Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 1609-1617.doi: 10.12307/2025.341
Previous Articles Next Articles
miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
Li Jun1, Gong Jingjing1, Sun Guobin1, Guo Rui1, Ding Yang1, Qiang Lijuan1, Zhang Xiaoli1, Fang Zhanhai2
- 1Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, 2Department of Neurosurgery, People’s Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (Ningxia Medical University Affiliated Autonomous Region People’s Hospital), Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-01-10Accepted:2024-04-03Online:2025-03-18Published:2024-07-05 -
Contact:Fang Zhanhai, Associate professor, Department of Neurosurgery, People’s Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (Ningxia Medical University Affiliated Autonomous Region People’s Hospital), Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Jun, Chief physician, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, People’s Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (Ningxia Medical University Affiliated Autonomous Region People’s Hospital), Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2023AAC03456 (to GR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
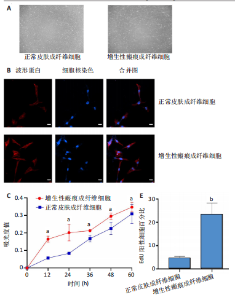
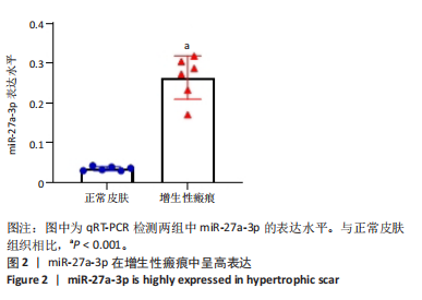
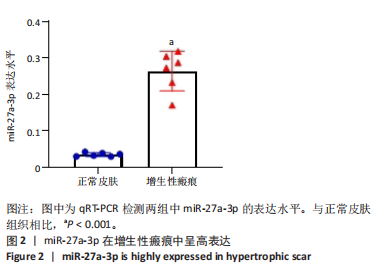
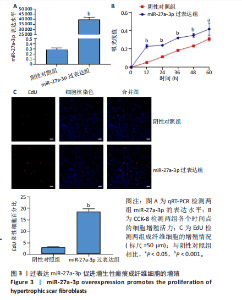
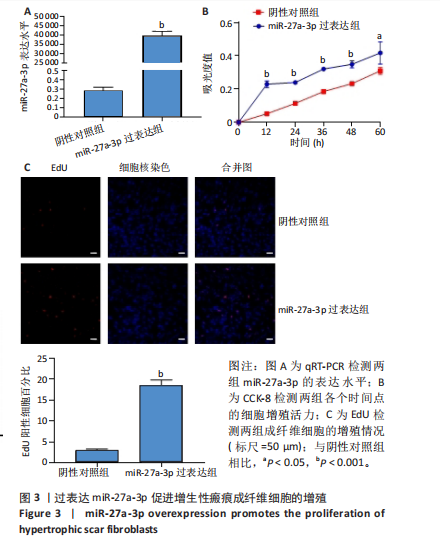
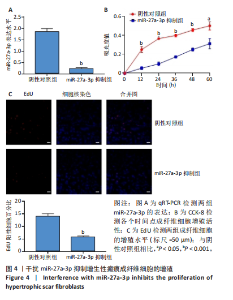
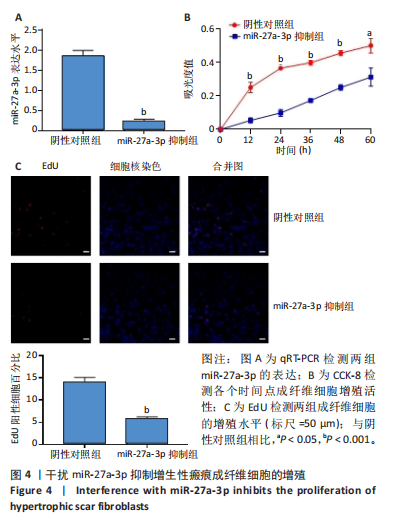
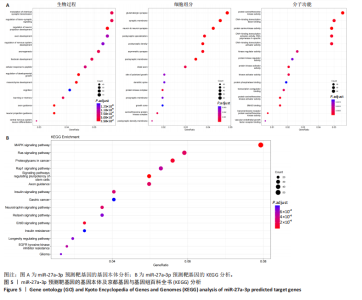
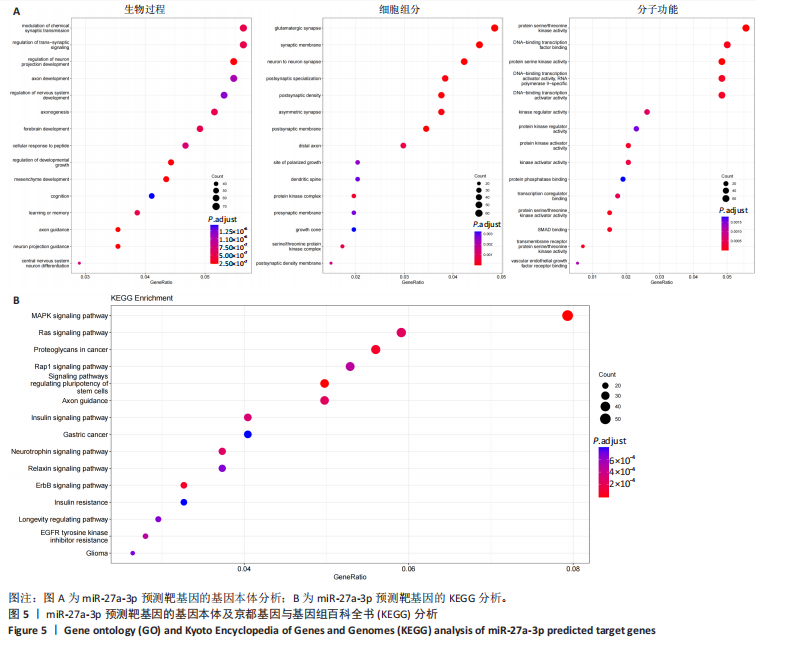
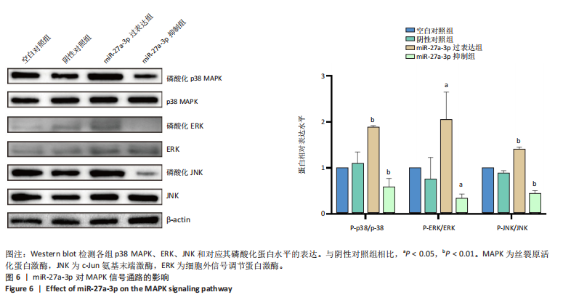
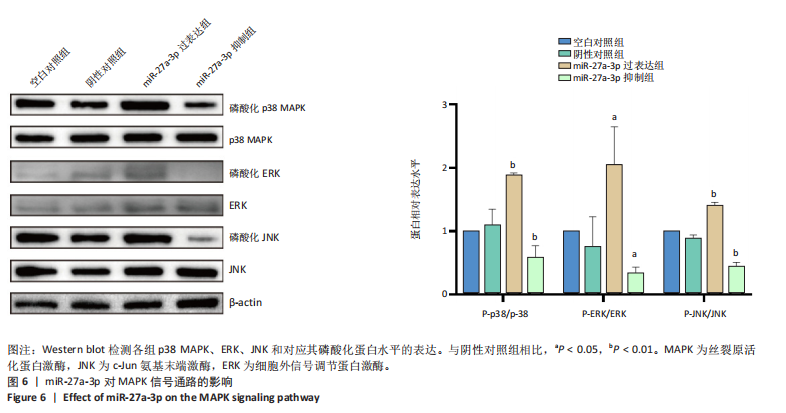
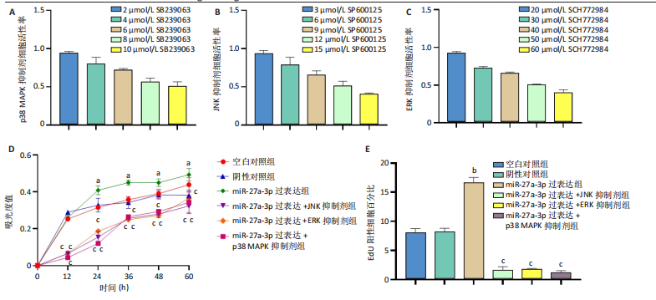
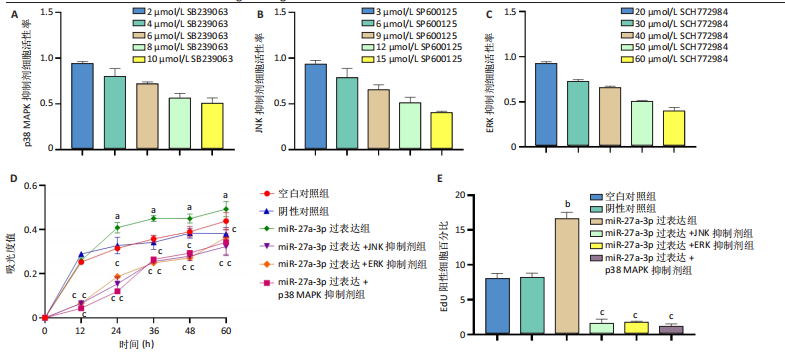
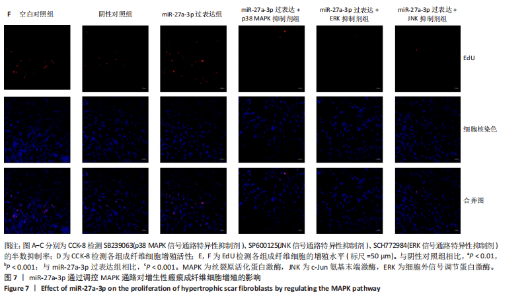
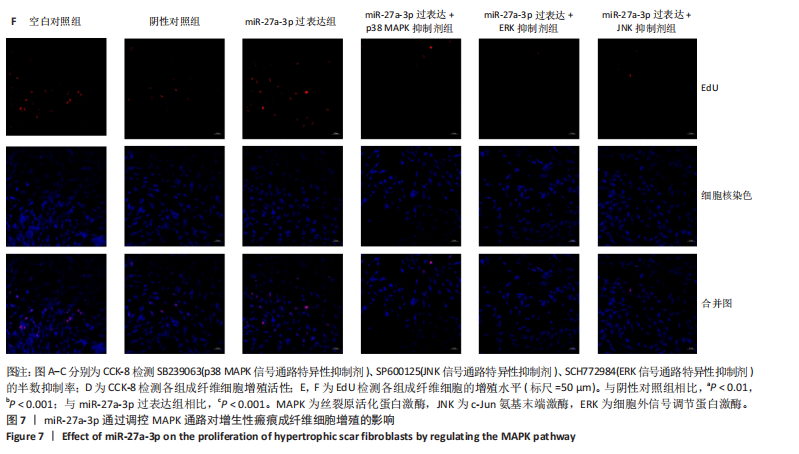
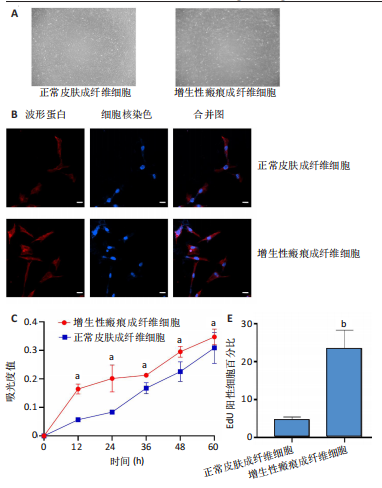
2.1 原代细胞的培养 显微镜观察显示,与正常成纤维细胞相比,增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞生长更加旺盛,细胞生长呈旋涡状(图1A);免疫荧光结果显示,所培养的细胞为成纤维细胞,波形蛋白染色为阳性,呈现在细胞质中,为红色荧光(图1B);CCK-8结果显示,与正常皮肤成纤维细胞相比,增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖活性更强(P < 0.05)(图1C);EdU结果显示,与正常皮肤成纤维细胞相比,增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞处于增殖期的更多(P < 0.001)(图1D,E)。以上结果表明成纤维原代细胞成功培养。 2.2 miR-27a-3p在增生性瘢痕组织中高表达 qRT-PCR结果显示,与正常皮肤组织相比,增生性瘢痕组织中miR-27a-3p呈高表达(P < 0.001),见图2。以上结果表明miR-27a-3p在增生性瘢痕中高表达。 2.3 过表达miR-27a-3p对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖的影响 qRT-PCR结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,miR-27a-3p的mRNA水平在miR-27a-3p过表达组中显著升高(P < 0.001),表明miR-27a-3p过表达在细胞中成功转染并表达(图3A);CCK-8结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,过表达miR-27a-3p组成纤维细胞的细胞增殖活力显著增加(P < 0.001)(图3B);EdU结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,过表达miR-27a-3p后成纤维细胞处于增殖期的更多(P < 0.001)(图3C)。表明过表达miR-27a-3p能够促进增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖。 2.4 抑制miR-27a-3p对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖的影响 qRT-PCR结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,miR-27a-3p的表达水平在miR-27a-3p抑制组中显著降低(P < 0.001),表明miR-27a-3p干扰载体在细胞中成功转染并表达(图4A);CCK-8实验显示,与阴性对照组相比,miR-27a-3p抑制组增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖活力显著降低(P < 0.05)(图4B),EdU结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,miR-27a-3p抑制组处于增殖期的成纤维细胞显著减少(P < 0.001)(图4C)。表明干扰miR-27a-3p能够抑制增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖。 2.5 miR-27a-3p预测靶基因的基因本体及KEGG分析 利用TargetScan数据库预测miR-27a-3p的靶基因,然后利用DAVID数据库对预测的靶基因进行基因本体和KEGG富集分析。miR-27a-3p靶基因按生物过程、细胞组分和分子功能进行了分类(图5A),KEGG信号通路分析结果表明miR-27a-3p的靶基因信号通路显著富集于MAPK信号通路(图5B)。 2.6 miR-27a-3p对MAPK信号通路的影响 分别转染过表达miR-27a-3p和干扰miR-27a-3p后,观察增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞中p38 MAPK、ERK、JNK的激活情况。Western blot结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,在转染过表达miR-27a-3p的瘢痕成纤维细胞中,p38 MAPK、ERK和JNK的磷酸化水平显著升高(P < 0.05),而在转染干扰miR-27a-3p的瘢痕成纤维细胞中,它们的磷酸化水平显著降低(P < 0.05),表明过表达miR-27a-3p能够促进MAPK通路的激活,而干扰miR-27a-3p能够抑制MAPK通路的激活,见图6。 2.7 miR-27a-3p通过MAPK通路对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖的影响 使用p38 MAPK(SB239063)、ERK(SCH772984)和JNK(SP600125)的特异性化学抑制剂来确定MAPK信号通路是否参与了miR-27a-3p调控的成纤维细胞增殖。采用0,2,4,6,8,10 μmol/L浓度梯度的SB239063处理增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞24 h后,采用0,3,6,9,12,15 μmol/L浓度梯度的SP6000125处理增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞24 h,采用0,20,30,40,50,60 μmol/L浓度梯度的SCH772984处理增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞24 h,然后用CCK-8法检测细胞活性,选择可以抑制细胞活性率约为50%的浓度,SB239063抑制细胞活性率约为50%的浓度为8 μmol/L(图7A),SP600125抑制细胞活性率约为50%的浓度为12 μmol/L(图7B),SCH772984抑制细胞活性率约为50%的浓度为50 μmol/L(图7C),所以选择了8 μmol/L的SB239063、12 μmol/L的SP600125和50 μmol/L的SCH772984用于后续实验。CCK-8检测细胞增殖结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,过表达miR-27a-3p促进了瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖;而与miR-27a-3p过表达组相比,分别加入抑制剂SCH772984、SB239063和SP600125后,发现它们可逆转miR-27a-3p过表达对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖活性的影响(图7D)。EdU结果显示,与阴性对照相比,miR-27a-3p过表达组的瘢痕成纤维细胞处于增殖期的较多;而与miR-27a-3p过表达组相比,分别加入抑制剂SCH772984、SB239063和SP600125后,发现它们可逆转miR-27a-3p过表达对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖周期的影响(图7E,F)。"
| [1] MONY MP, HARMON KA, HESS R,et al. An Updated Review of Hypertrophic Scarring. Cells. 2023;12(5):678. [2] BHARADIA SK, BURNETT L, GABRIEL V. Hypertrophic Scar. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2023;34(4):783-798. [3] DONG Y, CAO X, HUANG J, et al. Melatonin inhibits fibroblast cell functions and hypertrophic scar formation by enhancing autophagy through the MT2 receptor-inhibited PI3K/Akt /mTOR signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(1):166887. [4] SAAD N, DUROUX-RICHARD I, TOUITOU I, et al. MicroRNAs in inflammasomopathies. Immunol Lett. 2023;256-257:48-54. [5] KOMATSU S, KITAI H, SUZUKI HI. Network Regulation of microRNA Biogenesis and Target Interaction. Cells. 2023;12(2):306. [6] HAJIZADEH M, HAJIZADEH F, GHAFFAREI S, et al. MicroRNAs and their vital role in apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: miRNA-based diagnostic and treatment methods. Gene. 2023;888:147803. [7] ZONG Y, WANG X, CUI B, et al. Decoding the regulatory roles of non-coding RNAs in cellular metabolism and disease. Mol Ther. 2023;31(6): 1562-1576. [8] CUI Y, QI Y, DING L, et al. miRNA dosage control in development and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2024;34(1):31-47. [9] DUWE L, MUNOZ-GARRIDO P, LEWINSKA M, et al. MicroRNA-27a-3p targets FoxO signalling to induce tumour-like phenotypes in bile duct cells. J Hepatol. 2023;78(2):364-375. [10] LI M, GAO Z, WANG S, et al. miR27a3p upregulation by p65 facilitates cervical tumorigenesis by increasing TAB3 expression and is involved in the positive feedback loop of NFκB signaling. Oncol Rep. 2023; 50(1):132. [11] BONGOLO CC, THOKERUNGA E, YAN Q, et al. Exosomes Derived from microRNA-27a-3p Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Progression of Liver Cancer through Suppression of Golgi Membrane Protein 1. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:9748714. [12] ZHANG Z, HUANG X, YANG J, et al. Identification and functional analysis of a three-miRNA ceRNA network in hypertrophic scars. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):451. [13] YU B, ZHANG Y, WANG T, et al. MAPK Signaling Pathways in Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:1405-1418. [14] JASTRZĘBSKI MK, WÓJCIK P, STĘPNICKI P, et al. Effects of small molecules on neurogenesis: Neuronal proliferation and differentiation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(1):20-37. [15] Weems AD, Welf ES, Driscoll MK, et al. Blebs promote cell survival by assembling oncogenic signalling hubs. Nature. 2023;615(7952):517-525. [16] ZHAO ZJ, SUN YL, RUAN XF. Bornyl acetate: A promising agent in phytomedicine for inflammation and immune modulation. Phytomedicine. 2023;114:154781. [17] PARK HB, BAEK KH. E3 ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes regulating the MAPK signaling pathway in cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022;1877(3):188736. [18] DROSTEN M, BARBACID M. Targeting the MAPK Pathway in KRAS-Driven Tumors. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(4):543-550. [19] MOON H, RO SW. MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(12):3026. [20] Jiang T, Xia Y, Lv J, et al. A novel protein encoded by circMAPK1 inhibits progression of gastric cancer by suppressing activation of MAPK signaling. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):66. [21] YOU GR, CHANG JT, LI YL, et al. MYH9 Facilitates Cell Invasion and Radioresistance in Head and Neck Cancer via Modulation of Cellular ROS Levels by Activating the MAPK-Nrf2-GCLC Pathway. Cells. 2022; 11(18):2855. [22] CHAI CY, SONG J, TAN Z, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells inhibit hypertrophic scar (HS) fibrosis via p38/MAPK pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):4057-4064. [23] MA F, SHEN J, ZHANG H, et al. A novel lncRNA FPASL regulates fibroblast proliferation via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in hypertrophic scar. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;55(2): 274-284. [24] ASL ER, AMINI M, NAJAFI S, et al. Interplay between MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and MicroRNAs: A crucial mechanism regulating cancer cell metabolism and tumor progression. Life Sci. 2021;278: 119499. [25] FRECH FS, HERNANDEZ L, URBONAS R, et al. Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: Advances in Treatment and Review of Established Therapies. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24(2):225-245. [26] ZHONG Y, ZHANG Y, YU A, et al. Therapeutic role of exosomes and conditioned medium in keloid and hypertrophic scar and possible mechanisms. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1247734. [27] HILL M, TRAN N. miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech. 2021;14(4):dmm047662. [28] ZHANG X, ZHU L, WANG X, et al. Advances in the role and mechanism of miRNA in inflammatory pain. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;161:114463. [29] GONG K, YANG K, XIE T, et al. Identification of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network and its role in cardiac hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2023; 18(3):e0279638. [30] LI Y, WANG S, NING J, et al. The effects of miRNA-27a-3p on human epidermal melanocytes. Skin Res Technol. 2023;29(5):e13345. [31] Zhai C, Liu B, Kan F, et al. MicroRNA27a3p regulates the proliferation and chemotaxis of pulmonary macrophages in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma tissues through CXCL2. Oncol Lett. 2023;26(5):492. [32] SELVASKANDAN H, PAWLUCZYK I, BARRATT J. Clinical application of microRNAs in glomerular diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2023;38(6): 1375-1384. [33] WANG P, XUE Y, ZUO Y, et al. Exosome-Encapsulated microRNA-140-5p Alleviates Neuronal Injury Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Regulating IGFBP5-Mediated PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(12):7212-7228. [34] TANG SJ, FAN KH, YOU GR, et al. Tumor Suppressor miRNA-503 Inhibits Cell Invasion in Head and Neck Cancer through the Wnt Signaling Pathway via the WNT3A/MMP Molecular Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15900. [35] LIANG Y, TANG X, ZHANG X, et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes Carrying MiR-122-5p Antagonize the Inhibitory Effect of Dihydrotestosterone on Hair Follicles by Targeting the TGF-β1/SMAD3 Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5703. [36] YU B, ZHANG Y, WANG T, et al. MAPK Signaling Pathways in Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:1405-1418. [37] SALEEM S. Targeting MAPK signaling: A promising approach for treating inflammatory lung disease. Pathol Res Pract. 2024;254:155122. [38] MAO Y, OU S, ZHU C, et al. Downregulation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Ameliorates Tissue-Engineered Corneal Epithelium. Tissue Eng Part A. 2022;28(23-24):977-989. [39] ITAH Z, CHAUDHRY S, RAJU PONNY S, et al. HER2-driven breast cancer suppression by the JNK signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(4):e2218373120. [40] SU L, LI X, MAO X, et al. Circ-Ntrk2 acts as a miR-296-5p sponge to activate the TGF-β1/p38 MAPK pathway and promote pulmonary hypertension and vascular remodelling. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):78. [41] XU Q, YAO Y, NI H, et al. Hsa-circ-0052001 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion via the MAPK pathway. Cancer Med. 2023; 12(6):7246-7257. |
| [1] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [2] | Li Hao, Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Ding Qiang, Niu Chicheng, Huang Kai, Kang Hongyu. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway regulates the development of osteoarthritis: guiding targeted therapy with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [3] | Peng Tuanhui, Song Hongming, Yang Ling, Ding Xiaoge, Meng Pengjun. Effects of long-term endurance exercise on kl/FGF23 axis and calcium-phosphorus metabolism in naturally aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1089-1095. |
| [4] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [5] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [6] | Guo Jiachen, Gao Jun, Dai Wenhao, Liao Huayuan, Jiang You, Zhang Xi . Effect of compressive stress microenvironment on cytokines during fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 908-916. |
| [7] | Chen Ling, Mao Qiuhua, Xu Pu, Zhang Wenbo. Effect of water-soluble matrix of nano-pearl powder on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of mouse fibroblasts#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 338-344. |
| [8] | Wu Zhijing, Li Jiali, Zhang Jiaxin, Wang Tangrong, Zheng Yuzhou, Sun Zixuan. Alpha-ketoglutarate engineered small extracellular vesicles delay skin aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 120-129. |
| [9] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [10] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [11] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [12] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [13] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [14] | Dong Meilin, Du Haiyu, Liu Yuan. Quercetin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [15] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||