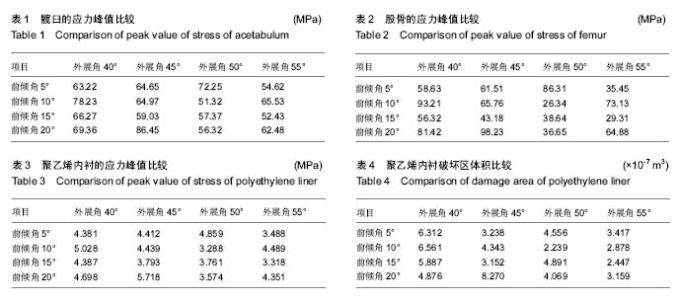
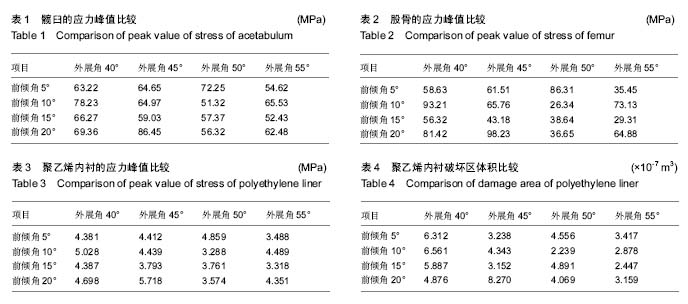
| [1] 王春生,史安利,张子琦,等. 拟行全髋关节置换术的不同病种前关节囊差异的对比研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(1): 27-31. [2] 蒋劲松.非骨水泥全髋关节置换术疗效评估和大腿痛临床研究[J].中国医学创新,2016,(2):54-57. [3] 张倜,郑充,马海洋,等.髋关节置换中期失败的原因分析[J].中华医学杂志,2015,95(3):214-216. [4] Gondusky JS, Pinkos KA, Choi L, et al.Simultaneous Bilateral Anterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty.Orthopedics. 2015; 38(7):e611-615. [5] Goveia VR, Mendoza IY, Couto BR,et al.Profile of hip arthroplasty patients in a teaching hospital.Rev Col Bras Cir. 2015;42(2):106-110.[6] 斯海波,陈世荣,刘淼,等.计算机模拟全髋关节置换术后假体位置对关节活动的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(3): 279-284. [7] 蒋梅花,何川,冯建民,等.髋关节置换术后常见并发症的MRI表现[J].中华放射学杂志,2015,(2):126-129. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2015.02.011. [8] Zuh SG, Zazgyva A, Gergely I,et al.Acetabuloplasty with bone grafting in uncemented hip replacement for protrusion.Int Orthop. 2015;39(9):1757-1763. [9] 王桂峰,王小林,杜伟,等.老年股骨颈骨折生物型人工髋关节置换术后股骨假体周围骨密度的变化[J].中国老年学杂志,2015, 35(17):4941-4942. [10] Tiberi JV 3rd, Antoci V, Malchau H, et al.What is the Fate of Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) Acetabular Component Orientation When Evaluated in the Standing Position? J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9):1555-1560. [11] Esposito CI, Gladnick BP, Lee YY,et al.Cup position alone does not predict risk of dislocation after hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2015 ;30(1):109-113. [12] Wan Z,Boutary M,Dorr LD,等.全髋关节置换中髋臼假体位置对磨损的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(3):285-288. [13] 杨显春,朱振安.臼假体位置对全髋关节置换术后假体受力及磨损的影响[J].医用生物力学,2008,23(4):332-336. [14] den Hartog YM, Mathijssen NM, Peters SJ, et al.The anterior supine intermuscular approach for total hip arthroplasty: reducing the complication rate by improving the procedure. Hip Int. 2015;25(1):28-33. [15] 刘福存,华江,任洁,等.全髋关节置换联合髋臼造盖术治疗CroweIII型发育性髋关节脱位的疗效观察[J]. 浙江医学,2016, 38(12):922-924.[16] 文武,张春雨,陈贤帅,等.不同结构牙科种植体及周围骨组织应力分布的三维有限元比较研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2013,29(6): 770-774. [17] Meena VK, Kumar M, Pundir A,et al.Musculoskeletal-based finite element analysis of femur after total hip replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2016 ;230(6):553-560. [18] 潘浩,胡庆丰,肖鲁伟,等.髋关节发育不良髋臼假体位置与稳定的三维有限元分析[J].浙江医学,2015,(1):44-48. [19] Kaku N, Hara K, Tabata T, et al.Influence of the volume of bone defect, bone grafting methods, and hook fixation on stress on the Kerboull-type plate and screw in total hip arthroplasty: three-dimensional finite element analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(2):321-329. [20] Hua X, Wang L, Al-Hajjar M, et al.Experimental validation of finite element modelling of a modular metal-on-polyethylene total hip replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228(7): 682-692. [21] Lerch M, Weigel N, Windhagen H,et al.Finite element model of a novel short stemmed total hip arthroplasty implant developed from cross sectional CT scans.Technol Health Care. 2013;21(5):493-500.[22] Boese CK, Lechler P, Rose L,et al.Calibration Markers for Digital Templating in Total Hip Arthroplasty.PLoS One. 2015; 10(7):e0128529. [23] Hamilton WG, Parks NL, Huynh C.Comparison of Cup Alignment, Jump Distance, and Complications in Consecutive Series of Anterior Approach and Posterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(11):1959-1962.[24] Ohlendorf D, Lehmann C, Heil D,et al.The impact of a total hip replacement on jaw position, upper body posture and body sway.Cranio. 2015;33(2):107-114. [25] Grammatopoulos G, Pandit HG, da Assunção R,et al.Pelvic position and movement during hip replacement.Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(7):876-883. [26] Wang J, Shi ZJ.Total hip arthroplasty via lateral approach in supine position.Orthop Surg. 2014;6(2):165-167. [27] Yuenyongviwat V, Iamthanaporn K, Harnroongroj T. Radiographic manifestation of hip dislocation after total hip arthroplasty.J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97(1):60-63.[28] Tamura S, Takao M, Sakai T,et al.Spinal factors influencing change in pelvic sagittal inclination from supine position to standingposition in patients before total hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12):2294-2297.[29] Barrack RL, Krempec JA, Clohisy JC,et al.Accuracy of acetabular component position in hip arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(19):1760-1768. [30] Eilander W, Harris SJ, Henkus HE, et al.Functional acetabular component position with supine total hip replacement.Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(10):1326-1331. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.95B10.31446.[31] Ezzet KA, McCauley JC.Use of intraoperative X-rays to optimize component position and leg length during total hiparthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(3):580-585. [32] 李敏龙.全髋关节置换术后假体位置参数与髋关节功能相关性分析[D].广州中医药大学,2014. [33] 张志奇,傅明,康焱,等.髋臼假体位置对人工股骨头应力分布的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2008,2(6):667-671. [34] Nadzadi ME, Pedersen DR, Callaghan JJ,et al.Effects of acetabular component orientation on dislocation propensity for small-head-size total hip arthroplasty.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2002;17(1):32-40.[35] 吴旭东. 人工全髋关节置换术中髋臼前倾角外展角与磨损的相关性研究. 浙江省医学会骨科学分会30年庆典暨2011年浙江省骨科学学术年会; 2011, 中国浙江杭州, 2011.[36] 戴雪松,严世贵,何荣新,等.全髋关节置换术中的髋臼外展角和磨损的关系[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(5):257-260. [37] D'Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al.The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(3):315-321. |