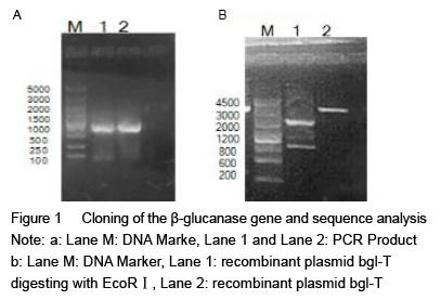
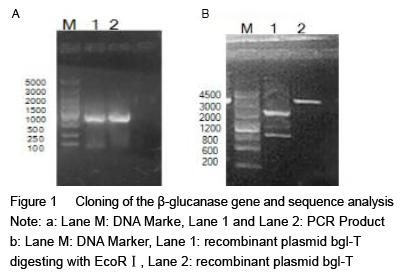
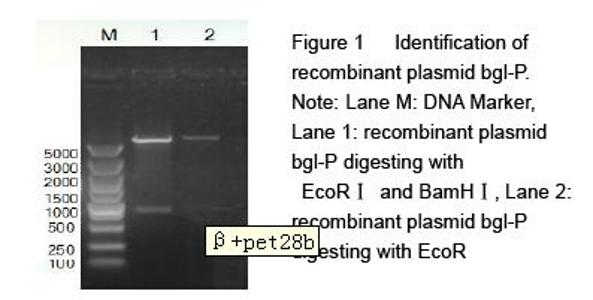
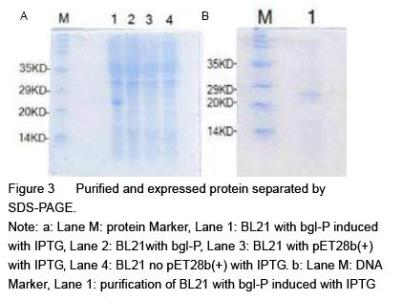
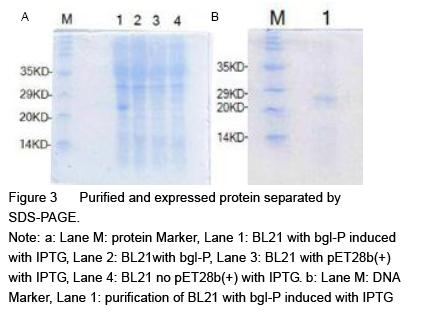
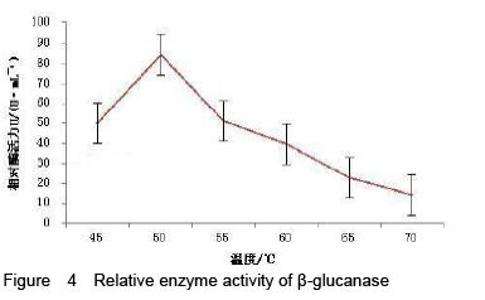
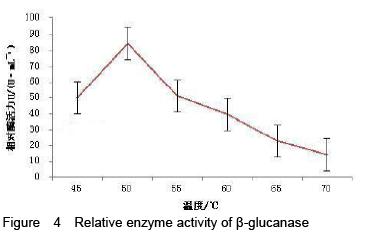
| [1] Yan J, Vetvicka V, Xia Y, et al. Critical role of Kupffer cell CR3 (CD11b/CD18) in the clearance of IgM-opsonized erythrocytes or soluble beta-glucan[J]. Immunopharmacology, 2000,46(1): 39-54.PMID: 10665778 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][2] Cassnoe A, Bistoni F, et al. Immunopotentiation of anticancer chemotherapy by Candida albicans, other yeasts and insoluble glucan in an experimental lymphoma model[J]. Saboraudia, 1982, 20(2): 115-125.PMID: 7051368 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][3] Tokunaka K, Ohno N, et al. Immunopharmacological and immunotoxicological activities of a water-soluble(1,3)-beta-D-glucan, CSBG from Candida spp[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2000, 22(5): 383-394.PMID: 10708886 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][4] Francelino A E, Vieira L R, Vasques A T, et al. Effect of beta-glucans in the control of blood glucose levels of diabetic patients: a systematicreview[J]. Nutr Hosp, 2014, 31(1): 170-177.PMID: 25561108 [PubMed - in process][5] Queenan K M, Stewart M L, Smith K N, et al. Concentrated oat beta-glucan, a fermentable fiber, lowers serum cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic adults in a randomized controlled trial[J]. Nutr J, 2007 26(6): 6.PMID: 17386092 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC1847683[6] Lee D H, Kim H W. Innate immunity induced by fungal beta-glucans via dectin-1 signaling pathway[J]. Int J Med Mushrooms, 2014, 16(1): 1-16.PMID: 24940900 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][7] Liu J, Gunn L, Yan J, et al. Yeast-derived beta-glucan in combination with anti-tumor monoclonal antibody therapy in cancer[J]. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov, 2009, 4(2):101-109.PMID: 19519533 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][8] [8] Galisteo M, Duarte J, Zarzuelo A. Effects of dietary fibers on disturbances clustered in the metabolic syndrome[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2008(19): 71-84.PMID: 17618108 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][9] Silva V O, Lobato R V, Andrade E F. β-Glucans (Saccharomyces cereviseae) reduce glucose levels and attenuate alveolar bone loss in diabetic rats with periodontal disease[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 20(10): 1-13.PMID: 26291983 [PubMed - in process] PMCID: PMC4546386[10] Tosh S M, Review of human studies investigating the post-prandial blood-glucose lowering ability of oat and barley food products[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2013, 67(4):310-317.PMID: 23422921 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][11] Robert N, Stacey J B, Bruce R B, et al. Plasma lipid changes after supplementation with β-glucan fiber from yeast[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 1999(70): 2208-2212.PMID: 10426696 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][12] Sekiguchi S, Tomisawa Y, Ohki T, et al. Suppression of macrophage- mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by soluble β-glucan due to a failure of PKC-β II translocation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2016(31): 195-199.PMID: 26745713 [PubMed -in process][13] Nisini R, Torosantucci A, Romagnoli G, et al. Beta-glucan of Candida albicans cell wall causes the subversion of human monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2007, 82(5): 1136-1142.17656653 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][14] Li B, Cramer D, Wagner S, et al. Yeast glucan particles activate murine resident macrophages to secrete proin ammatory cytokines via MyD88 and Syk kinase dependent pathways[J]. Clin Immunol, 2007, 124(2): 170-181.17572156 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC2017100[15] Charalampopoulos D, Wang R, Pandiella S S, et al. Application of cereals and cereal components in functional foods: a review[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2002, 79(1-2): 131-141.PMID: 12382693 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][16] Arashdeep S, Savita S. Bioactive components and functional properties of biologically activated cereal grains: a bibliographic review[J]. critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 2015, 00PMID: 26466514 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher][17] Jose D, Jayesh P, Gopinath P, et al. Potential application of beta-1, 3-glucanase from an environmental isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MCCB 123 in fungal DNA extraction[J]. Indian J Exp Biol, 2014, 52(1): 89-96. PMID: 24617020 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][18] Saito H, Minra KI. Preparation of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid by phenol treatment[J]. biochimica at biophgsica acta, 1963, 72: 619-629.PMID: 14071565 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][19] Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, et al. The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis[J]. Nature, 1997, 390(6657): 249-256.PMID: 9384377 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][20] Inoue H, Nojima H, Okayama H. High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids[J]. Gene, 1990, 96: 23-28.PMID: 2265755 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][21] Lucena S A, Moraes C S, Costa S G, et al. Miniaturization of hydrolase assays in thermocyclers[J]. Anal Biochem, 2013,434(1):39-43. PMID: 23123426 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][22] Teixeira R S, da Silva A S, Ferreira-Leitão V S, et al. Amino acids interference on the quantification of reducing sugars by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid assay mislead carbohydrase activity measurements[J].Carbohydr Res, 2012(363): 33-37.[23] Yan J, Allendorf D J, Brandley B. Yeast whole glucan particle (WGP) beta-glucan in conjunction with antitumour monoclonal antibodies to treat cancer[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2005,5(5): 691-702.PMID: 15934844 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][24] Sobrero A F, Maurel J, Fehrenbacher L, et al. EPIC: phase III trial of cetuximab plus irinotecan after fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2008, 26(14): 2311-2319.PMID: 18390971 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] [25] Salvador C, Li B, Hansen R, et al. Yeast-derived beta-glucan augments the therapeutic effcacy mediated by anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody in human carcinoma xenograft models[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(4): 1239-1247.18281559 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC2394864[26] Hong F, Hansen R D, Yan J, et al. Beta-glucan functions as an adjuvant for monoclonal antibody immunotherapy by recruiting tumoricidal granulocytes as killer cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2003, 63(24): 9023-9031.PMID: 14695221 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][27] Cramer D E, Allendorf D J, Baran J T, et al. Beta-glucan enhances complement mediated hematopoietic recovery after bone marrow injury[J]. Blood, 2006, 107(2): 835-840.PMID: 16179370 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC1895628[28] Vetvicka V. Glucan-immunostimulant, adjuvant, potential drug[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2011, 2(2): 115-119. PMID: 21603320 [PubMed] PMCID: PMC3095473[29] Vuksan V, Panahi S, Lyon M, et a1. Viscosity of fiber preloads affects food jntake in adolescents[J]. Nutrition, Metabolism & Cardiovascular Diseases, 2009, 19: 498-503.PMID: 19157816 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE][30] Liu J, Gunn L, Hansen R, et al. Combined yeast-derived β-glucan with anti-tumor monoclonal antibody for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2009, 86(3): 208-214.PMID: 19454271 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC2685877[31] Delaunois B, Colby T, Belloy N, et al. Large-scale proteomic analysis of the grapevine leaf apoplastic fluid reveals mainly stress-related proteins and cell wall modifying enzymes[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2013(13): 24.PMID: 23391302 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC3640900[32] Hendereon S W, Baumann U, Blackmore D H, et al. Shoot chloride exclusion and salt tolerance in grapevine is associated with differentialion transporter expression in roots[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2014(14): 273.PMID: 25344057 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] PMCID: PMC4220414[33] Kurakake, M, Yamanouchi, Y, Kinohara, K, et al. Enzymatic Properties of beta-1,3-Glucanase from Streptomyces sp Mo[J]. J Food Sci, 2013, 78 (4): C502.PMID: 23560994 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] |