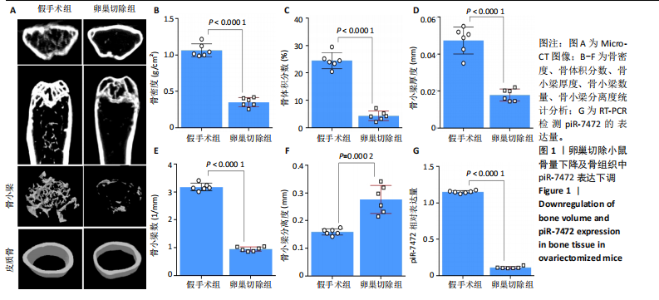
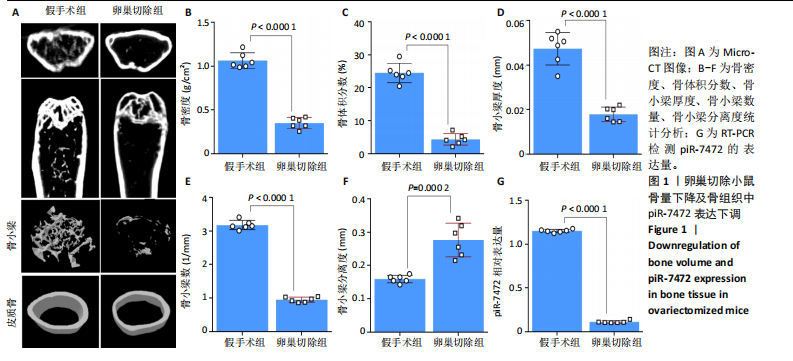
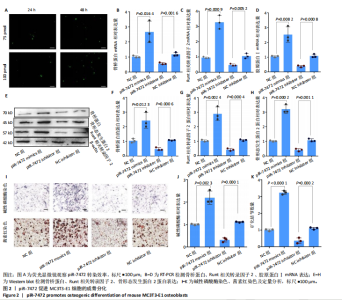
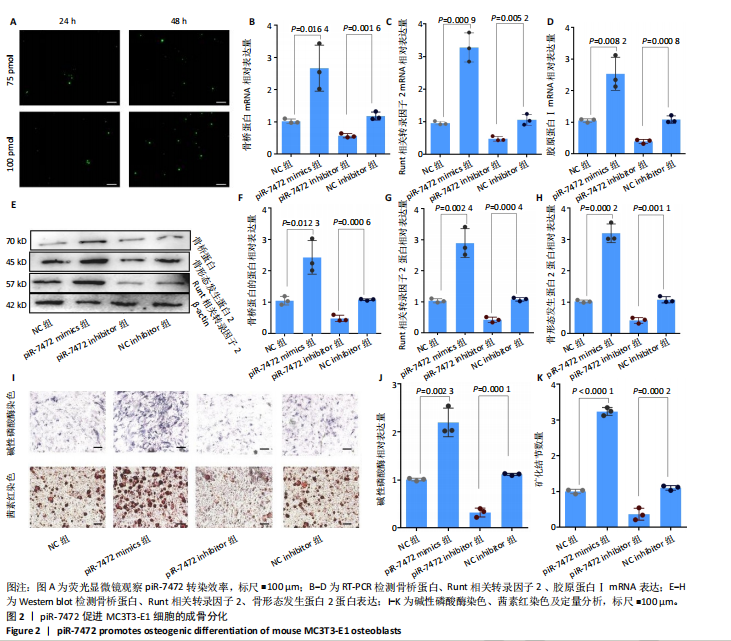
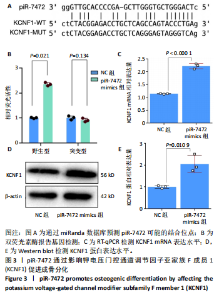
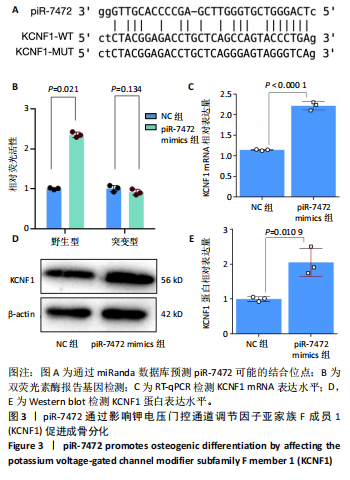
[1] 《中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2023)》工作组,中国老年学和老年医学学会骨质疏松分会,中国医疗保健国际交流促进会骨质疏松病学分会,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2023)[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(10):865-885.
[2] BAUTISTA LITARDO N, LÓPEZ GAVILANEZ E. First Ecuadorian consensus statement on the management of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2023;18(1):106.
[3] LIU YY, DING YF, SUI HJ, et al. Pilose antler (Cervus elaphus Linnaeus) polysaccharide and polypeptide extract inhibits bone resorption in high turnover type osteoporosis by stimulating the MAKP and MMP-9 signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;304:116052.
[4] HE X, WANG Y, LIU Z, et al. Osteoporosis treatment using stem cell-derived exosomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):72.
[5] LI N, CORNELISSEN D, SILVERMAN S, et al. An Updated Systematic Review of Cost-Effectiveness Analyses of Drugs for Osteoporosis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39(2):181-209.
[6] GARCÍA-GARCÍA P, REYES R, ÉVORA C, et al. Osteoprotective effect of the marine alkaloid norzoanthamine on an osteoporosis model in ovariectomized rat. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;147:112631.
[7] CHEN J, ZHONG K, QIN S, et al. Astragalin: a food-origin flavonoid with therapeutic effect for multiple diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14:1265960.
[8] HUANG X, WONG G. An old weapon with a new function: PIWI-interacting RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl Neurodegener. 2021;10(1):9.
[9] LEE EJ, BANERJEE S, ZHOU H, et al. Identification of piRNAs in the central nervous system. RNA. 2011;17(6):1090-1099.
[10] GALTON R, FEJES-TOTH K, BRONNER ME. Co-option of the piRNA pathway to regulate neural crest specification. Sci Adv. 2022;8(32): eabn1441.
[11] BRENNECKE J, ARAVIN AA, STARK A, et al. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;128(6):1089-1103.
[12] JONES BC, WOOD JG, CHANG C, et al. A somatic piRNA pathway in the Drosophila fat body ensures metabolic homeostasis and normal lifespan. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13856.
[13] KAMMINGA LM, LUTEIJN MJ, DEN BROEDER MJ, et al. Hen1 is required for oocyte development and piRNA stability in zebrafish. EMBO J. 2010;29(21):3688-3700.
[14] MOORE RS, KALETSKY R, MURPHY CT. Piwi/PRG-1 Argonaute and TGF-β Mediate Transgenerational Learned Pathogenic Avoidance. Cell. 2019;177(7):1827-1841.e12.
[15] GONG S, GACCIOLI F, DOPIERALA J, et al. The RNA landscape of the human placenta in health and disease. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2639.
[16] OZATA DM, GAINETDINOV I, ZOCH A, et al. PIWI-interacting RNAs: small RNAs with big functions. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(2):89-108.
[17] ISHIZU H, SIOMI H, SIOMI MC. Biology of PIWI-interacting RNAs: new insights into biogenesis and function inside and outside of germlines. Genes Dev. 2012;26(21):2361-2373.
[18] WANG X, RAMAT A, SIMONELIG M, et al. Emerging roles and functional mechanisms of PIWI-interacting RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023; 24(2):123-141.
[19] HAN H, FAN G, SONG S, et al. piRNA-30473 contributes to tumorigenesis and poor prognosis by regulating m6A RNA methylation in DLBCL. Blood. 2021;137(12):1603-1614.
[20] GAO XQ, ZHANG YH, LIU F, et al. The piRNA CHAPIR regulates cardiac hypertrophy by controlling METTL3-dependent N6-methyladenosine methylation of Parp10 mRNA. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(11):1319-1331.
[21] NILSSON KH, HENNING P, EL SHAHAWY M, et al. Osteocyte- and late osteoblast-derived NOTUM reduces cortical bone mass in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021;320(5):E967-E975.
[22] LEE WC, GUNTUR AR, LONG F, et al. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2017;38(3):255-266.
[23] MAI D, ZHENG Y, GUO H, et al. Serum piRNA-54265 is a New Biomarker for early detection and clinical surveillance of Human Colorectal Cancer. Theranostics. 2020;10(19):8468-8478.
[24] HAN YN, LI Y, XIA SQ, et al. PIWI Proteins and PIWI-Interacting RNA: Emerging Roles in Cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(1):1-20.
[25] PLEŠTILOVÁ L, NEIDHART M, RUSSO G, et al. Expression and Regulation of PIWIL-Proteins and PIWI-Interacting RNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0166920.
[26] LIU Y, DOU M, SONG X, et al. The emerging role of the piRNA/piwi complex in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):123.
[27] FENG J, YANG M, WEI Q, et al. Novel evidence for oncogenic piRNA-823 as a promising prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(16):9028-9040.
[28] DELLA BELLA E, MENZEL U, BASOLI V, et al. Differential Regulation of circRNA, miRNA, and piRNA during Early Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(2):398.
[29] MANNING D, SANTANA LF. Regulating voltage-gated ion channels with nanobodies. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7557.
[30] YANG JE, SONG MS, SHEN Y, et al. The Role of KV7.3 in Regulating Osteoblast Maturation and Mineralization. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17(3):407.
[31] WU J, ZHONG D, FU X, et al. Silencing of Ether à go-go 1 by shRNA inhibits osteosarcoma growth and cell cycle progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5570-5581.
[32] WU X, ZHONG D, GAO Q, et al. MicroRNA-34a inhibits human osteosarcoma proliferation by downregulating ether à go-go 1 expression. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10(6):676-682. |