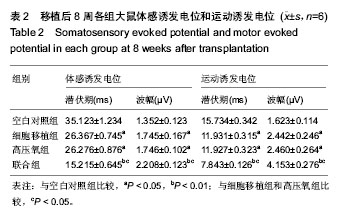
| [1] Duchossoy Y, David S, Baulieu EE, et al. Treatment of experimental spinal cord injury with 3β-methoxy- pregnenolone. Brain Res. 2011;1403:57-66.
[2] De Vries M, Cooper HM. Emerging roles for neogenin and its ligands in CNS development. J Neurochem. 2008;106(4): 1483-1492.
[3] Fehlings MG, Sekhon LH. Acute interventions in spinal cord injury: what do we know, what should we do. Clin Neurosurg. 2001;48:226-242.
[4] Chi GF, Kim MR, Kim DW, et al. Schwann cells differentiated from spheroid-forming cells of rat subcutaneous fat tissue myelinate axons in the spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2010; 222(2):304-317.
[5] Ban DX, Kong XH, Feng SQ, et al. Intraspinal cord graft of autologous activated Schwann cells efficiently promotes axonal regeneration and functional recovery after rat's spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2009;1256:149-161.
[6] Amar AP, Levy ML. Pathogenesis and pharmacological strategies for mitigating secondary damage in acute spinal cord injury. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(5):1027-1039.
[7] 万虹,林野,孙梅珍,等.雪旺氏细胞脑内移植前的体外培养[J].中华神经外科杂志,2003,19(3):213-215.
[8] Young W. Spinal cord contusion models. Prog Brain Res. 2002;137:231-255.
[9] Finch AM, Wong AK, Paczkowski NJ, et al. Low-molecular- weight peptidic and cyclic antagonists of the receptor for the complement factor C5a. J Med Chem. 1999;42(11):1965-1974.
[10] Pallini R, Vitiani LR, Bez A, et al. Homologous transplantation of neural stem cells to the injured spinal cord of mice. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(5):1014-1025.
[11] Albin RL, Mink JW. Recent advances in Tourette syndrome research. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29(3):175-182.
[12] Haku T, Okuda S, Kanematsu F, et al. Repair of cervical esophageal perforation using longus colli muscle flap: a case report of a patient with cervical spinal cord injury. Spine J. 2008;8(5):831-835.
[13] Pearse DD, Sanchez AR, Pereira FC, et al. Transplantation of Schwann cells and/or olfactory ensheathing glia into the contused spinal cord: Survival, migration, axon association, and functional recovery. Glia. 2007;55(9):976-1000.
[14] Papastefanaki F, Chen J, Lavdas AA, et al. Grafts of Schwann cells engineered to express PSA-NCAM promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 8): 2159-2174.
[15] Weaver FM, Burns SP, Evans CT, et al. Provider perspectives on soldiers with new spinal cord injuries returning from Iraq and Afghanistan. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90(3):517-521.
[16] Chu D, Bakaeen FG, Shenaq SA, et al. Open-heart operations in patients with a spinal cord injury. Am J Surg. 2007;194(5):663-667.
[17] Lepore AC, Neuhuber B, Connors TM, et al. Long-term fate of neural precursor cells following transplantation into developing and adult CNS. Neuroscience. 2006;139(2): 513-530.
[18] Saberi H, Moshayedi P, Aghayan HR, et al. Treatment of chronic thoracic spinal cord injury patients with autologous Schwann cell transplantation: an interim report on safety considerations and possible outcomes. Neurosci Lett. 2008; 443(1):46-50.
[19] Crowe MJ, Bresnahan JC, Shuman SL, et al. Apoptosis and delayed degeneration after spinal cord injury in rats and monkeys. Nat Med. 1997;3(1):73-76.
[20] Liu XZ, Xu XM, Hu R, et al. Neuronal and glial apoptosis after traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 1997;17(14): 5395-5406.
[21] Ohta S, Iwashita Y, Takada H, et al. Neuroprotection and enhanced recovery with edaravone after acute spinal cord injury in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(10):1154-1158.
[22] Banno M, Mizuno T, Kato H, et al. The radical scavenger edaravone prevents oxidative neurotoxicity induced by peroxynitrite and activated microglia. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48(2):283-290.
[23] Kwon BK, Tetzlaff W, Grauer JN, et al. Pathophysiology and pharmacologic treatment of acute spinal cord injury. Spine J. 2004;4(4):451-464.
[24] Crowe MJ, Bresnahan JC, Shuman SL, et al. Apoptosis and delayed degeneration after spinal cord injury in rats and monkeys. Nat Med. 1997;3(1):73-76.
[25] Liu XZ, Xu XM, Hu R, et al. Neuronal and glial apoptosis after traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 1997;17(14):5395- 5406.
[26] Ohta S, Iwashita Y, Takada H, et al. Neuroprotection and enhanced recovery with edaravone after acute spinal cord injury in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(10):1154-1158.
[27] Banno M, Mizuno T, Kato H, et al. The radical scavenger edaravone prevents oxidative neurotoxicity induced by peroxynitrite and activated microglia. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48(2):283-290.
[28] Björklund E, Lindberg E, Rundgren M, et al. Ischaemic brain damage after cardiac arrest and induced hypothermia--a systematic description of selective eosinophilic neuronal death. A neuropathologic study of 23 patients. Resuscitation. 2014;85(4):527-532.
[29] Ariake K, Ohtsuka H, Motoi F, et al. GCF2/LRRFIP1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis and liver invasion through integrin- dependent RhoA activation. Cancer Lett. 2012;325(1):99-107.
[30] Pearse DD, Sanchez AR, Pereira FC, et al. Transplantation of Schwann cells and/or olfactory ensheathing glia into the contused spinal cord: Survival, migration, axon association, and functional recovery. Glia. 2007;55(9):976-1000.
[31] Pallini R, Vitiani LR, Bez A, et al. Homologous transplantation of neural stem cells to the injured spinal cord of mice. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(5):1014-1025.
[32] Chuang SK. Limited evidence to demonstrate that the use of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy reduces the incidence of osteoradionecrosis in irradiated patients requiring tooth extraction. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2011;11(3):129-131.
[33] 丁进京.高压氧治疗对急性期脑梗死患者血清ACA水平的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2012,15(3): 34-36. |