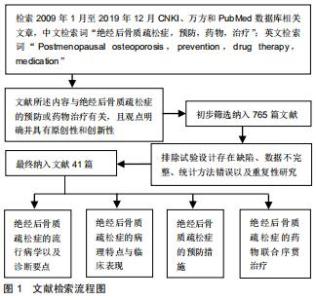
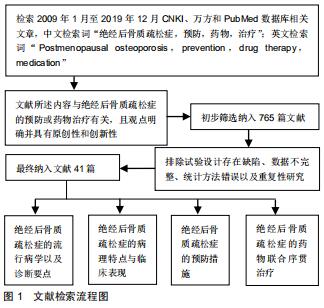
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (33): 5385-5390.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2338
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prevention and sequential therapies combined with drugs for postmenopausal osteoporosis
Sun Guoping1, Luo Xuanxiang2, Pan Bin2
- 1Nanjing Gaochun People’s Hospital, Nanjing 211300, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-25Revised:2020-02-29Accepted:2020-03-21Online:2020-11-28Published:2020-10-14 -
Contact:Luo Xuanxiang, Physician, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Sun Guoping, Associate chief pharmacist, Nanjing Gaochun People’s Hospital, Nanjing 211300, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81801213
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Guoping, Luo Xuanxiang, Pan Bin. Prevention and sequential therapies combined with drugs for postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5385-5390.
share this article
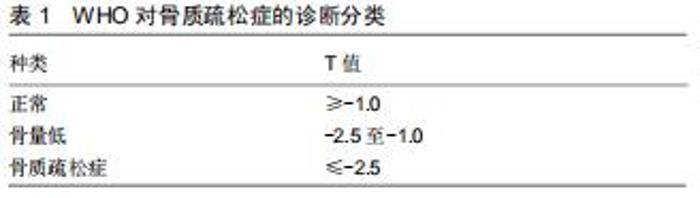
2.1.2 及时行骨质疏松筛查 脊柱、髋部或前臂双能X射线骨密度仪测量骨密度是诊断骨质疏松症的金标准,T值≤-2.5即可确诊[17],见表1。而在临床上,无论T值的高低,骨质疏松症可以在遭受低强度创伤或脆性骨折的患者中直接做出诊断。65岁及以上的妇女应至少进行一次骨质疏松筛查,同时有研究表明,65岁以下的高危绝经后妇女也应该接受筛查[18]。北美绝经协会认为,除了65岁及以上的妇女外,还应对风险较高的年轻绝经后妇女进行筛查,包括那些有骨丢失或其他危险因素的妇女,如脆性骨折(从站立高度坠落造成的骨折);还建议考虑筛查骨折(颅骨、手指、脚趾、面骨或脚踝除外)、骨质量指数<21 kg/m2或体质量<57.7 kg、双亲髋部骨折史、当前吸烟者、类风湿性关节炎或过量饮酒(超过2 U/d)的绝经后妇女[19]。 "
|
[1] YAN G, HUANG Y, CAO H, et al. Association of breastfeeding and postmenopausal osteoporosis in Chinese women: a community-based retrospective study. BMC Womens Health. 2019;19(1):110.
[2] SHEN Y, GRAY DL, MARTINEZ DS. Combined pharmacologic therapy in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2016;46(1):193-206.
[3] THOR U, LIS S, JENS B. Bone matrix levels of dickkopf and sclerostin are positively correlated with bone mass and strength in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(12):2896.
[4] TANG D, JU C, LIU Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of icariin combined with stem cells on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats. J Bone Miner Metabol. 2018;36(2):180-188.
[5] LIU H, LI B. Prospect of combination and sequential therapies for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Curr Pharm Design. 2017; 23(41):6251-6255. [6] CHAN DC, LEE YS, WU YJ, et al. A 12-year ecological study of hip fracture rates among older Taiwanese adults. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;93(5):397-404.
[7] MILLER DP. Management of severe osteoporosis. Exp Opin Pharmacother. 2016: 14656566.
[8] HILIGSMANN ML, EVERS SM, BEN SEDRINE W, et al. A systematic review of cost-effectiveness analyses of drugs for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015; 33(3):205-224.
[9] MIGNOT MA, TAISNE N, LEGROUX I, et al. Bisphosphonate drug holidays in postmenopausal osteoporosis: effect on clinical fracture risk. Osteoporosis Int. 2017;28(12): 3431-3438.
[10] JACKSON RD, MYSIW WJ. Insights into the epidemiology of postmenopausal osteoporosis: the Women's Health Initiative. Semin Reprod Med. 2014;32(6):454-462.
[11] PRENTICE RL, PETTINGER MB, JACKSON RD, et al. Health risks and benefits from calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Women's Health Initiative clinical trial and cohort study. Osteoporosis Int. 2013;24(2):567-580.
[12] VERBRUGGE FH, EVELIEN G, KOEN M, et al. Who should receive calcium and vitamin D supplementation? Age Ageing. 2012; (5): 5.
[13] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(3):281-309.
[14] BISCHOFF-FERRARI HA, WILLETT WC, ORAV EJ, et al. A Pooled Analysis of Vitamin D Dose Requirements for Fracture Prevention. Obstetr Gynecol Surv. 2013;367(1):40-49.
[15] 王建华.骨质疏松症治疗药物的分类与用药选择[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2019,5(5):297-300.
[16] ROSEN CJ, ADAMS JS, BIKLE DD, et al. The nonskeletal effects of Vitamin D: an endocrine society scientific statement. End Rev. 2012;33(3):456-492.
[17] DIAB DL, WATTS NB. Diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis in older adults. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2013;42(2):305-317.
[18] US PREVENTIVE SERVICES TASK FORCE, CURRY SJ, KRIST AH, et al. Screening for osteoporosis to prevent fractures: us preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;319(24):2521-2531.
[19] BONNICK SL, HARRIS ST, KENDLER DL, et al. Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: 2010 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2010;17(1):25-54.
[20] EVANS RK, NEGUS CH, CENTI AJ, et al. Peripheral QCT sector analysis reveals early exercise-induced increases in tibial bone mineral density. J Musculoskel Neur Int. 2012; 12(3):155-164.
[21] LIU GF, WANG ZQ, LIU L, et al. A network meta-analysis on the short-term efficacy and adverse events of different anti-osteoporosis drugs for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Cell Biochem.2018; 119(6):4469-4481.
[22] HSIAO FY, HSU WW. Comparative risks for cancer associated with use of calcitonin, bisphosphonates or selective estrogen receptor modulators among osteoporosis patients: a population-based cohort study. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2017;47(10):935-941. [23] BEAUDOIN C, JEAN S, BESSETTE L, et al. Denosumab compared to other treatments to prevent or treat osteoporosis in individuals at risk of fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2016; 27(9): 2835-2844.
[24] MA YL, MARIN F, STEPAN J, et al. Comparative effects of teriparatide and strontium ranelate in the periosteum of iliac crest biopsies in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Bone. 2011;48(5):972-978.
[25] LI X, OMINSKY MS, WARMINGTON KS, et al. Sclerostin antibody treatment increases bone formation, bone mass, and bone strength in a rat model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(4):578-588.
[26] APPELMAN-DIJKSTRA NM, PAPAPOULOS SE. Sclerostin inhibition in the management of osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;98(4):370-380.
[27] BLACK DM, REID IR, CAULEY JA, et al. The effect of 6 versus 9 years of zoledronic acid treatment in osteoporosis: a randomized second extension to the HORIZON-Pivotal Fracture Trial (PFT). J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(5):934-944.
[28] GENNARI L, ROTATORI S, BIANCIARDI S, et al. Treatment needs and current options for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Exp Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(8):1141-1152.
[29] TSAI JN, UIHLEIN AV, HANG L, et al. Teriparatide and denosumab, alone or combined, in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: The DATA study randomised trial. Lancet. 2013; 382(9886):50-56.
[30] TSAI J, UIHLEIN A, BURNETT-BOWIE S, et al. Effects of two years of teriparatide, denosumab, or both on bone microarchitecture and strength (DATA-HRpQCT study). J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2016:20161160.
[31] LEDER BZ, TSAI JN, UIHLEIN AV, et al. Denosumab and teriparatide transitions in postmenopausal osteoporosis (the DATA-Switch study): extension of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2015; 386(9999): 1147-1155.
[32] LEDER BZ, TSAI JN, NEER RM, et al. Response to therapy with teriparatide, denosumab, or both in postmenopausal women in the DATA (denosumab and teriparatide administration) study randomized controlled trial. J Clin Densitom. 2016;19(3):346-351. [33] FINKELSTEIN JS, WYLAND JJ, HANG L, et al. Effects of teriparatide, alendronate, or both in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(4):1838-1845.
[34] EASTELL R, NICKELSEN T, MARIN F, et al. Sequential treatment of severe postmenopausal osteoporosis after teriparatide: final results of the randomized, controlled European Study of Forsteo (EUROFORS). J Bone Miner Res. 2009; 24(4):726-736.
[35] MUSCHITZ C, KOCIJAN R, FAHRLEITNE-PAMMER A, et al. Overlapping and continued alendronate or raloxifene administration in patients on teriparatide: effects on areal and volumetric bone mineral density the CONFORS study. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(8):1777-1785.
[36] MCCLUNG MR, BROWN JP, DIEZ-PEREZ A, et al. Effects of 24 months of treatment with romosozumab followed by 12 months of denosumab or placebo in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density: a randomized, double-blind, phase 2, parallel group study. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(8): 1397-1406.
[37] ANASTASILAKIS AD, POLYZOS SA, EFSTATHIADOU ZA, et al. Denosumab in treatment-naïve and pre-treated with zoledronic acid postmenopausal women with low bone mass: Effect on bone mineral density and bone turnover markers. Metabolism. 2015;64(10): 1291-1297.
[38] ANASTASILAKIS AD, POLYZOS SA, GKIOMISI A, et al. Denosumab versus zoledronic acid in patients previously treated with zoledronic acid. Osteoporosis Int. 2015; 26(10): 2521-2527.
[39] LIN J, ZHU J, WANG Y, et al. Chinese single herbs and active ingredients for postmenopausal osteoporosis: From preclinical evidence to action mechanism. Biosci Trends. 2017;11(5): 496-506.
[40] KOMM BS, MORGENSTERN D, YAMAMOTO LA, et al. The safety and tolerability profile of therapies for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Exp Rev Clini Pharmacol. 2015;8(6):1-16. [41] MANDEMA JW, ZHENG J, LIBANATI C, et al. Time course of bone mineral density changes with denosumab compared with other drugs in postmenopausal osteoporosis: a dose-response–based meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(10):3746-3755. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||