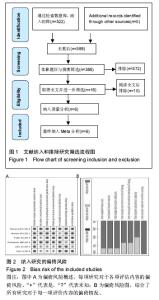
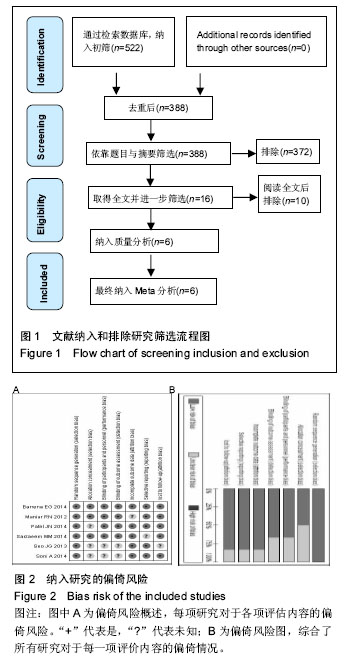
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (35): 5313-5320.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.35.021
Clinical outcomes of intra-articular route versus intravenous route of tranexamic acid during total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
Zhou Kai-di, Wang Hong-yi, Yan Yu-fei, Hong Wei-xiang, Feng Jian-min
- Department of Orthopedics, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Shanghai 200025, China
-
Revised:2016-06-06Online:2016-08-26Published:2016-08-26 -
Contact:Feng Jian-min, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Shanghai 200025, China -
About author:Zhou Kai-di, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Shanghai 200025, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Kai-di, Wang Hong-yi, Yan Yu-fei, Hong Wei-xiang, Feng Jian-min. Clinical outcomes of intra-articular route versus intravenous route of tranexamic acid during total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5313-5320.
share this article
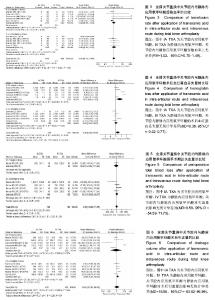
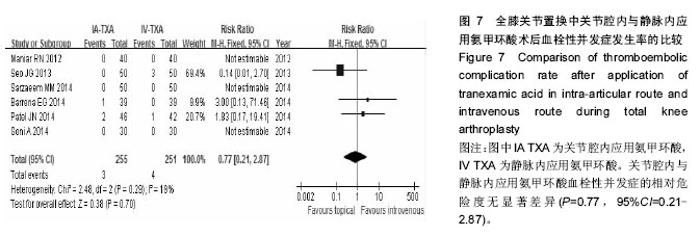
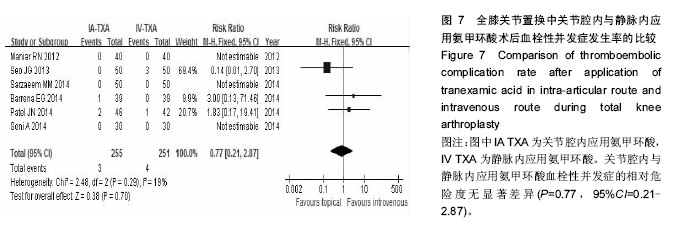
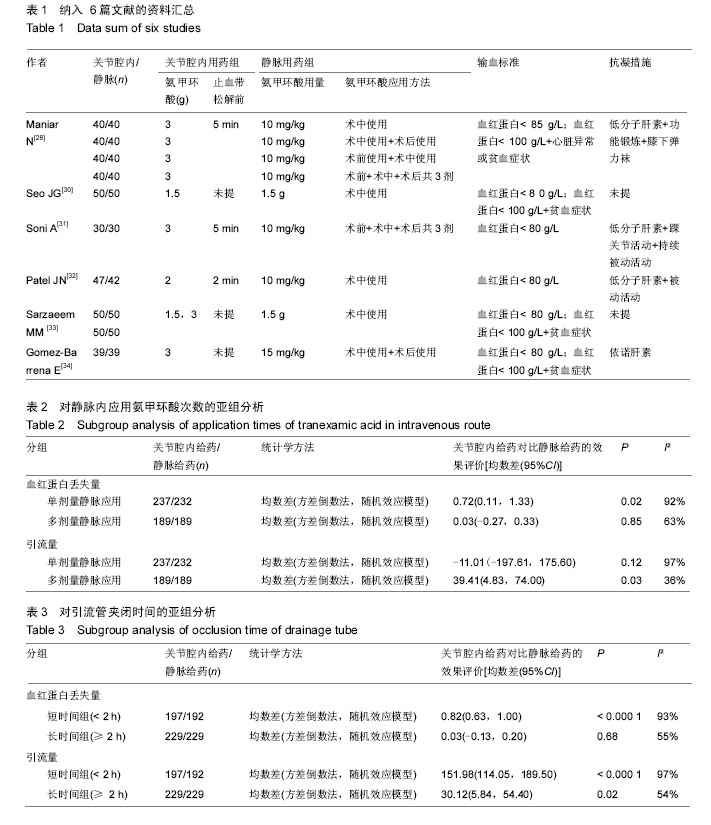
2.3 输血率 纳入研究都报告了输血率,共847例患者。合并数据分析得出,关节腔内应用氨甲环酸与静脉应用氨甲环酸在输血率上无差异(RR=1.02,95%CI= 0.70-1.49) ,纳入研究关于输血率的异质性较小(P=0.31,I²=15%),见图3。 2.4 血红蛋白丢失量 纳入的研究均有关于血红蛋白丢失量的报告。合并数据分析后发现,关节腔与静脉内应用氨甲环酸的术后血红蛋白丢失量比较无统计学差异(MD=0.38,95%CI=-0.02-0.77),但关于该指标各项研究之间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I²=90%),见图4。 2.5 总失血量 2项研究包含398 例患者提供了围手 术期总失血量的可用数据[28,34]。合并数据发现,关节腔内与静脉内应用氨甲环酸对失血量的影响无统计学差异(MD=8.58,95%CI=-54.59-71.75),关于该指标各项研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.20,I²=34%),见图5。 2.6 引流量 所有纳入的临床试验都报告了引流量。合并数据分析发现,关节腔内与静脉内应用氨甲环酸对术后引流量的影响无统计学差异(MD=16.68,95%CI=-63.62-96.99),但各研究之间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I²=93%),见图6。 2.7 血栓性并发症 所有研究对血栓性并发症都有记录,对患者的平均随访时间为30 d至18.3周。合并数据后,关节腔内与静脉内应用氨甲环酸血栓性并发症的相对危险度无显著差异(P=0.77,95%CI=0.21-2.87),各项研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.29,I²=19%),见图7。另外,将各项研究中可疑的下肢深静脉血栓病例合并入血栓性并发症后,得出的结论不变(RR=1.32,95%CI= 0.55-3.19),且无统计学异质性(P=0.57,I²=0)。"

| [1] Blanié A,Bellamy L,Rhayem Y,et al.Duration of Postoperative Fibrinolysis after Total Hip or Knee Replacement: A Laboratory Follow-up Study.Thromb Res.2013;131(1):e6-e11. [2] Li B,Wen Y,Wu H,et al.The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1263-1268. [3] Lopez-Balderas N,Bravo E,Camara M,et al.Seroprevalence of hepatitis viruses and risk factors in blood donors of Veracruz,Mexico.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2015;9(3):274-282. [4] Sehat KR,Evans R,Newman JH.How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?. Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee.2000;7(3):151-155. [5] Levine BR,Haughom B,Strong B,et al.Blood Management Strategies for Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2014;22(6):361-371. [6] Oberhofer D,Sakic K,Jankovic S,et al.How to improve perioperative blood management in patients undergoing total hip or knee replacement surgery? Lijec Vjesn.2012;134(11-12):322-327. [7] Shemshaki H,Nourian SM,Nourian N,et al.One step closer to sparing total blood loss and transfusion rate in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of different methods of tranexamic acid administration.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(4):573-588. [8] Wu Q,Zhang HA,Liu SL,et al.Is tranexamic acid clinically effective and safe to prevent blood loss in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of 34 randomized controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2015;25(3):525-541. [9] Sorin A,Claeys M,D'Haese J,et al.Reduction of blood loss by tranexamic acid in total knee replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1999;(Suppl.II):518-520. [10] Erstad BL. Systemic hemostatic medications for reducing surgical blood loss.Ann Pharmacother. 2001; 35(7-8):925-934. [11] Dunn CJ,Goa KL.Tranexamic acid-A review of its use in surgery and other indications.Drugs.1999;57(6): 1005-1032. [12] Lin C,Shuhaiber JH,Loyola H,et al.The Safety and Efficacy of Antifibrinolytic Therapy in Neonatal Cardiac Surgery. PLoS One.2015;10(5):e126514. [13] Verstraete M.Clinical application of inhibitors of fibrinolysis.Drugs.1985;29(3):236-261. [14] Suenson E,Lutzen O,Thorsen S.Initial plasmin-degradation of fibrin as the basis of a positive feed-back mechanism in fibrinolysis.Eur J Biochem. 1984;140(3):513-522. [15] Fergusson DA,Hebert PC,Mazer CD,et al.A comparison of aprotinin and lysine analogues in high-risk cardiac surgery.N Engl J Med.2008;358(22): 2319-2331. [16] Henry D,Carless P,Fergusson D,et al.The safety of aprotinin and lysine-derived antifibrinolytic drugs in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Can Med Assoc J. 2009;180(2):183-193. [17] Shakur H,Roberts I,Bautista R,et al.Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet.2010;376(9734):23-32. [18] Meybohm P,Herrmann E,Nierhoff J,et al.Aprotinin May Increase Mortality in Low and Intermediate Risk but Not in High Risk Cardiac Surgical Patients Compared to Tranexamic Acid and ε-Aminocaproic Acid-A Meta-Analysis of Randomised and Observational Trials of over 30 000 Patients.PloS One.2013;8(3):e58009. [19] McCormack PL.Tranexamic Acid: A Review of its Use in the Treatment of Hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs.2012; 72(5): 585-617. [20] Benoni G,Carlsson A,Petersson C,et al.Does tranexamic acid reduce blood loss in knee arthroplasty? Am J Knee Surg.1995;8(3):88-92. [21] Wong J,Abrishami A,El Beheiry H,et al.Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid Reduces Postoperative Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Randomized, Controlled Trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92A(15): 2503-2513. [22] Wang C,Xu G,Han Z,et al.Topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg.2015; 15:134-139. [23] Alshryda S,Sukeik M,Sarda P,et al.A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement. Bone Joint J.2014;96-B(8):1005-1015. [24] Ishida K,Tsumura N,Kitagawa A,et al.Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2011;35(11):1639-1645. [25] Iwai T,Tsuji S,Tomita T,et al.Repeat-dose intravenous tranexamic acid further decreases blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2013;37(3):441-445. [26] Moher D,Cook DJ,Eastwood S,et al.Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials: the QUOROM Statement.Rev Esp Salud Publica.2000;74(2):107-118. [27] Moher D,Liberati A,Tetzlaff J,et al.Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement.Int J Surg.2010;8(5):336-341. [28] Maniar RN,Kumar G,Singhi T,et al.Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012;470(9):2605- 2612. [29] Higgins JPT,Thompson SG.Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis.Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539-1558. [30] Seo JG,Moon YW,Park SH,et al. The comparative efficacies of intra-articular and IV tranexamic acid for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg.Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2013;21(8): 1869-1874. [31] Soni A,Saini R,Gulati A,et al.Comparison between intravenous and intra-articular regimens of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8):1525-1527. [32] Patel JN,Spanyer JM,Smith LS,et al.Comparison of intravenous versus topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study.J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8):1528-1531. [33] Sarzaeem MM,Razi M,Kazemian G,et al.Comparing efficacy of three methods of tranexamic acid administration in reducing hemoglobin drop following total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8): 1521-1524. [34] Gomez-Barrena E,Ortega-Andreu M,Padilla-Eguiluz NG,et al.Topical Intra-Articular Compared with Intravenous Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Blood Loss in Primary Total Knee Replacement: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Noninferiority Clinical Trial.J Bone J Surg.2014;96(23):1937-1944. [35] Benoni G,Lethagen S,Fredin H.The effect of tranexamic acid on local and plasma fibrinolysis during total knee arthroplasty.Thromb Res.1997;85(3): 195-206. [36] Jansen AJ,Andreica S,Claeys M,et al.Use of tranexamic acid for an effective blood conservation strategy after total knee arthroplasty.Br J Anaesth. 1999;83(4):596-601. [37] Panteli M,Papakostidis C,Dahabreh Z,et al.Topical tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Knee.2013;20(5):300-309. [38] Alshryda S,Sarda P,Sukeik M,et al.Tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93(12):1577- 1585. [39] Wang H,Shen B,Zeng Y.Comparison of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled and prospective cohort trials.Knee.2014;21(6):987- 993. [40] Shemshaki H,Nourian SMA,Nourian N,et al.One step closer to sparing total blood loss and transfusion rate in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of different methods of tranexamic acid administration.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(4):573-588. |
| [1] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [2] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [3] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [4] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [5] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [6] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [7] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [8] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [9] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [10] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [11] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [12] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [13] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| [14] | Zhang Yun-ge, Song Ke-guan. Periprosthetic osteolysis induced by wear particles: research progress of calcineurin/activated T cell nuclear factor signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1115-1122. |
| [15] | Liu Wei, Huang Jian. Applied research and progress of three-dimensional printing technology in joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1123-1130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||