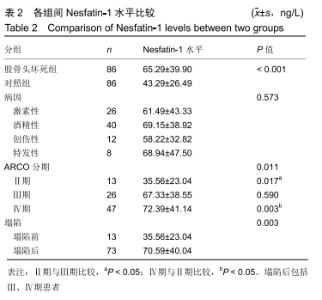
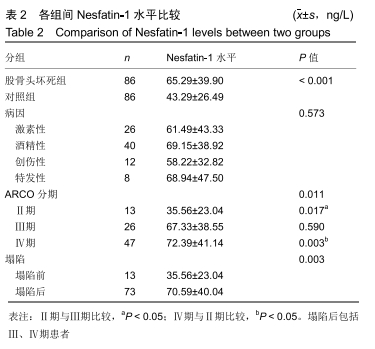
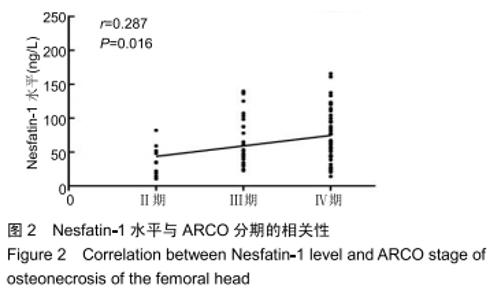
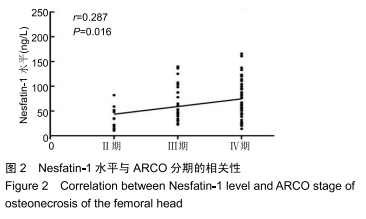
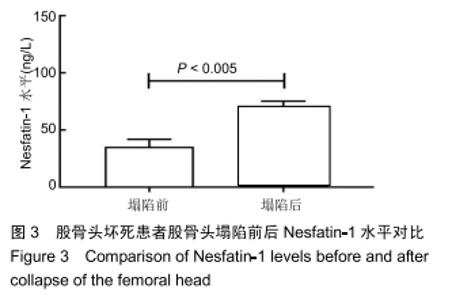
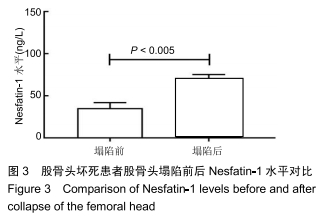
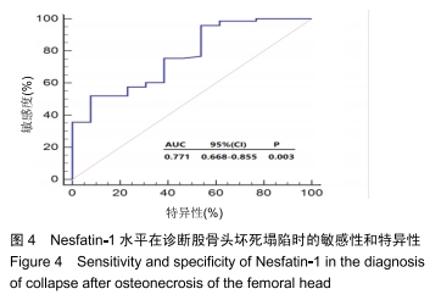
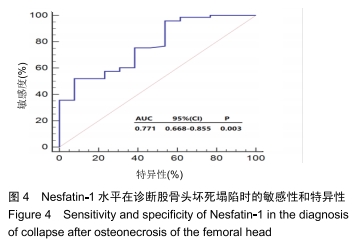
[1] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会显微修复工作委员会,中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组,中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组.成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2016)[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(15):945-954.
[2] MOYA-ANGELER J, GIANAKOS AL, VILLA JC, et al. Current concepts on osteonecrosis of the femoral head. World J Orthop. 2015;6(8):590-601.
[3] LAMB JN, HOLTON C, O'CONNOR P, et al. Avascular necrosis of the hip. BMJ. 2019;365:l2178.
[4] MONT MA, CHERIAN JJ, SIERRA RJ, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97 (19):1604-1627.
[5] 马剑雄,何伟伟,赵杰,等.股骨头坏死发病机制研究的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4397-4402.
[6] OH-I S, SHIMIZU H, SATOH T, et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature. 2006;443(7112):709-712.
[7] 王书瑶,唐妮,齐锦雯,等.Nesfatin-1调节脂肪代谢的研究进展[J].生命科学,2018,30(5):533-538.
[8] SCHALLA MA, STENGEL A. Current Understanding of the Role of Nesfatin-1. J Endocr Soc. 2018;2(10):1188-1206.
[9] FEIJÓO-BANDÍN S, RODRÍGUEZ-PENAS D, GARCÍA-RÚA V, et al. 24 h nesfatin-1 treatment promotes apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Endocrine. 2016;51(3):551-555.
[10] 王书瑶,唐妮,齐锦雯,等. Nesfatin-1调节脂肪代谢的研究进展[J].生命科学,2018,30(5):533-538.
[11] LI R, WU Q, ZHAO Y, et al. The novel pro-osteogenic activity of NUCB2(1-83.). PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61619.
[12] XUE F, WU Y, ZHAO X, et al. CHIP mediates down-regulation of nucleobindin-1 in preosteoblast cell line models. Cell Signal. 2016;28(8):1058-1065.
[13] ZHANG Y, SHUI X, LIAN X, et al. Serum and synovial fluid nesfatin-1 concentration is associated with radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21: 1078-1082.
[14] 张长春,李可大.中西医结合治疗股骨头缺血性坏死研究简况[J].实用中医内科杂志,2016,30(10):118-120.
[15] ZHANG Y, SUN R, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of blood biochemical factors on nontraumatic necrosis of the femoral head : Logistic regression analysis. Orthopade. 2017;46(9): 737-743.
[16] KOLGAZI M, OZDEMIR-KUMRAL ZN, CANTALI-OZTURK C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of nesfatin-1 on acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats: involvement of cyclo-oxygenase pathway. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;68(5): 765-777.
[17] 谢林,王坤正.骨、脂肪、神经三者相互作用在激素性股骨头坏死中作用的探讨[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(3): 390-392.
[18] LOPEZ-AGUILAR I, IBARRA-REYNOSO LDR, MALACARA JM. Association of Nesfatin-1, Acylated Ghrelin and Cortisol with Scores of Compulsion, Food Addiction, and Binge Eating in Adults with Normal Weight and with Obesity. Ann Nutr Metab. 2018;73(1):54-61.
[19] 王鼎元,李秋雅,尹悦,等.Nesfatin-1与细胞凋亡[J].生理科学进展, 2019,50(4):293-296.
[20] 李自茹.新脂肪因子nesfatin-1[J].生理科学进展,2011,42(6): 442.
[21] WANG C, WANG X, XU XL, et al. Bone microstructure and regional distribution of osteoblast and osteoclast activity in the osteonecrotic femoral head. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96361.
[22] 魏秋实,杨帆,陈哓俊,等.激素性与酒精性股骨头坏死患者骨标本坏死区域病理与显微结构特点分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(7):866-872.
[23] 石少辉. 股骨头坏死硬化带的观察[D].北京:中国协和医科大学, 2009.
[24] 何伟.如何把握股骨头坏死患者的保髋治疗时机[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(2):82-86.
[25] CHAN WP, LIU YJ, HUANG GS, et al. MRI of joint fluid in femoral head osteonecrosis. Skeletal Radiol. 2002;31(11): 624-630.
[26] YAMAGUCHI R, KAMIYA N, ADAPALA NS, et al. HIF-1-Dependent IL-6 Activation in Articular Chondrocytes Initiating Synovitis in Femoral Head Ischemic Osteonecrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(13):1122-1131.
[27] 郭万首.股骨头坏死早期的关节软骨改变[D].北京:中国协和医科大学,2008.
[28] SCOTECE M, CONDE J, ABELLA V, et al. NUCB2/nesfatin-1: a new adipokine expressed in human and murine chondrocytes with pro-inflammatory properties, an in vitro study. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(5):653-660.
[29] KVLIVIDZE TZ, ZAVODOVSKY BV, AKHVERDYAN YR, et al. Serum nesfatin-1 as a marker of systemic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Klin Lab Diagn. 2019;64(1):53-56.
[30] JIANG L, BAO J, ZHOU X, et al. Increased serum levels and chondrocyte expression of nesfatin-1 in patients with osteoarthritis and its relation with BMI, hsCRP, and IL-18. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:631251.
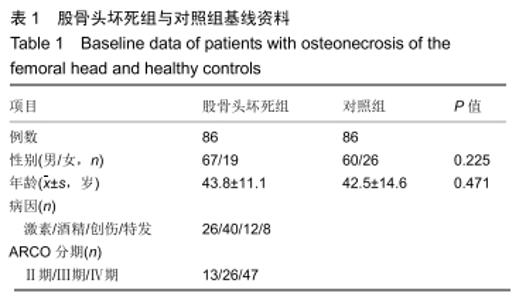
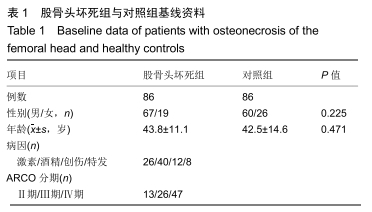
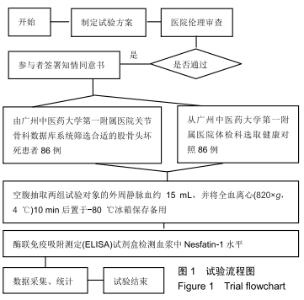
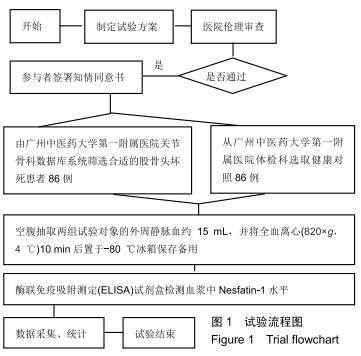
|