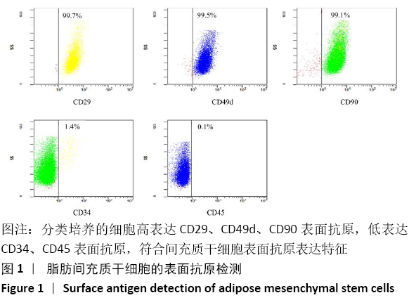
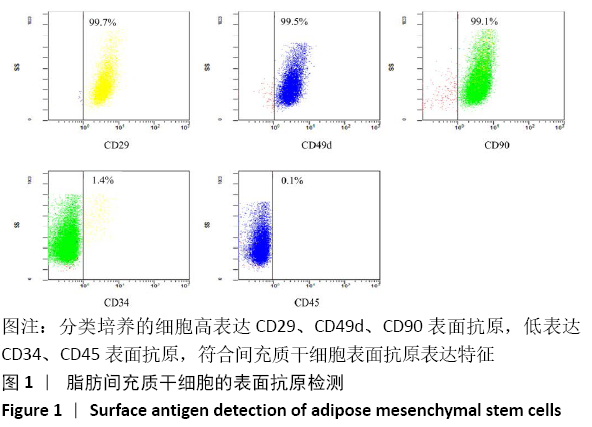
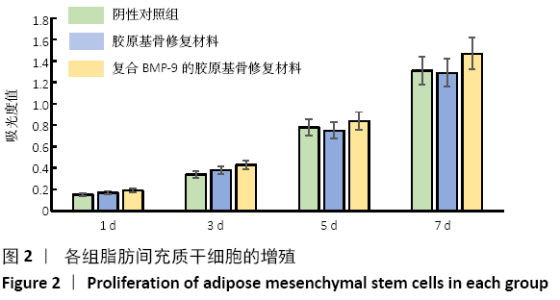
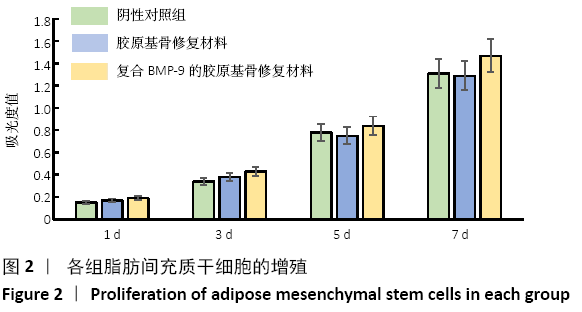
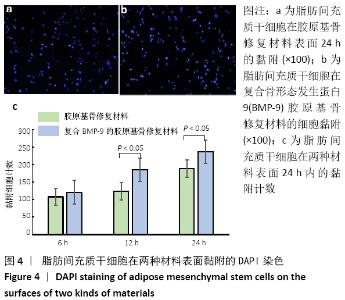
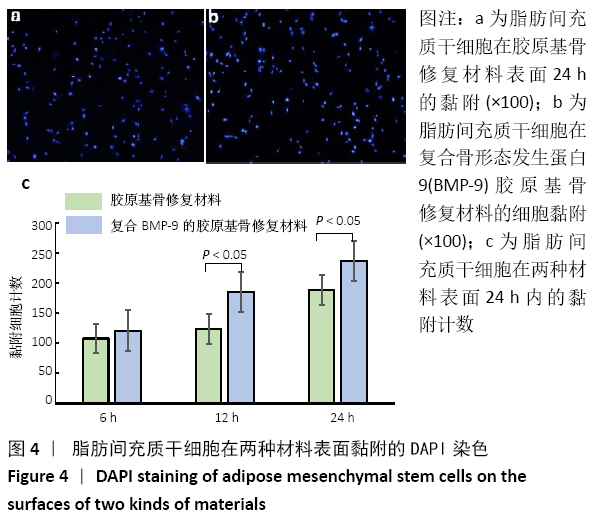
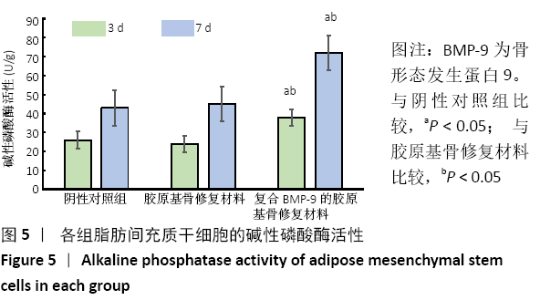
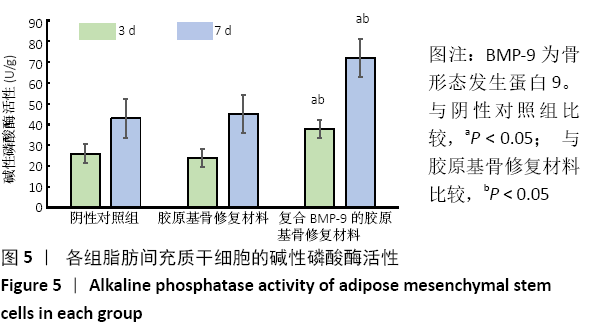
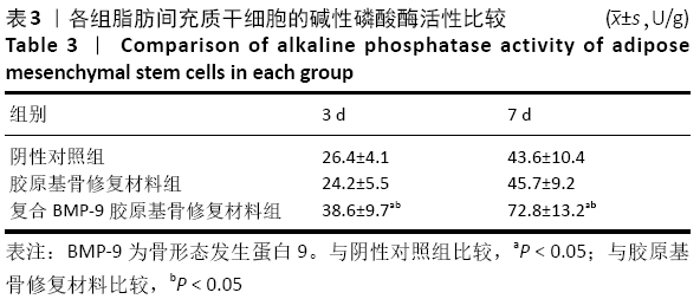
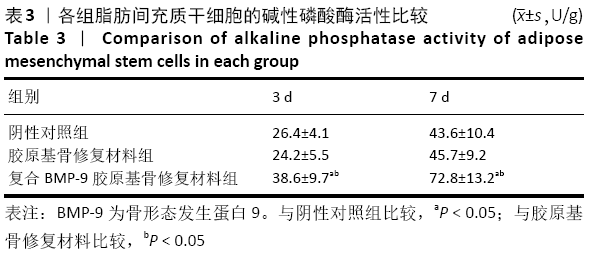
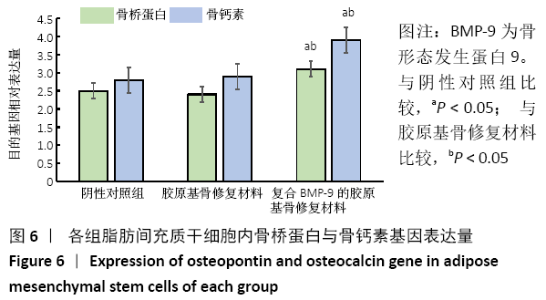
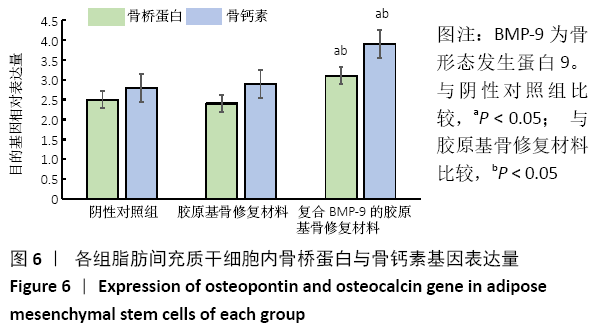
[1] 陈安富,黄凯,周永强.自体骨移植与骨形成蛋白治疗成人长骨骨折不愈合的Meta分析[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(1):87-92.
[2] 尼加提·阿不力米提,周开磊,李纲,等.双平面截骨加自体骨软骨移植治疗距骨骨软骨损伤合并距骨囊肿的临床效果[J].中华外科杂志, 2020,58(3):220-224.
[3] SHEIKH Z, QURESHI J, ALSHAHRANI AM, et al. Collagen based barrier membranes for periodontal guided bone regeneration applications. Odontology. 2017;105(1):1-12.
[4] MANOLEA HO, CRĂIŢOIU MM, MOGOANTĂ L, et al. An evaluation of a collagen-based material osseointegration. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2017; 58(1):161-165.
[5] ZHANG Z, MA Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Dehydrothermally crosslinked collagen/hydroxyapatite composite for enhanced in vivo bone repair. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;163:394-401.
[6] SEMYARI H, SALEHI M, TALEGHANI F, et al. Fabrication and characterization of collagen-hydroxyapatite-based composite scaffolds containing doxycycline via freeze-casting method for bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Appl. 2018;33(4):501-513.
[7] 覃建朴,王翀,张朋云,等.不同植骨融合材料在腰椎椎体间脊柱融合中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(25):3693-3698.
[8] KANG Q, SUN MH, CHENG H, et al. Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. Gene Ther. 2004;11(17):1312-1320.
[9] LIU W, DENG Z, ZENG Z, et al. Highly expressed BMP9/GDF2 in postnatal mouse liver and lungs may account for its pleiotropic effects on stem cell differentiation, angiogenesis, tumor growth and metabolism. Genes Dis. 2019;7(2):235-244.
[10] FU T, LIANG P, SONG J, et al. Matrigel Scaffolding Enhances BMP9-induced Bone Formation in Dental Follicle Stem/Precursor Cells. Int J Med Sci. 2019; 16(4):567-575.
[11] ZHU JH, LIAO YP, LI FS, et al. Wnt11 promotes BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation through BMPs/Smads and p38 MAPK in mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(11):9462-9473.
[12] LIN L, QIU Q, ZHOU N, et al. Dickkopf-1 is involved in BMP9-induced osteoblast differentiation of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells. BMB Rep. 2016;49(3):179-184.
[13] 张超,胡静,张君怡,等.周期性牵张力介导BMP9通过PI3K/AKT信号通路调控人牙周膜成纤维细胞成骨分化[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2019,37(6):656-661.
[14] 朱虹倩.骨形态发生蛋白9对人牙周膜干细胞增殖分化及信号通路的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2019,35(16):1770-1773.
[15] 王宗龙,张春红,谢磊.胶原基骨修复材料生物安全性评价[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2013,30(1):105-109.
[16] 黄奕智,郭俊,杨健.富血小板纤维蛋白对牙周膜成纤维细胞成骨能力影响的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(1):41-45.
[17] 曾继涛,涂小林,刘宏.TGF-βⅡ型受体小分子抑制剂ITD-1对骨髓基质细胞成骨分化和血管形成的作用[J].第三军医大学学报, 2020,42(4): 384-391.
[18] 才忠民,王欢,尚平,等.前列腺素E2诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中p38 MAPK信号通路蛋白的表达[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2020,55(1):61-65.
[19] 张腾飞,岳宗进,张璐璐.葛根素抑制强直性脊柱炎患者成纤维细胞的增殖和成骨分化[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020,41(2): 294-298.
[20] 宋永坡,郭英欣,李嘉萍.补充双歧杆菌四联活菌片对糖尿病性骨质疏松患者骨代谢指标影响的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020, 26(2):291-293.
[21] 刘红霞,施琼,周一青,等.过表达miR-155抑制BMP9诱导间充质干细胞C3H10T1/2成骨分化[J].中国生物工程杂志,2017,37(5): 9-18.
[22] 汪沛,曹志中.骨形态发生蛋白-9诱导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化及信号通路的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2015,28(12):1327-1332.
[23] 李福书,朱茄慧,胡莹,等.骨形态发生蛋白9诱导间充质干细胞骨向分化与Wnt11的关系[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(8): 1138-1144.
|