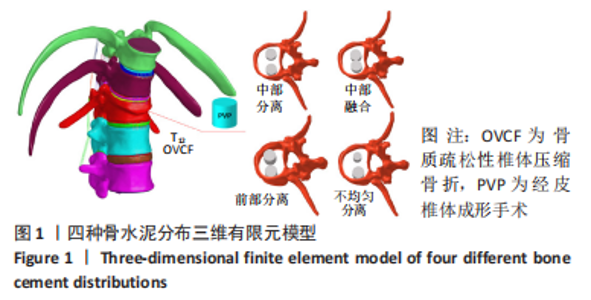
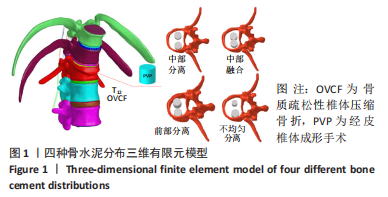
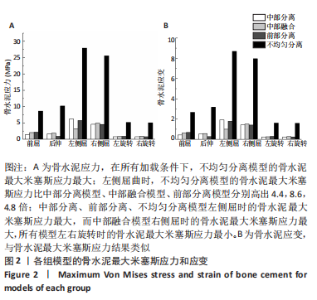
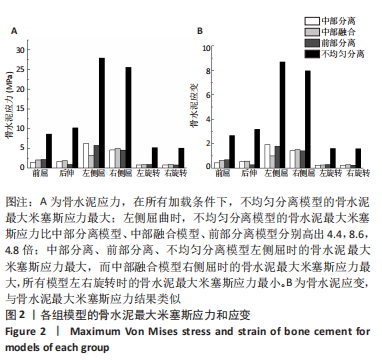
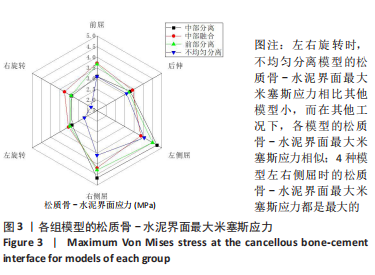
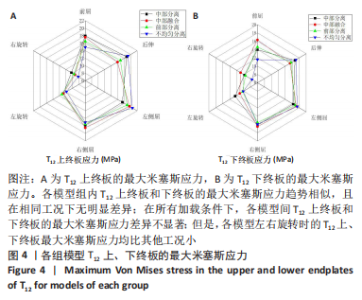
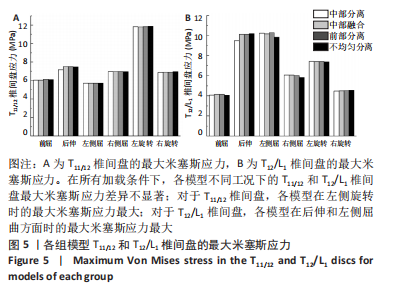
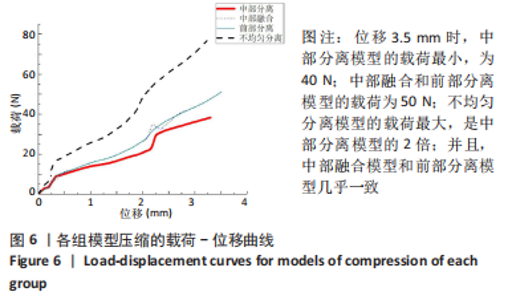
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4763-4768.doi: 10.12307/2023.831
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of biomechanical effects of bone cement dispersion type on the reinforced vertebrae
Wu Zhihua1, 2, Li Ren2, Pan Huiling2, Fan Fengjie2, Jiang Xiaobing3, Tang Fuyu1, 2
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, Liuzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Spinal Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-24Accepted:2022-11-16Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-01 -
Contact:Tang Fuyu, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Spine Surgery, Liuzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wu Zhihua, Master, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Spine Surgery, Liuzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2020GXNSFAA259082 (to TFY); Liuzhou Science and Technology Program, No. 2019BE10602 (to TFY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Zhihua, Li Ren, Pan Huiling, Fan Fengjie, Jiang Xiaobing, Tang Fuyu. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effects of bone cement dispersion type on the reinforced vertebrae[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4763-4768.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] KLAZEN CA, LOHLE PN, DE VRIES J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010; 376(9746):1085-1092. [2] LI HM, ZHANG RJ, GAO H, et al. New vertebral fractures after osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture between balloon kyphoplasty and nonsurgical treatment PRISMA. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(40):e12666. [3] KUTSAL FY, ERGIN ERGANI GO. Vertebral compression fractures: Still an unpredictable aspect of osteoporosis. Turk J Med Sci. 2021;51(2):393-399. [4] PARK JS, PARK YS. Survival analysis and risk factors of new vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Spine J. 2021;21(8):1355-1361. [5] MAO W, DONG F, HUANG G, et al. Risk factors for secondary fractures to percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):644. [6] SUZUKI N, OGIKUBO O, HANSSON T. The prognosis for pain, disability, activities of daily living and quality of life after an acute osteoporotic vertebral body fracture: its relation to fracture level, type of fracture and grade of fracture deformation. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(1):77-88. [7] LI Y, FENG X, PAN J, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in Patients with Distant Lumbosacral Pain. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E349-E356. [8] CHANG JZ, BEI MJ, SHU DP, et al. Comparison of the clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty vs. kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic Kümmell’s disease:a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):238. [9] SANLI I, VAN KUIJK SMJ, DE BIE RA, et al. Percutaneous cement augmentation in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVFs) in the elderly: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7): 1553-1572. [10] PAN M, GE J, LI Q, et al. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation in special Genant IV osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Orthop Translat. 2019;20:94-99. [11] ZHANG H, XU C, ZHANG T, et al. Does Percutaneous Vertebroplasty or Balloon Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Increase the Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures? A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E13-E28. [12] LI M, ZHANG Y, JIN P, et al. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation using drill rotation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral vacuum cleft. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(9):1459-1465. [13] YU W, XU W, JIANG X, et al. Risk Factors for Recollapse of the Augmented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111: 119-129. [14] RABEI R, PATEL K, GINSBURG M, et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Vertebral Compression Fractures: National Trends in the Medicare Population (2005-2015). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 44(2):123-133. [15] 叶林强,卢国樑,江晓兵,等.骨水泥填充位置对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的生物力学特性影响:一项三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4435-4440. [16] 蔡明,戚颖,刘肃,等.骨水泥不同分布对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学影响:三维有限元分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志, 2022,39(6):771-777. [17] HEDAYATI Z, SHOMALI M. Maxillary anterior en masse retraction using different antero-posterior position of mini screw: a 3D finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2016;17(1):31. [18] EL-ANWAR M, GHALI R, ABOELNAGGA M. 3D Finite Element Study on: Bar Splinted Implants Supporting Partial Denture in the Reconstructed Mandible. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2016;4(1):164-171. [19] SHAMAMI DZ, KARIMI A, BEIGZADEH B, et al. A 3D finite element study for stress analysis in bone tissue around single implants with different materials and various bone qualities. J Biom Tissue Eng. 2014;4(8): 632-637. [20] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022; 27(1):142. [21] LU H, ZHANG Q, DING F, et al.Finite Element Analysis of Unilateral versus Bipedicular Bone-Filling Mesh Container for the Management of Osteoporotic Compression Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022: 6850089. [22] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite-element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10):991-996. [23] BAROUD G, NEMES J, HEINI P, et al. Load shift of the intervertebral disc after a vertebroplasty: a finite-element study. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12(4):421-426. [24] YU W, XU W, JIANG X, et al. Risk Factors for Recollapse of the Augmented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111: 119-129. [25] HE D, LOU C, YU W, et al. Cement Distribution Patterns Are Associated with Recompression in Cemented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Retrospective Study. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:e1-e7. [26] WANG D, LI Y, YIN H, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020; 9(3):1062-1072. [27] JANSSEN D, MANN KA, VERDONSCHOT N. Micro-mechanical modeling of the cement-bone interface: the effect of friction, morphology and material properties on the micromechanical response. J Biomech. 2008;41(15):3158-3163. [28] LI YX, GUO DQ, ZHANG SC, et al. Risk factor analysis for re-collapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) or percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP). Int Orthop. 2018;42(9):2131-2139. [29] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):246-256. [30] LIU H, ZHANG J, LIANG X, et al. Distribution Pattern Making Sense: Patients Achieve Rapider Pain Relief with Confluent Rather Than Separated Bilateral Cement in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e1190-e1196. [31] 张大鹏,毛克亚,强晓军,等.椎体增强术后骨水泥分布形态分型及其临床意义[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(2):130-137. [32] HE S, ZHANG Y, LV N, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on clinical efficacy after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(50): e18217. [33] 任学平,杨松涛.基于LS-DYNA和HyperMesh的转炉倾动机构减速器不同步启动仿真[J].机械传动,2015,39(6):88-92. [34] 钟尖,刘唐志,陈柳晓.基于Hypermesh/Ls-Dyna的油桶拦挡安全性能与适用条件研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2015,37(10):51-56. [35] CHEN LH, HSIEH MK, LIAO JC, et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):927-933. [36] ZHAO WT, QIN DP, ZHANG XG, et al. Biomechanical effects of different vertebral heights after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):32. [37] PENG Y, DU X, HUANG L, et al. Optimizing bone cement stiffness for vertebroplasty through biomechanical effects analysis based on patient-specific three-dimensional finite element modeling. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(11):2137-2150. [38] ZHOU F, YANG S, LIU J, et al. Finite element analysis comparing short-segment instrumentation with conventional pedicle screws and the Schanz pedicle screw in lumbar 1 fractures. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(1):301-312. [39] KIM JM, SHIN DA, BYUN DH, et al. Effect of bone cement volume and stiffness on occurrences of adjacent vertebral fractures after vertebroplasty. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012;52(5):435-440. [40] HE SC, TENG GJ, DENG G, et al. Repeat vertebroplasty for unrelieved pain at previously treated vertebral levels with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(6):640-647. |
| [1] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [2] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Yang Wen, Ding Guangjiang, Li Peikun, Xiao Zhongyu, Chen Ying, Fang Xue, Zhang Teng. Dispersion effect of bone cement after vertebroplasty using individualized unilateral external pedicle approach and bilateral pedicle approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 800-808. |
| [4] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [5] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [6] | Su Dejun, Dong Wanpeng, Dong Yuefu, Zhang Jichao, Zhang Zhen. Design of asymmetric prosthesis and mechanical analysis of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 510-516. |
| [7] | Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Lu Ming. Repair strategies for nonunion in old osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a case analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 538-546. |
| [8] | Zhao Yuxin, Liang Liang, Jin Feng, Xu Yangyang, Kang Zhijie, Fang Yuan, He Yujie, Wang Xing, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Establishment and stress analysis of a finite element model for adolescent cervical disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 448-454. |
| [9] | Li Zhenggang, Shang Xuehong, Wu Zhang, Li Hong, Sun Chaojun, Chen Huadong, Sun Zhe, Yang Yi. Finite element analysis of three internal fixation modalities for treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures under different loading conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 455-463. |
| [10] | Liu Mengfei, Chen Gang, Shi Yihan, Zeng Lin, Jiang Kan, Yilihamujiang•Wusiman. Finite element analysis of optimization of femoral prosthesis implantation position in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in osteoporotic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 464-470. |
| [11] | Wang X, Wang Hm, Chen Sh, Feng Tx, Bu Hm, Zhu Lg, Chen Dd, Wei X. Stress and morphological characteristics of intervertebral foramen of cervical rotation-traction manipulation for treating cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 441-447. |
| [12] | Li Zhifei, Yang Yin, Chen Hualong, Liang Qinqiu, Zhong Yuanming, Zhang Yisheng. Finite element analysis of the correlation between tilt angle of titanium cage and postoperative subsidence of titanium cage after anterior subtotal cervical corpectomy, decompression and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1313-1319. |
| [13] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [14] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [15] | Yang Cekai, Cai Zhuoyan, Chen Ming, Liu Hao, Weng Rui, Cui Jianchao, Zhang Shuncong, Yao Zhensong. Relationship between degeneration of paraspinal muscle and refractures in postmenopausal women treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||