Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 1437-1447.doi: 10.12307/2025.030
Previous Articles Next Articles
Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Zhang Zhenyu1, 2, Liang Qiujian1, 2, Yang Jun1, Wei Xiangyu1, Jiang Jie1, Huang Linke1, Tan Zhen1
- 1Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530005, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-11-28Accepted:2024-02-06Online:2025-03-08Published:2024-06-27 -
Contact:Huang Linke, MD, Associate chief physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530005, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Tan Zhen, MD, Chief physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530005, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Zhenyu, Master candidate, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530005, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8216140155 (to TZ); 2023 Basic Research Ability Improvement Project Young and Middle-Aged Teachers of Guangxi Universities, No. 2023KY0109 (to HLK); Guangxi Natural Science Youth Science Foundation, No. 2022JJB140140 (to JJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
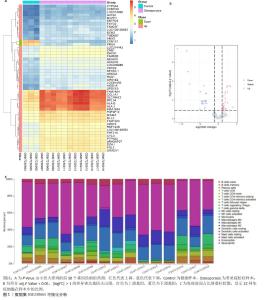
2.1 数据集获取及差异表达基因的生物信息学筛选与分析 从GEO数据库下载GSE230665芯片数据,获得人类女性绝经后股骨组织的基因表达谱,该数据集包含15例接受髋关节置换的绝经妇女样本,分别为3例绝经后健康妇女样本和12例绝经后原发性骨质疏松症患者样本。使用Excel表格筛选差异表达基因,去除重复项,条件为P Value < 0.01,获得符合筛选条件的9 253条差异表达基因。对P Value由小到大排列的前50个基因进行分析,对各基因的表达值进行log10转换,得到上调基因48个,下调基因2个,绘制热图,见图1A。 按照前述方法进行P Value校正,对差异表达基因进行分析,筛选条件为adj.P Value < 0.05,|logFC| > 1,得到上调基因23个,下调基因25个,绘制火山图,见图1B。按照adj.P Value由小到大排列的前5个上调基因分别为KIAA1654、FAM74A4、HLA-B、COL1A1、RPL34,前5个下调基因分别为CSN1S1、PRG4、AMTN、MMP3、CRTAC1。 采用CIBERSORT计算方法估计所有样本的肿瘤浸润性免疫细胞丰度谱,发现该组样本中活化的肥大细胞占优势,绘制占比堆叠柱状图,见图1C。 "
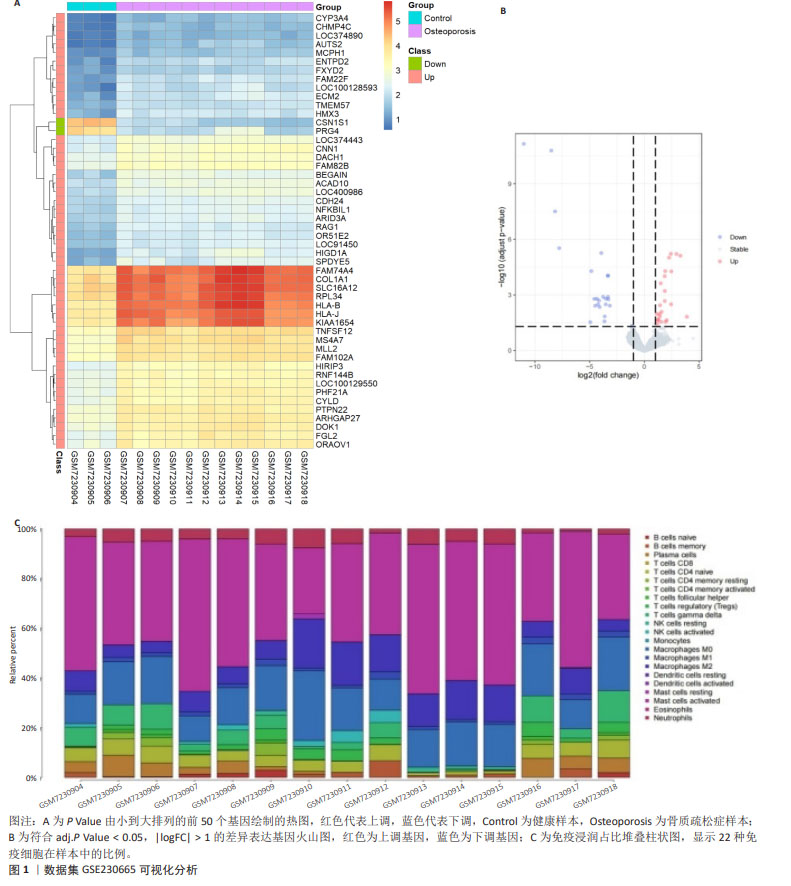
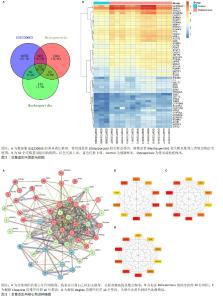
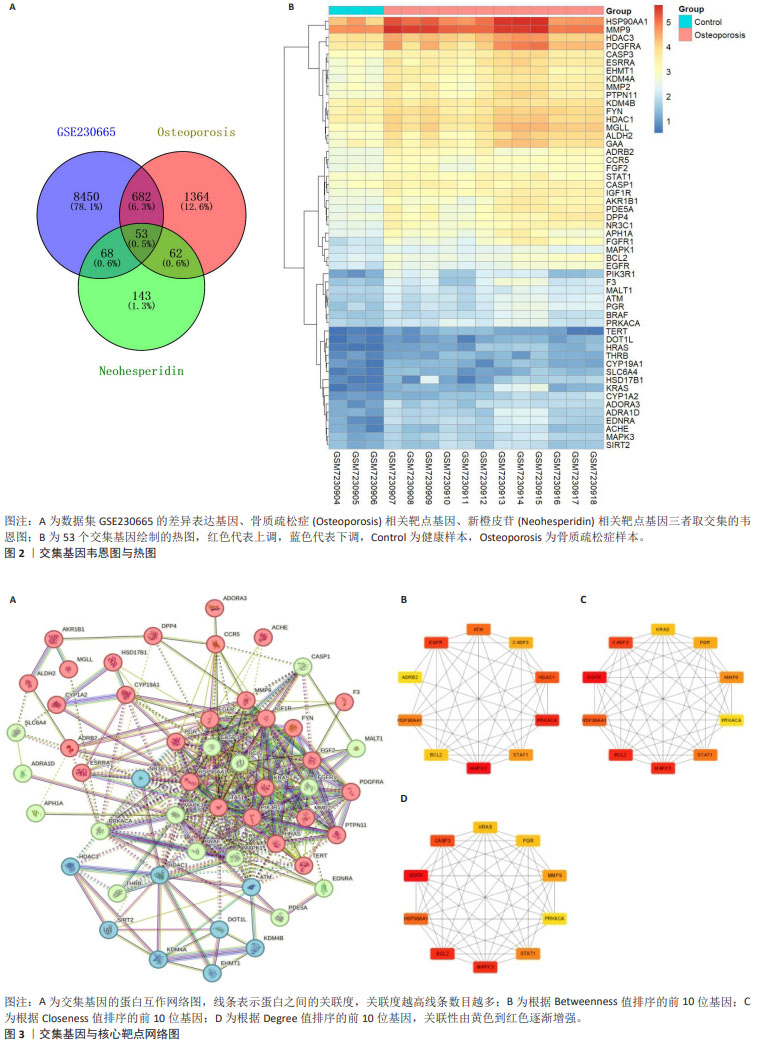
2.2 骨质疏松症相关靶点 在GeneCards数据库得到骨质疏松症相关的基因靶点信息5 630条,以Relevance score > 1为标准对得到的数据进行筛选,剩余1 659个基因靶点。在DisGeNET数据库得到基因靶点信息1 098条。将2个数据库的基因靶点信息进行整合,删除重复项,最终得到2 161个骨质疏松症相关靶点基因。 2.3 新橙皮苷相关靶点 在ChEMBL数据库中得到新橙皮苷相关的蛋白靶点信息255条,将筛选后的数据导入UniProt数据库匹配,得到相应的基因靶点255个。在SwissTarget Prediction数据库得到新橙皮苷相关的基因靶点信息100条。将以上两部分基因靶点信息进行整合,删除重复项,最终得到326个新橙皮苷相关靶点基因。 2.4 数据集、疾病靶点、药物靶点的交集基因 通过Venny 2.1.0在线作图工具对GEO芯片数据集GSE230665的差异表达基因、骨质疏松症相关靶点基因、新橙皮苷相关靶点基因取交集,并制作韦恩图,见图2A,得到交集基因53个。对交集基因在GSE230665中的表达值进行log10转换,发现53个交集基因的表达量在骨质疏松症样本中都上调,绘制热图,见图2B。 2.5 构建蛋白互作网络 将交集基因导入STRING数据库进行分析,绘制交集基因PPI网络图,见图3A。获取TSV数据文件并导入Cytoscape 3.9.1软件进行分析,使用CytoHubba插件根据Betweenness值、Closeness值、Degree值进行拓扑分析,筛选出前10位核心靶点,见图3B-D。 进一步研究发现,根据Betweenness值排序的前3位基因分别是MAPK3、PRKACA、EGFR,根据Closeness值和Degree值排序的前3位基因都是EGFR、BCL2、MAPK3,汇总得到4个核心靶点EGFR、MAPK3、BCL2、PRKACA。在中国知网以这4个核心靶点基因分别和“骨质疏松症”为主题进行高级检索,其中只有PRKACA基因未见与骨质疏松症相关的研究报道,因此将PRKACA作为进一步研究的目标靶点基因。"

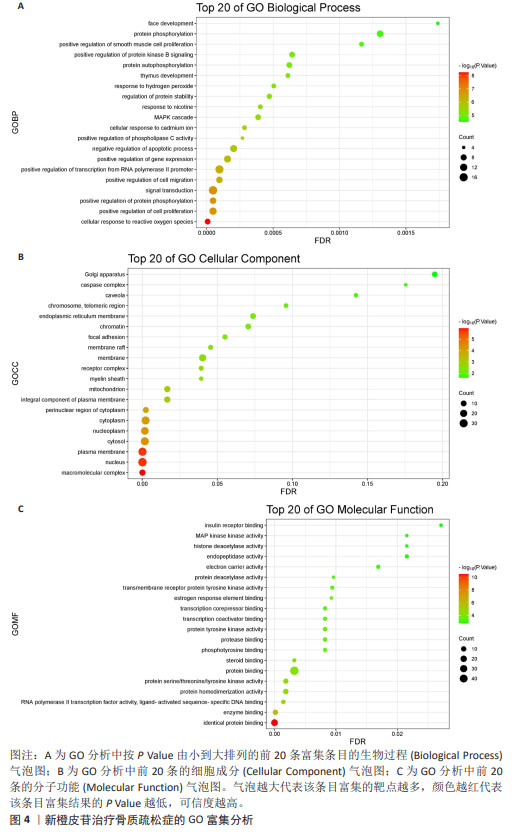
2.6 GO富集分析结果 将交集基因导入DAVID数据库进行GO富集分析,得到的分析结果按P.Value值由小到大排列,使用微生信在线作图软件对前20条富集结果制作气泡图进行可视化分析。其中生物过程(Biological Process,BP)主要涉及细胞对活性氧的反应、正向调节蛋白磷酸化和正向调节细胞增殖等,见图4A;细胞成分(Cellular Component,CC)主要涉及大分子复合物、核和质膜等,见图4B;分子功能(Molecular Function,MF)主要涉及相同蛋白质结合、酶结合和RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录因子活性,配体激活序列特异性DNA结合,见图4C。 目标靶点基因PRKACA涉及的生物过程有蛋白质磷酸化和蛋白质自身磷酸化,涉及的细胞成分主要有核、质膜、胞质等,涉及的分子功能有蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸/酪氨酸激酶活性和蛋白结合。"
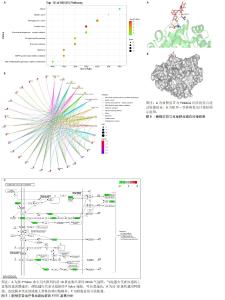
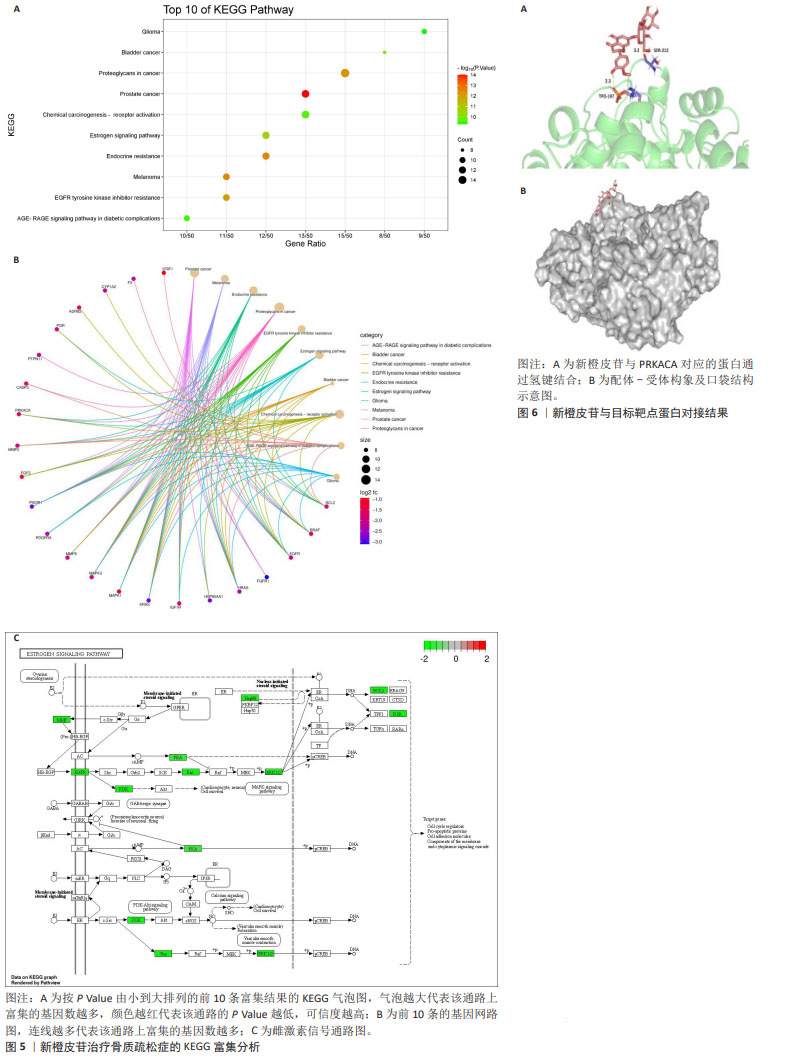
2.7 KEGG富集分析结果 将交集基因及其logFC值导入微生信在线作图软件进行KEGG富集分析,获得按P Value由小到大排列的前10条富集结果制作的富集气泡图和基因网路图,见图5A,B。主要涉及前列腺癌、黑素瘤、内分泌抵抗、癌症中的蛋白聚糖、EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药性、雌激素信号通路、膀胱癌、化学致癌作用-受体激活、AGE-RAGE信号通路在糖尿病并发症中的作用、胶质瘤等。 目标靶点基因PRKACA涉及的信号通路有内分泌抵抗、癌症中的蛋白聚糖、雌激素信号通路、化学致癌作用-受体激活,其中雌激素信号通路与女性绝经后骨质疏松症的发生最为密切,绘制相应的信号通路图,见图5C。 2.8 分子对接结果 将新橙皮苷与目标靶点基因PRKACA对应的蛋白进行分子对接,见图6A,分子与靶点蛋白的最低结合能为-12.05 kJ/mol < 0,说明配体和受体可以自发结合。选择该配体-受体构象及口袋结构绘制对接示意图,见图6B,说明新橙皮苷与PRKACA对应的蛋白之间可以通过氢键结合。"
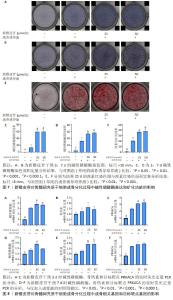
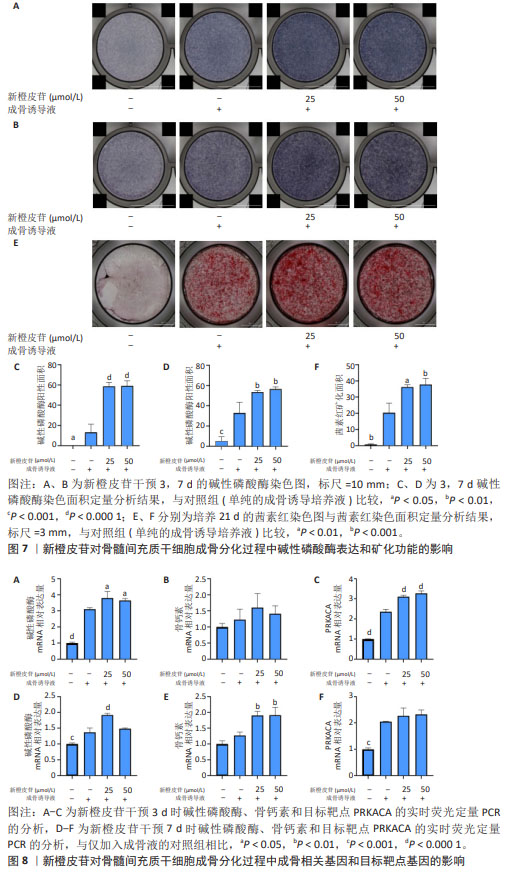
2.9 新橙皮苷对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化和目标靶点基因的影响 碱性磷酸酶染色结果显示,空白对照组培养3 d时碱性磷酸酶染色呈阴性,培养7 d时呈现阳性;其余3组培养3,7 d时碱性磷酸酶染色均呈阳性,相较于对照组,实验组染色加深,说明新橙皮苷可以显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化早期碱性磷酸酶的表达,见图7A-D。 培养21 d的茜素红染色结果显示,空白对照组茜素红染色呈阴性,其余3组茜素红染色呈阳性,并且相较于对照组,实验组茜素红染色明显加深,提示矿化结节明显增多,说明新橙皮苷可以显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的矿化,见图7E,F。 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与空白对照组比较,对照组培养3,7 d的碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达、培养3,7 d的PRKACA mRNA表达升高(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1);与对照组比较,低浓度新橙皮苷组培养3,7 d的碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.000 1),高浓度新橙皮苷组培养3 d的碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05),低、高浓度新橙皮苷组培养7 d的骨钙素mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01),低、高浓度新橙皮苷组培养3 d的PRKACA mRNA表达升高(P < 0.000 1),见图8。"
| [1] GAO S, ZHAO Y. Quality of life in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Qual Life Res. 2023;32(6):1551-1565. [2] ARMAS LA, RECKER RR. Pathophysiology of osteoporosis: new mechanistic insights. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012; 41(3):475-486. [3] YUAN S, ZHANG C, ZHU Y, et al. Neohesperidin Ameliorates Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Inhibiting the Histone Modification of lncRNA HOTAIR. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:5419-5430. [4] WANG XH, DAI C, WANG J, et al. Therapeutic effect of neohesperidin on TNF-α-stimulated human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chin J Nat Med. 2021;19(10):741-749. [5] TAN Z, CHENG J, LIU Q, et al. Neohesperidin suppresses osteoclast differentiation, bone resorption and ovariectomised-induced osteoporosis in mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017;439:369-378. [6] NOGALES C, MAMDOUH ZM, LIST M, et al. Network pharmacology: curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(2):136-150. [7] BARRETT T, WILHITE SE, LEDOUX P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; 41(Database issue):D991-995. [8] XIE L, FENG E, LI S, et al. Comparisons of gene expression between peripheral blood mononuclear cells and bone tissue in osteoporosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(20):e33829. [9] STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016; 54:1.30.31-31.30.33. [10] PIÑERO J, RAMÍREZ-ANGUITA JM, SAÜCH-PITARCH J, et al. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(D1):D845-d855. [11] ZDRAZIL B, FELIX E, HUNTER F, et al. The ChEMBL Database in 2023: a drug discovery platform spanning multiple bioactivity data types and time periods. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(D1):D1180-D1192. [12] UNIPROT CONSORTIUM. UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D523-d531. [13] KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T, et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023; 51(D1):D1373-d1380. [14] DAINA A, MICHIELIN O, ZOETE V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W357-w364. [15] SZKLARCZYK D, KIRSCH R, KOUTROULI M, et al. The STRING database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D638-d646. [16] SHERMAN BT, HAO M, QIU J, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(W1):W216-w221. [17] TANG D, CHEN M, HUANG X, et al. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS One. 2023;18(11): e0294236. [18] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [19] TOYOTA A, GOTO M, MIYAMOTO M, et al. Novel protein kinase cAMP-Activated Catalytic Subunit Alpha (PRKACA) inhibitor shows anti-tumor activity in a fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;621:157-161. [20] Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: the 2021 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2021; 28(9):973-997. [21] GOSSET A, POUILLÈS JM, TRÉMOLLIERES F. Menopausal hormone therapy for the management of osteoporosis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;35(6):101551. [22] PRESTWOOD KM, PILBEAM CC, RAISZ G. Treatment of osteoporosis. Annu Rev Med. 1995;46:249-256. [23] BROWN JP. Long-Term Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021;36(3):544-552. [24] ZHANG ND, HAN T, HUANG BK, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine formulas for the treatment of osteoporosis: Implication for antiosteoporotic drug discovery. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;189:61-80. [25] LIU G, XIE Y, SU J, et al. The role of EGFR signaling in age-related osteoporosis in mouse cortical bone. Faseb J. 2019;33(10): 11137-11147. [26] XIAO P, CHEN Y, JIANG H, et al. In vivo genome-wide expression study on human circulating B cells suggests a novel ESR1 and MAPK3 network for postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(5): 644-654. [27] HU X H, YANG X Y, LIAN J, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf attenuate osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by modulating gut microbiota composition and MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;161:114434. [28] VAKILI S, ZAL F, MOSTAFAVI-POUR Z, et al. Quercetin and vitamin E alleviate ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by modulating autophagy and apoptosis in rat bone cells. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5): 3495-3509. [29] ZHU C, SHEN S, ZHANG S, et al. Autophagy in Bone Remodeling: A Regulator of Oxidative Stress. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13: 898634. [30] FATOKUN AA, STONE TW, SMITH RA. Responses of differentiated MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells to reactive oxygen species. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;587(1-3):35-41. [31] BĂDILĂ AE, RĂDULESCU DM, ILIE A, et al. Bone Regeneration and Oxidative Stress: An Updated Overview. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):318. [32] YAMAGUCHI Y, KANZAKI H, KATSUMATA Y, et al. Dimethyl fumarate inhibits osteoclasts via attenuation of reactive oxygen species signalling by augmented antioxidation. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(2):1138-1147. [33] LEE J, SON HS, LEE H I, et al. Skullcapflavone II inhibits osteoclastogenesis by regulating reactive oxygen species and attenuates the survival and resorption function of osteoclasts by modulating integrin signaling. Faseb J. 2019;33(2):2026-2036. [34] YE Y, ZHONG H, HUANG S, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Hydrogel Regulates Stem Cell Behavior and Promotes Bone Healing in Osteoporosis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(6):981-992. [35] TURNHAM RE, SCOTT JD. Protein kinase A catalytic subunit isoform PRKACA; History, function and physiology. Gene. 2016; 577(2):101-108. [36] JEONG JH, CHOI JY. Interrelationship of Runx2 and estrogen pathway in skeletal tissues. BMB Rep. 2011;44(10):613-618. [37] CHENG CH, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. Osteoporosis Due to Hormone Imbalance: An Overview of the Effects of Estrogen Deficiency and Glucocorticoid Overuse on Bone Turnover. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(3):1376. [38] CUI J, SHEN Y, LI R. Estrogen synthesis and signaling pathways during aging: from periphery to brain. Trends Mol Med. 2013; 19(3):197-209. [39] ALMEIDA M, IYER S, MARTIN-MILLAN M, et al. Estrogen receptor-α signaling in osteoblast progenitors stimulates cortical bone accrual. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1): 394-404. [40] CHEN D, PACE PE, COOMBES RC, et al. Phosphorylation of human estrogen receptor alpha by protein kinase A regulates dimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19(2): 1002-1015. [41] HU HY, ZHANG ZZ, JIANG XY, et al. Hesperidin Anti-Osteoporosis by Regulating Estrogen Signaling Pathways. Molecules. 2023;28(19): 6987. [42] NIU J, WANG Y, MENG Y, et al. Asperosaponin VI induces osteogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via the estrogen signaling pathway. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(50):e32344. [43] KOBYLKA P, KUCINSKA M, KUJAWSKI J, et al. Resveratrol Analogues as Selective Estrogen Signaling Pathway Modulators: Structure-Activity Relationship. Molecules. 2022;27(20):6973. [44] WANG L, SHAO YY, BALLOCK RT. Thyroid hormone interacts with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in the terminal differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22(12):1988-1995. [45] SHARMA R, WU X, RHODES SD, et al. Hyperactive Ras/MAPK signaling is critical for tibial nonunion fracture in neurofibromin-deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(23):4818-4828. [46] CHEN T, WANG Y, HAO Z, et al. Parathyroid hormone and its related peptides in bone metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021; 192:114669. [47] DIXIT M, POUDEL SB, YAKAR S. Effects of GH/IGF axis on bone and cartilage. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;519:111052. [48] ZHANG J, WANG X, DUAN H, et al. The Association of Calcium Signaling Pathway Gene Variants, Bone Mineral Density and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Elderly People. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(4): 828. [49] VIMALRAJ S. Alkaline phosphatase: Structure, expression and its function in bone mineralization. Gene. 2020;754:144855. [50] HAN Y, YOU X, XING W, et al. Paracrine and endocrine actions of bone-the functions of secretory proteins from osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Bone Res. 2018;6:16. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [3] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [6] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [7] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [8] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [9] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [10] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [11] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [12] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [13] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [14] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [15] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||