Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (22): 3227-3234.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.22.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Novel Zero-P versus titanium plate with cage interbody fixation and fusion system in repairing cervical spondylosis: early stability
Xu Yi-qi, Zhang Xue-song, Sun Tai-cun, Jing Dan-feng, Chen Hai-ning, Cui Xue-wen
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2016-03-15Online:2016-05-27Published:2016-05-27 -
Contact:Cui Xue-wen, M.D., Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Xu Yi-qi, Physician, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Zhenjiang City Science and Technology Plan (Technology Support-Social Development) in 2012, No. SH2012026
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yi-qi, Zhang Xue-song, Sun Tai-cun, Jing Dan-feng, Chen Hai-ning, Cui Xue-wen. Novel Zero-P versus titanium plate with cage interbody fixation and fusion system in repairing cervical spondylosis: early stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3227-3234.
share this article
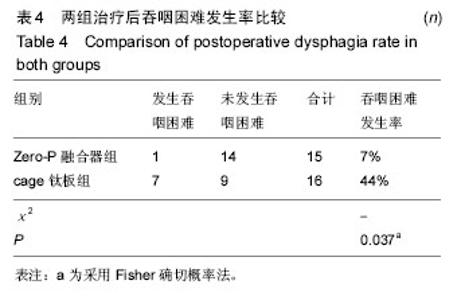
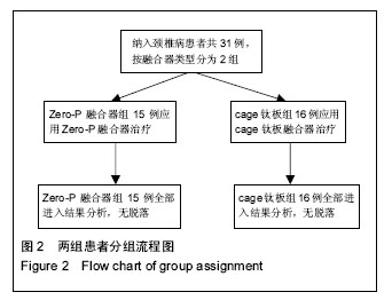
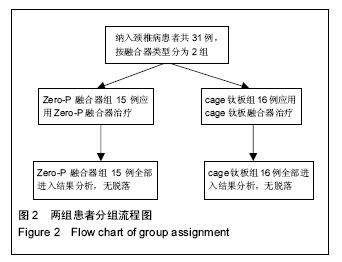
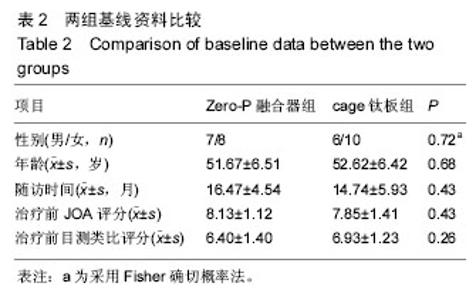
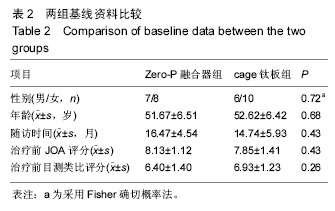
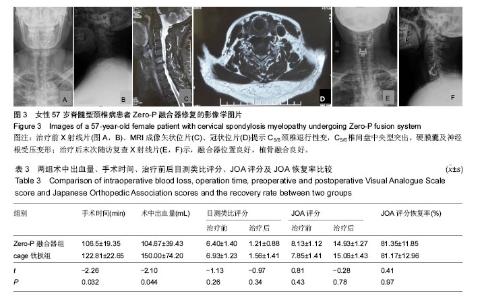
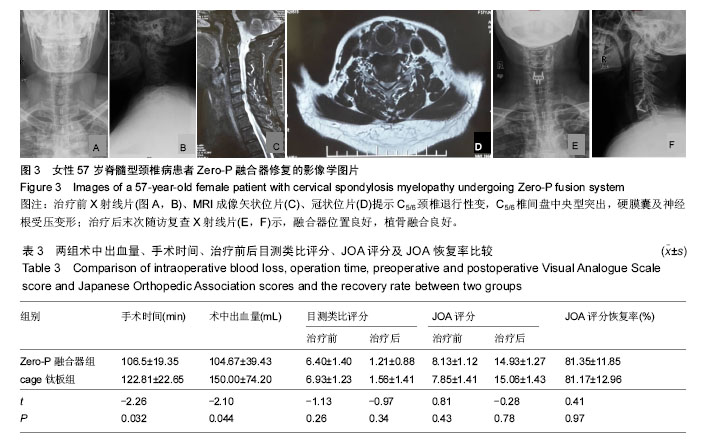
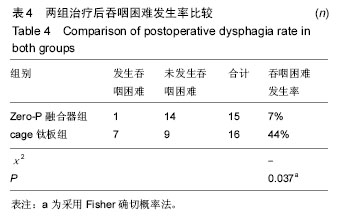
2.4 并发症情况 两组中均未发生切口感染、术后出血、喉咙水肿等严重并发症,无螺丝松动、螺丝及钛板断裂情况发生。 根据Bazaz标准,在Zero-P融合器组中有1例在术后2周发生吞咽困难,术后2个月消失;cage钛板组有7例患者发生术后吞咽困难,其中5例在术后2周轻度吞咽困难,1例术后3周中度吞咽困难,1例在术后3周有重度吞咽困难,经保守治疗后,4例在术后2个月恢复,2例在术后6个月恢复,但有1例在末次随访时并无明显减轻。两组的术后吞咽困难发生率差异有显著性意义(P=0.037),见表4。 2.5 关节退变情况 根据末次随访影像学数据可以发现,Zero-P融合器组32个相邻关节中5个相邻关节有椎间盘退化情况,相邻水平关节退化率为16%;cage钛板组共32个相邻关节中,8个相邻关节有椎间盘退化情况,比率为25%。两组相邻关节退变比率差异无显著性意义(P=0.48)。 2.6 典型病例 Zero-P融合器组脊髓型颈椎病患者,详细影像学资料见图3。"
| [1] Cloward RB. The anterior approach for removal of ruptured cervical disks. J Neurosurg. 1958;15(6): 602-617.[2] Ahn SS, So WS, Ku MG, et al. Radiologic Findings and Risk Factors of Adjacent Segment Degeneration after Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion : A Retrospective Matched Cohort Study with 3-Year Follow-Up Using MRI. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016; 59(2): 129-136.[3] Kienapfel H, Koller M, Hinder D, et al. Integrated outcome assessment after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: myelocompression but not adjacent instability affect patient-reported quality of life and cervical spine symptoms. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(22): 2501-2509.[4] Kalb S, Reis MT, Cowperthwaite MC, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: incidence and risk factors. World Neurosurg. 2012;77(1): 183-187.[5] Kim SW, Limson MA, Kim SB, et al. Comparison of radiographic changes after ACDF versus Bryan disc arthroplasty in single and bi-level cases. Eur Spine. 2009;18(2): 218-231.[6] Guo L, Fan S. [Effectiveness Comparison between Anterior Cervical Zero- Profile Interbody Fusion Device and Anterior Cervical Plate Cage Benezech]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015; 29(7): 840-844.[7] Xie Y, Li H, Yuan J, et al. A prospective randomized comparison of PEEK cage containing calcium sulphate or demineralized bone matrix with autograft in anterior cervical interbody fusion. Int Orthop. 2015;39(6): 1129-1136.[8] Bunyaratavej K, Montriwiwatnchai P, Siwanuwatn R, et al. Localizing value of pain distribution patterns in cervical spondylosis. Asian Spine J. 2015; 9(2): 210-217.[9] Yan D, Wang Z, Deng S, et al. Anterior corpectomy and reconstruction with titanium mesh cage and dynamic cervical plate for cervical spondylotic myelopathy in elderly osteoporosis patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 131(10): 1369-1374.[10] Bhatia K, Frydenberg E, Steel T, et al. An anterior expandable titanium cage in Mycobacterium avium vertebral osteomyelitis. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(3): 431-434.[11] Shao H, Chen J, Ru B, et al. Zero-Profile implant versus conventional cage-plate implant in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for the treatment of degenerative cervical spondylosis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10: 148.[12] Scholz M, Schnake KJ, Pingel A, et al. A new Zero-Profile implant for stand-alone anterior cervical interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3): 666-673.[13] Alvin MD, Lubelski D, Abdullah KG, et al. Cost-Utility Analysis of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion With Plating (ACDFP) Versus Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy (PCF) for Patients With Single-level Cervical Radiculopathy at 1-Year Follow-up. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(2): E67-72.[14] Son DK, Son DW, Kim HS, et al. Comparative study of clinical and radiological outcomes of a Zero-Profile device concerning reduced postoperative Dysphagia after single level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014;56(2): 103-107.[15] Ament JD, Yang Z, Chen Y, et al. A Novel Quality-of-Life Utility Index in Patients With Multilevel Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease: Comparison of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion With Total Disc Replacement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2015. 40(14): 1072-1078.[16] Fraioli MF, Marciani MG, Umana GE, et al. Anterior Microsurgical Approach to Ventral Lower Cervical Spine Meningiomas: Indications, Surgical Technique and Long Term Outcome. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015;14(4): 505-510.[17] Burkus JK, Schuler TC, Gornet MF, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion for the management of chronic lower back pain: current strategies and concepts. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004;35(1): 25-32.[18] Wang C, Zhang Y, Yuan W. Early Clinical Outcomes and Radiographic Features After Treatment of Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease with the New Zero-Profile Implant: A One-year Follow-up Retrospective Study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014.[19] Li GL, Hu JZ, Lu HB, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy with arthroplasty versus anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for cervical spondylosis. J Clin Neurosci. 2015; 22(3): 460-467.[20] Bazaz R, Lee MJ, Yoo JU. Incidence of dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a prospective study. Spine. 2002;27(22): 2453-2458.[21] Burns SP, Weaver F, Chin A, et al. Cervical stenosis in spinal cord injury and disorders. J Spinal Cord Med. 2015.[22] Barbagallo GM, Romano D, Certo F, et al. Zero-P: a new Zero-Profile cage-plate device for single and multilevel ACDF. A single institution series with four years maximum follow-up and review of the literature on Zero-Profile devices. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 6: S868-878.[23] Li Y, Hao D, He B, et al. The Efficiency of Zero-Profile Implant in Anterior Cervical Discectomy Fusion: A Prospective Controlled Long-term Follow-up Study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013; 24(7): E315-320.[24] Vanek P, Bradac O, Saur K. Anterior interbody fusion of the cervical spine with a Zero-P spacer: radiographic results with a minimum follow-up of one year in a prospective study. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2011;78(6): 562-567.[25] Vanek P, Bradac O, Delacy P, et al. Anterior interbody fusion of the cervical spine with Zero-P spacer: prospective comparative study-clinical and radiological results at a minimum 2 years after surgery. Spine. 2013;38(13): E792-797.[26] Epstein NE, Hollingsworth R. Diagnosis and management of traumatic cervical central spinal cord injury: A review. Surg Neurol Int. 2015;6(Suppl 4): S140-153.[27] Hofstetter CP, Kesavabhotla K, Boockvar JA. Zero-Profile Anchored Spacer Reduces Rate of Dysphagia Compared With ACDF With Anterior Plating. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(5): E284-290.[28] Dong J, Lu M, Lu T, et al. Meta-Analysis Comparing Zero-Profile Spacer and Anterior Plate in Anterior Cervical Fusion. PLoS One. 2015;10(6): e0130223.[29] McGrory BJ, Klassen RA. Arthrodesis of the cervical spine for fractures and dislocations in children and adolescents. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(11): 1606-1616.[30] Murphy SM, Laura M, Blake J, et al. Conduction block and tonic pupils in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease caused by a myelin protein zero p.Ile112Thr mutation. Neuromuscul Disord. 2011;21(3): 223-226.[31] Nguyen C, Sanchez K, Roren A, et al. Anatomical specificities of the degenerated cervical spine: a narrative review of clinical implications, with special focus on targeted spinal injections. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016.[32] Nakagawa H, Okazaki T, Saito K. Surgical Strategies in Management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. World Neurosurg. 2015;84(2): 220-221.[33] Chen Y, Chen H, Cao P, et al. Anterior cervical interbody fusion with the Zero-P spacer: mid-term results of two-level fusion. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(8): 1666-1672.[34] Azab W, Abdel-Razek M, Ali A, et al. Outcome evaluation of a Zero-Profile implant for anterior cervical diskectomy with fusion. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22(5): 611-617.[35] Wang ZD, Zhu RF, Yang HL, et al. The application of a Zero-Profile implant in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(3):462-466.[36] Njoku IJ, Alimi M, Leng LZ, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with a Zero-Profile integrated plate and spacer device: a clinical and radiological study: Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(4): 529-537.[37] Miao J, Shen Y, Kuang Y, et al. Early follow-up outcomes of a new Zero-Profile implant used in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(5): E193-197.[38] Cloward RB. The anterior approach for removal of ruptured cervical disks. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(5): 496-511.[39] Goodwin CR, Desai A, Khattab MH, et al. Cervical Fusion for Absent Pedicle Syndrome Manifesting with Myelopathy. World Neurosurg. 2016;86: 515. e17-22.[40] He L, Qian Y, Jin YJ, et al. [The clinical value of end plate rings in preventing subsidence of titanium cage in anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion surgery]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(9): 738-744. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||