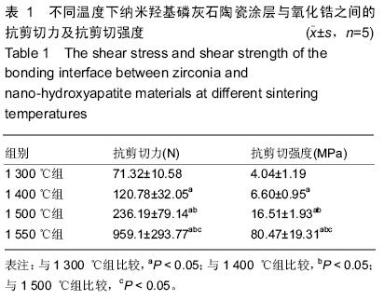
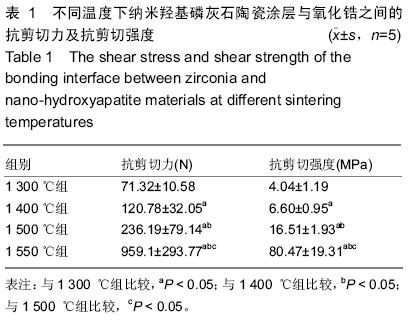
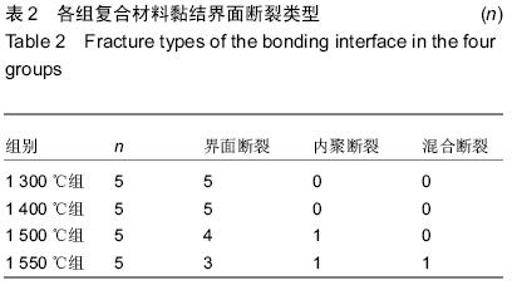
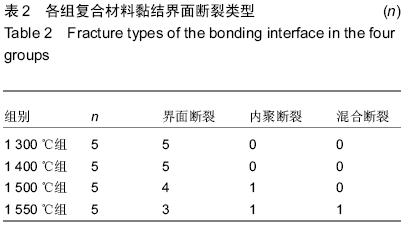
| [1] Piconi C,Maccauro G.Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials.1999; 20(1):1-25.[2] Vaquero-Aguilar C,Jiménez-Melendo M, Torres-Lagares D,et al. Zirconia implant abutments: microstructural analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(4):785-791.[3] Assal P.The osseointegration of zirconia dental implants.Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed. 2013; 123 (7-8): 644-654.[4] 吴成铁,常江.硅酸盐生物活性陶瓷用于骨组织修复及再生的研究[J].无机材料学报,2013,28(1):29-36.[5] Dalal A,Pawar V,Mcallister K,et al.Orthopedic implant cobalt-alloy particles produce greater toxicity and inflammatory cytokines than titanium alloy and zirconium alloy-based particles in vitro, in human osteoblasts, fibroblasts and macrophages. J Biomed Mater Res A.2012;100(8):2147-2158.[6] 唐月军,王心玲,周中华,等.纳米级二氧化锆增韧羟基磷灰石生物复合陶瓷对兔骨髓基质干细胞增殖、分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(3):450-452.[7] 肖秀峰,刘榕芳,郑炀曾.羟基磷灰石/氧化锆复合涂层热稳定性和结合强度的研究[J].无机化学学报,2005,21(7): 965-970.[8] Li W,Gao L.Fabrication of Hap-ZrO2(3Y) nano-composite by SPS.Biomater. 2003; 24(6): 937- 940.[9] Shen Z,Adolfsson E,Nygren M,et a1.Dense Hydroxyapatite-Zirconia Ceramic Composites with High Strength for Biological Applications.Adv Mater. 2001;13(3):214-216.[10] Richards RG,Moriarty TF,Miclau T,et al.Advances in biomaterials and surface technologies.J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(12):703-707.[11] Papia E,Jimbo R,Chrcanovic BR,et al.Surface structure and mechanical properties of impaction-modified Y-TZP.Dent Mater.2014; 30(8): 808-816.[12] 刘继进,阮建明,邹俭鹏,等.羟基磷灰石-氧化锆复合材料的致密化及其力学性能研究[J].中国有色金属学报, 2005,15(6):952-957.[13] Kurtz SM,Devine JN. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials.2007; 28(32):4845-4869.[14] 黄勇,严静雅,李滚,等.柠檬酸根对电沉积羟基磷灰石氧化锆过渡涂层的影响[J].无机化学学报,2012,28(6): 1105- 1110. [15] 游滢滢,冯云枝.纳米含氟羟基磷灰石牙种植体的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12):1901-1906.[16] 李凌云,刘璐琪,汤龙程,等.二氧化硅纳米颗粒增强炭纤维/环氧树脂界面性能[J].材料工程,2012,40(6):32-36.[17] Moller B,Terheyden H,Aci Y,et al.A comparison of biocompati-bility and osseointegration of ceramic and titanium implants: an in vivo and in vitro study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2012;41(5):638-645.[18] Prithviraj DR,Deeksha S,Regish KM,et al.A systematic review of zirconia as an implant material.Indian J Dent Res.2012;23(5):643-649.[19] Lima EM,Koo H,Vacca Smith AM,et al.Adsorption of salivary and serum proteins, and bacterial adherence on titanium and zirconia ceramic surfaces.Clin Oral Impl Res.2008; 19(8):780-785.[20] Hisbergues M,Vendeville S,Vendeville P.Zinconia:established facts and perspectives for a biomaterial in dental implantology.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;88(2):519-529.[21] Shon WJ,Chung SH,Kim HK,et al.Peri-implant bone formation of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma-treated zirconia implants with different surface roughness in rabbit tibiae.Clin Oral Implants Res.2014; 25(5): 573-579.[22] 阳杰,罗雪婷,吴丽萍,等.纳米二氧化锆的制备和性能应用研究进展[J].应用化工,2014,43(9):1694-1696.[23] 袁明,陈萍华,蒋华麟,等.氧化锆陶瓷增韧方法的研究进展[J].江西化工,2013,29(1):1-4.[24] 王瑜,龚玲,计艳,等.溶胶-凝胶法制备硅涂层提高牙科高强度陶瓷与复合树脂的粘接强度[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2012,28(1):30-33.[25] Xuereb M,Camilleri J,Attard NJ.Systematic review of current dental implant coating materials and novel coating techniques.Int J Prosthodont.2015;28(1): 51-59. [26] Zhang N,Zhai D,Chen L,et al.Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Si and Sr co-substituted hydroxyapatite nanowires using strontium containing calcium silicate as precursors.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;37(1):286-291.[27] 杜桥,牛光良.氧化锆的表面粗化和改性[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(1):97-101.[28] 於学良,唐月军,曹美玉,等.纳米级二氧化锆增韧羟基磷灰石的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2010, 14(16):2895-2898.[29] Mistry S,Kundu D,Datta S,et al.Comparison of bioactive glass coated and hydroxyapatite coated titanium dental implants in the human jaw bone.Aust Dent J.2011;56(1):68-75.[30] 许景顺,鲍雨梅,高海明,等.等离子喷涂羟基磷灰石涂层的增韧改性方法及磨损机理研究进展[J].中国陶瓷,2015, 51(5):9-13.[31] Wu A,Liu X,Gao C.Role of adsorbed proteins on hydroxyapatite-coated titanium in osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation.Sci Bull.2015;60(7): 691 -700.[32] 王春燕,全仁夫,汪宏斌,等.HA粉末与烧结体的高温分解及再生特性[J].武汉理工大学学报,2010,32(21):18-22.[33] 李小倩,夏海斌,高戈,等.HA- ZrO2复合陶瓷烧结致密化过程中的晶粒行为[J].硅酸盐通报,2012,31(4):827-831.[34] 罗民华,徐琼琼,朱庆霞.羟基磷灰石分解和恢复的研究[J].中国陶瓷,2007,43(4):15-17.[35] Champion E. Sintering of calcium phosphate bioceramics.Acta Biomaterialia .2013;9(4):5855-5875.[36] 张慧敏,杨建军,林映辉,等.烧结温度对氧化锆基台材料机械性能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(8):1421-1424. |