Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4757-4762.doi: 10.12307/2023.809
Correlation between CT value of vertebral body partition and bone cement distribution after percutaneous vertebroplasty
Guan Jianbin1, Feng Ningning1, Yu Xing1, 2, Liu Tao1, Jiang Guozheng1, Yang Yongdong2, Zhao He2
- 1Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2022-09-14Accepted:2022-11-16Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-01 -
Contact:Yu Xing, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China -
About author:Guan Jianbin, Doctoral candidate, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China -
Supported by:Weifang Aojing Biomimetic Bone Multi-Center Clinical Research Project, No. HX-DZM-2018010 (to YX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guan Jianbin, Feng Ningning, Yu Xing, Liu Tao, Jiang Guozheng, Yang Yongdong, Zhao He. Correlation between CT value of vertebral body partition and bone cement distribution after percutaneous vertebroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4757-4762.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
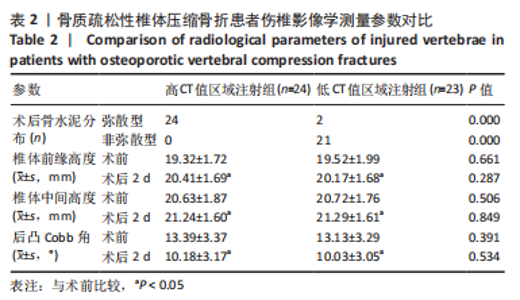
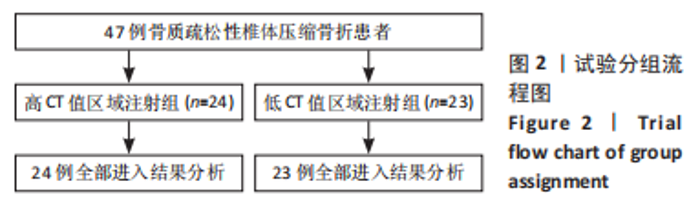
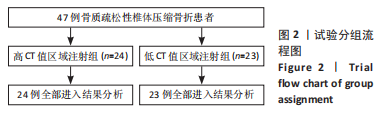
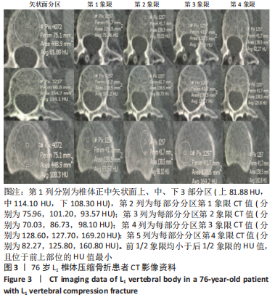
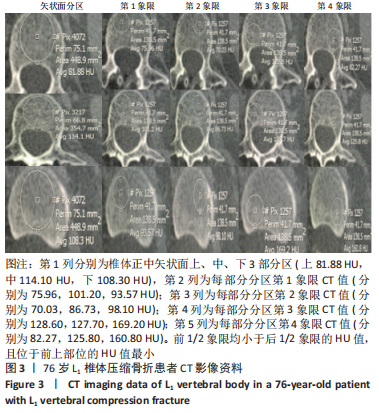
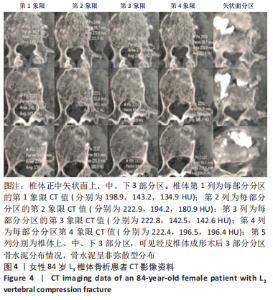
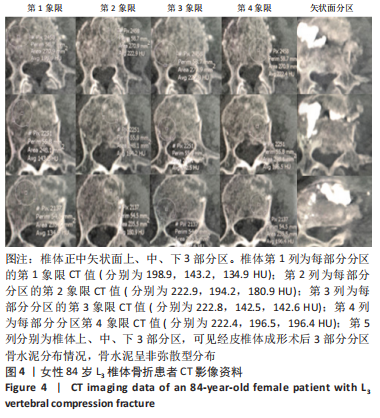
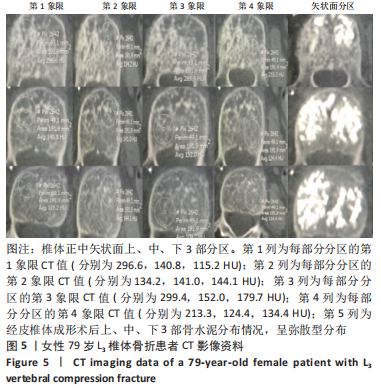
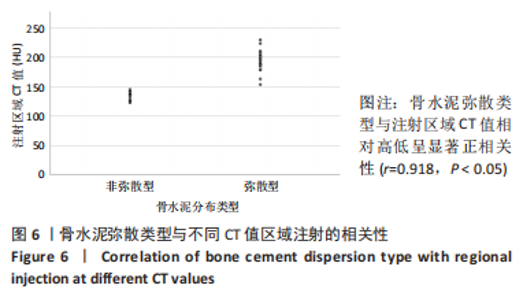
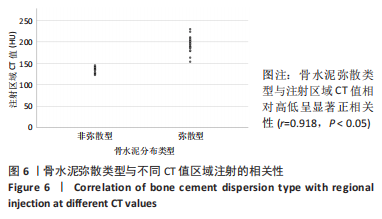
2.4 患者伤椎CT值检测结果 47例骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者,伤椎水平分区CT均值:椎体上1/3部分为(216.7±35.3) Hu,中1/3部分为(169.1±38.2) Hu,下1/3部分为(163.7±40.2) Hu;前后分区CT均值:椎体前半部分为(178.8±35.4) Hu,后半部分为(203.8±33.4) Hu。椎体上1/3部分CT均值显著高于中1/3和下1/3(P均< 0.05),椎体中1/3和下1/3的CT均值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),椎体前半部分CT均值显著低于后半部分(P < 0.05)。 2.5 患者不同区域注入骨水泥的骨水泥分布情况 高CT值区域注射组24例骨水泥分布均为弥散型,低CT值区域注射组骨水泥分布弥散型2例、非弥散型21例,两组间骨水泥分布存在显著差异(P=0.000),见表2。骨水泥分布典型影像资料,见图4,5。"
| [1] YANG EZ, XU JG, HUANG GZ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in aged patients with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective randomized controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(8):653-660. [2] LAINEZ AJ, LOPEZ D, RUIZ F. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment and placebo in osteoporotic vertebral fractures: meta-analysis and critical review of the literature. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(11):8542-8553. [3] PROST S, PESENTI S, FUENTES S, et al. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(1S):102779. [4] CHEN Z, CHEN Z, WU Y, et al. Risk factors of secondary vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: a retrospective study of 650 patients. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9255-9261. [5] RHO YJ, CHOE WJ, CHUN YI. Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):905-911. [6] MO L, WU Z, LIANG D, et al. Influence of bone cement distribution on outcomes following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective matched-cohort study. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(7):3000605211022287. [7] LV B, JI P, FAN X, et al. Clinical Efficacy of Different Bone Cement Distribution Patterns in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty: A Retrospective Study. Pain Physician. 2020;23(4):E409-E416. [8] TAN L, WEN B, GUO Z, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on the outcome of percutaneous Vertebroplasty: a case cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):541. [9] CHEN JB, XIAO YP, CHEN D, et al. Clinical observation of two bone cement distribution modes of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar Kummell’s disease. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):250. [10] PICKHARDT PJ, LEE LJ, DEL RA, et al. Simultaneous screening for osteoporosis at CT colonography: bone mineral density assessment using MDCT attenuation techniques compared with the DXA reference standard. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(9):2194-2203. [11] PAPAIOANNOU A, MORIN S, CHEUNG AM, et al. 2010 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada: summary. CMAJ. 2010;182(17):1864-1873. [12] SCHREIBER JJ, ANDERSON PA, ROSAS HG, et al. Hounsfield units for assessing bone mineral density and strength: a tool for osteoporosis management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(11):1057-1063. [13] MARINOVA M, EDON B, WOLTER K, et al. Use of routine thoracic and abdominal CT scans for assessing bone mineral density and detecting osteoporosis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015;31(10):1871-1881. [14] ZOU D, MUHEREMU A, SUN Z, et al. Computed tomography Hounsfield unit-based prediction of pedicle screw loosening after surgery for degenerative lumbar spine disease. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020:1-6.doi: 10.3171/2019.11.SPINE19868. [15] 廖亦佳,舒启航,王程.胸腰椎骨折三维有限元模型构建的研究进展[J].中南医学科学杂志,2022,50(1):153-156. [16] WONG CP, GANI LU, CHONG LR. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry bone densitometry and pitfalls in the assessment of osteoporosis: a primer for the practicing clinician. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):135. [17] 王晨光,肖湘生,陈星荣,等.人腰椎体标本的区域骨密度分布特征[J].中华放射学杂志,1998,32(8):53-56. [18] 刘云,李培岭,郭永杰,等.中老年骨质疏松症患者腰1-3椎体骨密度值与CT值相关性研究[J].风湿病与关节炎,2021,10(6):29-31. [19] JOHANNESDOTTIR F, ALLAIRE B, KOPPERDAHL DL, et al. Bone density and strength from thoracic and lumbar CT scans both predict incident vertebral fractures independently of fracture location. Osteoporos Int. 2021;32(2): 261-269. [20] ROSKI F, HAMMEL J, MEI K, et al. Opportunistic osteoporosis screening: contrast-enhanced dual-layer spectral CT provides accurate measurements of vertebral bone mineral density. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(5):3147-3155. [21] ZHANG X, ZHU CX, HE JQ, et al. Correlation of CT Values and Bone Mineral Density in Elderly Chinese Patients with Proximal Humeral Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(8):2271-2279. [22] 杨欣建,王正国,朱佩芳,等.胸腰段脊柱爆裂骨折瞬态损伤机制及节段稳定性研究[J].中华创伤杂志,1999,15(2):103-106. [23] GERETY EL, BEARCROFT PW. L1 vertebral density on CT is too variable with different scanning protocols to be a useful screening tool for osteoporosis in everyday practice. Br J Radiol. 2018;91(1084):20170395. [24] ABBOUCHIE H, RAJU N, LAMANNA A, et al. Screening for osteoporosis using L1 vertebral density on abdominal CT in an Australian population. Clin Radiol. 2022;77(7):e540-e548. [25] ZOU D, YE K, TIAN Y, et al. Characteristics of vertebral CT Hounsfield units in elderly patients with acute vertebral fragility fractures. Eur Spine J. 2020; 29(5):1092-1097. [26] DE NEGRI P, TIRRI T, PATERNOSTER G, et al. Treatment of painful osteoporotic or traumatic vertebral compression fractures by percutaneous vertebral augmentation procedures: a nonrandomized comparison between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Clin J Pain. 2007;23(5):425-430. [27] FILIPPIADIS DK, MARCIA S, MASALA S, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Current Status, New Developments and Old Controversies. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40(12):1815-1823. [28] WANG B, ZHAO CP, SONG LX, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):264. [29] ZHANG H, XU C, ZHANG T, et al. Does Percutaneous Vertebroplasty or Balloon Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Increase the Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures? A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E13-E28. [30] LI Y, FENG X, PAN J, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in Patients with Distant Lumbosacral Pain. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E349-E356. [31] ROUSING R, KIRKEGAARD AO, NIELSEN M, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty as treatment of malignant vertebral lesions: a systematic review and GRADE evaluation resulting in a Danish national clinical guideline. Eur Spine J. 2020; 29(7):1573-1579. [32] KYRIAKOU C, MOLLOY S, VRIONIS F, et al. The role of cement augmentation with percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures in multiple myeloma: a consensus statement from the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG). Blood Cancer J. 2019;9(3):27. [33] WANG H, SRIBASTAV SS, YE F, et al. Comparison of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Single Level Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Meta-analysis of the Literature. Pain Physician. 2015;18(3):209-222. [34] LI W, WANG J, LIU W, et al. Machine Learning Applications for the Prediction of Bone Cement Leakage in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty. Front Public Health. 2021;9:812023. [35] XIE L, ZHAO ZG, ZHANG SJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: An updated meta-analysis of prospective randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2017;47:25-32. [36] DAI SQ, QIN RQ, SHI X, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty for the treatment of neurologically intact osteoporotic Kümmell’s disease. BMC Surg. 2021;21(1):65. [37] STEVENSON M, GOMERSALL T, LLOYD JONES M, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(17):1-290. [38] ZUO XH, ZHU XP, BAO HG, et al. Network meta-analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty, nerve block, and conservative treatment for nonsurgery options of acute/subacute and chronic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in short-term and long-term effects. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(29):e11544. [39] XIE LL, CHEN XD, YANG CY, et al. Efficacy and complications of 125I seeds combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for metastatic spinal tumors: A literature review. Asian J Surg. 2020;43(1):29-35. [40] SEMAAN H, OBRI T, BAZERBASHI M, et al. Clinical outcome and subsequent sequelae of cement extravasation after percutaneous kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: a comparative review. Acta Radiol. 2018;59(7):861-868. [41] WU XF, PING Y, ZENG XQ, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Side-Opening Cannula or Front-Opening Cannula in the Treatment of Kummell Disease? Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1190-1198. [42] GRIFFONI C, LUKASSEN JNM, BABBI L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective randomized comparison. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7):1614-1620. [43] 徐宝山,胡永成,闫广辉,等.经皮椎体成形术和后凸成形术的相关问题探讨[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(5):430-435. [44] PARK J S, PARK YS. Survival analysis and risk factors of new vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Spine J. 2021;21(8):1355-1361. [45] 周永春,肖培芬,罗婧,等.椎体骨密度与PVP骨水泥弥散体积的关系[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(1):9-12. [46] LEE BG, CHOI JH, KIM DY, et al. Risk factors for newly developed osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures following treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine J. 2019;19(2):301-305. [47] SUN G, TANG H, LI M, et al. Analysis of risk factors of subsequent fractures after vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(6):1339-1345. [48] ZHANG T, WANG Y, ZHANG P, et al. What Are the Risk Factors for Adjacent Vertebral Fracture After Vertebral Augmentation? A Meta-Analysis of Published Studies. Global Spine J. 2022;12(1):130-141. [49] YI X, LU H, TIAN F, et al. Recompression in new levels after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty compared with conservative treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(1):21-30. [50] WANG M, WU Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Application of Dual-Energy Spectral Computed Tomography in Bone Mineral Density Measurement: Phantom and Clinical Research. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15(29):6887-6896. [51] JANG S, GRAFFY PM, ZIEMLEWICZ TJ, et al. Opportunistic Osteoporosis Screening at Routine Abdominal and Thoracic CT: Normative L1 Trabecular Attenuation Values in More than 20 000 Adults. Radiology. 2019;291(2): 360-367. |
| [1] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [3] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [4] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [5] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [6] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [7] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [8] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| [9] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [10] | Zhang Lichuang, Yang Wen, Ding Guangjiang, Li Peikun, Xiao Zhongyu, Chen Ying, Fang Xue, Zhang Teng. Dispersion effect of bone cement after vertebroplasty using individualized unilateral external pedicle approach and bilateral pedicle approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 800-808. |
| [11] | Liu Mengfei, Chen Gang, Shi Yihan, Zeng Lin, Jiang Kan, Yilihamujiang•Wusiman. Finite element analysis of optimization of femoral prosthesis implantation position in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in osteoporotic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 464-470. |
| [12] | Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Ran Dongcheng, Xu Jiamu, Wu Wangxiang, Xu Jiafu, Chen Jingjing, Jiang Guangfu, Wang Chunqing. Ferroptosis and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 554-562. |
| [13] | Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Lu Ming. Repair strategies for nonunion in old osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a case analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 538-546. |
| [14] | Du Zhongqiu, Qi Xiaoyang, Yang Ping, Yu Jianglin, Chen Yixin, Zhang Linjian, Qiu Xusheng. Effects of the prolyl hydroxylase 2 inhibitor cpd17 on mouse osteogenic precursor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 238-244. |
| [15] | Hou Chengzhi, Han Jiatong, Wei Guangcheng, Zhuo Zechuan, Li Qiuyue, Zhao Yong, Yu Zhangjingze . Gushukang interferes with osteoclasts: activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 regulates the c-Fos/NFATc1 pathway in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 279-285. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||