Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2536-2543.doi: 10.12307/2025.324
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-obesity effect of insulin-like growth factor 1 in naturally aging mice
Zhu Peng1, 2, Li Yingyu1, 2, Lu Xiaoqian1, 2, Wu Qiong1, 2
- 1Guangxi Universities Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Biopharmaceutical Technology (Guangxi Normal University), Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2College of Life Sciences, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-01-23Accepted:2024-04-03Online:2025-04-28Published:2024-09-10 -
Contact:Wu Qiong, PhD, Professor, Guangxi Universities Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Biopharmaceutical Technology (Guangxi Normal University), Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; College of Life Sciences, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhu Peng, Master candidate, Guangxi Universities Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Biopharmaceutical Technology (Guangxi Normal University), Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; College of Life Sciences, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32160170 (to WQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Peng, Li Yingyu, Lu Xiaoqian, Wu Qiong. Anti-obesity effect of insulin-like growth factor 1 in naturally aging mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2536-2543.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
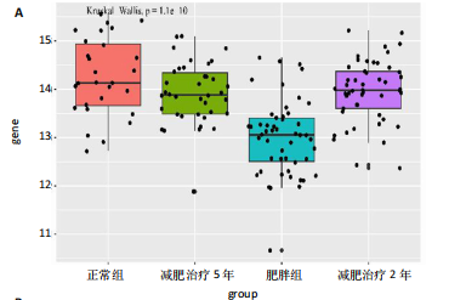
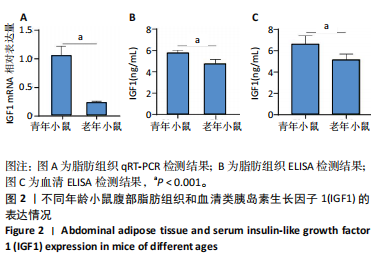
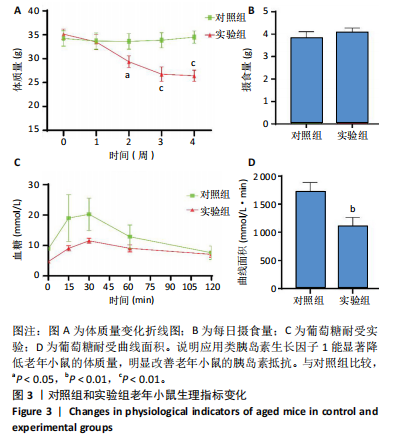
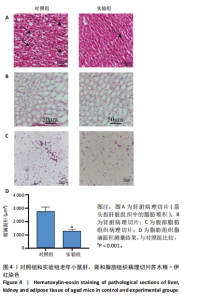
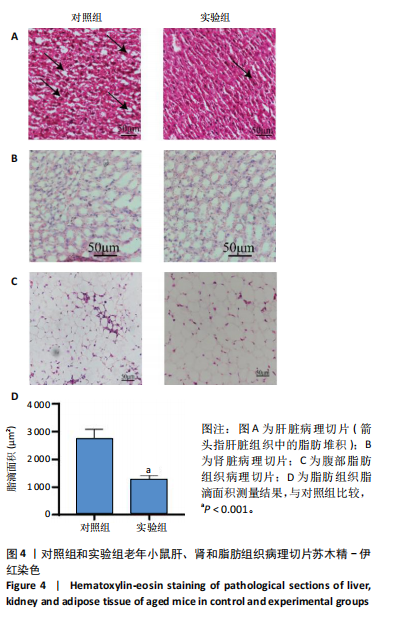
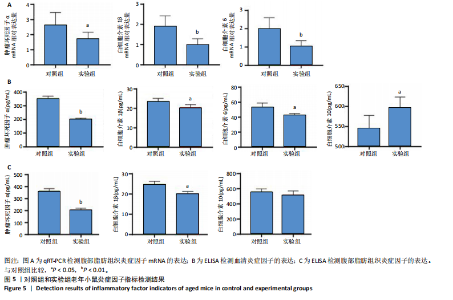
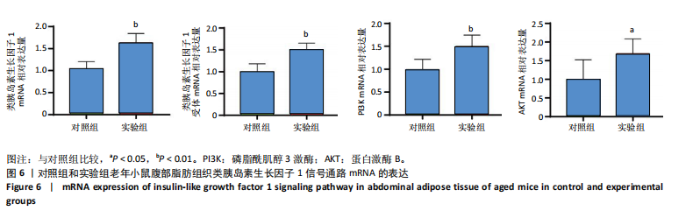
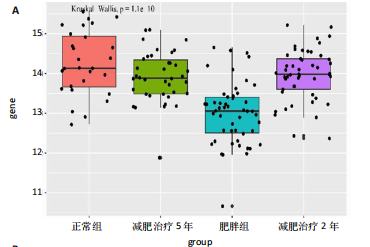
2.1 生信分析类胰岛素生长因子1表达情况 ①通过GEO数据库中样本为人脂肪组织的测序分析,结果如图1A所示,肥胖组中的类胰岛素生长因子1表达显著降低,但在减肥手术后类胰岛素生长因子1的表达回升。②对青年小鼠脂肪干细胞和老年小鼠脂肪干细胞进行了转录组学测序,结果如图1B所示,发现老年脂肪干细胞低表达类胰岛素生长因子1。因此推测类胰岛素生长因子1可能对于衰老和肥胖具有重要作用。 2.2 动物实验验证结果 2.2.1 实验动物数量分析 ①实验选用2月龄小鼠6只,20月龄小鼠6只进行ELISA和qRT-PCR检测;②选用20月龄C57BL/6J小鼠12只,分为2组,实验过程中无小鼠死亡、脱失等情况发生,进入结果分析12只。 2.2.2 小鼠类胰岛素生长因子1表达 为了验证上述生信分析结果,采用qRT-PCR和ELISA检测了青年和老年小鼠腹部脂肪组织和血清类胰岛素生长因子1的表达情况。①qRT-PCR检测小鼠腹部脂肪组织,结果如图2A所示,发现老年小鼠低表达类胰岛素生长因子1 mRNA。②ELISA检测小鼠腹部脂肪组织,结果如图2B所示,同样发现老年小鼠低表达类胰岛素生长因子1。③ELISA检测小鼠血清,结果如图2C所示,依然发现老年小鼠低表达类胰岛素生长因子1。这个结果与上述生信分析结果一致,据此推测类胰岛素生长因子1可能对治疗老年小鼠的肥胖体征具有一定的作用。 2.2.3 小鼠体质量与摄食量 为了探究类胰岛素生长因子1对于老年小鼠的具体作用,分别对老年、青年小鼠注射类胰岛素生长因子1蛋白或同等剂量的PBS,定期监测小鼠体质量变化及摄食量。①小鼠体质量变化如图3A所示,从第2周开始,实验组小鼠的体质量与对照组相比有显著性的变化(P < 0.05),实验结束时,实验组小鼠平均减少体质量7 g,结果表明注射类胰岛素生长因子1蛋白能显著降低老年小鼠体质量。②小鼠摄食量情况如图3B所示,结果表明注射类胰岛素生长因子1蛋白对小鼠摄食量无影响。③连续注射4周类胰岛素生长因子1蛋白后,小鼠的葡萄糖耐受结果如图3C所示,曲线面积如图3D所示,结果发现注射类胰岛素生长因子1有效降低了小鼠的初始血糖,且曲线面积与对照组相比显著降低,说明类胰岛素生长因子1能够改善老年小鼠的胰岛素抵抗。 2.2.4 小鼠肝、肾和脂肪组织病理学观察 ①对照组和实验组小鼠的肝脏病理学切片如图4A所示,在对照组中发现老年小鼠肝脏具有脂肪堆积的情况,注射类胰岛素生长因子1蛋白后,显著改善了这种脂肪堆积。②对照组与实验组肾脏病理学切片如图4B所示,通过观察发现,对照组小鼠肾脏病理学切片与实验组小鼠肾脏病理学切片相比无明显差异。③对照组小鼠与实验组小鼠腹部脂肪组织病理学切片如图4C所示,通过Image J软件对脂滴大小面积进行测量,测量结果如图4D所示,发现实验组小鼠脂滴大小显著减小,说明类胰岛素生长因子1可能是通过减小脂肪组织脂滴大小来减轻体质量的。 2.2.5 小鼠炎症因子检测结果 ①小鼠腹部脂肪组织qRT-PCR检测结果如图5A所示,发现类胰岛素生长因子1能显著降低脂肪组织炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6 mRNA的表达水平。②小鼠血清炎症因子的检测结果如图5B所示,发现类胰岛素生长因子1能显著降低小鼠体内炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6的表达水平,显著增加白细胞介素10的表达水平。③小鼠腹部脂肪组织ELISA检测结果如图5C所示,发现类胰岛素生长因子1能显著降低脂肪组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素β的表达水平。这些结果表明,类胰岛素生长因子1能改善老年小鼠体内炎症状况,但具体机制需进一步探究。 2.2.6 小鼠脂肪组织PI3K-AKT信号通路表达情况 为了探究类胰岛素生长因子1的作用机制,采用qRT-PCR检测了小鼠腹部脂肪组织PI3K-AKT信号通路mRNA的表达,如图6所示。结果表明,与对照组相比,类胰岛素生长因子1显著提升了腹部脂肪组织PI3K-AKT信号通路的表达,提示类胰岛素生长因子1可能是通过类胰岛素生长因子1信号通路对老年小鼠发挥相关作用的。"
| [1] LIU C, WONG PY, CHUNG YL, et al. Deciphering the “obesity paradox” in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis of sarcopenic obesity. Obes Rev. 2023;24(2):e13534. [2] COMPSTON JE, WATTS NB, CHAPURLAT R, et al. Obesity is not protective against fracture in postmenopausal women: GLOW . Am J Med. 2011;124(11):1043-50. [3] SCOTT D, DALY RM, SANDERS KM, et al. Fall and Fracture Risk in Sarcopenia and Dynapenia With and Without Obesity: the Role of Lifestyle Interventions. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13(4):235-244. [4] SHAPSES SA, POP LC, WANG Y. Obesity is a concern for bone health with aging. Nutr Res. 2017;39:1-13. [5] SCOTT D, SEIBEL M, CUMMING R, et al. Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Temporal Associations With Changes in Bone Mineral Density, Incident Falls, and Fractures in Older Men: The Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project.J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(3):575-583. [6] CRUDDEN C, GIRNITA A, GIRNITA L. Targeting the IGF-1R: The Tale of the Tortoise and the Hare. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015;6:64. [7] SIMPSON A, PETNGA W, MACAULAY VM, et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Pathway Targeting in Cancer: Role of the IGF Axis and Opportunities for Future Combination Studies. Target Oncol. 2017; 12(5):571-597. [8] SCOTLANDI K, PICCI P. Targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in sarcomas. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20(4):419-427. [9] SINAI-LIVNE T, PASMANIK-CHOR M, COHEN Z, et al. Proteomic analysis of combined IGF1 receptor targeted therapy and chemotherapy identifies signatures associated with survival in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2020;11(17):1515-1530. [10] WERNER H. The IGF1 Signaling Pathway: From Basic Concepts to Therapeutic Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14882. [11] WU Q, HE S, ZHU Y, et al. Antiobesity Effects of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells in a Naturally Aged Mouse Model. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021;29(1):133-142. [12] CHEN YC, TSAI YJ, WANG CC, et al. Decisive gene strategy on osteoporosis: a comprehensive whole-literature-based approach for conclusive candidate gene targets. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(8): 3484-3528. [13] SOHOULI MH, BANIASADI M, NABAVIZADEH R, et al. Trends in insulin-like growth factor-1 levels after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2022;46(5):891-900. [14] SABZIKARIAN M, MAHMOUDI T, TABAEIAN SP, et al. The common variant of rs6214 in insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF1) gene: a potential protective factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023;129(1):10-15. [15] CHEN HT, CHUNG YC, CHEN YJ, et al. Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, and IGF-1 in the Elderly with Sarcopenic Obesity. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(4):827-832. [16] REA F, SAVARé L, VALSASSINA V, et al. Adherence to antidiabetic drug therapy and reduction of fatal events in elderly frail patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):53. [17] MYAKOTNYKH VS. [The diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease the representatives of elderly and senile age.]Adv Gerontol. 2019;32(1-2): 112-120.
[18] PTOK U, PAPASSOTIROPOULOS A, MAIER W, et al. Advanced parental age: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease or depression in the elderly? Int Psychogeriatr. 2000;12(4):445-451. [19] PENCINA KM, VALDERRABANO R, WIPPER B, et al. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Augmentation in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Physiologic Study. Clin J Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108(8):1968-1980. [20] WATERS DL, AGUIRRE L, GURNEY B, et al. Effect of Aerobic or Resistance Exercise, or Both, on Intermuscular and Visceral Fat and Physical and Metabolic Function in Older Adults With Obesity While Dieting.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022;77(1):131-139. [21] KAPLAN A, ZELICHA H, YASKOLKA MEIR A, et al. The effect of a high-polyphenol Mediterranean diet (Green-MED) combined with physical activity on age-related brain atrophy: the Dietary Intervention Randomized Controlled Trial Polyphenols Unprocessed Study (DIRECT PLUS) . Am J Clin Nutr. 2022;115(5):1270-1281. [22] OSTROWSKA L, GIER D, ZYŚK B. The Influence of Reducing Diets on Changes in Thyroid Parameters in Women Suffering from Obesity and Hashimoto’s Disease. Nutrients. 2021;13(3):862. [23] BARNER C, PETERSSON M, EDéN ENGSTRöM B, et al. Effects on insulin sensitivity and body composition of combination therapy with GH and IGF1 in GH deficient adults with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;167(5):697-703. [24] SAWICKA AK, HARTMANE D, LIPINSKA P, et al. l-Carnitine Supplementation in Older Women. A Pilot Study on Aging Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function. Nutrients. 2018;10(2):255. [25] KOEGELENBERG AS, SCHUTTE R, SMITH W, et al. Bioavailable IGF-1 and its Relation to the Metabolic Syndrome in a Bi-Ethnic Population of Men and Women. Horm Metab Res. 2016;48(2):130-136. [26] HERNDON DN, HAWKINS HK, NGUYEN TT, et al. Characterization of growth hormone enhanced donor site healing in patients with large cutaneous burns. Ann Surg. 1995;221(6):649-656; discussion 656-659. [27] MIHĂESCU GF, OLINESCU RM, GRIGORESCU A. Is IGF-1 involved in the regulatory modifications of cholesterolemia following the administration of embryonary peptides? Rom J Intern Med. 2006; 44(4):443-453. [28] SHAH K, STUFFLEBAM A, HILTON TN, et al. Diet and exercise interventions reduce intrahepatic fat content and improve insulin sensitivity in obese older adults. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17(12): 2162-2168. [29] DESPEGHEL M, REICHEL T, ZANDER J, et al. Effects of a 6 Week Low-Dose Combined Resistance and Endurance Training on T Cells and Systemic Inflammation in the Elderly. Cells. 2021;10(4):843. [30] DORIA P LS, MOSCOVITZ T, TCHERNIAKOVSKY M, et al. Association of IGF-1 CA(n) and IGFBP3 rs2854746 Polymorphisms with Endometrial Polyp Risk. Biomed Res Int. 2018:2018:8704346. [31] STANLEY TL, FOURMAN LT, ZHENG I, et al. Relationship of IGF-1 and IGF-Binding Proteins to Disease Severity and Glycemia in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(2):e520-e533. [32] ARCIDIACONO D, ZARAMELLA A, FABRIS F, et al. Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Is Downregulated in Barrett’s Esophagus Patients Undergoing a Moderate Calorie and Protein Restriction Program: A Randomized 2-Year Trial. Nutrients. 2021;13(10):3638. [33] VAN BUNDEREN CC, MEIJER R I, LIPS P, et al. Titrating Growth Hormone Dose to High-Normal IGF-1 Levels Has Beneficial Effects on Body Fat Distribution and Microcirculatory Function Despite Causing Insulin Resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:619173. [34] KOLEVZON A, BREEN MS, SIPER PM, et al. Clinical trial of insulin-like growth factor-1 in Phelan-McDermid syndrome. Mol Autism. 2022; 13(1):17. [35] ZHAO H, HUANG R, JIANG M, et al. Myocardial Tissue-Level Characteristics of Adults With Metabolically Healthy Obesity.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023;16(7):889-901. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [3] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [4] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [5] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [6] | Yu Hui, Yang Yang, Wei Ting, Li Wenli, Luo Wenqian, Liu Bin. Gadd45b alleviates white matter damage in chronic ischemic rats by modulating astrocyte phenotype [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7797-7803. |
| [7] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [8] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [9] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [10] |
Li Zhipeng, Xing Rongxin, Hu Lianghong.
Roles of SOX5 in bone metabolism and prevention of bone diseases and the relationship with exercise#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7589-7600.
|
| [11] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [12] | Pan Chun, Fan Zhencheng, Hong Runyang, Shi Yujie, Chen Hao. Effect and mechanism of polystyrene microplastics on prostate in male mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7353-7361. |
| [13] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [14] | Li Jing, Lu Guangqi, Zhuang Minghui, Cui Ying, Yu Zhangjingze, Sun Xinyue, Ma Mingming, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie. Development of a clinical prediction model for cervical instability in young and middle-aged adults based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7203-7210. |
| [15] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||