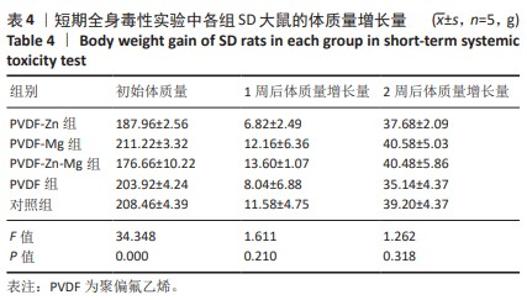
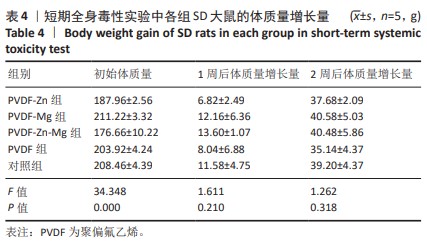
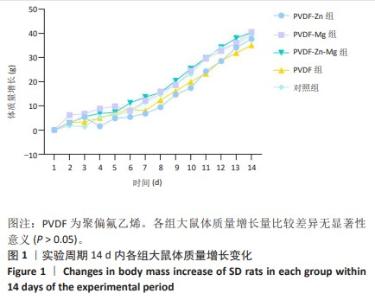
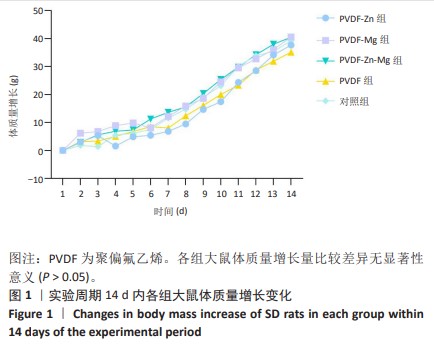
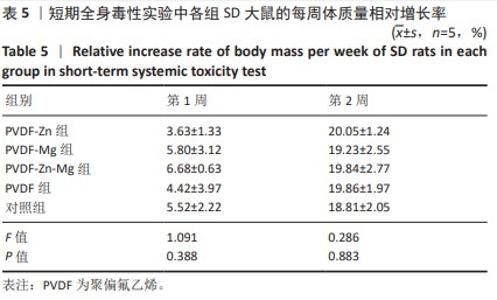
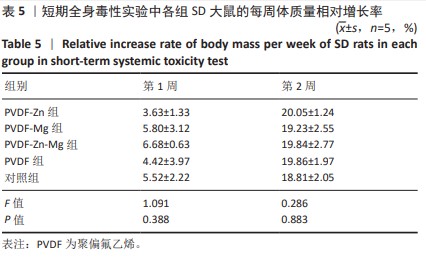
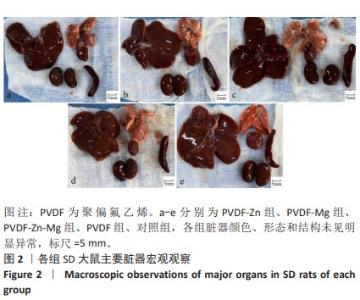
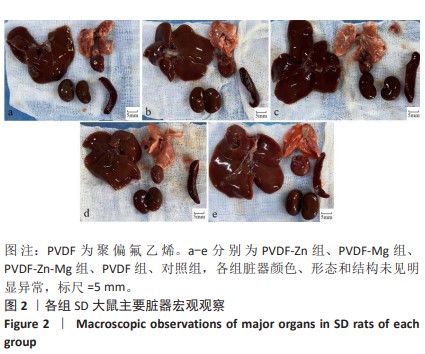
[1] ZHOU K, YU P, SHI X, et al. Hierarchically porous hydroxyapatite hybrid scaffold incorporated with reduced graphene oxide for rapid bone ingrowth and repair. ACS Nano. 2019;13(8):9595-9606.
[2] LEE YC, CHAN YH, HSIEH SC, et al. Comparing the osteogenic potentials and bone regeneration capacities of bone marrow and dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit calvarial bone defect model. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5015.
[3] TENG C, TONG Z, HE Q, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells–Hydrogel Microspheres System for Bone Regeneration in Calvarial Defects. Gels. 2022;8(5):275.
[4] JO SH, KIM YK, CHOI YH. Histological evaluation of the healing process of various bone graft materials after engraftment into the human body. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(5):714.
[5] 程玮璐,张译丹,刘英慧.骨填充材料的临床应用进展[J].中国医疗器械信息,2023,29(21):43-47.
[6] 赵蓝波,王东波.口腔种植领域中自体牙骨移植材料的应用价值分析[J].中国卫生标准管理,2023,14(3):124-127.
[7] WUBNEH A, TSEKOURA EK, AYRANCI C, et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;80:1-30.
[8] LIN Z, FATEH A, SALEM DM, et al. Periosteum: biology and applications in craniofacial bone regeneration. J Dent Res. 2014;93(2):109-116.
[9] TSUZUNO T, TAKAHASHI N, NAGATA M, et al. Characterization of the cellular heterogeneity and bone regenerative potential of cultured human periosteal cells. Regen Ther. 2023;24:642-650.
[10] ZHOU Z, LIU Y, LI W, et al. A Self‐Adaptive Biomimetic Periosteum Employing Nitric Oxide Release for Augmenting Angiogenesis in Bone Defect Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(3):e2302153.
[11] HUH JY, CHOI BH, KIM BY, et al. Critical size defect in the canine mandible. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005; 100(3):296-301.
[12] 蒋昇源,宫智浩,宋凯凯,等.骨膜在骨折愈合及骨组织修复过程中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(30):4860-4865.
[13] KHARE D, BASU B, DUBEY AK. Electrical stimulation and piezoelectric biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2020;258: 120280.
[14] KAMEL NA. Bio-piezoelectricity: Fundamentals and applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biophys Rev. 2022;14(3): 717-733.
[15] 何逸恒,程鸣威,朱培君,等.电活性生物膜促进大鼠的体内成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4446-4451.
[16] 张学慧.电活性骨修复材料的研究现状与挑战[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2022,31(1):1-5.
[17] LAY R, DEIJS GS, MALMSTRÖM J. The intrinsic piezoelectric properties of materials–a review with a focus on biological materials. RSC Adv. 2021;11(49):30657-30673.
[18] BAI Y, LIU Y, LV H, et al. Processes of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-based nanofibers, their piezoelectric properties, and several fantastic applications. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(20):4311.
[19] ZHENG T, HUANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Mimicking the electrophysiological microenvironment of bone tissue using electroactive materials to promote its regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(45):10221-10256.
[20] 温棚.静电纺聚合物/肉桂精油纳米纤维膜的制备及性能研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2014.
[21] JIANG Z, ZHENG Z, YU S, et al. Nanofiber scaffolds as drug delivery systems promoting wound healing. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(7):1829.
[22] MA W, ZHANG S, XIE C, et al. Preparation of High Mechanical Strength Chitosan Nanofiber/NanoSiO2/PVA Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering Using Sol–Gel Method. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(10):2083.
[23] LI H, XU M, SHI R, et al. Advances in Electrostatic Spinning of Polymer Fibers Functionalized with Metal-Based Nanocrystals and Biomedical Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(17):5548.
[24] GONG M, CHI C, YE J, et al. Icariin-loaded electrospun PCL/gelatin nanofiber membrane as potential artificial periosteum. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:201-209.
[25] YIN S, ZHANG W, ZHANG Z, et al. Recent advances in scaffold design and material for vascularized tissue‐engineered bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(10):1801433.
[26] BOSE S, FIELDING G, TARAFDER S, et al. Understanding of dopant-induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in calcium phosphate ceramics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013;31(10):594-605.
[27] ZHOU B, JIANG X, ZHOU X, et al. GelMA-based bioactive hydrogel scaffolds with multiple bone defect repair functions: therapeutic strategies and recent advances. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):86.
[28] ZENG R, DIETZEL W, WITTE F, et al. Progress and challenge for magnesium alloys as biomaterials. Adv Eng Mater. 2008;10(8):B3-B14.
[29] 周莹,王丽洁,杜晟威,等.医疗器械生物学评价与质量管理[J].中国医疗器械信息,2018,24(19):17-19.
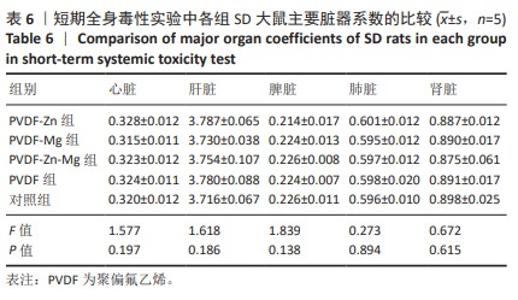
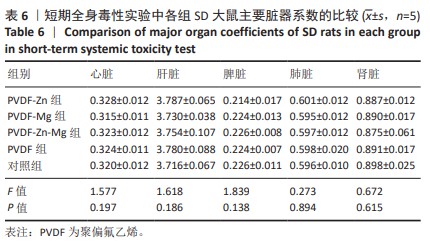
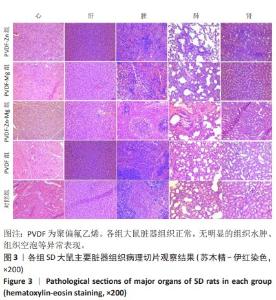
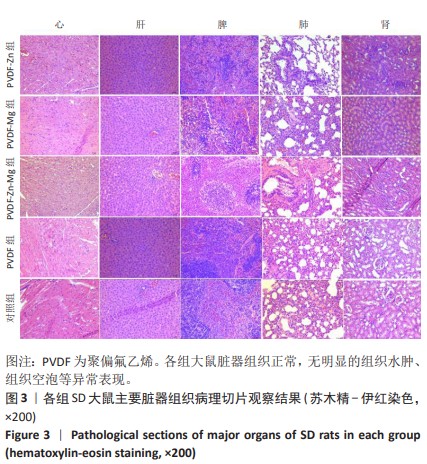
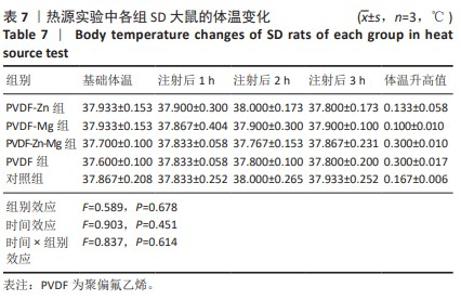
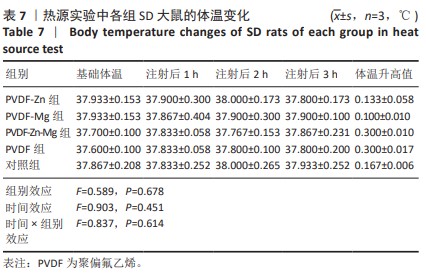
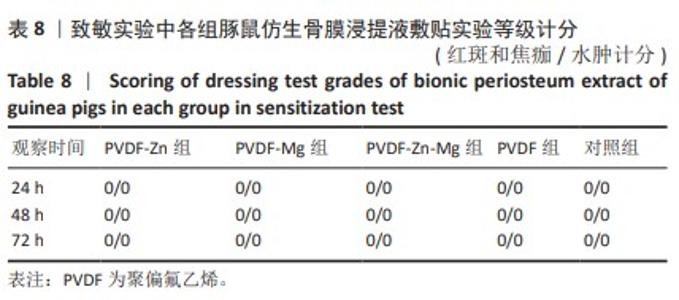
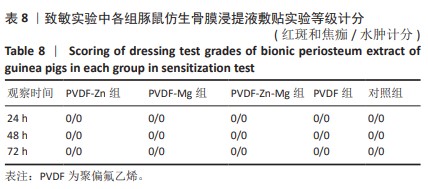
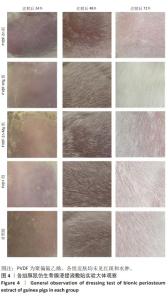
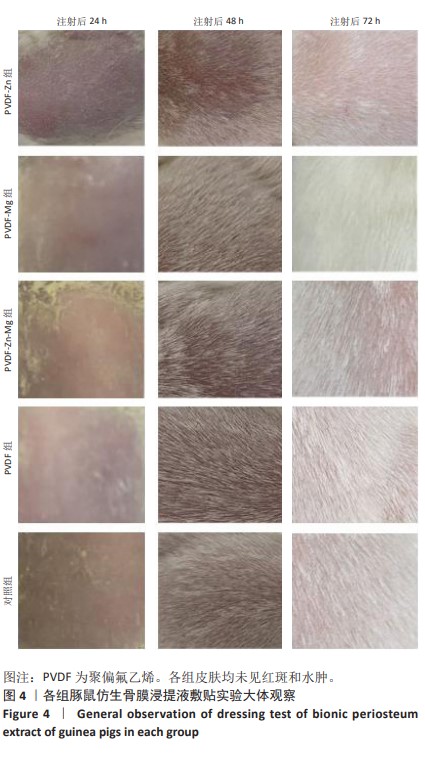
[30] 魏岁艳,曹怡静,赵帅,等.静电纺丝聚偏氟乙烯压电仿生骨膜的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(15):2351-2357.
[31] 中国标准出版社第一编辑室.医疗器械生物学评价标准汇编[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2005:84-299.
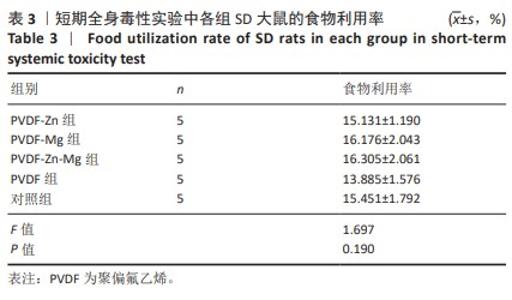
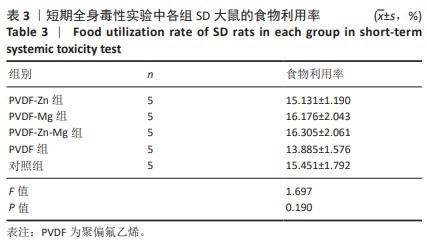
[32] 史晓萍,宗阿南,陶钧,等.《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2007,36(4):493.
[33] GB/T 16886.12-2017,医疗器械生物学评价 第12部分:样品制备与参照材料[S].
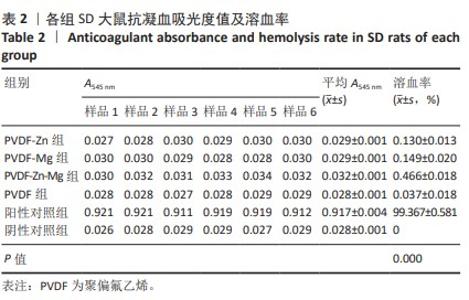
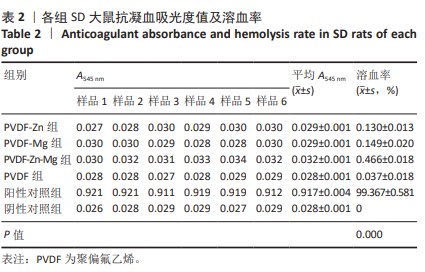
[34] 栾庆玲,隋馨,高雅松,等.溶血试验方法在医疗器械领域的应用[J].国际感染病学(电子版),2020,9(2):20.
[35] 程志琳,秦豪,许林.治疗骨缺损的组织工程支架研究进展[J].微创医学,2022,17(6):780-783.
[36] 常文辽,赵杰,孙晓亮,等.人工骨膜的材料选择、理论设计及生物仿生功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4):600-606.
[37] SAMAVEDI S, WHITTINGTON AR, GOLDSTEIN AS. Calcium phosphate ceramics in bone tissue engineering: a review of properties and their influence on cell behavior. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(9):8037-8045.
[38] AGARWAL R, GARCÍA AJ. Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:53-62.
[39] 于久越,贾雯昊,方丽,等.利用Bio-Oss Collagen进行上颌磨牙拔除后拔牙位点保存的临床分析[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2023, 28(2):90-96.
[40] RODRÍGUEZ-CABELLO JC, DE TORRE IG, IBAÑEZ-FONSECA A, et al. Bioactive scaffolds based on elastin-like materials for wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;129:118-133.
[41] 刘一凡,朱伟伟,方敏.聚偏氟乙烯在医学上的研究进展和应用[J].浙江化工,2017,48(11):1-3.
[42] HABIBOVIC P, BARRALET JE. Bioinorganics and biomaterials: bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(8):3013-3026.
[43] BROWN EM. Is the calcium receptor a molecular target for the actions of strontium on bone? Osteop Int. 2003;14:25-34.
[44] SARKAR K, KUMAR V, DEVI KB, et al. Anomalous in vitro and in vivo degradation of magnesium phosphate bioceramics: role of zinc addition. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(10):5097-5106.
[45] 马晓洁.标本溶血对生化检验中心肌酶、血脂、电解质、肝功能指标的影响[J].临床研究,2022,30(9):139-143. |