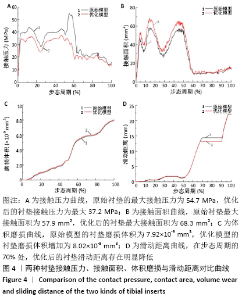
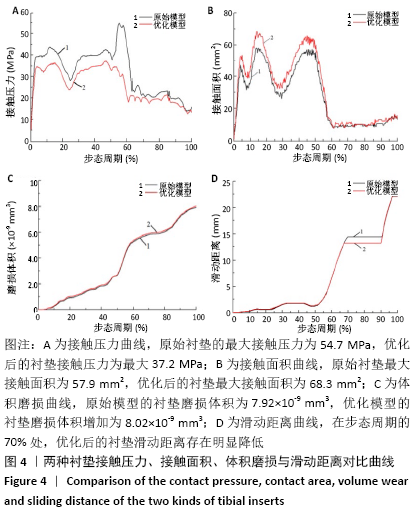
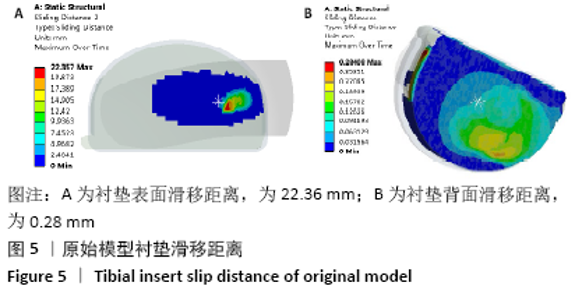
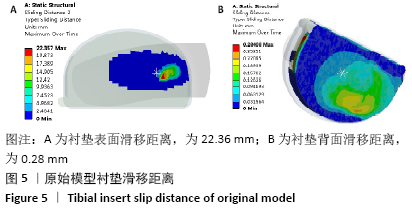
[1] SUGGS JF, LI G, PARK SE, et al. Knee biomechanics after UKA and its relation to the ACL--a robotic investigation.Orthop Res. 2006;24: 588-594.
[2] NEWMAN J, PYDISETTY RV, ACKROYD C. Unicompartmental or total knee replacement: the 15-year results of a prospective randomised controlled trial.J Bone Joint Surg. 2009;91:52-57.
[3] O’DONNELL T, NEIL MJ. The Repicci II(R) unicondylar knee arthroplasty: 9-year survivorship and function. J Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468: 3094-3102.
[4] KNIGHT LA, PAL S, COLEMAN JC, et al. Comparison of long-term numerical and experimental total knee replacement wear during simulated gait loading. J Biomech. 2007;40(7):1550-1558.
[5] TODO M, TAKAHASHI Y, NAGAMINE R. Computational Analysis of Stress Concentration and Wear for Tibial Insert of PS Type Knee Prosthesis under Deep Flexion Motion.ICBME 2008,Proceedings 23:1559-1563, 2009.
[6] WILLING R, KIM ILY. Three dimensional shape optimization of total knee replacements for reduced wear.J Medical and Bioengineering Application. 2009;38:405-414.
[7] 王川,赵峰,丁文宇,等.上楼梯对人工膝关节假体磨损影响的有限元研究[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(2):109-114.
[8] 丁文宇,马淑芹,周星辰,等. 高吻合度股胫关节面人工膝关节假体的磨损[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(3):193-199.
[9] SATHASIVAM S, WALKER PS. Computer model to predict subsurface damage in tibial inserts of total knees. J Orthop Res. 1998;16(5): 564-571.
[10] BARBOUR PS, BARTON DC, FISHER J. The influence of stress conditions on the wear of UHMWPE for total joint replacements.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1997;8(10):603-611.
[11] NETTER J, HERMIDA JC, STEKLOV K, et al. Prediction of Wear in Crosslinked Polyethylene Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. J Lubricants. 2015;3:381-393.
[12] HEISEL C, SILVA M, DELA ROSA MA. Short-term in vivo wear of cross-linked polyethylene. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(4):748.
[13] ASHRAF T, NEWMAN JH, DESAI VV, et al. Polyethylene wear in a non-congruous unicompartmental knee replacement:a retrieval analysis.Knee. 2004;11(3):177-181.
[14] KRETZER J P, JAKUBOWITZ E, REINDERS J, et al. Wear analysis of unicondylar mobile bearing and fixed bearing knee systems:A knee simulator study. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(2):710-715.
[15] BURTON A, WILLIAMS S, BROCKETT C L, et al. In Vitro Comparison of Fixed- and Mobile Meniscal–Bearing Unicondylar Knee Arthroplasties.J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8):1452-1459.
[16] HATTON A, NEVELOS JE, Metthews JB, et al. Effects of clinically relevant alumina ceramic wear particles on TNF-A production by human peripheral blood mononuclear phagocytes. Biomaterials. 2003;24(7): 1193-1204. |