Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1450-1463.doi: 10.12307/2026.573
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration
Lai Jiaming1, 2, Song Yuling3, Chen Zixi4, Wei Jinghuan5, Cai Hao1, 2, Li Guoquan1, 6
- 1Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Qinghai University Medical College, Xining 810016, Qinghai Province, China; 2Radiation Oncology Department, 3Physical Technology Engineering Department, 4Office of Medical Information, 5Hospital Office, Fifth People’s Hospital/Cancer Hospital of Qinghai Province, Xining 810007, Qinghai Province, China; 6Department of Oncology, Qinghai Provincial People’s Hospital, Xining 810007, Qinghai Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-22Accepted:2025-01-21Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-16 -
Contact:Li Guoquan, PhD, Chief physician, Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Qinghai University Medical College, Xining 810016, Qinghai Province, China; Department of Oncology, Qinghai Provincial People’s Hospital, Xining 810007, Qinghai Province, China Co-corresponding author: Cai Hao, PhD, Associate chief physician, Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Qinghai University Medical College, Xining 810016, Qinghai Province, China; Radiation Oncology Department, Fifth People’s Hospital/Cancer Hospital of Qinghai Province, Xining 810007, Qinghai Province, China -
About author:Lai Jiaming, Master candidate, Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Qinghai University Medical College, Xining 810016, Qinghai Province, China; Radiation Oncology Department, Fifth People’s Hospital/Cancer Hospital of Qinghai Province, Xining 810007, Qinghai Province, China -
Supported by:2019 Qinghai Province “Kunlun Talents - High-end Innovation and Entrepreneurial Talents” Project for Directly Introducing Leading Talents, No. QHKLYC-GDCXCY-2019-026 (to LGQ); Qinghai Provincial Health and Wellness Commission Guiding Subject, No. 2021-wjzdx-79 (to CH); Qinghai Provincial Health and Wellness Commission Guiding Project, No. J2024013 (to CH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
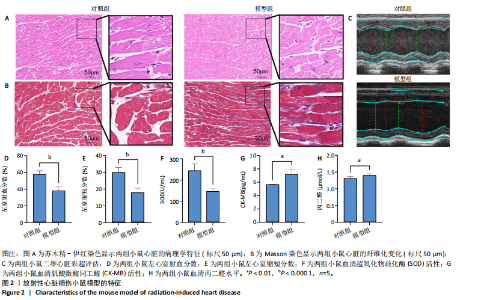
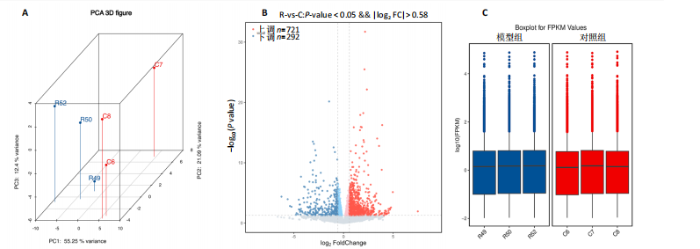
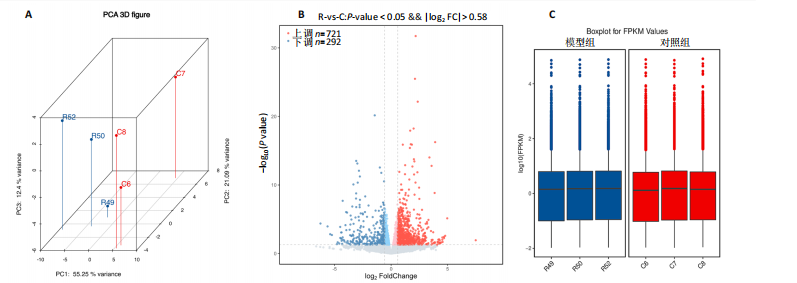
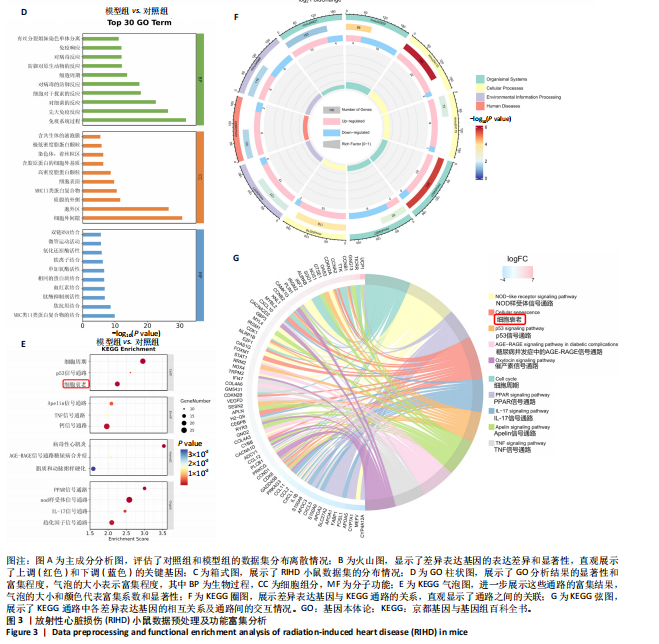
2.1 实验动物数量分析 共有20只小鼠参加实验,采用随机数字表法将小鼠分为对照组和RIHD模型组,每组10只小鼠进行血常规检测,每组随机选择5只小鼠进行血清肌酸激酶同工酶、丙二醛和超氧化物歧化酶水平检测,每组随机选择5只小鼠进行心脏彩超检测。 2.2 RIHD小鼠的心脏病理学、超声心动图特征、血清氧化应激指标分析 在小鼠胸部心脏照射后16周,与对照组相比,苏木精-伊红染色显示模型组小鼠心脏结构发生显著变化,表现为心脏组织中空泡数量增加、细胞间隙扩张,Masson染色显示心脏纤维化面积增大(图2A,B)。左心功能评估结果(图2C-E)显示,模型组小鼠左室射血分数和左室缩短分数较对照组显著下降(P < 0.05)。ELISA结果(图2F-H)显示,与对照组相比,模型组小鼠血清肌酸激酶同工酶和丙二醛水平显著升高(P < 0.05),而超氧化物歧化酶水平显著降低(P < 0.05)。这表明小鼠心脏照射后16周引发了明显的心脏组织结构改变以及氧化应激反应。 2.3 RIHD小鼠差异表达基因的鉴定和富集分析 前期发现小鼠接受心脏照射出现了明显结构改变[26],为了探寻其中关键的调控基因,进行了RIHD小鼠转录组学测序。首先对RIHD小鼠数据集进行了主成分分析,结果表明两组存在明显区分(图3A),火山图展示721个上调基因和292个下调基因(图3B),箱式图显示成功消除了批次效应,实现了良好的数据归一化(图3C)。 GO富集分析表明,差异表达基因主要富集在细胞周期、病毒防御反应、干扰素反应、细菌反应、先天免疫反应以及氧化还原酶活性等生物过程中(图3D)。 KEGG通路分析结果(图3E-G)表明,差异表达基因主要参与细胞周期、p53信号通路、细胞衰老、凋亡、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路等,揭示了RIHD的发病机制涉及复杂的调控网络,尤其是细胞衰老和炎症失调。"

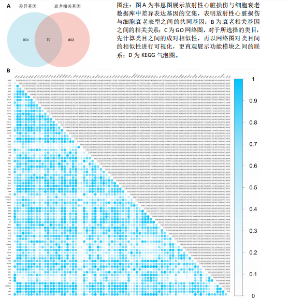
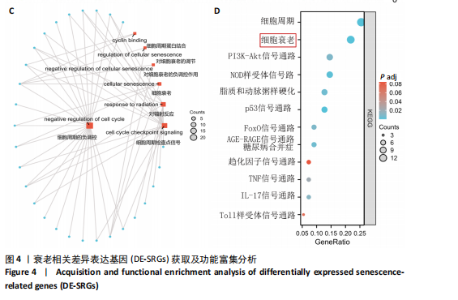
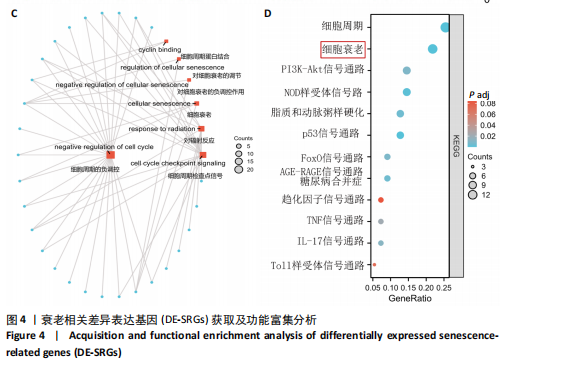
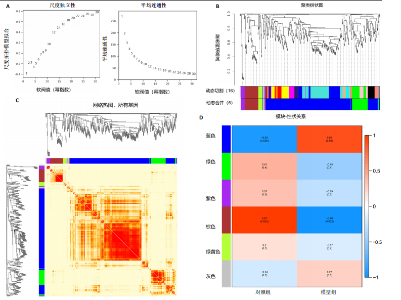
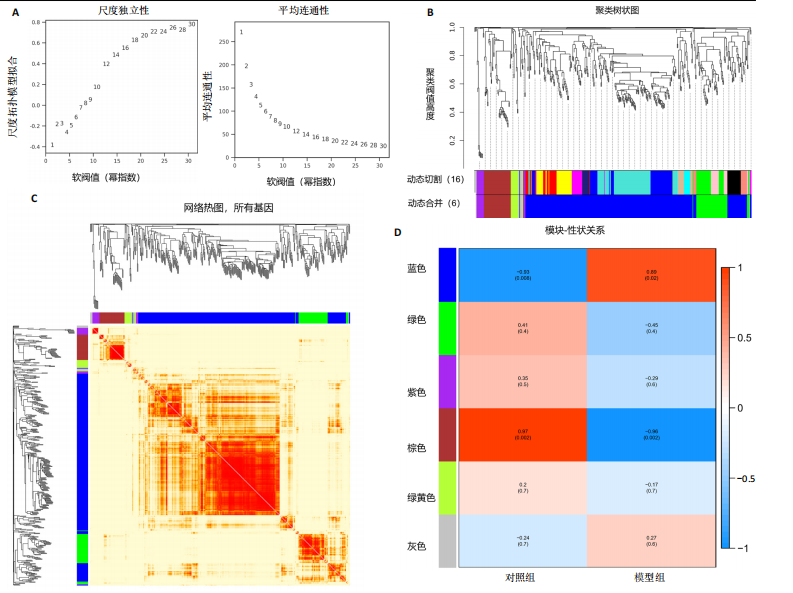
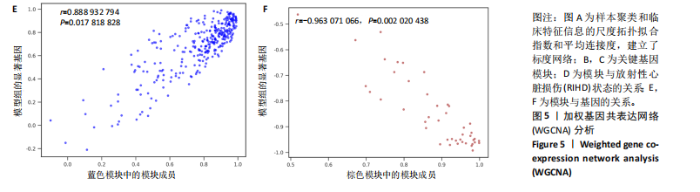
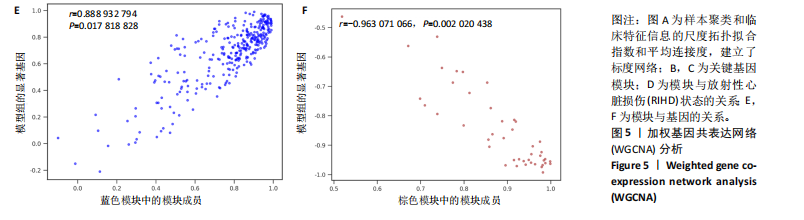
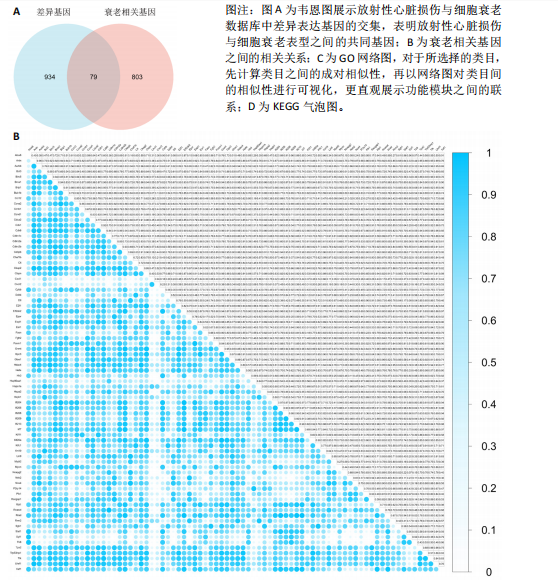
2.4 衰老相关差异表达基因的鉴定及富集分析 KEGG分析发现细胞衰老相关基因在RIHD中显著富集,1 013个差异表达基因与882个衰老相关基因进行交集分析,共鉴定出79个衰老相关差异表达基因 (图4A)。Spearman相关性分析揭示了衰老相关差异表达基因之间的显著相互关联(图4B)。GO分析显示:衰老相关差异表达基因显著富集于对细胞衰老的调控、对细胞衰老的负调控作用、细胞衰老、细胞周期蛋白结合、对辐射的响应、细胞周期检查点信号等生物过程(图4C)。KEGG分析表明,衰老相关差异表达基因富集于细胞周期、细胞衰老、PI3K-Akt信号通路、p53信号通路、FoxO信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、白细胞介素17信号通路等(图4D),进一步证明了细胞衰老在RIHD中的重要作用。 2.5 RIHD基因的识别模块 通过WGCNA识别出与RIHD显著相关的基因模块。使用样本聚类和临床特征信息建立了无标度网络(图5A),最终识别出6个基因模块(图5B,C),并评估了模块与RIHD状态的关系,其中蓝色模块(314个基因,r=0.89,P=0.02)、棕色模块(44个基因,r=-0.96,P=0.002)与RIHD状态显著相关(图5D)。此外,蓝色模块(314个基因,r=0.888 932 794,P=0.017 818 828)、棕色模块(44个基因,r=-0.963 071 066,P=0.002 020 438)与基因重要性极显著相关(图5E,F)。最终,从这2个模块中筛选出358个关键基因进行后续分析。 2.6 机器学习筛选Hub基因并验证 近年来,机器学习技术,尤其是随机森林模型[31],已被广泛应"
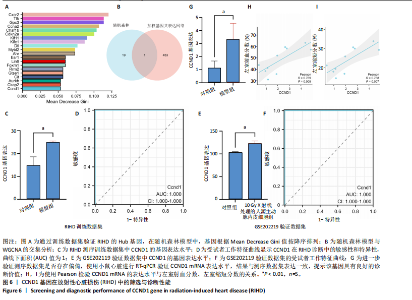
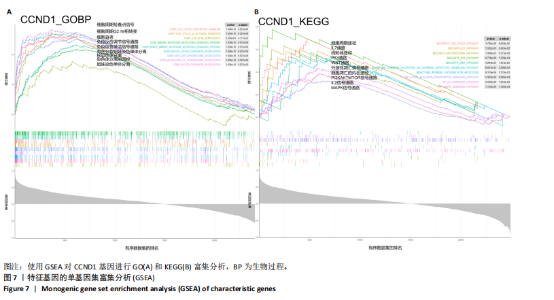
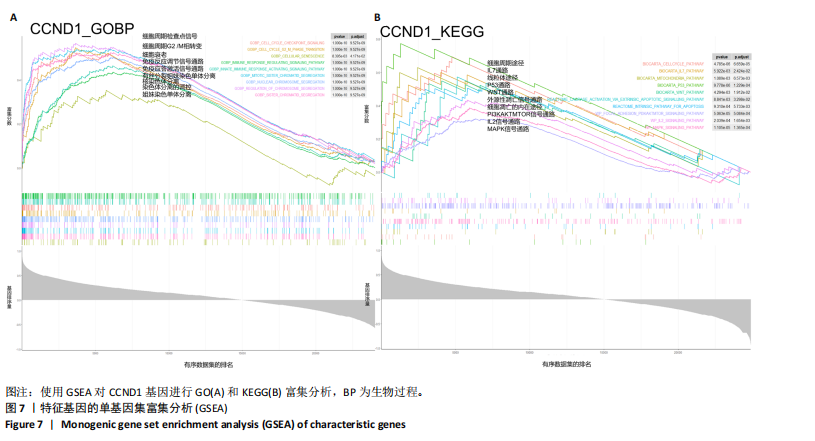
线测定,CCND1的曲线下面积为1,具有极高的诊断价值且模型组CCND1表达量较对照组上调(P < 0.05) (图6C,D)。在验证数据集GSE202119中,CCND1的表达模式与训练集一致,显著上调(P < 0.05),曲线下面积为1,进一步证明了CCND1在RIHD中的关键作用(图6E,F)。此外通过小鼠RIHD模型进行验证,模型组CCND1 mRNA表达较对照组显著上调(P < 0.01)(图6G)。进一步分析显示,CCND1与小鼠的左室射血分数(Pearson系数=0.770)、左室缩短分数(Pearson系数=0.789)呈显著正相关(图6H,I)。这表明CCND1可以作为RIHD中内皮细胞衰老的诊断标志物,且与心功能改变相关。 2.7 单基因GSEA分析 为进一步了解CCND1相关的生物学功能和信号通路,采用单基因GSEA方法进行GO和KEGG富集分析。图7A,B分别展示了CCND1在GO和KEGG中的主要富集条目。CCND1参与的生物学过程包括细胞衰老、细胞周期G2/M期转变、细胞周期检查点信号传导、先天免疫反应激活信号通"

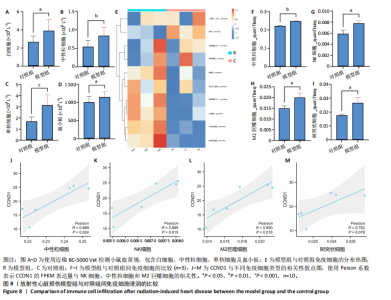
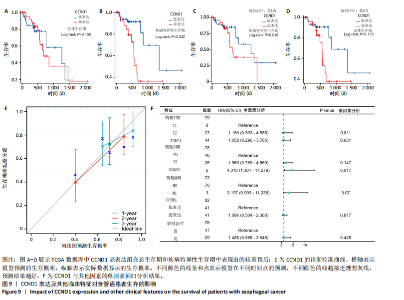
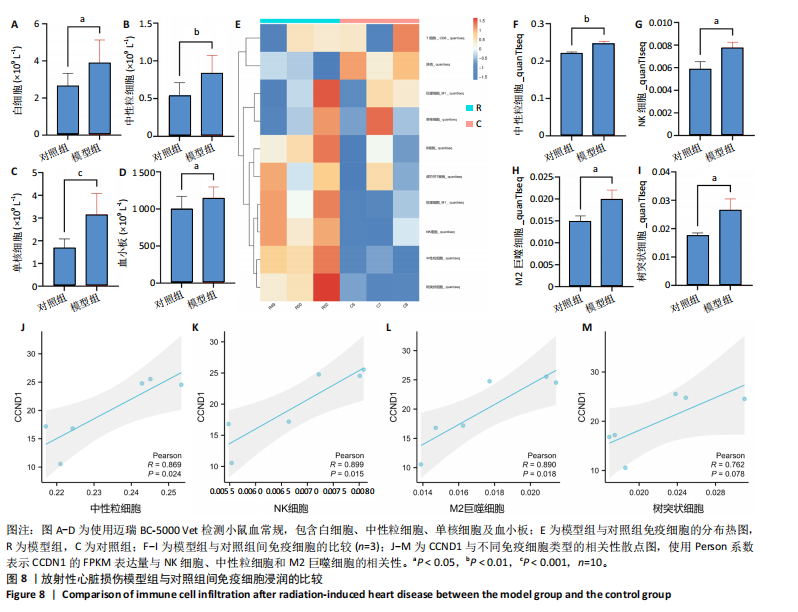
路、免疫反应调节信号通路、外源性凋亡信号通路、CGAS-STING信号通路等。KEGG通路包括p53信号通路、细胞周期通路、内源性凋亡通路、MAPK信号通路等。GSEA结果提示,CCND1可能在调节细胞衰老、细胞存活、免疫浸润和代谢中发挥重要作用。 2.8 免疫细胞浸润与CCND1在RIHD中的关联性分析 小鼠血常规显示,与对照组相比,模型组白细胞(P < 0.05)、中性粒细胞(P < 0.01)、单核细胞(P < 0.001)、血小板(P < 0.05)显著升高(图8A-D),提示心脏放射后炎症细胞升高。在心血管疾病的发生发展中发现有免疫失调现象导致疾病进一步进展[31-33],基于此,进行免疫浸润quanTIseq分析,结果显示,模型组与对照组在树突细胞、NK细胞、M2巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞的浸润量方面存在显著差异(P < 0.05) (图8E-I)。考虑到放疗引发免疫失调,使用Pearson相关性分析进一步探讨了CCND1与免疫细胞之间的潜在关联,结果显示CCND1与以下免疫细胞均存在显著正相关性:NK细胞(Pearson系数=0.899)、M2巨噬细胞(Pearson系数=0.890)、中性粒细胞(Pearson系数=0.869)(图8J-M),这进一步说明CCND1可能通过调控免疫炎症反应在RIHD中发挥作用。 2.9 CCND1在食管鳞癌放疗患者中的预后价值 CCND1在泛癌中与患者预后明显相关[34],为了解CCND1在食管鳞癌患者中的预后价值,尤其是接受胸部放疗后患者。使用TCGA数据库进行分析,结果显示,CCND1高表达组患者在疾病特异性生存期方面预后较差(P=0.018,图9A,B),并且与放疗后患者的疾病特异性生存期(P=0.042)显著相关(图9C,D)。这些结果表明,CCND1的高表达是胸部放疗后食管鳞癌患者预后的不良预测因子。通过单变量和多变量COX回归模型构建了1,3,5年的预后风险列线图,并绘制了预后校准曲线(图9E),结果显示,CCND1在食管鳞癌患者的预后评估中具有良好的预测能力。进一步分析表明,CCND1的表达水平与食"
| [1] JAHNG JWS, LITTLE MP, NO HJ, et al. Consequences of ionizing radiation exposure to the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;21(12):880-898. [2] BEDI R, AHMAD A, HORBAL P, et al. Radiation-associated Arrhythmias: Putative Pathophysiological Mechanisms, Prevalence, Screening and Management Strategies. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev. 2023;12:e24. [3] KIM L, LOCCOH EC, SANCHEZ R, et al. Contemporary Understandings of Cardiovascular Disease After Cancer Radiotherapy: a Focus on Ischemic Heart Disease. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020;22(11):151. [4] DONOVAN EK, POND GR, SEOW H, et al. Cardiac Morbidity Following Chemoradiation in Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2023; 35(2):e182-e188. [5] DARBY SC, EWERTZ M, MCGALE P, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(11):987-998. [6] BASELET B, SONVEAUX P, BAATOUT S, et al. Pathological effects of ionizing radiation: endothelial activation and dysfunction. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(4):699-728. [7] PHILIPP J, AZIMZADEH O, SUBRAMANIAN V, et al. Radiation-Induced Endothelial Inflammation Is Transferred via the Secretome to Recipient Cells in a STAT-Mediated Process. J Proteome Res. 2017;16(10):3903-3916. [8] LEE CL, MODING EJ, CUNEO KC, et al. p53 functions in endothelial cells to prevent radiation-induced myocardial injury in mice. Sci Signal. 2012;5(234):ra52. [9] ZAGAR TM, CARDINALE DM, MARKS LB. Breast cancer therapy-associated cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13(3):172-184. [10] KORPELA E, LIU SK. Endothelial perturbations and therapeutic strategies in normal tissue radiation damage. Radiat Oncol. 2014;9:266. [11] BLOOM SI, ISLAM MT, LESNIEWSKI LA, et al. Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial cell senescence. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023; 20(1):38-51. [12] HAN Y, KIM SY. Endothelial senescence in vascular diseases: current understanding and future opportunities in senotherapeutics. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(1):1-12. [13] HARTMAN RJG, OWSIANY K, MA L, et al. Sex-Stratified Gene Regulatory Networks Reveal Female Key Driver Genes of Atherosclerosis Involved in Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Switching. Circulation. 2021;143(7):713-726. [14] MOCCI G, SUKHAVASI K, ÖRD T, et al. Single-Cell Gene-Regulatory Networks of Advanced Symptomatic Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2024; 134(11):1405-1423. [15] LEWIS GD, FARACH A. Cardiovascular Toxicities of Radiation Therapy. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2019;15(4):274-281. [16] DA SILVA RMFL. Effects of Radiotherapy in Coronary Artery Disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2019;21(12):50. [17] DUNN AN, DONNELLAN E, JOHNSTON DR, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Patients With Mediastinal Radiation-Associated Coronary Artery Disease Undergoing Coronary Revascularization With Percutaneous Coronary Intervention and Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Circulation. 2020;142(14):1399-1401. [18] WU W, MASRI A, POPOVIC ZB, et al. Long-term survival of patients with radiation heart disease undergoing cardiac surgery: a cohort study. Circulation. 2013;127(14):1476-1485. [19] DEO RC. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation. 2015;132(20): 1920-1930. [20] HAMPE N, WOLTERINK JM, VAN VELZEN SGM, et al. Machine Learning for Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease in Cardiac CT: A Survey. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019;6:172. [21] HUANG AA, HUANG SY. Computation of the distribution of model accuracy statistics in machine learning: Comparison between analytically derived distributions and simulation-based methods. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6(4):e1214. [22] WENGROFSKY P, FELDMAN S. The Role of Multimodality Cardiac Imaging in Patients Undergoing Cancer Treatment. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023;25(1):1-8. [23] CHEN X, MUMME RP, CORRIGAN KL, et al. Deep learning-based automatic segmentation of cardiac substructures for lung cancers. Radiother Oncol. 2024;191:110061. [24] MORRIS ED, GHANEM AI, DONG M, et al. Cardiac substructure segmentation with deep learning for improved cardiac sparing. Med Phys. 2020;47(2):576-586. [25] PETRICCIUOLO S, DELLE DONNE MG, AIMO A, et al. Pre-treatment high-sensitivity troponin T for the short-term prediction of cardiac outcomes in patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51(4):e13400. [26] SU X, HUO HH, ZENG Y, et al. Effective Echocardiography Parameters to Identify Radiation-Induced Heart Disease in the Mouse Model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022;114(3, Supplement):e516. [27] WU T, HU E, XU S, et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (Camb). 2021;2(3):100141. [28] LIU Y, WANG Y, ZHANG J. New machine learning algorithm: Random forest//Information Computing and Applications: Third International Conference, ICICA 2012, Chengde, China, September 14-16, 2012. Proceedings 3. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2012:246-252. [29] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559. [30] FINOTELLO F, MAYER C, PLATTNER C, et al. Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq data. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):34. [31] ISHWARAN H, KOGALUR UB, BLACKSTONE EH, et al. Random survival forests. Ann Appl Stat. 2008;2(3):841-860. [32] LIU T, CHEN Y, HOU L, et al. Immune cell-mediated features of atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024;11:1450737. [33] SCHLAAK RA, FREI A, FISH BL, et al. Acquired Immunity Is Not Essential for Radiation-Induced Heart Dysfunction but Exerts a Complex Impact on Injury. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(4):983. [34] TAHA MY, MOHAMED NO, ALHAJ LG, et al. CCND1 as a Prognostic and Diagnostic Biomarker and the Impact of Its Epigenetic Alterations on Cancer Survival. Cureus. 2024;16(7):e65504. [35] JIANG D, SONG Q, ZHANG F, et al. Prognostic significance of CCND1 amplification/overexpression in smoking patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Genet. 2023;278-279:1-8. [36] BELZILE-DUGAS E, EISENBERG MJ. Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: Review of an Underrecognized Pathology. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(18):e021686. [37] KRUG P, GEETS X, BERLIÈRE M, et al. Cardiac structure, function, and coronary anatomy 10 years after isolated contemporary adjuvant radiotherapy in breast cancer patients with low cardiovascular baseline risk. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024;25(5):645-656. [38] SANTRA MK, WAJAPEYEE N, GREEN MR. F-box protein FBXO31 mediates cyclin D1 degradation to induce G1 arrest after DNA damage. Nature. 2009;459(7247):722-725. [39] LEONTIEVA OV, DEMIDENKO ZN, BLAGOSKLONNY MV. MEK drives cyclin D1 hyperelevation during geroconversion. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20(9):1241-1249. [40] BURTON DG, SHEERIN AN, OSTLER EL, et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression permits the reproducible detection of senescent human vascular smooth muscle cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1119:20-31. [41] LEONTIEVA OV, LENZO F, DEMIDENKO ZN, et al. Hyper-mitogenic drive coexists with mitotic incompetence in senescent cells. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(24):4642-4649. [42] CAMPISI J, D’ADDA DI FAGAGNA F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(9):729-740. [43] DU C, ZHAO S, SHAN T, et al. Cellular nucleic acid binding protein facilitates cardiac repair after myocardial infarction by activating β-catenin signaling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024;189:66-82. [44] VALENZUELA C, BROWN NE. Cyclin D1, metabolism, and the autophagy-senescence balance//HINDS PW, BROWN NE. D-type Cyclins and Cancer. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018:111-131. [45] JIA G, AROOR AR, JIA C, et al. Endothelial cell senescence in aging-related vascular dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(7):1802-1809. [46] LIU L, LI J, WANG R, et al. MicroRNA-298 Exacerbates Myocardial Ischemic Injury via Targeting Cyclin D1. Pharmazie. 2019;74(6):369-373. [47] SMITH TA, KIRKPATRICK DR, SMITH S, et al. Radioprotective agents to prevent cellular damage due to ionizing radiation. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):232. [48] JEONG K, KIM JH, MURPHY JM, et al. Nuclear Focal Adhesion Kinase Controls Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Neointimal Hyperplasia Through GATA4-Mediated Cyclin D1 Transcription. Circ Res. 2019;125(2):152-166. [49] QI Y, ZHANG Y, GUAN S, et al. Common ground on immune infiltration landscape and diagnostic biomarkers in diabetes-complicated atherosclerosis: an integrated bioinformatics analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1381229. [50] WITARTO BS, VISUDDHO V, ALDIAN FM, et al. Blood-based circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for subclinical carotid atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis with bioinformatics analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2023;17(10):102860. [51] SILVESTRE-ROIG C, BRASTER Q, ORTEGA-GOMEZ A, et al. Neutrophils as regulators of cardiovascular inflammation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020; 17(6):327-340. [52] WANG B, HAN J, ELISSEEFF JH, et al. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype and its physiological and pathological implications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(12):958-978. [53] FASANARO P, MAGENTA A, ZACCAGNINI G, et al. Cyclin D1 degradation enhances endothelial cell survival upon oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2006;20(8):1242-1244. [54] GENG X, WANG DW, LI H. The pivotal role of neutrophil extracellular traps in cardiovascular diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;179:117289. [55] KHOURY MK, YANG H, LIU B. Macrophage Biology in Cardiovascular Diseases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(2):e77-e81. [56] CHEN R, ZHANG H, TANG B, et al. Macrophages in cardiovascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):130. [57] ZHANG H, ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. WTAP/CCND1 axis accelerates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by MAPK signaling pathway. Neoplasma. 2024;71(4):359-373. [58] WANG JZ, WANG Y, SHAO Q, et al. Dynamic changes in cardiac biomarkers in radiotherapy for oesophageal cancer and their correlations with cardiac radiation dosimetry. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024;45:100750. [59] UNGER K, LI Y, YEH C, et al. Plasma metabolite biomarkers predictive of radiation induced cardiotoxicity. Radiother Oncol. 2020;152:133-145. [60] AZIMZADEH O, MERL-PHAM J, SUBRAMANIAN V, et al. Late Effects of Chronic Low Dose Rate Total Body Irradiation on the Heart Proteome of ApoE-/- Mice Resemble Premature Cardiac Ageing. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(13):3417. [61] LIU Z, WANG K, JIANG C, et al. Morusin Alleviates Aortic Valve Calcification by Inhibiting Valve Interstitial Cell Senescence Through Ccnd1/Trim25/Nrf2 Axis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(20):e2307319. [62] CAI W, SHU LZ, LIU DJ, et al. Targeting cyclin D1 as a therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2023;13: 1145082. |
| [1] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [2] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [3] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [4] | Guan Yujie, Zhao Bin. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [5] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [6] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [7] | Qi Xiang, Cao Shan, Chen Jian, Zhang Yijia, Liu Keke, Xu Zifu, Liu Wang, Fu Xiaoxiao, Yin Xiaolei. Screening of genes related to mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis in atherosclerosis and target prediction of regulatory traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2641-2652. |
| [8] | Wang Yaping, Gao Tianyun, Wang Bin. Senescence of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells with increasing age is not dependent on the mediation of endogenous retroviruses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 10-20. |
| [9] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [10] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [11] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [12] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [13] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [14] | Chen Ying, Guo Xiaojing, Mo Xueni, Ma Wei, Wu Shangzhi, Li Xiangling, Xie Tingting. Analysis of diagnostic biomarkers for ischemic stroke and experimental validation of targeted cuproptosis related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7562-7570. |
| [15] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||