2Shanghai Guanghua Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; 3Institute of Arthritis Research of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China
-
Received:2024-01-12Accepted:2024-03-09Online:2025-03-28Published:2024-10-11 -
Contact:Xiao Lianbo, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; Shanghai Guanghua Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; Institute of Arthritis Research of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China -
About author:肖涟波,主任医师,博士生导师,上海中医药大学,上海市 201203;上海市光华中西医结合医院,上海市 200052;上海市中医药研究院中西医结合关节炎研究所,上海市 200052 -
Supported by:Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (General Project), No. 22ZR1453100 (to XLB); Key Specialized Project of Changning District Health Commission, No. 20231003 (to XLB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
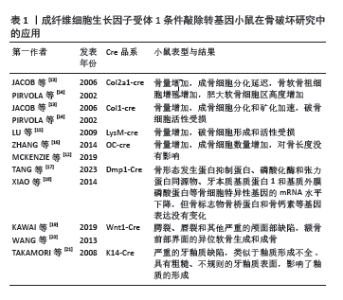
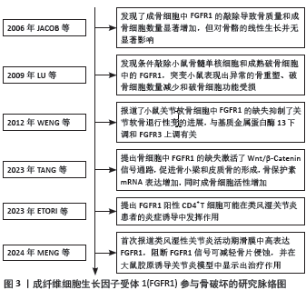
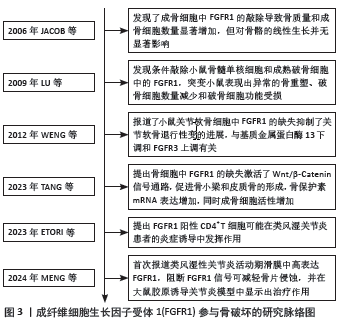
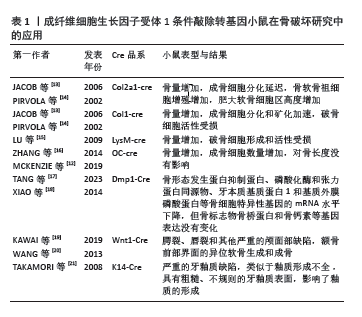
2.2 FGFR1参与类风湿关节炎病程进展 成纤维细胞生长因子受体是一种跨膜蛋白,由细胞外结构域、跨膜结构域和细胞内酪氨酸激酶结构域组成[8]。FGFR1属于成纤维细胞生长因子受体家族,FGFR1通过与配体结合诱导受体胞质尾部的酪氨酸残基发生磷酸化,进而触发受体的二聚化和随后的胞质酪氨酸激酶活化。激活的FGFR1可进一步调控多条细胞内信号传导途径,包括磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/AKT)途径、Ras/Raf-丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase,MEK)-丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinases,MAPKs)级联反应、蛋白激酶C-γ(protein kinase C-γ,PKC-γ)及信号转导和转录激活因子(signal transducers and activators of transcription,STATs)等,从而介导细胞增殖、分化、迁移和存活等多种生物学过程[9]。FGFR1抑制剂已用于治疗胆管癌和膀胱癌患者,但在类风湿关节炎中的作用尚未清楚。最新研究发现,类风湿关节炎活动期滑膜中高表达成纤维细胞生长因子10及FGFR1,阻断FGFR1信号通路可减轻体外骨片侵蚀,并在大鼠胶原诱导关节炎模型中显示出治疗作用[6]。此外,FGFR1还在骨膜、间充质细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞等细胞中广泛表达[9-10]。通过调控FGFR1信号靶向滑膜细胞、软骨细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞[11-12],可以影响关节炎中骨组织的重塑,靶向FGFR1信号通路可为复发类风湿关节炎患者提供新的治疗机会。FGFR1条件敲除转基因小鼠在骨破坏研究中的应用,见表1。"

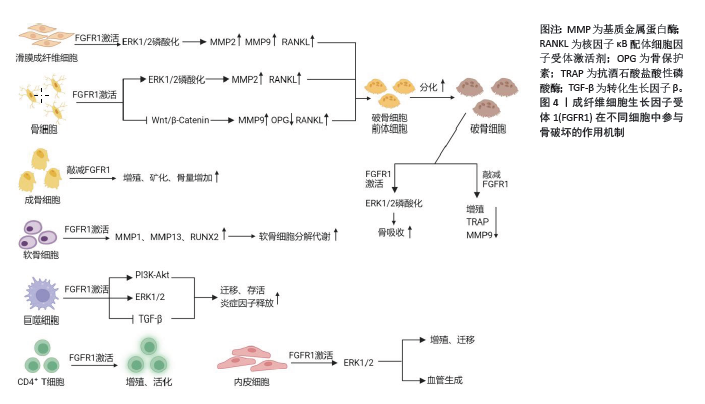
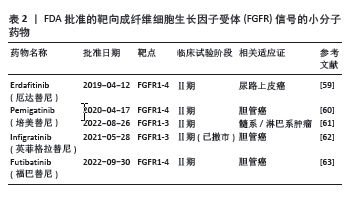
2.3 FGFR1参与骨破坏的作用机制 2.3.1 骨细胞中的FGFR1信号 类风湿关节炎骨破坏离不开骨组织的重塑及骨稳态的维持。骨组织中含有3种细胞,即骨细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞。成人骨中最丰富的细胞类型是骨细胞,它是终末分化的成骨细胞,控制着骨重塑。骨细胞调节成骨细胞分化和合成代谢活动以及破骨细胞活动,通过树突直接接触或分泌重要的调节因子,如硬化蛋白和NF-κB配体细胞因子受体激活剂 (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand,RANKL)[22]。 骨细胞是RANKL的主要来源之一,FGFR1在骨发育和骨稳态中起着重要作用。研究证实FGFR1活化后,可以通过促进ERK1/2的磷酸化,进而促进基质金属蛋白酶2和RANKL的表达[23-24]。缺乏FGFR1或同时缺乏FGFR1和FGFR2的小鼠在出生时表型正常;然而,这些小鼠(> 6周龄)成熟后会出现高骨量表型,骨膜附着增加,皮质内骨增加和紊乱,孔隙率增加,生物力学特性反映了骨量增加。虽然敲除特定的成纤维细胞生长因子受体可导致骨质量增加,但材料属性受损,这意味着虽然骨骼的总体质量(如密度和体积)可能增加,但这些骨骼在物理性能(如强度和韧性)上却不如正常骨骼。这些数据确定了FGFR1信号在成熟成骨细胞/成骨细胞中的作用,这直接或间接地说明FGFR1对成骨细胞的存活和在生后骨骼生长期间骨质量的调节是必需的[12]。骨细胞中FGFR1的缺失激活了Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路,促进骨小梁和皮质骨的形成,骨保护素mRNA表达增加,同时成骨细胞活性增加[17]。此外,骨细胞中FGFR1缺失导致破骨细胞形成减少,皮质骨和原代骨细胞中RANKL mRNA表达降低,骨吸收相关基因如基质金属蛋白酶9和组织蛋白酶K的mRNA表达减少,提示骨细胞中FGFR1丢失产生的信号抑制了破骨细胞的形成[17]。这些结果表明,FGFR1可能是预防骨丢失的潜在治疗靶点,靶向FGFR1预防骨质丢失值得深入研究。 2.3.2 成骨细胞中的FGFR1信号 成骨细胞是骨形成、骨骼发育与成长的重要细胞,这些细胞分泌细胞外基质蛋白,如Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素和碱性磷酸酶。成骨细胞的分化成熟可分为3个阶段:成骨前细胞、骨前体细胞和成骨细胞[25]。在小鼠和人类中进行的遗传学研究强调了FGFR1/2信号通路在控制成骨细胞基因表达和骨形成中的重要作用[26]。骨祖细胞中FGFR1的条件失活导致细胞增殖增加、分化延迟和基质矿化,而成骨细胞中FGFR1的缺失导致矿化增强和FGFR3的表达增加[13]。因此,有人提出FGFR1促进间充质祖细胞向成骨前细胞分化,但抑制间充质祖细胞的增殖以及成骨细胞的成熟和矿 化[13]。但在出生后生长的骨骼中,成熟成骨细胞和骨细胞中的FGFR1表达又是骨骼平衡和维持骨细胞活力所必需的。体内研究证实,FGFR1可以控制着不同成熟阶段的成骨细胞[13]。FGFR1和FGFR2在未成熟成骨细胞和成骨细胞中表达,体外培养的未成熟成骨细胞表达相对较高的FGFR1水平,而成熟成骨细胞表达相对较高的FGFR2水平[27]。通过采用特定的遗传操纵技术,即利用Ⅰ型胶原蛋白-Cre(Col1-Cre)和骨钙素Osteocalcin-Cre(OC-Cre)系统,实现了成熟成骨细胞特异性的FGFR1基因敲除。实验结果表明,成熟成骨细胞中FGFR1的敲除导致骨质量和成骨细胞数量显著增加,这反映了骨代谢活动的增强和骨形成能力的提升。然而,这种遗传操纵对于骨骼的线性生长并无显著影响,表明FGFR1在成骨细胞中的作用主要与骨质量的调控相关,而非骨骼长度的增长[13,16]。与之相反的是,另一项研究利用牙本质基质蛋白1-Cre(Dmp1-Cre)系统在小鼠骨细胞中敲除FGFR1后,FGFR1 mRNA表达下降了50%,成纤维生长因子23、骨形态发生蛋白抑制蛋白、磷酸化酶和张力蛋白同源物、牙本质基质蛋白1和基质外膜磷酸蛋白等骨细胞特异性基因的mRNA表达下降,但骨标志物骨桥蛋白和骨钙素等基因表达没有变化;此外,小鼠的骨结构如骨体积、骨质量等参数没有变化,骨组织学也没有差异[18]。LEE等[28]研究表明,成纤维细胞生长因子受体抑制剂多维替尼通过增加成骨细胞靶基因的表达来增强体外成骨细胞的分化。一项研究表明,成骨细胞中FGFR1的激活还导致成年小鼠成纤维细胞生长因子23的分泌增加,抑制磷酸盐重吸收[29]。根据这些研究,FGFR1在维持骨骼平衡和骨细胞活力中发挥了作用,一方面促进早期成骨细胞的成熟,另一方面抑制了成熟成骨细胞矿化,从而促进骨代谢、抑制骨形成。 2.3.3 破骨细胞中的FGFR1信号 破骨细胞是一种大的多核细胞,主要功能是骨吸收。这些细胞起源于造血谱系,并通过巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL的相互作用分化为成熟的破骨细胞。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子促进破骨细胞前体的增殖,而RANKL促进破骨细胞前体向成熟破骨细胞的分化[25]。FGFR1对破骨细胞的分化和功能具有重要作用。早期研究表明,激活FGFR1和MAPK直接作用于成熟破骨细胞以刺激骨吸收[30]。在分离的小鼠破骨细胞上检测到FGFR1的表达[31]。此外,在骨折部位附近的破骨细胞中也检测到FGFR1的表达[32]。为了探讨FGFR1对破骨细胞的直接影响,LU等[15]条件性地敲除了小鼠骨髓单核细胞和成熟破骨细胞中的FGFR1,突变小鼠表现出异常的骨重塑、破骨细胞数量减少和破骨细胞功能受损,抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达降低。FGFR1的缺失降低了小鼠破骨细胞的数量和活性,表明FGFR1对破骨细胞有积极调控作用。FGFR1对于小鼠破骨细胞的完全分化和激活是不可或缺的。进一步研究发现,FGFR1可以通过增强ERK1/2通路直接促进破骨细胞的分化和活化,从而增强它们分解骨质的能力[15]。AUKES等[33]研究结果表明,在破骨细胞和乳腺癌细胞共培养环境中,FGFR抑制剂BGJ398降低了FGFR介导的信号通路的激活,降低了破骨细胞靶基因的表达。这些结果表明,FGFR1通过直接或间接的方式促进了破骨细胞的分化和 成熟。 2.3.4 软骨细胞中的FGFR1信号 FGF信号通路在骨和软骨发育中起着关键作用[34]。FGFR1和FGFR3是软骨中主要表达的FGFR。在生长板形成过程中,FGFR1主要在肥厚前区和肥厚区表达,FGFR3主要在增殖区和肥厚前区表达[35]。FGFR3在软骨细胞中的表达抑制细胞增殖,而FGFR1在肥大软骨细胞中的表达促进终末成熟[13,36]。为了确定维持关节软骨是否需要FGFR1信号,条件敲除8周龄小鼠软骨细胞中的FGFR1基因,老化至18个月后,野生型对照组小鼠的颞下颌关节表面出现自发性退化,而条件性基因敲除小鼠则受到保护[37]。然而,FGFR信号在关节软骨软骨细胞中的作用研究较少。据报道,FGFR1和FGFR3主要在人关节软骨细胞中表达[38],FGFR1介导分解代谢活性,而FGFR3介导软骨细胞的合成代谢活性[39]。 激活FGFR1能够上调成人关节软骨细胞中基质金属蛋白酶1和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达促进基质降解[40]。而成年小鼠关节软骨细胞中FGFR1的缺失抑制了关节软骨退行性变的进展,这与基质金属蛋白酶13下调和FGFR3上调有关[40]。FGFR1信号通路对软骨细胞分解代谢作用的分子机制仍然不明确。Runt相关转录因子2是一个众所周知的转录因子,通过促进细胞外基质降解酶的表达和软骨细胞肥大,在软骨稳态中发挥关键作用,从而加速骨关节炎的发展[41]。ZHOU等[42]表明FGFR1信号通过上调Runt相关转录因子2的表达正向调控膜内骨形成。P250R突变的FGFR1促进了Runt相关转录因子2在体内的表达。此外,FGFR1缺失降低了Runt相关转录因子2在体内和体外的表达来保护颞下颌关节软骨免受变性[43]。其他文献也报道了针对FGFR1信号调控的研究。经过白细胞介素1β处理上调了大鼠软骨细胞中FGFR3的表达,而下调了FGFR1的表达。FGF18可以上调大鼠软骨细胞中FGFR3的表达,下调FGFR1的表达[44]。 DELUCCHI等[45]从胎鼠中提取胫骨,将这些胫骨置于体外培养系统中,构建了胎鼠胫骨外植体的体外模型,用于研究骨骼生长、发育和疾病。对胫骨外植体中FGFRs的表达分析显示,糖皮质激素下调了FGFR1的表达,而FGFR3则显著上调[45]。FGFR1的突变改变了软骨内成骨,生长板中FGFR1特异性敲除后,观察到生长板的肥厚区面积扩大[35]。FGFR1在人骨关节炎软骨细胞中增加,会导致软骨破坏[38],而敲除FGFR1后可以减轻手术引起的膝关节不稳小鼠软骨破坏的发展[40]。与之相反的是,FGFR3在人骨关节炎软骨细胞中增加,则会促进软骨的合成[46],FGFR3缺失加速了小鼠骨关节炎发生[39,47]。因此,FGFR1的激活可能促进了软骨细胞的分解代谢,FGFR1缺失对软骨的退变具有保护作用。 2.3.5 巨噬细胞中的FGFR1信号 FGFR1能够在人类单核巨噬细胞中表达[48],并通过下游信号通路如PI3K-Akt和MEK1/2-ERK1/2影响肿瘤巨噬细胞的迁移和生存。FGFR1的激活能够促进巨噬细胞的迁移和聚集,间接促进细胞微环境的炎症反应产生[49]。此外,FGFR1还能够直接影响高脂饮食引起的巨噬细胞极化并增加炎症细胞因子水平。具体来说,巨噬细胞表面的FGFR1受到多种生长因子的刺激,激活下游通路,包括ERK、PI3K/AKT和STAT3,进而刺激多种炎症递质的产生和释放,从而加剧炎症反应。特异性敲低巨噬细胞中FGFR1能够减少促炎细胞因子表达[50]。另一项研究也表明,FGFR1活化会导致巨噬细胞中转化生长因子β基因表达下调,从而减弱TGF-β/Smad3信号通路活性[51],而TGF-β/Smad3通路在调控炎症反应中起抑制作用,其下调会导致炎性细胞因子和趋化因子表达上调。总之,巨噬细胞上FGFR1的活化,一方面能够影响巨噬细胞的迁移和生存,另一方面能够加剧巨噬细胞的炎症反应。 2.3.6 滑膜成纤维细胞中的FGFR1信号 成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞在类风湿关节炎的病理生理中扮演关键角色,成为调控关节稳态及类风湿关节炎病理进程的核心细胞群[52]。 在正常生理状况下,成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞负责合成关节润滑剂和透明质酸,以维持关节腔内环境的稳定[53]。然而,在关节炎症条件下,成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞向促炎和组织破坏性表型转化,引发软骨和骨质的退行性改变[54-55]。特别是,这些破坏性成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞过度表达基质金属蛋白酶,促进软骨的分解,并表达NF-κB配体,激活破骨细胞的成熟与功能,从而加剧骨破坏[56-57]。鉴于成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞在类风湿关节炎中的作用,其作为治疗靶点的潜力已引起广泛关注。通过对活动期和缓解期类风湿关节炎患者膝关节滑膜细胞进行单细胞测序,发现FGFR1通路在活动期类风湿关节炎的衬里层成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞中被高度激活[6]。通过建立血管翳细胞骨片侵蚀实验系统,利用人重组FGF10蛋白及FGFR1抑制剂进行体外干预活动期类风湿关节炎血管翳细胞,验证了FGF10/FGFR1信号通路对血管翳细胞骨片侵蚀能力的潜在作用[6]。体内实验证明阻断FGFR1信号通路可以明显减轻胶原诱导关节炎大鼠关节炎症、滑膜侵蚀及关节破坏[6]。尽管美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)至今尚未批准任何直接针对成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的治疗方法[58],但目前已有4种FGFR1小分子抑制剂被FDA批准并进入临床试验阶段,见表2,这也为靶向滑膜成纤维细胞FGFR1的药物研究提供了参考。目前已证明了FGFR1活化与类风湿关节炎疾病活动相关,FGFR1的激活促进了滑膜成纤维细胞的迁移、侵袭,并最终导致了骨侵蚀的进展,但其直接或间接发挥作用仍然需要进一步验证。 2.3.7 T细胞中的FGFR1信号 新确诊的类风湿关节炎患者经甲氨蝶呤治疗后,CD4+ T细胞中FGFR1表达显著下 调[64]。ZHAO等[65]描述了FGFR1阳性T细胞产生白细胞介素2,并在激活后促进细胞增殖。一些研究已经确定成纤维细胞生长因子浓度与类风湿关节炎疾病活性之间存在正相关[66-68],但FGFR1阳性T细胞的作用仍不清楚。最新研究通过对活动期和缓解期类风湿关节炎患者滑膜组织细胞进行筛选,发现了活动期表达FGFR1阳性的CD4+T细胞亚群[69-70]。在产生干扰素γ的CD4+T细胞中,FGFR1阳性CD4+T细胞高于FGFR1阴性CD4+T细胞[69]。然而遗憾的是,在FGFR1阳性的CD4+T细胞中,产生促炎因子白细胞介素17A的细胞比例没有增加。尽管FGFR1的表达不足以获得促炎特性,但FGFR1阳性细胞可能在类风湿关节炎患者的炎症诱导中发挥作用[69]。FGFR1可能以直接或间接的方式促进T细胞炎症反应还需要更多的研究去论证。 2.3.8 血管内皮细胞中的FGFR1信号 血管生成在维持和促进类风湿关节炎进展中发挥了重要作用[71]。研究表明,血管生成素、低氧诱导因子、血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等在抑制类风湿关节炎滑膜血管生成中发挥重要作用,提示靶向血管生成可能是治疗类风湿关节炎疾病的有效治疗方法[72-73]。这些生长因子与受体结合导致血管内皮细胞变形、分裂、迁移和增殖,诱导新生血管;此外,滑膜组织血管增生进一步刺激血管内物质外渗,加重滑膜炎症和滑膜血管的形成[74]。靶向FGFR1能够抑制血管生成在肿瘤治疗的研究中已经得到证明[75-77]。在类风湿关节炎新生血管形成过程中,许多促血管生成因子,包括血管内皮生长因子和鞘氨醇-1-磷酸,可诱导血管内皮细胞的异常激活,促进血管生成[78]。研究表明,激活的FGFR1上调血管内皮生长因子A表达[79]。另一项研究则表明,促进血管内皮生长因子A表达和分泌能够介导FGFR1激活诱导血管生成[80]。降低FGFR1的蛋白水平会影响内皮细胞的功能,特别是在血管生成过程中[81]。此外,FGFR1的活化是通过激活MAPK信号通路促进内皮细胞的增殖和迁移[82]。目前,尚未有研究将FGFR1与类风湿关节炎的血管生成和骨破坏联系起来。因此,研究FGFR1在抑制类风湿关节炎滑膜血管化中的作用,为针对类风湿关节炎血管化的治疗以及改善类风湿关节炎骨破坏提供了可能性。 FGFR1在不同细胞中参与骨破坏的作用机制,见图4。"
| [1] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ RBM, BERGSTRA SA, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):3-18. [2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, BARTON A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001. [3] WINTHROP KL, WEINBLATT ME, CROW MK, et al. Unmet need in rheumatology: reports from the Targeted Therapies meeting 2018. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(7):872-878. [4] VISSER H, LE CESSIE S, VOS K, et al. How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: a prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(2):357-365. [5] FINZEL S, RECH J, SCHMIDT S, et al. Repair of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors is based on bone apposition at the base of the erosion. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(9):1587-1593. [6] MENG X, CHEN Z, LI T, et al. Role and Therapeutic Potential for Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor 10/FGFR1 in Relapsed Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024;76(1):32-47. [7] SCHETT G, TANAKA Y, ISAACS JD. Why remission is not enough: underlying disease mechanisms in RA that prevent cure. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(3):135-144. [8] ORNITZ DM, ITOH N. New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022;14(4):e1549. [9] XIE Y, SU N, YANG J, et al. FGF/FGFR signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):181. [10] ORNITZ DM. FGF signaling in the developing endochondral skeleton. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16(2):205-213. [11] TAN Q, CHEN B, WANG Q, et al. A novel FGFR1-binding peptide attenuates the degeneration of articular cartilage in adult mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(12):1733-1743. [12] MCKENZIE J, SMITH C, KARUPPAIAH K, et al. Osteocyte Death and Bone Overgrowth in Mice Lacking Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors 1 and 2 in Mature Osteoblasts and Osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(9):1660-1675. [13] JACOB AL, SMITH C, PARTANEN J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling in the osteo-chondrogenic cell lineage regulates sequential steps of osteoblast maturation. Dev Biol. 2006;296(2):315-328. [14] PIRVOLA U, YLIKOSKI J, TROKOVIC R, et al. FGFR1 is required for the development of the auditory sensory epithelium. Neuron. 2002;35(4): 671-680. [15] LU X, SU N, YANG J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulates the differentiation and activation of osteoclasts through Erk1/2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390(3):494-499. [16] ZHANG Y, SU N, LUO F, et al. Deletion of Fgfr1 in osteoblasts enhances mobilization of EPCs into peripheral blood in a mouse endotoxemia model. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(9):1064-1071. [17] TANG Y, YANG P, JIN M, et al. Fgfr1 deficiency in osteocytes leads to increased bone mass by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone. 2023;174:116817. [18] XIAO Z, HUANG J, CAO L, et al. Osteocyte-specific deletion of Fgfr1 suppresses FGF23. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104154. [19] KAWAI M, HERRMANN D, FUCHS A, et al. Fgfr1 conditional-knockout in neural crest cells induces heterotopic chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in mouse frontal bones. Med Mol Morphol. 2019;52(3):156-163. [20] WANG C, CHANG JY, YANG C, et al. Type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor in cranial neural crest cell-derived mesenchyme is required for palatogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(30):22174-22183. [21] TAKAMORI K, HOSOKAWA R, XU X, et al. Epithelial fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulates enamel formation. J Dent Res. 2008;87(3): 238-243. [22] COMPTON JT, LEE FY. A review of osteocyte function and the emerging importance of sclerostin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(19):1659-1668. [23] WANG K, JI W, YU Y, et al. FGFR1-ERK1/2-SOX2 axis promotes cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis in FGFR1-amplified lung cancer. Oncogene. 2018;37(39):5340-5354. [24] CHEN LC, SHIBU MA, LIU CJ, et al. ERK1/2 mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced upregulation of FGF-2, uPA, MMP-2, MMP-9 and cellular migration in cardiac fibroblasts. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;306:62-69. [25] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711. [26] WILKIE AO. Bad bones, absent smell, selfish testes: the pleiotropic consequences of human FGF receptor mutations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16(2):187-203. [27] RICE DP, RICE R, THESLEFF I. Fgfr mRNA isoforms in craniofacial bone development. Bone. 2003;33(1):14-27. [28] LEE Y, BAE KJ, CHON HJ, et al. A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Dovitinib (TKI-258), Enhances BMP-2-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation In Vitro. Mol Cells. 2016;39(5):389-394. [29] WU AL, FENG B, CHEN MZ, et al. Antibody-mediated activation of FGFR1 induces FGF23 production and hypophosphatemia. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57322. [30] KAWAGUCHI H, CHIKAZU D, NAKAMURA K, et al. Direct and indirect actions of fibroblast growth factor 2 on osteoclastic bone resorption in cultures. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(3):466-473. [31] CHIKAZU D, HAKEDA Y, OGATA N, et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 directly stimulates mature osteoclast function through activation of FGF receptor 1 and p42/p44 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(40): 31444-31450. [32] NAKAJIMA A, NAKAJIMA F, SHIMIZU S, et al. Spatial and temporal gene expression for fibroblast growth factor type I receptor (FGFR1) during fracture healing in the rat. Bone. 2001;29(5):458-466. [33] AUKES K, FORSMAN C, BRADY NJ, et al. Breast cancer cell-derived fibroblast growth factors enhance osteoclast activity and contribute to the formation of metastatic lesions. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0185736. [34] ORNITZ DM, ITOH N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2015;4(3):215-266. [35] KAROLAK MR, YANG X, ELEFTERIOU F. FGFR1 signaling in hypertrophic chondrocytes is attenuated by the Ras-GAP neurofibromin during endochondral bone formation. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(9):2552-2564. [36] TUZON CT, RIGUEUR D, MERRILL AE. Nuclear Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Skeletal Development and Disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(3):138-146. [37] WANG Z, HUANG Y, HE Y, et al. Myocardial protection by heparin-based coacervate of FGF10. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(7):1867-1877. [38] YAN D, CHEN D, COOL SM, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is principally responsible for fibroblast growth factor 2-induced catabolic activities in human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(4):R130. [39] TANG J, SU N, ZHOU S, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3 Inhibits Osteoarthritis Progression in the Knee Joints of Adult Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(10):2432-2443. [40] WENG T, YI L, HUANG J, et al. Genetic inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in knee cartilage attenuates the degeneration of articular cartilage in adult mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(12):3982-3992. [41] SHEN J, LI J, WANG B, et al. Deletion of the transforming growth factor β receptor type II gene in articular chondrocytes leads to a progressive osteoarthritis-like phenotype in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(12):3107-3119. [42] ZHOU YX, XU X, CHEN L, et al. A Pro250Arg substitution in mouse Fgfr1 causes increased expression of Cbfa1 and premature fusion of calvarial sutures. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9(13):2001-2008. [43] WANG Z, HUANG J, ZHOU S, et al. Loss of Fgfr1 in chondrocytes inhibits osteoarthritis by promoting autophagic activity in temporomandibular joint. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(23):8761-8774. [44] YAO X, ZHANG J, JING X, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 18 exerts anti-osteoarthritic effects through PI3K-AKT signaling and mitochondrial fusion and fission. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:314-324. [45] DELUCCHI Á, TORO L, ALZAMORA R, et al. Glucocorticoids Decrease Longitudinal Bone Growth in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients by Stimulating the FGF23/FGFR3 Signaling Pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(10):1851-1861. [46] DAVIDSON D, BLANC A, FILION D, et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 18 signals through FGF receptor 3 to promote chondrogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(21):20509-20515. [47] VALVERDE-FRANCO G, BINETTE JS, LI W, et al. Defects in articular cartilage metabolism and early arthritis in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(11):1783-1792. [48] TAKASE N, KOMA Y, URAKAWA N, et al. NCAM- and FGF-2-mediated FGFR1 signaling in the tumor microenvironment of esophageal cancer regulates the survival and migration of tumor-associated macrophages and cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;380(1):47-58. [49] REED JR, STONE MD, BEADNELL TC, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 activation in mammary tumor cells promotes macrophage recruitment in a CX3CL1-dependent manner. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45877. [50] ZHAO YN, LIU ZD, YAN T, et al. Macrophage-specific FGFR1 deletion alleviates high-fat-diet-induced liver inflammation by inhibiting the MAPKs/TNF pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024;45(5):988-1001. [51] BOHRER LR, SCHWERTFEGER KL. Macrophages promote fibroblast growth factor receptor-driven tumor cell migration and invasion in a CXCR2-dependent manner. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10(10):1294-1305. [52] DAVIDSON S, COLES M, THOMAS T, et al. Fibroblasts as immune regulators in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(11):704-717. [53] MARSH LJ, KEMBLE S, REIS NISA P, et al. Fibroblast pathology in inflammatory joint disease. Immunol Rev. 2021;302(1):163-183. [54] BUCKLEY CD, OSPELT C, GAY S, et al. Author Correction: Location, location, location: how the tissue microenvironment affects inflammation in RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(4):246. [55] KOMATSU N, TAKAYANAGI H. Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis - immune cell-fibroblast-bone interactions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(7):415-429. [56] DANKS L, KOMATSU N, GUERRINI MM, et al. RANKL expressed on synovial fibroblasts is primarily responsible for bone erosions during joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):1187-1195. [57] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010;233(1):233-255. [58] NYGAARD G, FIRESTEIN GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(6):316-333. [59] SIEFKER-RADTKE AO, NECCHI A, PARK SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: long-term follow-up of a phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(2):248-258. [60] ABOU-ALFA GK, SAHAI V, HOLLEBECQUE A, et al. Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(5):671-684. [61] GOTLIB J, KILADJIAN J, VANNUCCHI A, et al. A Phase 2 Study of Pemigatinib (FIGHT-203; INCB054828) in Patients with Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms (MLNs) with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1) Rearrangement (MLN FGFR1). Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):385. [62] JAVLE MM, ROYCHOWDHURY S, KELLEY RK, et al. Final results from a phase II study of infigratinib (BGJ398), an FGFR-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with previously treated advanced cholangiocarcinoma harboring an FGFR2 gene fusion or rearrangement. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(3_suppl):265. [63] GOYAL L, MERIC-BERNSTAM F, HOLLEBECQUE A, et al. Futibatinib for FGFR2-Rearranged Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(3):228-239. [64] SHODA J, TANAKA S, ETORI K, et al. Semaphorin 3G exacerbates joint inflammation through the accumulation and proliferation of macrophages in the synovium. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):134. [65] ZHAO XM, BYRD VM, MCKEEHAN WL, et al. Costimulation of human CD4+ T cells by fibroblast growth factor-1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor). J Immunol. 1995;155(8):3904-3911. [66] MANABE N, ODA H, NAKAMURA K, et al. Involvement of fibroblast growth factor-2 in joint destruction of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999;38(8):714-720. [67] SATO H, KAZAMA JJ, MURASAWA A, et al. Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Intern Med. 2016;55(2):121-126. [68] GOULD PW, ZEMEL BS, TARATUTA EG, et al. Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Associations With Disease Characteristics, Body Composition, and Physical Functioning. J Rheumatol. 2021;48(4):504-512. [69] ETORI K, TANAKA S, TAMURA J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 as a potential marker of terminal effector peripheral T helper cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(11):3763-3769. [70] BYRD V, ZHAO XM, MCKEEHAN WL, et al. Expression and functional expansion of fibroblast growth factor receptor T cells in rheumatoid synovium and peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(6):914-922. [71] BALOGH E, BINIECKA M, FEARON U, et al. Angiogenesis in Inflammatory Arthritis. Isr Med Assoc J. 2019;21(5):345-352. [72] LEBLOND A, ALLANORE Y, AVOUAC J. Targeting synovial neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2017; 16(6):594-601. [73] WANG Y, WU H, DENG R. Angiogenesis as a potential treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;910:174500. [74] ZHANG YF, GAO SS, LI JL, et al. Comparison and correlation study of synovial ultrasound indices and serum VEGF in rheumatoid wrist arthritis before and after treatment. Clin Rheumatol. 2022;41(9): 2677-2683. [75] LEE C, CHEN R, SUN G, et al. VEGF-B prevents excessive angiogenesis by inhibiting FGF2/FGFR1 pathway. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):305. [76] ZHU X, QIU C, WANG Y, et al. FGFR1 SUMOylation coordinates endothelial angiogenic signaling in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(26):e2202631119. [77] TAN Q, WANG Z, WANG Q, et al. A novel FGFR1-binding peptide exhibits anti-tumor effect on lung cancer by inhibiting proliferation and angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(10):1389-1398. [78] WANG Y, WU H, GUI BJ, et al. Geniposide alleviates VEGF-induced angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGFR2/PKC/ERK1/2-mediated SphK1 translocation. Phytomedicine. 2022;100:154068. [79] WU Q, HAN L, GUI W, et al. MiR-503 suppresses fibroblast activation and myofibroblast differentiation by targeting VEGFA and FGFR1 in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(24): 14339-14348. [80] GAO M, LI X, YANG M, et al. TNFAIP3 mediates FGFR1 activation-induced breast cancer angiogenesis by promoting VEGFA expression and secretion. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022;24(12):2453-2465. [81] OBERKERSCH RE, PONTARIN G, ASTONE M, et al. Aspartate metabolism in endothelial cells activates the mTORC1 pathway to initiate translation during angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 2022;57(10):1241-1256.e8. [82] NOURSE MB, ROLLE MW, PABON LM, et al. Selective control of endothelial cell proliferation with a synthetic dimerizer of FGF receptor-1. Lab Invest. 2007;87(8):828-835. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [5] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [6] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [7] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [8] | Lang Mecuo, Zhang Yilin, Wang Li. MiR-338-3p affects proliferation and apoptosis of alveolar bone osteoblasts by targeting receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 899-907. |
| [9] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [10] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [11] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [12] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [13] | Wang Tao, Wang Shunpu, Min Youjiang, Wang Min, Li Le, Zhang Chen, Xiao Weiping. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis: data analysis in European populations based on GWAS data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7663-7668. |
| [14] | Lu Xiuli, Xu Huazhen, Chen Yuxing, Yao Nan, Hu Zixuan, Huang Dane. Mechanism of Jiangu Formula in treating osteoporosis based on osteoclast-osteoblast coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6828-6835. |
| [15] | Zhu Jiaping, Gao Bo, Lou Chunbiao, Yang Fengyong, Yang Kun. Monomeric traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: regulation of T cell balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6955-6962. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||