Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (22): 3565-3570.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3184
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application
Chen Song1, He Yuanli2, Xie Wenjia1, Zhong Linna1, Wang Jian1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, 2Department of Conservative and Endodontic Dentisty, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-06-13Revised:2020-06-17Accepted:2020-07-20Online:2021-08-08Published:2021-01-21 -
Contact:Wang Jian, MD, Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Chen Song, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Project), No. 81771122(to WJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570.
share this article
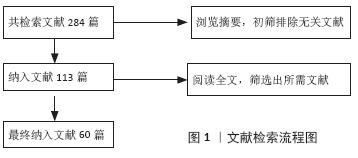
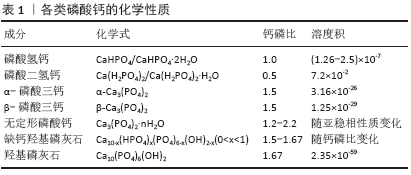
2.2 磷酸钙纳米颗粒的种类及特性 磷酸钙类药物递送体系是以磷酸钙纳米颗粒为载体,抗生素、金属离子、蛋白质及核酸分子等各类药物通过吸附、化学结合、静电吸引等方式结合在载体上,从而构成的纳米复合物。在不同反应条件下(温度、湿度、钙磷比等)可以制备出多种磷酸钙晶体,但它们所表现出的生物相容性和降解性各有不同。在众多的磷酸钙晶体中,磷酸二氢钙和磷酸氢钙具有较高的溶解度,在体液环境中会发生迅速溶解并局部释放过多的钙磷离子,导致明显的细胞毒性。另一些溶解度较小的磷酸钙纳米颗粒如羟基磷灰石、α-磷酸三钙、β-磷酸三钙、无定形磷酸钙及双相磷酸钙等,表现出更好的生物相容性[1]。缺钙羟基磷灰石的钙磷比大部分介于1.50-1.67之间,成分构成复杂,但与骨磷灰石的成分组成十分接近[2],因而具有优秀的成骨活性与骨黏结性,并常常用于植入材料中以促进骨修复。具有相似成分的β-磷酸三钙和无定形磷酸钙同样表现出了极大的潜力,其中β-磷酸三钙因溶解度高于羟基磷灰石,被称为生物可吸收性陶瓷。此外,近年来为了更好地控制磷酸钙的降解性能,由β-磷酸三钙和羟基磷灰石按不同比例组合而成的双相磷酸钙开始被研究并应用于骨组织工程领域[3]。上述各类磷酸钙的化学性质已总结在表1中。 基于磷酸钙纳米颗粒的上述性质,当其用于药物递送时常常可表现出下列特性:①良好的生物相容性和降解性:与其他无机粒子不同,磷酸钙类纳米颗粒的成分与天然骨和牙釉质的无机成分十分相似,能在体液环境中缓慢降解并释放出钙离子和磷酸根离子,因为这两种离子在血液中天然含量较高(1- 5 mmol/L),所以磷酸钙降解带来的离子释放不易激起免疫反应。②可控的粒径:不同的钙磷比和合成条件可以制备出粒径各异的磷酸钙纳米颗粒。BOHNER等[4]发现通过化学沉积法可制备直径10-300 nm的磷酸钙纳米颗粒,而利用挤压成形等方法则可获得直径超100 μm的磷酸钙微球。③高比表面积:通过调整钙磷比、反应温度和时间可制得高比表面积的磷酸钙纳米颗粒,进而优化载药效率[5-6]。④温和的制备条件:以蛋白类生长因子、脱氧核糖核酸、核糖核酸等为代表的生物活性分子,多具有较大的分子质量和较为复杂的分子结构,容易在高温、强酸碱及富含酶的环境中失活,因此温和条件下合成的药物递送系统更加有利于保护药物活性,提高相对负载效率。磷酸钙纳米颗粒可以在温和的条件下(水溶剂、非高温、适中的pH值等)通过水热法、沉积法等相对简单的方法有效合成,为其有效保护负载药物的活性提供了有利条件[4,7]。⑤pH值响应性:炎症组织、肿瘤组织的局部pH值通常低于正常组织(pH<5)[8],溶酶体、内涵体等细胞器内的pH值也明显低于膜外体液[9]。磷酸钙在pH≈7.4的生理环境中溶解度较低,但在弱酸性环境中溶解度逐渐变高,降解速度加快[10],这一特性为其作为pH值响应性药物递送系统实现靶向给药提供了可能性。 2.3 磷酸钙载药机制 磷酸钙纳米颗粒作为核心主要通过氢键作用与静电吸引作用与药物分子结合,并达到高效吸附并长期缓释的效果。据DONG等[11]的研究,骨形成蛋白2可通过羟基、氨基和羧基这3个活性功能基团与羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒相连接,库仑力和氢键作用在其中具有重要作用;同时这种吸附-解吸过程会根据蛋白质的不同而改变:如果某一侧具有多组吸收基团位点,那么该过程可能是分步进行的;而如果只有一个吸附位点,那么这个过程只存在一个关键吸附期。XIE等[12]在研究中发现,骨形成蛋白2通过静电吸附于羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒后可在37 ℃的生理盐水中长效缓释超15 d;类似地,当磷酸钙纳米颗粒作为核酸分子载体时,小分子核酸主要通过静电吸引力和沟槽结合作用与之相连[13]。根据SOKOLOVA等[14]的研究,制备负载脱氧核糖核酸的磷酸钙纳米颗粒时,水溶液中的钙离子与脱氧核糖核酸中的磷酸根通过静电作用相结合,使得脱氧核糖核酸分子最终吸附于磷酸钙纳米颗粒表面。 此外在药物负载过程中,磷酸钙纳米颗粒的比表面积、粒径大小及特殊结合位点都会对其效率产生影响。在RAO等[15]的研究中,与羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒相比,拥有更高比表面积的双相磷酸钙纳米颗粒表面能够吸附更多的骨形成蛋白2。RAO等认为更大的比表面积可能带来了更多的吸附位点,以提供给蛋白分子与载体更多的反应机会,从而获得了更大的负载效率。ZHOU等[16]制备了高比表面积的羟基磷灰石纳米微球,显著提高了骨形成蛋白2的负载效率并有效降低了其初始阶段的爆发性释放,羟基磷灰石纳米球(80-150 nm)的骨形成蛋白2负载能力明显高于微球(75-100μm),同时证明了磷酸钙纳米颗粒粒径对于其药物负载的重要意义。当四环素类药物负载于磷酸钙颗粒时,除氢键和静电吸附力外还可与钙离子发生螯合,这可能与其表面的β-二酮、烯醇、酰胺基团相关[17]。 2.4 磷酸钙纳米颗粒药物递送体系的应用 2.4.1 促成骨分化与血管化 在骨缺损区域,新骨形成区域需要足够的成骨细胞分化与血管生成,以支持局部骨基质的快速合成、分泌与矿化,进而获得新生骨组织。虽然磷酸钙纳米颗粒自身已经显示出一定程度促进成骨的潜力[18],但加入促成骨与血管化的生长因子可以进一步增强磷酸钙的生物功能。例如,骨形成蛋白家族、转化生长因子β、血小板源性生长因子、血管内皮生长因子等可有效促进成骨细胞增殖、分化及诱导血管生成,此类生长因子大多为蛋白质,拥有复杂的空间结构与较大的分子质量,易在强酸强碱、高温等环境中失活,因此将此类药物负载于磷酸钙纳米颗粒上时需注意保持相对温和的环境,以保存其生物活性。在体内外实验中,有效负载并缓释骨形成蛋白2的磷酸钙纳米颗粒均展现出了优秀的骨诱导性,有效促进了前成骨细胞的增殖、分化及骨缺损的修复[16,19-21]。WANG等[21]将骨形成蛋白2负载于纳米双相磷酸钙纳米颗粒上,可持续释放达35 d并在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中取得优秀的成骨效果;同时,骨形成蛋白2的负载还可提高双相磷酸钙的降解效率,增强其生物相容性。在LI等[22]的研究中,骨形成蛋白2更易吸附于疏水和粗糙的表面,但材料的比表面积对蛋白吸附的影响大于其疏水性,该结果可能与骨形成蛋白2表面的色氨酸和酪氨酸残基有关。局部血管再生是骨缺损修复不可或缺的一环,随着研究者对于促进骨缺损区域血管化的深入研究,血管内皮生长因子作为促血管生成的代表性的生长因子也被负载于磷酸钙纳米颗粒上,用于促进血管再生和骨形成[23-25]。SCHUMACHER等[24]在制备磷酸钙纳米颗粒时通过加入不同含量介孔生物玻璃改变其孔隙率,进而提高了血管内皮生长因子的负载与释放效率,增强了人成骨肉瘤细胞的代谢活性。BEDELOGLU等[26]将血管内皮生长因子与双相磷酸钙混合后用于大鼠股骨的大体积缺损处,有效促进了骨缺损的修复。 2.4.2 抑制破骨 在骨再生研究中骨质疏松为临床治疗提出了巨大的挑战,而双膦酸盐类药物至今仍是预防和治疗骨质疏松症等骨质流失疾病的主要工具,常用的双膦酸盐类药物有阿仑膦酸钠、利塞膦酸钠等,他们主要通过抑制破骨细胞的活性来减少骨质吸收[27]。尽管长期的临床试验表明双膦酸盐是一类相对安全的药物,但是其长期全身应用可能导致非典型骨吸收、骨坏死及应力性骨折等严重并发症[28]。将磷酸钙纳米颗粒负载双膦酸盐并局部应用已被证明可提高药物治疗效果,并减少非靶向区的不良反应[29-30]。在构建磷酸钙/双膦酸盐载药体系时,常用的方法仍是化学吸附法和共沉淀法。PAULO等[31]使用化学吸附法将唑仑膦酸钠负载于双相磷酸钙,可显著降低唑仑膦酸钠对人牙龈成纤维细胞的毒性。类似地,SUN等[32]将阿仑膦酸钠负载于多孔的无定形磷酸钙纳米颗粒上获得了良好的生物相容性,并使得药物可缓释超22 d。因为双膦酸盐类药物对钙离子具有高亲和力,所以共沉淀法制备的载药体系会拥有更高的药物负载效率和更缓慢的释放速率[33],然而这种高亲和力可能也会带来问题,如形成的双膦酸钙复合物可能会影响磷酸钙自身的沉积和结晶过程。为了避免此过程对羟基磷灰石沉积的影响,BOANINI等[34]在晶体成核过程开始后再加入阿仑膦酸钠成功制备了羟基磷灰石/阿仑膦酸钠复合体,并有效降低骨溶解、促进骨矿化沉积。 2.4.3 抗菌 如何有效抑制局部细菌感染是骨组织工程研究中不可回避的问题之一。无论是外科创伤还是骨移植手术所带来的骨组织暴露,均会增加局部骨创感染的概率。常见的骨感染大多是由金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞杆菌等机会致病菌引起,传统治疗方法多采取口服或全身注射抗生素[35-36],但全身使用抗生素不可避免地会造成较大的肝肾代谢负担,增大了耐药菌株形成的可能性及发生药物并发症的风险[36]。因此,局部使用抗菌药物看起来是一个更为精准且代价更小的治疗方式。磷酸钙纳米颗粒因其良好的生物相容性和抗菌活力已被广泛应用于局部抗菌,特别是在骨组织手术的区域[37]。部分学者利用锌、银、铜等金属离子置换磷酸钙纳米颗粒中的钙离子,通过金属离子在骨创微环境中的释放,从而抑制细菌的生长与生物膜的形成[38-39],然而这类纳米颗粒常常会引起局部金属离子浓度过高,导致较大的细胞毒性。为此,更多学者更加倾向于将抗生素负载于磷酸钙纳米颗粒上,使其在术区缓慢释放,以确保局部药物浓度达到足够抗菌效果的同时尽可能降低其带来的毒副作用[40]。到目前为止,抗生素被负载于各类磷酸钙纳米颗粒上展现出了优秀的抗菌性能,常用载药方法是吸附法和共沉淀法,二者皆可获得较好的负载率和释放效果,但抗生素种类、磷酸钙晶体种类、比表面积及纳米颗粒形态等因素会影响载药率和释放曲线。USKOKOVIC[41]将万古霉素和环丙沙星负载于无定形羟基磷灰石和晶体羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒上,发现无定形羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒中的万古霉素释放更快,而晶体羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒中的环丙沙星释放更快。USKOKOVIC等[42]在另一项研究中发现,比表面积最大的球形磷酸钙纳米颗粒具有最大的药物负载和释放量,可在21 d中持续释放克林霉素,并表现出最强的抗菌活性。CHOPRA等[17]通过改变羟基磷灰石的粒径及质量比可有效调整万古霉素和环丙沙星的释放动力学。此外在抗生素负载体系中,四环素类药物较特殊,除了常见的氢键作用和范德华力的作用,四环素类药物还可与磷酸钙纳米颗粒中的钙离子发生螯合,这可能与其表面的β-二酮、烯醇、酰胺基团相关。MADHUMATHI等[43]研究发现,当四环素负载于羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒时更高的比表面积并不能带来更高的载药量,与钙离子的螯合作用可能对于该过程的影响更大。 2.4.4 骨免疫调节 近年来的研究人员发现,免疫系统与骨骼系统间存在诸多关联,如两系统的关键细胞的直接相互作用,转录因子、细胞因子、受体之间发生的间接联系[44]。上述这类联系与调控在免疫系统和骨骼系统中均发挥着重要作用,因而诞生了一门新兴的学科——骨免疫学[45]。随着免疫调节作用对成骨过程的重要性逐渐被认识,部分学者不再仅仅追求刺激前成骨细胞的增殖分化,而是希望开发出骨免疫调节特性的生物材料应用于骨组织工程[46]。 随着骨免疫相关研究的兴起,磷酸钙类材料已被发现具有显著的免疫调节功能。WANG等[47]研究发现,双相磷酸钙颗粒及其降解产物可促进巨噬细胞分泌炎性细胞因子(如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、单核细胞趋化因子1等)和生长因子(血小板源性生长因子、血管内皮生长因子等),在间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨分化中发挥着积极作用。类似地,磷酸钙陶瓷可导致巨噬细胞向材料植入区域浸润,进而诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的归巢和异位骨生成[48]。鉴于磷酸钙自身的免疫调节性能,部分学者尝试将非类固醇类抗炎药负载其上,协同调节损伤区域的骨修复与重建。ZARINS等[49]将锶负载于双相磷酸钙颗粒上,可明显上调骨形成蛋白2/4、白细胞介素1等细胞因子,在家兔骨质疏松模型中展现出优秀的抗炎及促成骨作用。白细胞介素1的高表达可加速局部损伤区域的骨改建过程,同时还可以通过促进成骨细胞增殖,影响骨折愈合过程[50]。 2.4.5 基因治疗 为了解决蛋白类生长因子在局部环境中低存留率和高需求量等问题,基因治疗可能是一种更好的替代方案,能够在骨损伤部位提供可控且持续的蛋白释放以促进骨组织愈合。然而核酸分子极易被组织液或血浆内的核酸酶降解,导致基因传递的效率低下[51];此外,核酸分子表面所带负电荷会导致细胞膜的静电排斥,进一步降低转染效率[52]。因此,一种合适的基因运载系统对于基因治疗的应用具有重要意义。载体的表面电荷对其入胞效率具有重要影响,无机金属化合物纳米颗粒表面常常带正电,可显著提高其负载核酸分子的转染效率[14]。不同于其他无机载体,磷酸钙拥有良好的生物相容性和降解性、较高的负载效率及其介导的溶酶体逃逸效应等优势,已被研究人员广泛应用于基因治疗领域[53-54]。 CHERNOUSOVA等[55]将编码骨形成蛋白7和血管内皮生长因子A的质粒脱氧核糖核酸负载于磷酸钙纳米颗粒上,转染效果优于商用的脂质体转染试剂Lipofectamine? 2000。TENKUMO等[56]通过脱氧核糖核酸和鱼精蛋白功能化修饰磷酸钙纳米颗粒,显著改善了转染率,并取得了优秀的促成骨效果,然而,磷酸钙载体的早期降解可能导致转染效率下降,因此部分学者设计了多层壳核结构的磷酸钙纳米颗粒,可有效减缓其降解速率并保护搭载的脱氧核糖核酸分子[1]。此外,有报道称多层外壳的保护还可保证核酸分子持续缓释并长期稳定贮存长达两三个月[37]。 不同于脱氧核糖核酸需要进入细胞核才能发挥作用的机制,核糖核酸分子在细胞质内通过转录后水平调控基因的表达可以避免插入突变的风险,核糖核酸调控可能是一种更安全、更可行的基因治疗方案[57]。但是与双链结构的脱氧核糖核酸分子相比,单链核糖核酸分子极不稳定且更易被酶解,使其难以在胞内达到有效丰度[57-58]。磷酸钙纳米颗粒载体可显著提高核糖核酸的胞内含量,保证其发挥调控作用,例如,MENCIA CASTA?O等[59]将微小核糖核酸133a拮抗剂负载于羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒上,显著促进了人间充质干细胞成骨向增殖与分化;LEE等[60]通过搅拌混合法将编码骨形成蛋白2的质粒和微小核糖核酸148b共同负载于双相磷酸钙纳米颗粒上,通过CD44介导的内吞作用提高了入胞效率,显著上调骨形成蛋白2蛋白的表达并促进成骨细胞分化。"
| [1] BOSE S, TARAFDER S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: a review. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(4):1401-1421. [2] LEGEROS, ZAPANTA R. Calcium phosphate-based osteoinductive materials. Chem Rev. 2008;108(11):4742-4753. [3] EBRAHIMI M, BOTELHO M, LU W, et al. Synthesis and characterization of biomimetic bioceramic nanoparticles with optimized physicochemical properties for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019; 107(8):1654-1666. [4] BOHNER M, TADIER S, VAN GARDEREN N, et al. Synthesis of spherical calcium phosphate particles for dental and orthopedic applications. Biomatter. 2013;3(2):e25103. [5] CAO X, WANG G, WANG K, et al. Organic phosphorous and calcium source induce the synthesis of yolk-shell structured microspheres of calcium phosphate with high-specific surface area: Application in hel adsorption. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020;15(1):69. [6] MAAZOUZ Y, RENTSCH I, LU B, et al. In vitro measurement of the chemical changes occurring within beta-tricalcium phosphate bone graft substitutes. Acta Biomater. 2020;102:440-457. [7] MAURO VD, IAFISCO M, SALVARANI N, et al. Bioinspired negatively charged calcium phosphate nanocarriers for cardiac delivery of micrornas. Nanomedicine. 2016;11(8):891-906. [8] DEGLI ESPOSTI L, CARELLA F, ADAMIANO A, et al. Calcium phosphate-based nanosystems for advanced targeted nanomedicine. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(8):1223-1238. [9] 程映,余冰琼,刘艳红,等.用于细胞成像的溶酶体ph荧光探针研究进展[J].武汉大学学报(理学版),2018,64(4):283-294. [10] HE Y, ZENG B, LIANG S, et al. Synthesis of ph-responsive biodegradable mesoporous silica-calcium phosphate hybrid nanoparticle as a high potential drug carrier. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:44402-44409. [11] DONG X, WANG Q, WU T, et al. Understanding adsorption-desorption dynamics of bmp-2 on hydroxyapatite (001) surface. Biophys J. 2007; 93(3):750-759. [12] XIE G, SUN J, ZHONG G, et al. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a controlled-release carrier of bmp-2: absorption and release kinetics in vitro. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(6):1875-1880. [13] BANIK M, BASU T. Calcium phosphate nanoparticles: A study of their synthesis, characterization and mode of interaction with salmon testis DNA. Dalton Trans. 2014;43(8):3244-3259. [14] SOKOLOVA V, EPPLE M. Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers of nucleic acids into cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47(8):1382-1395. [15] RAO H, LU Z, LIU W, et al. The adsorption of bone-related proteins on calcium phosphate ceramic particles with different phase composition and its adsorption kinetics. Surf Interface Anal. 2016;48(10):1048-1055. [16] ZHOU P, WU J, XIA Y, et al. Loading bmp-2 on nanostructured hydroxyapatite microspheres for rapid bone regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:4083-4092. [17] CHOPRA I. Tetracycline antibiotics : Mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001;65(2):232-260. [18] 张亚楠,严霞,孟增东. Zn、mg增强羟基磷灰石骨修复材料临床应用与机制:生物活性及成骨诱导的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):606-611. [19] LEE GH, MAKKAR P, PAUL K, et al. Development of bmp-2 immobilized polydopamine mediated multichannelled biphasic calcium phosphate granules for improved bone regeneration. Mater Lett. 2017;208:122-125. [20] LEE GH, MAKKAR P, PAUL K, et al. Incorporation of bmp-2 loaded collagen conjugated bcp granules in calcium phosphate cement based injectable bone substitutes for improved bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77:713-724. [21] WANG D, TABASSUM A, WU G, et al. Bone regeneration in critical-sized bone defect enhanced by introducing osteoinductivity to biphasic calcium phosphate granules. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(3):251-260. [22] LI X, LIU M, CHEN F, et al. Design of hydroxyapatite bioceramics with micro-/nano-topographies to regulate the osteogenic activities of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and bone marrow stromal cells. Nanoscale. 2020;12(13):7284-7300. [23] STEGEN S, VAN GASTEL N, CARMELIET G. Bringing new life to damaged bone: the importance of angiogenesis in bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 2015;70:19-27. [24] SCHUMACHER M, REITHER L, THOMAS J, et al. Calcium phosphate bone cement/mesoporous bioactive glass composites for controlled growth factor delivery. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(3):578-588. [25] MLLER-SIEGERT J, PARMENTIER J, LAQUERRIèRE P, et al. Physicochemical regulation of tgf and vegf delivery from mesoporous calcium phosphate bone substitutes. Nanomedicine. 2017;12(15):1835-1850. [26] BEDELOGLU E, ERSANLI S, ARISAN V. Vascular endothelial growth factor and biphasic calcium phosphate in the endosseous healing of femoral defects: An experimental rat study. J Dent Sci. 2017;12(1):7-13. [27] 付福建,郑周海,史晓红,等.双膦酸盐诱导破骨细胞凋亡的作用机理研究[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2019,38(10):4726-4731. [28] GIGER EV, CASTAGNER B, LEROUX JC. Biomedical applications of bisphosphonates. J Control Release. 2013;167(2):175-188. [29] BIGI A, BOANINI E. Calcium phosphates as delivery systems for bisphosphonates. J Funct Biomater. 2018;9(1):6. [30] ROOHANI-ESFAHANI SI, ZREIQAT H. Nanoparticles: a promising new therapeutic platform for bone regeneration? Nanomedicine. 2017; 12(5):419-422. [31] PAULO S, LARANJO M, ABRANTES AM, et al. Synthetic calcium phosphate ceramics as a potential treatment for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Materials. 2019;12(11):1840. [32] SUN R, AHLEN M, TAI CW, et al. Highly porous amorphous calcium phosphate for drug delivery and bio-medical applications. Nanomaterials . 2019;10(1):20. [33] NEAMTU J, BUBULICA MV, ROTARU A, et al. Hydroxyapatite–alendronate composite systems for biocompatible materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;127(2):1567-1582. [34] BOANINI E, GAZZANO M, RUBINI K, et al. Composite nanocrystals provide new insight on alendronate interaction with hydroxyapatite structure. Adv Mater. 2007;19(18):2499-2502. [35] SPELLBERG B, LIPSKY BA. Systemic antibiotic therapy for chronic osteomyelitis in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(3):393-407. [36] LI HK, ROMBACH I, ZAMBELLAS R, et al. Oral versus intravenous antibiotics for bone and joint infection. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(5): 425-436. [37] TURON P, DEL VALLE L, ALEMáN C, et al. Biodegradable and biocompatible systems based on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Appl Sci. 2017;7(1):60. [38] POPA CL, DENIAUD A, MICHAUD-SORET I, et al. Structural and biological assessment of zinc doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J Nanomater. 2016;(1): 1-10. [39] SHANMUGAM S, GOPAL B. Copper substituted hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial properties. Ceramics International. 2014;40(10):15655-15662. [40] POUNTOS I, GEORGOULI T, BIRD H, et al. The effect of antibiotics on bone healing: Current evidence. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011;10(6): 935-945. [41] USKOKOVIC V. Mechanism of formation governs the mechanism of release of antibiotics from calcium phosphate nanopowders and cements in a drug-dependent manner. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(25): 3982-3992. [42] USKOKOVIC V, BATARNI SS, SCHWEICHER J, et al. Effect of calcium phosphate particle shape and size on their antibacterial and osteogenic activity in the delivery of antibiotics in vitro. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(7):2422-2431. [43] MADHUMATHI K, RUBAIYA Y, DOBLE M, et al. Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and bone-regenerative dual-drug-loaded calcium phosphate nanocarriers—in vitro and in vivo studies. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018;8(5):1066-1077. [44] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: Evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(10):626-642. [45] 刘伟,宋慧,董鹏.骨免疫学研究进展[J].骨科临床与研究杂志, 2020,5(2):124-126. [46] CHEN Z, KLEIN T, MURRAY RZ, et al. Osteoimmunomodulation for the development of advanced bone biomaterials. Materials Today. 2016; 19(6):304-321. [47] WANG J, LIU D, GUO B, et al. Role of biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic-mediated secretion of signaling molecules by macrophages in migration and osteoblastic differentiation of mscs. Acta Biomater. 2017; 51:447-460. [48] WANG M, CHEN F, WANG J, et al. Calcium phosphate altered the cytokine secretion of macrophages and influenced the homing of mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(29):4765-4774. [49] ZARINS J, PILMANE M, SIDHOMA E, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation after sr-enriched biphasic ceramic implantation in rabbits femoral neck: Comparison of seven different bone conditions. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(8):119. [50] LANGE J, SAPOZHNIKOVA A, LU C, et al. Action of il-1beta during fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(6):778-784. [51] XU ZP, ZENG QH, LU GQ, et al. Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers for efficient cellular delivery. Chem Eng Sci. 2006;61(3):1027-1040. [52] TAI W. Chemical modulation of sirna lipophilicity for efficient delivery. Journal of Controlled Release. 2019;307:98-107. [53] LIU J, LI L, ZHANG R, et al. Development of cap nanocomposites as photothermal actuators for doxorubicin delivery to enhance breast cancer treatment. J Mater Sci Technol. 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.02.029 [54] QADIR A, GAO Y, SURYAJI P, et al. Non-viral delivery system and targeted bone disease therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):565. [55] CHERNOUSOVA S, KLESING J, SOKLAKOVA N, et al. A genetically active nano-calcium phosphate paste for bone substitution, encoding the formation of bmp-7 and vegf-a. RSC Advances. 2013;3(28):11155. [56] TENKUMO T, VANEGAS SAENZ JR, TAKADA Y, et al. Gene transfection of human mesenchymal stem cells with a nano-hydroxyapatite-collagen scaffold containing DNA-functionalized calcium phosphate nanoparticles. Genes Cells. 2016;21(7):682-695. [57] KELLY DC, RAFTERY RM, CURTIN CM, et al. Scaffold-based delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics for enhanced bone and cartilage repair. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(8):1671-1680. [58] PATEL S, ATHIRASALA A, MENEZES PP, et al. Messenger rna delivery for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(1-2):91-112. [59] MENCIA CASTAÑO I, CURTIN CM, DUFFY GP, et al. Next generation bone tissue engineering: Non-viral mir-133a inhibition using collagen-nanohydroxyapatite scaffolds rapidly enhances osteogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27941. [60] LEE JE, YIN Y, LIM S Y, et al. Enhanced transfection of human mesenchymal stem cells using a hyaluronic acid/calcium phosphate hybrid gene delivery system. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(5):798. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [4] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [5] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [6] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [7] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [8] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [9] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [10] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [11] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [12] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [13] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [14] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [15] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||