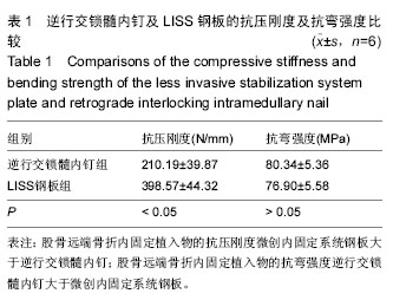
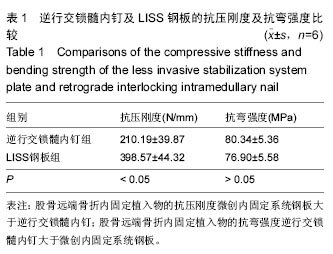
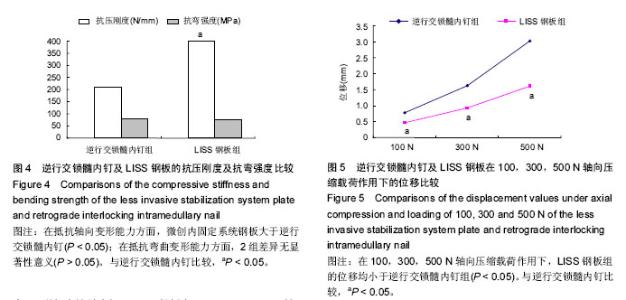
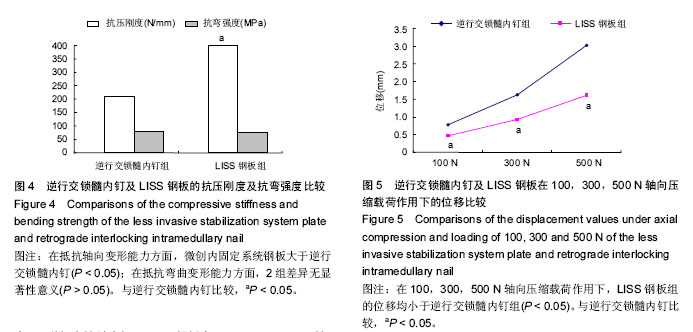
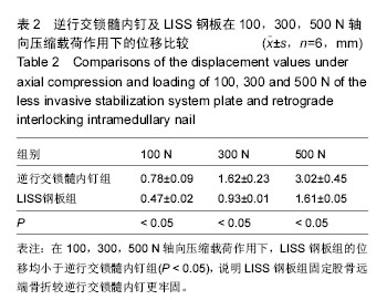
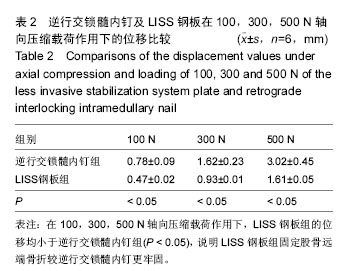
| [1] Bliemel C, Buecking B, Mueller T, et al.Distal femoral fractures in the elderly: biomechanical analysis of a polyaxial angle-stable locking plate versus a retrograde intramedullary nail in a human cadaveric bone model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(1):49-58.
[2] Cao J, Liu Y, Wang Y, et al. Salvage thrombolysis and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for massive pulmonary embolism during the distal femur fracture surgery. Am J Emerg Med. 2015. pii: S0735-6757 (15)00970-5.
[3] Märdian S, Rau D, Schwabe P, et al. [Operative therapy of fractures of the distal femur : Predictive factors for a complicated course]. Orthopade. 2015; 45(1):32-37.
[4] Lill M, Attal R, Rudisch A, et al.Does MIPO of fractures of the distal femur result in more rotational malalignment than ORIF? A retrospective study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015. [Epub ahead of print]
[5] Ennaciri B, Vasile C, Lebredonchel T, et al.Knee megaprosthesis: a salvage solution for severe open and complex distal femoral fracture associated with an ipsilateral brachial plexus injury (a case report with literature review). Pan Afr Med J. 2015;21:207.
[6] Tosounidis TH, Lampropoulou-Adamidou K, Kanakaris NK. Intramedullary nailing of sequential bilateral atypical subtrochanteric fractures and the management of distal femoral intraoperative fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2015.
[7] Massoud EI. Fixation of distal femoral fractures: Restoration of the knee motion. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015;21(3):197-203.
[8] Thukral R, Marya S, Singh C. Management of distal femoral periprosthetic fractures by distal femoral locking plate: A retrospective study. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(2):199-207.
[9] Heng CH, Wang Bde H, Chang PC. Distal femoral fracture after double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(4): 953-956.
[10] Bedes L, Bonnevialle P, Ehlinger M, et al. External fixation of distal femoral fractures in adults' multicentre retrospective study of 43 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(8):867-872.
[11] Gahlot N, Saini UC, Ss S, et al.Triplane fracture of distal femur in an adult rare case study and review. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2014;16(5):523-530.
[12] 关继奎,赵丽,张英,等.股骨髁上骨折动力髁螺钉内固定方法的临床应用研究[J].中国民康医学,2007,19(4): 254-256.
[13] 杨兆军,肖索青.逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨髁上骨折临床观察[J].山东医药,2008,48(37):22.
[14] 董恒纲,王存,张志宏,等.股骨远端骨折治疗方案的探讨[J].中国骨伤,2007,20(3):186.
[15] 韩擎天,汤红伟.股骨髁上髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折59 例报告[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(5):338-339.
[16] Heiney JP,Barnett MD,Vrabec GA, et al. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of trigen retrograde intramedullary (i.m.) nail, dynamic condylar screw (DCS), and locking compression plate (LCP) condylar plate. J Trauma. 2009;66(2):443-449.
[17] 汤继磊,沈向阳,陈春美,等. 股骨远端骨折逆行交锁髓内钉和微创内固定系统手术对软组织血清标志物的影响[J]. 江苏医药,2013,39(18):2196-2197.
[18] 宫涛,孙占胜,王伯珉,等. LISS钢板与逆行交锁髓内钉内固定术治疗C2型股骨髁间骨折疗效比较[J].山东医药, 2014,54(42):81-83.
[19] Chen YT, Yang JW, Hou HB, et al. [Comparative study of less invasive stabilization system (LISS) and the condylar support plates for the treatment of AO type C distal femoral fractures in adults]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(2):136-140.
[20] 余智锋,刘亚云,唐国英. 两种不同治疗股骨远端骨折方法的疗效比较[J].广东微量元素科学,2015,22(12):46-49.
[21] 张计超,宁宇,崔冰,等.微创内固定系统治疗股骨远端骨折的临床疗效[J].国际医药卫生导报,2015,21(24): 3580-3581.
[22] Yadav A. Management of implant-stable distal femoral periprosthetic fractures by distal femoral locking plate: A retrospective study. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(6):680.
[23] Ebraheim NA, Kelley LH, Liu X, et al. Periprosthetic Distal Femur Fracture after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(4):297-305.
[24] Johnston TE, Marino RJ, Oleson CV, et al. Cycling with Functional Electrical Stimulation Before and After a Distal Femur Fracture in a Man with Paraplegia. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2015;21(4):275-281.
[25] Gawri V, Garg Y, Singh D, et al. Complex Open Distal Femur Fracture Managed By Primary Autogenous Fibular Graft in Conjunction with DFLP- A Case Report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(11):RD01-03.
[26] Smith JR, Halliday R, Aquilina AL, et al. Distal femoral fractures: The need to review the standard of care. Injury. 2015;46(6):1084-1088.
[27] Ebrahimzadeh MH, Birjandinejad A, Moradi A, et al. Clinical instability of the knee and functional differences following tibial plateau fractures versus distal femoral fractures. Trauma Mon. 2015;20(1):e21635.
[28] Beltran MJ, Gary JL, Collinge CA. Management of distal femur fractures with modern plates and nails: state of the art. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(4):165-172.
[29] Märdian S, Schaser KD, Duda GN, et al. Working length of locking plates determines interfragmentary movement in distal femur fractures under physiological loading. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(4):391-396.
[30] Yoo JH, Kim SW, Kwak YH, et al. Overlapping intramedullary nailing after failed minimally invasive locked plating for osteoporotic distal femur fractures--Report of 2 cases. Injury. 2015;46(6):1174-1177.
[31] 黄利斌,尹宗生. 逆行髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(8): 678-682. |